Nantong
Nantong (Chinese: 南通; pinyin: Nántōng; alternate names: Nan-t'ung, Nantung, Tongzhou, or Tungchow; Qihai dialect: [nie tʰoŋ]) is a prefecture-level city in Jiangsu province, China. Located on the northern bank of the Yangtze River, near the river mouth. Nantong is a vital river port bordering Yancheng to the north, Taizhou to the west, Suzhou, Wuxi and Shanghai to the south across the river, and the East China Sea to the east. Its current population is 7,282,835 at the 2010 census, 1,994,708 of whom live in the built-up area made up of three urban districts.
Nantong 南通市 Nantung | |
|---|---|
 The skyline of Nantong flanking the Hao River, a historical moat. | |

| |
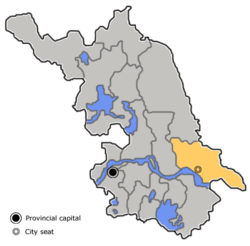 Location of Nantong City jurisdiction in Jiangsu | |
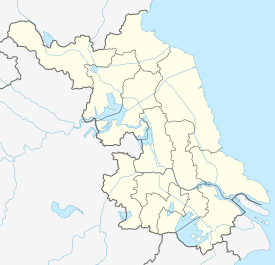 Nantong Location of the city center in Jiangsu  Nantong Nantong (Eastern China)  Nantong Nantong (China) | |
| Coordinates (Nantong municipal government): 31°58′52″N 120°53′38″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Jiangsu |
| Municipal seat | Chongchuan District |
| Government | |
| • CPC Municipal Secretary | Lu Zhipeng (陆志鹏) |
| • Mayor | Han Liming (韩立明) |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 8,544.1 km2 (3,298.9 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,692 km2 (653 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,692 km2 (653 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2 m (7 ft) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 7,282,835 |
| • Density | 850/km2 (2,200/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 1,994,708 |
| • Urban density | 1,200/km2 (3,100/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 1,994,708 |
| • Metro density | 1,200/km2 (3,100/sq mi) |
| [1] | |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 226000 (Urban centre) 226100-226600 (Other areas) |
| Area code(s) | 513 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-JS-06 |
| GDP | ¥842.7 billion (2018) |
| GDP per capita | ¥92,715 (2016) |
| Major Ethnicity | Han |
| County-level divisions | 8 |
| Township-level divisions | 146 |
| Licence Plate Prefixes | 苏F |
| Website | nantong |
In September 26, 2004, the first World Metropolitan Development Forum was held in Nantong. In 2005, Nantong had a GDP growth of 15.4%, the highest growth rate in Jiangsu province, and in 2016 Nantong's GDP had a total of about 675 billion yuan, ranking the 21st in the whole country.
Although the city took a blow from the economic depression of the 1930s, as well as the Japanese occupation of the 1930s and 40s, Nantong has remained an important center for the textile industry. Because of its deepwater harbor and connections to inland navigational canals, it was one of 14 port cities opened to foreign investment in recent Chinese economic reforms.
Geography and climate
| Nantong | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 南通 | ||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Nantung | ||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | southern passage | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Tongzhou | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 通州 | ||||||||
| Postal | Tungchow | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Because the coast of the East China Sea is constantly expanding eastward as the Yangtze River adds silt to its delta, the distance between Nantong and the seashore is getting longer than it once was in ancient times.
Nantong has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), with four distinct seasons. Winters are chilly and damp, and cold northwesterly winds caused by the Siberian high can force temperatures to fall below freezing at night although snowfall is relatively uncommon. Summers are hot and humid, and downpours or freak thunderstorms often occur. Monthly daily average temperatures range from 3.1 °C (37.6 °F) in January to 27.2 °C (81.0 °F) in July, and the annual mean is 15.33 °C (59.6 °F). With the plum rains in June and early July comes the rainiest part of the year.
