Pančevo
| Pančevo Панчево | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
| City of Pančevo | |||
 Pančevo collage (Roman catholic church, One of two lighthouses in a spot where Tamis flowes into Danube, Slovak Evangelical church, National Museum, High School "Nikola Tesla" Pančevo, Saint Florian Statue, Serbian orthodox church Assumption of Holy Virgin, Windmill-restaurant) | |||
| |||
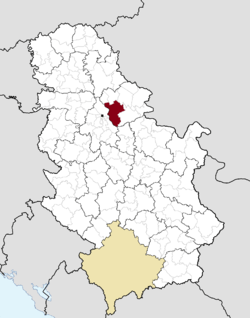 Location of city of Pančevo within Serbia | |||
| Coordinates: 44°52′14″N 20°38′25″E / 44.87056°N 20.64028°ECoordinates: 44°52′14″N 20°38′25″E / 44.87056°N 20.64028°E | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Province | Vojvodina | ||
| District | South Banat | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Saša Pavlov (SNS) | ||
| Area | |||
| Area rank | 29th in Serbia | ||
| • Urban | 161.09 km2 (62.20 sq mi) | ||
| • Administrative | 755.66 km2 (291.76 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 77 m (253 ft) | ||
| Population (2011 census)[1] | |||
| • Rank | 9th in Serbia | ||
| • Urban | 76,203 | ||
| • Urban density | 470/km2 (1,200/sq mi) | ||
| • Administrative | 123,414 | ||
| • Administrative density | 160/km2 (420/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | ||
| Postal code | 26000 | ||
| Area code(s) | +381(0)13 | ||
| ISO 3166 code | SRB | ||
| Car plates | PA | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Pančevo (Serbian Cyrillic: Панчево, pronounced [pâːntʃeʋo], Hungarian: Pancsova, Romanian: Panciova, Slovak: Pánčevo) is a city and the administrative center of the South Banat District in autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia.
Pančevo is the fourth largest city in Vojvodina by population. According to results of the 2011 census, a total of 76,203 inhabitants live in the urban area, while the city administrative area of Pančevo has 123,414 inhabitants.[2]
Name
In Serbian and Macedonian, the town is known as Pančevo (Панчево), in Hungarian as Pancsova, in Slovak as Pánčevo, in Romanian as Panciova and in German as Pantschowa. The place name is probably derived from an old Slavonic term and meant location of marsh.[3]
Geography

Pančevo is located on flat plains at 44°52′14″N 20°38′25″E / 44.87056°N 20.64028°E, approximately 17 km NE of Pančevo bridge to Belgrade and 43 km NW of Smederevo. The altitude above sea level is 77 meters. The southern city quarters are located on the bank of the Danube, the western quarters on the bank of Tamiš. The town is located nearby the wetland Pančevački Rit in the southern part of the geographical region of Banat. The river islands Forkontumac and Čakljanac are the southernmost part of the urban area.
Climate
Pančevo has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification: Cfa).
