Dickinson County, Kansas
| Dickinson County, Kansas | |
|---|---|
| County | |
|
Dickinson County Courthouse in Abilene | |
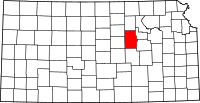 Location in the U.S. state of Kansas | |
 Kansas's location in the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°53′N 97°10′W / 38.883°N 97.167°W | |
| Founded | February 20, 1857 |
| Named for | Daniel S. Dickinson |
| Seat | Abilene |
| Largest city | Abilene |
| Area | |
| • Total | 852 sq mi (2,207 km2) |
| • Land | 847 sq mi (2,194 km2) |
| • Water | 4.9 sq mi (13 km2), 0.6% |
| Population (est.) | |
| • (2016) | 19,064 |
| • Density | 23/sq mi (9/km2) |
| Area code(s) | 785 |
| Congressional district | 1st |
| Time zone | Central: UTC−6/−5 |
| Website | DkCoKS.org |
Dickinson County (county code DK) is a county located in Central Kansas. As of the 2010 census, the county population was 19,754.[1] Its county seat and most populous city is Abilene.[2] The county was named in honor of Daniel S. Dickinson.[3]
History
Early history
For many millennia, the Great Plains of North America was inhabited by nomadic Native Americans. From the 16th century to 18th century, the Kingdom of France claimed ownership of large parts of North America. In 1762, after the French and Indian War, France secretly ceded New France to Spain, per the Treaty of Fontainebleau. In 1802, Spain returned most of the land to France, but keeping title to about 7,500 square miles.
In 1803, most of the land for modern day Kansas was acquired by the United States from France as part of the 828,000 square mile Louisiana Purchase for 2.83 cents per acre. In 1848, after the Mexican–American War, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo with Spain brought into the United States all or part of land for ten future states, including southwest Kansas. In 1854, the Kansas Territory was organized, then in 1861 Kansas became the 34th U.S. state.
19th century
In 1857, Dickinson County was founded.
The first railroad in Dickinson County was built through that territory in 1866.[4]
In 1887, Mr. Herington successfully got the Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway to build through Herington. He gave the land and right-of-way for Herington to become a division point with shops, two round houses, freight house, bridge yards, telegraph office and many other buildings. He furnished the limestone for the freight house, and for a two story depot that was 28 by 66 feet (8.5 m × 20.1 m) and later enlarged to 28 by 105 feet (8.5 m × 32.0 m).[5]
In 1887, the Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway built a main line from Topeka to Herington.[6] This main line connected Topeka, Valencia, Willard, Maple Hill, Vera, Paxico, McFarland, Alma, Volland, Alta Vista, Dwight, White City, Latimer, Herington.
In 1887, the Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway extended its main line from Herington to Pratt.[6] This main line connected Herington, Ramona, Tampa, Durham, Waldeck, Canton, Galva, McPherson, Groveland, Inman, Medora, Hutchinson, Whiteside, Partridge, Arlington, Langdon, Turon, Preston, Natrona, Pratt. In 1888, this main line was extended to Liberal. Later, this line was extended to Tucumcari, New Mexico and El Paso, Texas. This line is called the "Golden State Limited".
In 1887, the Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway built a branch line north-south from Herington to Caldwell.[6] This branch line connected Herington, Lost Springs, Lincolnville, Antelope, Marion, Aulne, Peabody, Elbing, Whitewater, Furley, Kechi, Wichita, Peck, Corbin, Wellington, Caldwell. By 1893, this branch line was incrementally built to Fort Worth, Texas. This line is called the "OKT".
The Chicago, Kansas and Nebraska Railway was foreclosed in 1891 and was taken over by Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railway, which shut down in 1980 and reorganized as Oklahoma, Kansas and Texas Railroad, merged in 1988 with Missouri Pacific Railroad, merged in 1997 with Union Pacific Railroad. Most locals still refer to this railroad as the "Rock Island".