| Climate data for Nantong (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.4 (65.1) |
24.7 (76.5) |
26.1 (79.0) |
31.1 (88.0) |
34.4 (93.9) |
36.0 (96.8) |
38.2 (100.8) |
37.0 (98.6) |
38.5 (101.3) |
31.1 (88.0) |
27.6 (81.7) |
20.7 (69.3) |
38.5 (101.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
8.2 (46.8) |
12.1 (53.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
24.1 (75.4) |
27.4 (81.3) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.9 (87.6) |
26.8 (80.2) |
22.0 (71.6) |
15.9 (60.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
19.5 (67.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) |
4.2 (39.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.4 (74.1) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.0 (80.6) |
22.8 (73.0) |
17.6 (63.7) |
11.6 (52.9) |
5.6 (42.1) |
15.3 (59.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.2 (32.4) |
1.2 (34.2) |
4.7 (40.5) |
10.1 (50.2) |
15.5 (59.9) |
20.2 (68.4) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.2 (75.6) |
19.8 (67.6) |
14.1 (57.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
2.2 (36.0) |
12.0 (53.7) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.6 (14.7) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
5.5 (41.9) |
12.8 (55.0) |
15.6 (60.1) |
16.5 (61.7) |
9.9 (49.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 43.5 (1.71) |
48.9 (1.93) |
81.3 (3.20) |
72.8 (2.87) |
92.7 (3.65) |
197.2 (7.76) |
164.5 (6.48) |
129.5 (5.10) |
102.8 (4.05) |
55.7 (2.19) |
47.7 (1.88) |
28.3 (1.11) |
1,064.9 (41.93) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 8.5 | 9.1 | 12.0 | 10.5 | 11.1 | 12.2 | 13.3 | 11.2 | 9.9 | 8.3 | 7.1 | 5.4 | 118.6 |
| Source: Weather China | |||||||||||||
Administration
The prefecture-level city of Nantong administers eight county-level divisions, including three districts, four county-level cities, and one county.
These are further divided into 146 township-level divisions.
| Map | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdivision | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010) | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
| City Proper | |||||
| Chongchuan District | 崇川区 | Chóngchuān Qū | 868,262 | 426.35 | 2,036.50 |
| Gangzha District | 港闸区 | Gǎngzhá Qū | 266,326 | 151.97 | 1,752.49 |
| Suburban | |||||
| Tongzhou District | 通州区 | Tōngzhōu Qū | 1,138,738 | 1,561.97 | 729.04 |
| Rural | |||||
| Rudong County | 如东县 | Rúdōng Xiàn | 995,983 | 2,791.17 | 356.83 |
| Satellite cities (County-level cities) | |||||
| Qidong City | 启东市 | Qǐdōng Shì | 972,525 | 1,714.59 | 567.21 |
| Rugao City | 如皋市 | Rúgāo Shì | 1,267,066 | 1,576.12 | 803.91 |
| Haimen City | 海门市 | Hǎimén Shì | 907,598 | 1,143.51 | 793.69 |
| Hai'an City | 海安市 | Hǎi'ān Shì | 866,337 | 1,183.57 | 731.97 |
| Total | 7,282,835 | 10,549.25 | 690.37 | ||
History
Ancient era
Because the coast of the East China Sea is constantly expanding eastward as the Yangtze River adds silt to its delta, the distance between Nantong and the seashore is getting longer than it once was in ancient times.
The area that is now Nantong was originally part of the State of Wu during the Spring and Autumn period, which was later conquered by the State of Yue in 473 BC. After yet again being subjected to a new foreign rule by the State of Chu in 334 BC, the inhabitants of present-day Nantong would again experience another regime change during the first unification of China by the State of Qin.
Imperial era
From the Han dynasty up until the Tang dynasty, what is now called Nantong was a minor city county subordinate to Yangzhou. By AD 958, that city county had already gained sufficient importance for it to be upgraded to an independent prefecture called Tongzhou ("Opening Prefecture", possibly from its position near the mouth of the Yangtze) to be created. The increasing wealth of Yangzhou caused Tongzhou to be once again eclipsed as an administrative center in 1368.
When Tongzhou finally regained prefecture status in 1724 during the Qing Dynasty, it was renamed to its present name Nantong ("Southern Tong") to avoid confusion with another administrative division also named Tongzhou, located near Beijing.
Modern era
Nantong was the first place in China to be developed into a modern city after the collapse of the Qing Dynasty, and was also the birthplace of China's modern industry.