| Climate data for Pančevo | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.8 (38.8) |
6.5 (43.7) |
12.3 (54.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
23.1 (73.6) |
25.8 (78.4) |
28.3 (82.9) |
28.4 (83.1) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.3 (64.9) |
10.6 (51.1) |
5.2 (41.4) |
17 (62.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.0 (33.8) |
3.0 (37.4) |
7.4 (45.3) |
12.5 (54.5) |
17.2 (63) |
20.2 (68.4) |
22.2 (72) |
22.2 (72) |
18.2 (64.8) |
13.2 (55.8) |
7.1 (44.8) |
2.4 (36.3) |
12.2 (54) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
2.5 (36.5) |
7.1 (44.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
14.7 (58.5) |
16.1 (61) |
16.1 (61) |
12.3 (54.1) |
8.1 (46.6) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
7.5 (45.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 45 (1.77) |
43 (1.69) |
43 (1.69) |
52 (2.05) |
68 (2.68) |
84 (3.31) |
67 (2.64) |
46 (1.81) |
47 (1.85) |
39 (1.54) |
53 (2.09) |
60 (2.36) |
647 (25.48) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org [4] | |||||||||||||
History
In the late 19th and early 20th century were found many archaeological artifacts of the Stone Age period, remains of settlements and places of burial from the times of Bronze Age (Urnfield culture) and Ancient Rome on the urban area. Most of the objects are exhibited at the National Museum of the town.[5][6]
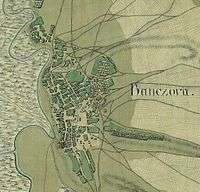
In 1153, the Muslim geographer Muhammad al-Idrisi described the settlement as an important mercantile place and that is the first historical mentioning of the town. There is no deed or other evidence of founding the city. Today's urban area was administered by the Bulgarian Empire until the begin of the 11th century, then by the Kingdom of Hungary until the 16th century, when it became part of the Ottoman Empire in 1521. During the Ottoman rule, the city was part of the Temeşvar Eyalet and mostly populated by ethnic Serbs. In 1660, Evliya Çelebi described the town as a quadrangular fortification being diameter of one hundred Turkish feet. During the Austro-Turkish War, the fortification was conquered by Claude Florimond de Mercy and his troops in 1716. There is an impression of the old city and its fortification recorded on maps from 1717 and 1720 which are located at National Széchényi Library and Institute of Military History in Budapest.[7][8][9]
After the Treaty of Požarevac, the city belonged to Habsburg's Banat. The town was a garrison place of temporarily stationed Regiments of Imperial Army. In December 1764, a military commission of Viennese Hofkriegsrat registered 564 Rascian people who lived in 203 more or less habitable houses. Since this time Habsburg's administration encouraged massive immigration of German settlers to develop the new district of Military Frontier, established in 1765. In January 1794, Francis II signed the charter of borough rights of Pančevo. Approximately, in the middle of the 19th century, the fortification has been slighted for urban expanding. In 1873, the military frontier was abolished and Pančevo included into Torontál county of Austria-Hungary. In 1902, cadastral maps of the town were recorded which are located at the National Archives of Hungary.[10][11][12][13][14]


After World War I, the city was part of provisional Torontalsko-tamiške županja (Treaty of Trianon), in 1922 of Belgrade oblast and since 1929 of the Danube Banovina in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. In April 1941, Pančevo was occupied during the invasion of Yugoslavia by Germany. Soldiers of Division Grossdeutschland committed a war crime in the city when 36 Serbian civilians were executed by hanging and shooting as a reprisal for the deaths of 9 Danube Swabian members of the paramilitary formation Deutsche Mannschaft, a member of SS Division Das Reich and a wounded member of that division, shot by unknown soldiers of Royal Yugoslav Army after Yugoslav surrender. Propaganda photos and film of the executions were used decades after the event to help chronicle the Wehrmacht's complicity in German atrocities during the war.[15][16][17][18]