In 1887, Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway built a branch line from Neva (3 miles west of Strong City) to Superior, Nebraska. This branch line connected Strong City, Neva, Rockland, Diamond Springs, Burdick, Lost Springs, Jacobs, Hope, Navarre, Enterprise, Abilene, Talmage, Manchester, Longford, Oak Hill, Miltonvale, Aurora, Huscher, Concordia, Kackley, Courtland, Webber, Superior. At some point, the line from Neva to Lost Springs was pulled but the right of way has not been abandoned. This branch line was originally called "Strong City and Superior line" but later the name was shortened to the "Strong City line".
In 1996, the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway merged with Burlington Northern Railroad and renamed to the current BNSF Railway. Most locals still refer to this railroad as the "Santa Fe".
21st century
In 2010, the Keystone-Cushing Pipeline (Phase II) was constructed north to south through Dickinson County, with much controversy over tax exemption and environmental concerns.[7][8] A pumping station named Hope was built along the pipeline.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 852 square miles (2,210 km2), of which 847 square miles (2,190 km2) is land and 4.9 square miles (13 km2) (0.6%) is water.[9]
Adjacent counties
- Clay County (north)
- Geary County (east)
- Morris County (southeast)
- Marion County (south)
- McPherson County (southwest)
- Saline County (west)
- Ottawa County (northwest)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1860 | 378 | — | |
| 1870 | 3,043 | 705.0% | |
| 1880 | 15,251 | 401.2% | |
| 1890 | 22,273 | 46.0% | |
| 1900 | 21,816 | −2.1% | |
| 1910 | 24,361 | 11.7% | |
| 1920 | 25,777 | 5.8% | |
| 1930 | 25,870 | 0.4% | |
| 1940 | 22,929 | −11.4% | |
| 1950 | 21,190 | −7.6% | |
| 1960 | 21,572 | 1.8% | |
| 1970 | 19,993 | −7.3% | |
| 1980 | 20,175 | 0.9% | |
| 1990 | 18,958 | −6.0% | |
| 2000 | 19,344 | 2.0% | |
| 2010 | 19,754 | 2.1% | |
| Est. 2016 | 19,064 | [10] | −3.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[11] 1790-1960[12] 1900-1990[13] 1990-2000[14] 2010-2016[1] | |||
As of the 2000 census,[15] there were 19,344 people, 7,903 households, and 5,421 families residing in the county. The population density was 23 people per square mile (9/km²). There were 8,686 housing units at an average density of 10 per square mile (4/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 96.44% White, 0.58% Black or African American, 0.49% Native American, 0.30% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.82% from other races, and 1.36% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.30% of the population.
There were 7,903 households out of which 31.10% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 57.90% were married couples living together, 7.70% had a female householder with no husband present, and 31.40% were non-families. 28.10% of all households were made up of individuals and 14.10% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.40 and the average family size was 2.94.
In the county, the population was spread out with 25.70% under the age of 18, 6.30% from 18 to 24, 26.30% from 25 to 44, 23.10% from 45 to 64, and 18.60% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females there were 95.10 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 91.60 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $35,975, and the median income for a family was $43,952. Males had a median income of $30,889 versus $18,526 for females. The per capita income for the county was $17,780. About 5.30% of families and 7.50% of the population were below the poverty line, including 8.70% of those under age 18 and 11.30% of those age 65 or over.