The prosperity of Nantong has traditionally depended on salt production on the nearby seacoast, rice and cotton agriculture, and manufacture of cotton textiles, especially Nantong blue calico. A local statesman and industrialist named Zhang Jian founded Nantong's first modern cotton mills in 1899. He then developed an industrial complex that included flour, oil, and silk reeling mills, a distillery, and a machinery shop. He also founded a shipping line and reclaimed saline agricultural land to the east of Nantong for cotton production. Thanks to these efforts, by 1911 Nantong was commonly called "Zhang Jian's Kingdom". In the early Republican period, the Nantong Special Administrative District included Chongming County, now part of Shanghai.[2]
Culture
- Xuanmiao Temple, structure built during the Song era.
- Nantong Confucian Temple
- Nantong Museum
Dialect
Nantong city and its six counties (or county-level cities) are rich in linguistic diversity, featuring both important Northern Wu varieties and highly divergent dialects of Mandarin (see Nantong dialect). People in the city of Nantong speak a unique dialect which sounds nothing like standard Mandarin or any other dialect, and it is also holds distinctive differences from surrounding dialects. About 2 million people in the southern parts of Tongzhou, Haimen, and Qidong speak the Wu dialect, which is often referred to as "Qi-hai Hua" (启海话), meaning Qidong-Haimen speech. It is about the same as the dialect spoken on the neighbouring island of Chongming, Shanghai. People in northern parts of these counties speak "Tongdong dialect" (Chinese: 通东话; pinyin: Tōngdōng Huà; lit.: '"Eastern Tong Talk"'. People in Rugao, Hai'an speak other dialects.
Tourism
The Hao River, known as the Emerald Necklace of Nantong, surrounds the city with a total length of 15 km (9.3 mi). Most city scenery lines this river.[3]

Popular tourist sites include Langshan ("Wolf Hill"), which is around 110 meters high. On top of the hill is a Buddhist temple dedicated to a Song dynasty monk. Because of the monk's legendary powers over water demons, sailors pray to him for protection on their voyages.
The Cao Gong Zhu Memorial Temple commemorates a local hero who defended the city against Japanese pirates in 1557.
Shuihuiyuan Garden, meaning Water Garden, is unique of all Chinese classical gardens due its creation in the Hui style. It includes the tombs of several notable people, such as Luo Binwang, a famous poet of Tang Dynasty; Wen Tianxiang, the national hero of Nansong Dynasty; Zhang Jian, the number one scholar of the late Qing Dynasty who was a modern industrialist and supporter of education.
Economy
Nantong was historically known as an agricultural area and a traditional site for salt-making. Its principal agricultural products include cotton, rice, wheat, fishing, fruit, and more. Currently, the city is making efforts to upgrade its farming sectors and increase production of organic foods.
Nantong is one of the 14 port cities opened to foreign investment projects under China's current policies of modernization. Nantong was traditionally an industrial city, especially around the turn of the 20th century, specializing in salt and cotton textile production. Today's industrial corporations have made Nantong into an industrial hub since it opened its door to the outside world in the 1990s. With its excellent geographic location and the completion of two Yangtze River bridges, the prefecture is attracting more investment funding nationwide. Many of these investments come from international corporations. In October 2007, Singapore RGM International signed an agreement with Rudong, a county under Nantong's jurisdiction, to invest in a port project, costing 9 billion Yuan or US$1.33 billion, at Rudong Yangkou Port.
Today, Nantong is one of many fast-growing coastal cities in China. With the opening of Sutong Bridge in April 2008 and Chonghai Bridge in 2009, the city has been listed as the number one city in the Yangtze River Delta Economic Zone for foreign investment, surpassing its rivals Suzhou, Hangzhou and Nanjing.
As a sprawling metropolis, Nantong has experienced environment damage from its industrialization as well. The municipal government has been putting stiffer environmental policies into practice over the years and has spent tremendous amounts of money to curb pollution and plant more trees along its roads. The city is active in shutting down factories that do not meet its environment laws.
Nantong has developed rapidly in the last 25 years, as have most of the cities in the Yangtze River Delta. Nantong's rapid economic growth is generally attributed to its advantageous location just north of Shanghai. Nantong's Sutong Bridge is expected to further Nantong's integration with Shanghai, cutting transportation time between the cities down from three hours to one hour.[4]
The shipping corporation Cosco has a large port and ship repair yard on the river. Cosco (Nantong) Shipyard Co., Ltd, the first shipyard of the Cosco group, has placed itself adjacent to the busy port of Nantong. The yard has 1120 m of coastline and is equipped with one cape-size and one panamax size floating dock. Cosco Shipyard handles approximately 150 vessels per year.[5] Nantong Mingde Heavy Industries originally operated a shipyard in Nantong, but declared bankruptcy in 2014.[6] Minde's parent company, Jiangsu Sainty Marine Corporation, would cease operations in 2017.[7]
Some companies in Nantong:[8]
- Empire Clothing Co. Ltd. - Manufacturer of garments for men, women and children. Products gallery.