During World War II in Yugoslavia, Pančevo was a part of the Autonomous Banat within German-occupied Serbia. Political prisoners of National Socialism and Communism has been killed on a location named Stratište near to Jabuka. Most of local Danube Swabian men were recruited or conscripted in the Waffen-SS, the majority of them in the Division Das Reich, in German Police and in the SS Freiwilligen Gebirgsjäger Division Prinz Eugen. Almost all of the local German women and youth were organized in formations Deutsche Frauenschaft and Deutsche Jugend and dedicated to national socialism of Danube Swabians. The town was a regional center of this extremist movement. In 1944, after the defeat of German Wehrmacht and Waffen-SS during the Belgrade Offensive by Allied Armies, one part of the German people left the city, together with defeated German army. The other part of German people remained in the country. They were sent into local imprisonments which existed until 1948. After prison camps were dissolved, many of German population left Yugoslavia because of economic reasons. Since 1945, the city belonged to the Srez Pančevo of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The city was the administrative center of the region from all these centuries to the present.[19][20][21][22]
Administration

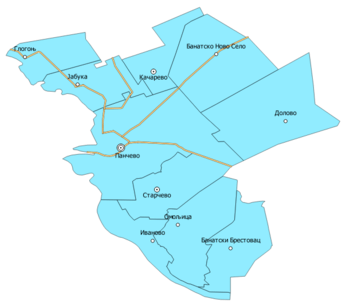
The administration of the municipality of Pančevo is structured in 9 local communities (Mesna zajednica, singular; abbreviation MZ) of seven villages, two towns and the city of Pančevo, structured in eight local communities of eight city districts with several quarters.[23]
Administrative area structure
| Community (MZ) | Banatski Brestovac | Banatsko Novo Selo | Dolovo | Glogonj | Ivanovo | Jabuka | Kačarevo | Omoljica | Starčevo | Pančevo City |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | 61,905 | 98,955 | 117,176 | 42,775 | 42,567 | 51,786 | 39,706 | 77,262 | 62,066 | 161,373 |
The administrative area differs to the historical administrative area. From 1946 to 1959, the historical municipality (Srez) was structured in 23 communities, including today's communities and the villages and cities of Baranda, Borča, Crepaja, Debeljača, Idvor, Kovačica, Opovo, Ovča, Padina, Sakule, Sefkerin, Uzdin and Vojlovica. The city district Vojlovica was added to the town in 1978.
City administrative structure
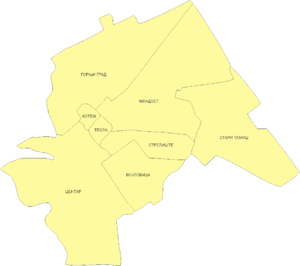
- Donji grad
- Zelengora
- Mali London (Mali Rit)
- Sodara
- Topola
- Utvina kolonija
MZ Gornji grad:
- Karaula
- Skrobara
MZ Kotež:
- Kotež 1
- Kotež 2
MZ Mladost:
- Kudeljarski nasip
- Stara Misa
- Misa vinogradi (Nova Misa)
MZ Stari Tamiš
MZ Strelište
MZ Tesla
MZ VojlovicaDemographics
Municipal area population
| Year | 1961 | 1971 | 1981 | 1991 | 2002 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 93,744 | 110,780 | 123,791 | 125,261 | 127,162 | 123,414 |
Demography of city population
| Year | 1869 | 1890 | 1910 | 1931 | 1948 | 1961 | 1981 | 2002 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 16,888 | 17,948 | 20,808 | 22,089 | 30,516 | 46,679 | 71,009 | 78,938 |
Demography of municipal population by ethnicity
| Year | Total | Serbs | Macedonians | Hungarians | Romanians | Roma | Slovaks | Croats | Other nationalities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 123,414 | 97,499 | 4,558 | 3,422 | 3,173 | 2,118 | 1,411 | 880 | 10,353 |
Culture
Cultural institutions and events

The oldest and most traditional cultural institution of the city is the Serbian Church Choral Society, founded in 1838 and the oldest still existing Choral Society of today's Serbia. Since its inception, probably the most famous of all honorable choirmasters is Davorin Jenko, who conducted the choir from 1863 to 1865. In the present, the choir is conducted for the fourth time in a continuous sequence by a woman. The most important Cultural Center of the city (Kulturni Centar Pančeva) is located in the former theater building of the city, founded in 1947 and named National Theater which realized play productions in cooperation with National Theater Novi Sad. In 1956, the political authorities of the town decided the creation of a cultural center which is representing variety of all Arts. The center has a gallery of Modern art, and it promotes continuous festivals like Biennial of Art (Bijenale umetnosti), the music festival Ethno.com and the Pančevački Jazz Festival with artists from all over the world. In addition, some theater productions are shown annually in cooperation with National Theater Belgrade and other famous institutions. In 2012, the center published all popular stories of Zigomar Comics in a collected edition. Since 1977, the House of Youth (Dom omladine) is venue of the event Rukopisi (Manuscripts) where young writers are presented each year. The facility also promotes many other events like FreeDOM Art Festival. There is also the continuous Film festival PAFF worth mentioning which has a good reputation beyond the region. In the past, the city has been filming location for many national and international movie productions, including well known movies such as La Tour, prends garde!, The Mongols, I Even Met Happy Gypsies, Balkan Express, Black Cat, White Cat and Coriolanus.[24][25][26][27][28][29]