Government
Presidential elections
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 73.4% 6,029 | 19.6% 1,609 | 7.0% 572 |
| 2012 | 72.5% 5,832 | 25.1% 2,020 | 2.4% 190 |
| 2008 | 70.2% 6,081 | 28.0% 2,422 | 1.9% 164 |
| 2004 | 71.6% 6,295 | 26.9% 2,364 | 1.5% 132 |
| 2000 | 64.8% 5,243 | 29.8% 2,413 | 5.4% 436 |
| 1996 | 60.5% 5,174 | 28.4% 2,423 | 11.1% 951 |
| 1992 | 41.8% 3,851 | 27.3% 2,518 | 30.9% 2,852 |
| 1988 | 63.3% 5,121 | 35.5% 2,870 | 1.3% 101 |
| 1984 | 74.0% 6,487 | 24.7% 2,168 | 1.3% 116 |
| 1980 | 67.6% 5,654 | 25.2% 2,108 | 7.1% 597 |
| 1976 | 55.2% 4,759 | 42.6% 3,672 | 2.2% 186 |
| 1972 | 75.3% 6,515 | 22.6% 1,957 | 2.0% 175 |
| 1968 | 64.3% 5,574 | 27.7% 2,399 | 8.0% 693 |
| 1964 | 53.2% 4,704 | 46.0% 4,070 | 0.8% 73 |
| 1960 | 69.2% 6,956 | 30.4% 3,054 | 0.5% 45 |
| 1956 | 74.9% 7,422 | 24.8% 2,452 | 0.3% 34 |
| 1952 | 81.8% 8,969 | 17.9% 1,967 | 0.3% 31 |
| 1948 | 60.0% 5,918 | 38.7% 3,815 | 1.4% 134 |
| 1944 | 65.9% 6,227 | 33.8% 3,190 | 0.3% 29 |
| 1940 | 63.3% 6,931 | 36.1% 3,957 | 0.6% 70 |
| 1936 | 52.6% 5,936 | 47.1% 5,313 | 0.3% 34 |
| 1932 | 49.0% 5,320 | 49.2% 5,339 | 1.8% 190 |
| 1928 | 77.0% 7,758 | 22.3% 2,246 | 0.7% 66 |
| 1924 | 64.6% 6,178 | 17.7% 1,690 | 17.8% 1,698 |
| 1920 | 69.1% 5,761 | 28.6% 2,387 | 2.3% 189 |
| 1916 | 45.1% 4,323 | 51.9% 4,974 | 3.1% 296 |
| 1912 | 18.3% 988 | 40.4% 2,182 | 41.2% 2,225[lower-alpha 1] |
| 1908 | 53.3% 2,886 | 42.2% 2,282 | 4.6% 246 |
| 1904 | 66.9% 3,185 | 25.6% 1,219 | 7.5% 358 |
| 1900 | 52.9% 2,771 | 44.9% 2,352 | 2.1% 112 |
| 1896 | 48.3% 2,291 | 50.6% 2,399 | 1.1% 52 |
| 1892 | 47.1% 2,419 | 52.9% 2,712 | |
| 1888 | 54.2% 2,746 | 33.4% 1,695 | 12.4% 630 |
Laws
Dickinson County was a prohibition, or "dry", county until the Kansas Constitution was amended in 1986 and voters approved the sale of alcoholic liquor by the individual drink with a 30% food sales requirement.[17]
Education
Unified school districts
- USD 393, Solomon
- Solomon, Rural Areas
- USD 435, Abilene
- Abilene, Rural Areas
- USD 473, Chapman
- Chapman, Carlton, Manchester, Enterprise, Rural Areas
- USD 487, Herington
- Herington, Rural Areas
- District Office In Neighboring County
- USD 481, Rural Vista (headquarters in White City)
Communities
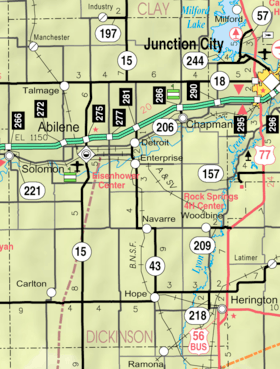
Cities
- Abilene
- Carlton
- Chapman
- Enterprise
- Herington
- Hope
- Manchester
- Solomon (partly in Saline County)
- Woodbine
Census-designated places
Other unincorporated places
Townships
Dickinson County is divided into twenty-four townships. The cities of Abilene and Herington are considered governmentally independent and are excluded from the census figures for the townships. In the following table, the population center is the largest city (or cities) included in that township's population total, if it is of a significant size.