- Nantong No.2 Yarn-dyed Weaving Mill - Cloth and garment manufacturer.
- Nantong Taierte Clothing Co. Ltd. - Textile production and processing.
- Nantong Freezing Equipment Factory - Refrigeration and quick freezing equipment for the food industry.
- Nantong Printing and Dyeing Co. Ltd. - Textile processor. Product specifications.
- Nantong Suzhong Textile Co. Ltd. - Yarn and thread manufacturer. Product specifications.
- Nantong General Pharmaceutical Factory - Manufacturer of pharmaceutical materials such as tablets, capsules and injections. Product specifications.
- Nantong Xiaoxing Transformer Co., Ltd. -Various range of electric transformers
- Nantong Fujitsu Microelectronics Co Ltd [9]
Industrial zones
- Nantong Binhai Park
Established in January 2012 under the State-level development zone standard, Nantong Binhai Park is directly governed and intensively invested by the Nantong Municipality, shares superior policies and occupies a land area as much as 820 km2 (320 sq mi). Binhai park is located at 50 km (31 mi) east to Nantong downtown, nearly 1.5 hrs drive to Shanghai Pudong and Hongqiao airports. Binhai park possesses unique transportation conditions both in expressways (Tongyang to Nantong downtown, Haiqi to Qidong and Shanghai Pudong) and sea ports (500 berths from 50,000 tons to 300,000 tons in Tongzhou Bay port cluster). Binhai park's industries focus on maritime & offshore, logistics, equipment manufacturing, new energy, advanced materials, electronics, etc.
- Nantong Economic & Technological Development Area
Established in 1984, Nantong Economic & Technological Development Area (NETDA) was one of the first state-level development zones approved by the Chinese Central Government and has been certified as an ISO 14000 National Demonstration Zone. The zone benefits from superior transportation facilities by both rail and road. NETDA has direct links to two railways: the Xinyi-Changxing Railway and the Nanjing-Qidong Railway. Su-Tong Yangtze River Bridge feeds into the center of NETDA and connects the Nanjing-Nantong and Yancheng-Nantong Expressways to the north, and Shanghai-Nanjing and Suzhou-Jiaxing-Hangzhou Expressways and Riverside Expressways to the south.
NETDA includes several subsidiary zones including Nantong Export Processing Zone, New Material Park, Opto-mechatronics Industrial Park and NETDA Business Park. Special incentives are offered for investments in areas of modern equipment manufacturing, such as in new materials, engineering, fine chemicals, new medicines, new energy and modern services. At present, NETDA has attracted a large number of renowned companies to settle in Nantong, such as Vonnex Allied IT Services, OJI Paper, Maxion, Johnson Controls, ITOCHU, TSRC Corporation, and Merck KGaA.[10][11]
- China Singapore[12]
Established in 2009, STP is one of the key projects of Jiangsu Province coastal development. It's also a joint-venture park between Suzhou and Nantong, linking them on either side of the Yangtze River. The intended area is 50 km2 (19 sq mi) and is to be developed in three phases. It claims the project as "An International Enterprise Park and Eco-friendly City in Yangtze Delta".
- Nantong Export Processing Zone
Nantong Export Processing Zone (NTEPZ) is situated in the Nantong Economic and Technological Development Area with a planned area of 2.98 km2 (1.15 sq mi). The Tong-Qi canal marks its western and northern boundaries, with Dongfang Avenue and Fuxin Road its eastern and southern boundaries respectively. NTPEZ is located at a communication hub, adjoining the main coastal artery of communications between north and south, close to the estuary of the Yangtze River, only 8 kilometers to the Su(Suzhou)-Tong(Nangtong) Changjiang Bridge.[13]
Transportation
Air
Nantong Xingdong Airport, located in the town of Xingdong in Tongzhou District, 9.8 kilometers northeast of city center and 120 kilometers from Shanghai, serves Nantong and its neighboring areas. The construction of terminal 2 was completed in 2014, marking an important step towards serving international flights.[14]
Road
Nantong has two bridges across the Yangtze to the south. The Chongming–Qidong Yangtze River Bridge, completed in 2011, carries the G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway from Qidong to Chongming Island. The Sutong Yangtze River Bridge, which carries the G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway from Nantong to Changshu, was completed in 2008 and is one of the longest cable-stayed bridges in the world.