Since 2004, each year in June the Pančevački Carnival become the most important event of its kind in Serbia. The highlight of the event is the parade which goes through the center with more than over 3,000 international participants and up to 100,000 visitors annually. The city is a member of the Federation of European Carnival Cities.[30][31]
The National Museum was founded in 1923 and it is located in former neoclassical city hall since several decades. The institution has a valuable permanent exhibition and it is one of the most important museums of Vojvodina. The Vajfert Brewery is located in the town's center and it is the oldest one of today's Serbia, founded in 1722 by Abraham Kepiš from Bratislava. The brewery was run by the Vajfert family for several generations and its most famous represent was Đorđe Vajfert. After closing in 2008 and a conflagration in 2010, the building complex was a ruin in recent years. In 2015, the city began to realize a concept for revitalizing the industrial heritage and in the following year, the Đorđe Vajfert Brewery Museum was opened in the presence of the Austrian and German ambassadors. In the same year, a new summer festival called Vajfert Days was held for the first time. The intention of the organizer is to promote the tourist, cultural, artistic and economic potential of the city. And last but not least, there is an Archive of the City, founded in 1947 and it is located in former barracks of Austrian-Hungarian Army. The archive collects and preserves materials of town's history from all centuries.[32][33][34][35][36][37]
Cultural monuments
Pančevo's Vojlovica monastery is one of the oldest monasteries of Vojvodina, the oldest sacral building complex of the city and declared Cultural Monument of Exceptional Importance. In 1542, the monastery was first mentioned by hegumen Jeronomah Parfenije in a Serbian almanac of Božidar Vuković. The church of the monastery is dedicated to Archangels Michael and Gabriel and was transformed into neoclassical stile towards the end of 18th century. From 1942 to 1944, some Orthodox dignitaries such as Gavrilo V were temporarily imprisoned in the monastery and the entire building complex was observed by local members of Banater Staatswache. The oldest church in town is the Roman Catholic Church Saint Charles Borromeo, built from 1756 to 1757 and in 1768, the building was extended with a steeple which was equipped with a turret clock in 1868 to mark its centenary. Its column in the square in front of the building with statue of Abraham and Isaac was built in 1722. The building was previously used as a provisional church of a Minorite monastery. The religious order provided the military chaplains for the garrison of the Imperial Army. The Serbian Orthodox Church Assumption of Holy Virgin was built from 1807 to 1811. The iconostasis of the church was designed by the painter Konstantin Danil from 1828 to 1833. The urban Institute for Protection of Cultural Monuments supports the maintenance and restoration of Pančevo's Cultural Heritage.[38][39][40][41][42][43]
Local mass media
The weekly newspaper Pančevac is the oldest one of still existing print media in Serbia, founded in 1869. The weekly newspaper Libertatea is one of the most important print media of Romanians in Serbia. The first edition has been published in May 1945. The most used local mass media is RTV Pančevo. The TV station started broadcasting its programs in 1992.[44][45][46]
Economy and Environment

Pančevo is the economic center of South Banat District. There are many industrial companies in processing of oil, steel, aluminum, glass, corn, grain, in metalworking, in producing petrochemicals, fertilizer, commercial packaging, PET molding machines, clothes, grain mill products, bacon and other food, in construction of aircraft, thermal power stations and buildings of steel beams.
