Thérouanne
Thérouanne (Dutch: Terwaan; French Flemish Terenburg) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located 10 km (6.2 mi) west of Aire-sur-la-Lys and 13 km (8.1 mi) south of Saint-Omer, on the D 157 and D 341 road junction. Located on the river Lys.
Thérouanne | |
|---|---|
The centre of Thérouanne | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Thérouanne 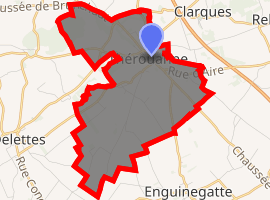
| |
 Thérouanne 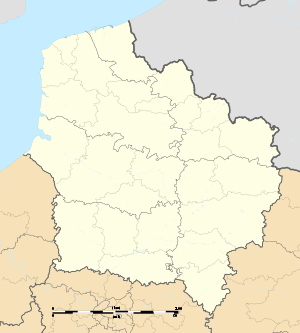 Thérouanne | |
| Coordinates: 50°38′15″N 2°15′35″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Hauts-de-France |
| Department | Pas-de-Calais |
| Arrondissement | Saint-Omer |
| Canton | Fruges |
| Intercommunality | Pays de Saint-Omer |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2001–2008) | Alain Chevalier |
| Area 1 | 8.37 km2 (3.23 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 1,115 |
| • Density | 130/km2 (350/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 62811 /62129 |
| Elevation | 31–116 m (102–381 ft) (avg. 38 m or 125 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Population
| Year | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 868 | 877 | 886 | 943 | 971 | 1,045 | 1,082 |
| From the year 1962 on: No double counting—residents of multiple communes (e.g. students and military personnel) are counted only once. | |||||||
History
At the time of the Gauls, Tarwanna or Tervanna was the capital of the Belgian tribe of the Morini. After the Romans conquered Gaul, they too made the city the capital of the Civitas Morinorum district.
The origin of the name has several theories. According to the historian Malbracq, it got its name from its founder "Lucius Tauruannus",[2] others say it is derived from "Terra avanae" The land of Oats. But this second derivation seems to be a generic used term.[3]
In the 7th century, probably around 639, Saint Audomar (Saint Omer) established the bishopric of Terwaan or Terenburg, the diocese of Thérouanne, which during the Middle Ages controlled a large part of the left bank of the river Scheldt. Territorially it was part of the county of Artois which belonged to the county of Flanders. In 1303 the town was burnt by Flemish forces during the Franco-Flemish War.
Thanks to that ecclesiastical control of some of the most prosperous cities north of the Alps, like Arras and Ypres, the bishopric was able to build a cathedral which was at the time the largest in France.
The town was captured by the Emperor Maximilian and Henry VIII from the French in 1513 after the battle of the Spurs. In 1553 Charles V besieged Thérouanne, then a French enclave in the Holy Roman Empire, in revenge for a defeat by the French at the siege of Metz. After he captured the city he ordered it to be razed, the roads to be broken up, and the area to be ploughed and salted.[4] Only a small commune which lay outside the city walls, then named Saint-Martin-Outre-Eaux, was left standing, and later (probably around 1800) took over the name Thérouanne. Part of the portal of the cathedral was acquired by Saint-Omer; a colossal statue of Christ is all that is left of it these days.
The disappearance of the former bishopric led to a reform of sees at the Council of Trent, and the bishopric of Thérouanne was split between those of Saint-Omer and Ypres.
Therouanne lies on the Via Francigena.
Bishops
- Saint Audomar, founder, 637-c.670
- Hunfrid of Prüm (d. 871)
- A certain Adam, 1213–1229 List of religious leaders in 1220
- Antipope Clement VII, 1361–1368
- John, Cardinal of Lorraine (d. 1550)
Places of interest
- The church of Saint Martin, rebuilt in the nineteenth century (and was renovated in 2000-2001) on the foundations of a much older church.
- The archaeological museum and site, remains of the medieval city.
- The ruin of the Abbey of St. Jean-du-Mont, contains the remnants of a gothic cathedral which has a seventh century Episcopal group and a Carolingian edifice, which are considered a registered historical monument[5]
Twin towns
Thérouanne is twinned with Hamstreet in Kent (in southern England, across the English Channel).
Notable people
- The football manager Gérard Houllier was born in Thérouanne.
Hugh of Saint Omer (also Hugh of Falkenberg or Hugh of Fauquembergues, died 1106) was the Prince of Galilee and Lord of Tiberias
References
- Jeff Rider and Benoît-Michel Tock (editors). 2010. Le Diocèse de Thérouanne au Moyen Âge. Arras: Commission départementale d’Histoire et d’Archéologie du Pas-de-Calais. ISBN 9782900643242.
- INSEE commune file
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Godmond, Christopher (1836). Memoir of Therrouanne, the ancient capital of the Morini in Gaul ... also a discourse on the Portus Itius of Cæsar.
- Postan, Michael Moïssey (1973). The Medieval Economy and Society: An Economic History of Britain, 1100-1500. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-02325-3.
- salting is mentioned in Elise Whitlock Rose, Cathedrals and Cloisters of Northern France, p. 8, but this is not a reliable historical source.
- The abbey in Base Merimée