Points of Interest
The Eisenhower Library is located in Abilene. In addition to exhibits relating to the life and presidency of the 34th US President, the site is also the location of the tombs of President Eisenhower, First Lady Mamie Eisenhower, and their son who died in infancy.
Notable people

Dwight David "Ike" Eisenhower was born in Texas but moved to Abilene at an early age and always considered Abilene to be his home. He was the 34th President of the United States from 1953 until 1961. Prior to that he was a five-star general in the United States Army. During World War II, he served as Supreme Commander of the Allied Forces in Europe; he had responsibility for planning and supervising the invasion of North Africa in Operation Torch in 1942–43 and the successful invasion of France and Germany in 1944–45, from the Western Front. In 1951, he became the first supreme commander of NATO.[18] The Eisenhower Library (see above) is located in Abilene.
Joe Engle is a retired U.S. Air Force colonel and a former NASA astronaut. Engle helped to flight test the joint NASA-Air Force X-15 rocket airplane. During the course of testing, Engle earned his USAF astronaut wings, a Distinguished Flying Cross and other awards. Engle was one of the first astronauts in the Space Shuttle program, having flight tested the Space Shuttle Enterprise in 1977. He was commander of the second orbital test flight of the Space Shuttle Columbia in 1981. Engle was born and raised in Chapman.
Several figures from the American Old West spent time in the county. Folk hero James Butler "Wild Bill" Hickok, gunfighter John Wesley Hardin, and dance hall girl/prostitute Libby Thompson all made their mark in Abilene when it was in its wild cattle-town days.
US Army Chaplains John H. Eastwood and Emil Kapaun were both stationed at Herington Army Airfield for part of their tour of duty during World War II.
Pop Hollinger pioneered the industry of comic book collecting and also managed to secure several patents. He grew up in Chapman.
See also
References
- 1 2 "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 9, 2011. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- ↑ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. p. 106.
- ↑ Blackmar, Frank Wilson (1912). Kansas: A Cyclopedia of State History, Embracing Events, Institutions, Industries, Counties, Cities, Towns, Prominent Persons, Etc. Standard Publishing Company. p. 519.
- ↑ Herington History
- 1 2 3 Rock Island Rail History
- ↑ Keystone Pipeline - Marion County Commission calls out Legislative Leadership on Pipeline Deal; April 18, 2010. Archived October 22, 2011, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Keystone Pipeline - TransCanada inspecting pipeline; December 10, 2010.
- ↑ "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- ↑ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on May 12, 2015. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 24, 2014.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2013-09-11. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- ↑ http://uselectionatlas.org/RESULTS
- ↑ "Map of Wet and Dry Counties". Alcoholic Beverage Control, Kansas Department of Revenue. November 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-10-08. Retrieved 2007-12-28.
- ↑ "Former SACEURs". Aco.nato.int. Archived from the original on 2012-07-28. Retrieved 2012-01-26.
- Notes
- ↑ Includes 1,937 votes (35.9%) for Progressive Theodore Roosevelt and 288 votes (5.3%) for Socialist Eugene V. Debs.
Further reading
- County
- The Scully Land System in Marion County, Kansas; Homer Socolofsky; Kansas State University; 110 pages; 1944/1947. (includes Dickinson County)
- Standard Atlas of Dickinson County, Kansas; Geo. A. Ogle & Co; 82 pages; 1921.
- Plat Book and Complete Survey of Dickinson County, Kansas; Kenyon Company ; 54 pages; 1909.
- Standard Atlas of Dickinson County, Kansas; Geo. A. Ogle & Co; 63 pages; 1901.
- Portrait and Biographical Record of Dickinson, Saline, McPherson, and Marion Counties, Kansas; Chapman Bros; 614 pages; 1893.
- Trails
- The National Old Trails Road To Southern California, Part 1 (LA to KC); Automobile Club Of Southern California; 64 pages; 1916. (Download 6.8MB PDF eBook)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dickinson County, Kansas. |
- County
- Historical
- Maps