The industrial site of NIS refinery is the largest one of all refineries in Serbia. In 1999, the industrial site was strategically bombed by NATO during Operation Allied Force. Precise targets included the refinery, the town's airport, the Utva aircraft industry and HIP factory. The UNEP reported in studies about soil and groundwater contaminations caused by NATO bombardment. The contamination is a long-term threat to natural environment and human health. There are two protected natural resources located in surroundings of the city, the natural monument Ivanov's island (Serbian Ivanovačka ada) and the Nature Park Ponjavica.[47][48][49][50]
The following table gives a preview of total number of employed people per their core activity (as of 2016):[51]
| Activity | Total |
|---|---|
| Agriculture, forestry and fishing | 860 |
| Mining | 225 |
| Processing industry | 6,982 |
| Distribution of power, gas and water | 446 |
| Distribution of water and water waste management | 702 |
| Construction | 1,278 |
| Wholesale and retail, repair | 5,377 |
| Traffic, storage and communication | 1,548 |
| Hotels and restaurants | 812 |
| Media and telecommunications | 473 |
| Finance and insurance | 491 |
| Property stock and charter | 32 |
| Professional, scientific, innovative and technical activities | 1,154 |
| Administrative and other services | 863 |
| Administration and social assurance | 1,648 |
| Education | 1,894 |
| Healthcare and social work | 2,743 |
| Art, leisure and recreation | 406 |
| Other services | 582 |
| Total | 28,517 |
Public Transportation
The most important road that runs through Pančevo is the European route E70 which forms a bypass around the city center, connecting the city with Belgrade. The IB-14 highway to Smederevo via Kovin starts here, and so does the IIA-130 highway to Ečka. As the most important regional mode of transport on road is made available a bus route network for public passenger traffic by Autotransport Pančevo since 1948.[52]
Having a relatively small population, Pančevo has no less than four passenger railway stations: Pančevo Glavna stanica, Pančevo Varoš, Pančevo Strelište and Pančevo Vojlovica. Apart from these, Serbian railways also serve some important industries, such as NIS oil refinery and HIP Azotara. In April of 1894, the city was connected to the European railways net.[53]
The municipality lays on the left bank of the Danube which is one of the Europe's most important waterways. The new port was built in 1947. The river Tamiš discharges into the Danube just outside the town of Pančevo.[54]
Sports
There are some popular sporting clubs in town, the football (soccer) team FK Dinamo Pančevo, the women's football club ŽFK, the basketball club KK Tamiš and the American football team Pančevo Panthers. Currently, the most successful athlete is Slobodan Bitević who lives in the city.
Image Gallery
 Roman Catholic church Saint Charles Borromeo built 1756-57 and column with statue of Abraham and Isaac
Roman Catholic church Saint Charles Borromeo built 1756-57 and column with statue of Abraham and Isaac Serbian orthodox church Assumption of Holy Virgin, built 1807-1811
Serbian orthodox church Assumption of Holy Virgin, built 1807-1811 Iconostasis of Serbian orthodox church
Iconostasis of Serbian orthodox church Street of old central quarter
Street of old central quarter- Urban park Narodna bašta in the center
- Tamiš lighthouse
Twin Towns, Sister Cities and Regions














Notable People
- Vasa Živković (1819-1891), poet and priest
- Dragomir Krančević (1847-1929), violinist
- Đorđe Vajfert (1850-1937), industrialist and Governor of the National Bank of Serbia and later Yugoslavia
- Ljubica Luković (1858-1915), President of Circle of Serbian Sisters
- Ludwig von Graff (1851-1924), zoologist
- Heinrich Knirr (1862-1944), painter of official portrait of Adolf Hitler
- Jovan Erdeljanović (1874-1944), ethnologist
- Milan Ćurčin (1880-1960), poet and editor
- Milorad Bata Mihailović (1923-2011), painter
- Alexis Guedroitz (1923-1992), professor of Russian language and literature
- Olja Ivanjicki (1931-2009), artist
- Stevan Bena (1935-2012), football player
- Zlatoje Martinov (*1953), journalist and writer
- Zoran Gajić (*1958), volleyball trainer
- Milan Orlić (*1962), laureate of several literary awards
- Aleksandar Zograf (*1963), cartoonist
- Slobodan Beštić (*1964), actor
- Milenko Topić (*1969), basketball player, World and European champion
- Bobby Despotovski (*1971), Australian footballer
- Marina Munćan (*1982), athlete, Universiade champion
- Dušan Borković (*1984), auto racing driver, two time European champion.
- Nađa Higl (*1987), swimmer, World champion
- Anja Crevar (*2000), swimmer, Gold medalist at the European Junior Championships
Articles
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Pančevo. |
References
- ↑ "2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia: Comparative Overview of the Number of Population in 1948, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1981, 1991, 2002 and 2011, Data by settlements" (PDF). Statistical Office of Republic Of Serbia, Belgrade. 2014. ISBN 978-86-6161-109-4. Retrieved 2014-06-27.
- ↑ 2011 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in the Republic of Serbia, Volume 2, Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia, Belgrade 2012, p. 82.
- ↑ Felix Milleker, Geschichte der Stadt Pančevo, Pančevo 1925, p. 4-5.
- ↑ "Climate: Pančevo, Serbia". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved January 8, 2018.
- ↑ Felix Milleker, Geschichte der Stadt Pančevo, Pančevo 1925, p. 5-7.
- ↑ Virtual visit at the National Museum on the Website by National Museum of Pančevo (in English), Retrieved on 2017-01-18.
- ↑ Felix Milleker, Geschichte der Stadt Pančevo, Pančevo 1925, p. 12-20.
- ↑ Map of the city and the fortification in 1717, Retrieved on 2017-01-23.
- ↑ Map of the fortification in 1720, Retrieved 2017-01-23.
- ↑ Erik Roth, Die planmäßig angelegten Siedlungen im Deutsch-Banater Militärgrenzbezirk 1765-1821, Munich 1988, ISBN 3-486-54741-0, p. 348 (German biography and bibliography of Erik Roth on Academia.edu, retrieved on 2018-01-12.
- ↑ Felix Milleker, Geschichte der Stadt Pančevo, Pančevo 1925, p. 55-90.
- ↑ Luka Ilić, Historische Skizze der kaiserlich königlichen Militär-Communität Pantschowa, Pančevo 1855, Enclosing Map of 1814.
- ↑ Pančevo on the Map of Franciscan Land Survey (1806-1869) at National Archives of Austria, Retrieved 2017-01-23.
- ↑ Cadastre maps Pancsova, Retrieved on 2017-01-20
- ↑ Ulrike Jureit and Hans Mommsen, Verbrechen der Wehrmacht, Hamburg 2002, ISBN 3-930908-74-3, p. 536-537.
- ↑ Jürgen Martschukat and Silvan Niedermeier, Violence and Visibility in Modern History, New York 2013, ISBN 978-1-137-37868-2, p.182.
- ↑ Donauschwäbische Kulturstiftung, Leidensweg der Deutschen im kommunistischen Jugoslawien, Volume 2, Munich 1993, ISBN 3-926276-17-7, p. 131-133.
- ↑ Crime of the Wehrmacht, Pančevo in April of 1941—different numbers of victims, audio commentaries, sequences, film scores of TV-documentaries with original materials: version 1 (36 Serbs) (in German) and version 2 (18 Serbs) (in German) on the Website by YouTube, Retrieved on 2017-05-22.
- ↑ Akiko Shimizu, Die deutsche Okkupation des serbischen Banats 1941-1944 unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der deutschen Volksgruppe in Jugoslawien. Regensburger Schriften aus Philosophie, Politik, Gesellschaft und Geschichte. Band 5, Münster 2003, ISBN 3-8258-5975-4, p. 67, 105, 194-196, 152-154.
- ↑ Genozid nad Podunavskim Nemcima (in Serbian) on the Website Google Sites, Retrieved on 2017-01-19.
- ↑ Otto Vogenberger, Pantschowa – Zentrum des Deutschtums im Banat (Pantschowa – Center of German Being), Pannonia, Freilassing 1961.
- ↑ Srpske sinagoge kojih nema, History of the Synagogue on ARS Magine, Retrieved on 2017-05-20.
- ↑ City administrative area (PDF) on the Website by the Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia, Retrieved on 2017-01-17.
- ↑ Website by Serbian Church Choral Society on Facebook, Retrieved on 2017-12-11. Serbian Church Coral Society on YouTube, Retrieved on 2017-10-27.
- ↑ Article on Davorin Jenko in: Stanoje Stanojević, Narodna enciklopedija srpsko-hrvatsko-slovenačka, Volume 2, Zagreb 1926, p. 153.
- ↑ Official Website by the Kulturni Centar Pančeva (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Dom omladine (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by PAFF (in English), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Pančevo in film frames, 1956-2010 (PDF) (in English), Publication by the Web archive of Pančevo, Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Pančevački Karneval, Retrieved on 2017-03-27
- ↑ Hotspot impressions 2016 and 2017 by K-013 and RTV of Pančevački Karneval on YouTube, retrieved on 2017-12-26.
- ↑ Official Website by Narodni Muzej (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Rezultati konkursa za idejno rešenje rekonstrukcje Vajfertove Pivare Super prostor, web portal for architecture and cultural space (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Georg Weifert Museum opened in Pančevo (in English), article by Diplomacy&Commerce, Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Muzej Pivarstva Đorđe Vajfert on Facebook (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official website of Vajfert Days, retrieved on 2018-05-10.
- ↑ Official Website by Istorijski arhiv u Pančevu, Retrieved on 2017-01-22.
- ↑ Ivanikije Milković, Pověst’ vo kratcě spisanaja o obščežitel’nom monastyrě Vojlovicě (Short History of monastery by hegumen Joanikije Milković, 1765–1822), Buda 1801, Online edition of National Library of Austria.
- ↑ History of Roman Catholic Church on the Official Website by Diocese of Zrenjanin, Retrieved on 2017-05-25.
- ↑ History of Serbian Orthodox Church on the Official Website by Eparchy of Banat, Retrieved on 2017-05-25.
- ↑ History of the iconostasis on the Official Website by the Church Assumption of Holy Virgin, Retrieved on 2017-09-27.
- ↑ Cultural monuments on the Official Website by Turistička organizacija Pančevo (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Institute for Protection of Cultural Monuments of Pančevo (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Pančevac (in Serbian), Retrieved on 2017-01-18.
- ↑ Official Website by RTV and its YouTubeChannel, Retrieved on 2017-01-21.
- ↑ Official Website by Libertatea, Retrieved on 2017-01-25.
- ↑ Official commercial address book of the City (PDF), Retrieved on 2017-01-22.
- ↑ UNEP final report Pančevo (PDF), Retrieved on 2017-01-22.
- ↑ Official Website by Nature Park Ponjavica, Retrieved on 2017-01-23.
- ↑ ОПШТИНЕ И РЕГИОНИ У РЕПУБЛИЦИ СРБИЈИ, (PDF; Municipalities and Regions of the Republic of Serbia), Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia 2016, Belgrade 2017, p. 17, 30, 68-69, 97, 103, 110, 115, 140, 148, 172, 176, 195-197, 216-217, 236, 240, 248 and 284, Retrieved on 2017-12-10.
- ↑ "ОПШТИНЕ И РЕГИОНИ У РЕПУБЛИЦИ СРБИЈИ, 2017" (PDF). stat.gov.rs (in Serbian). Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. p. 152, 153. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ↑ Official website of Autotransport Pančevo, retrieved on 2018-01-12.
- ↑ Felix Milleker, Die Banater Eisenbahnen 1847–1917, Vršac 1927, p.17.
- ↑ Official Website by Luka Dunav, Retrieved on 2017-03-23.