Rail
The Nanjing-Qidong (Ningqi) and Xinyi-Changxing (Xinchang) Railways intersect at Hai'an in the northwestern part of Nantong Prefecture.
Plans also exist for a cross-river connection from Nantong to the Shanghai metropolitan area (the Shanghai–Nantong Railway). It will connect to the Nanjing–Qidong Railway at Pingdong Station (平东站) on the northwestern outskirts of Nantong's urban core. Construction work started in 2013 and is expected to be finished in 2019.[15]
Currently, Nantong Railway station and Hai'An railway station have the highest train volume in the city. Due to the single-track nature of the Nanjing-Qidong railway east of Nantong railway station, Electrified Multiple Unit service are not available beyond Nantong railway station; Qidong railway station currently receives 4 round trip trains per day operated as "K" trains. A line from Hai'an also connects Rudong county to the national rail network, with daily departures bounding for Nanjing.
Education

Nantong hosts a comprehensive university, Nantong University (made by the merger of the former Nantong Medical College, former Nantong Normal College, and former Nantong Engineer College). It includes 21 schools and had around 22,000 registered students in 2007.
Nantong has contributed to China's educational development with several firsts: establishment of the first school for teacher training, the first folk museum (Nantong Museum[16]), the first school for industrial textile manufacturing, the first school for embroidery, the first drama school, and the first school for the deaf and the blind.[17][18][19]
Zhang Jian founded the first normal school in modern China, Nantong Normal College. Zhang also founded museums, libraries, and theaters, making Nantong into an important cultural center.
- Secondary schools (incomplete list):
- Universities and colleges:
- International Schools
- Nantong Stalford International School http://en.ntsis.com/
Social Welfare Institute
Established in 1906, Nantong Social Welfare Institute was originally created by Zhang Jian as a house for orphans, the aged, and the disabled.
Located on the banks of the Haohe, the site of the institute has an area of 13.2 mu (8,800 m²). At present, there are 79 staff members who care for around 170 orphans, widows, and handicapped children, plus 70 retirees.
References
- "China: Provinces and Major Cities - Population Statistics in Maps and Charts". Citypopulation.de. Archived from the original on 2015-07-04. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
- "Chongming County" in the Encyclopedia of Shanghai, pp. 50 ff. Archived 2013-03-02 at the Wayback Machine Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers (Shanghai), 2010. Hosted by the Municipality of Shanghai.
- "A paradise on the water". China Daily. 2007-01-08. Archived from the original on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
- Jiao, Xiaoyang (June 19, 2007). "New milestone for record-breaking bridge". China Daily. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved 2014-08-04.
- Archived February 12, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-03-25. Retrieved 2019-03-25.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2019-03-25. Retrieved 2019-03-25.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Nantong at Curlie
- Liu, Baijia (April 9, 2007). "High stakes chips". China Daily. Archived from the original on October 9, 2012. Retrieved 2008-08-04.
- "Jiangsu Industrial Park-Nantong Economic & Technological Development Area (NETDA) - China Industrial Space". Archived from the original on 11 June 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany (15 November 2013). "Merck Strengthens its Presence in China with New Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Facility". Archived from the original on 9 October 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- "Invest in Nantong-China Singapore Sutong Science & Technology Park | China Industrial Space". Rightsite.asia. Archived from the original on 2015-07-03. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
- "Nantong Export Processing Zone". Archived from the original on 9 January 2016. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- Pan Dongdong (潘冬冬); Ma Jun (马骏). "Archived copy" 南通兴东机场2号航站楼正式试运行. Archived from the original on 9 January 2016. Retrieved 12 June 2015.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- 沪通铁路太仓段开建 [Construction work on the Taicang Part of Hu-Tong Railway has started] (in Chinese). 2014-10-15. Archived from the original on 2015-07-23. Retrieved 2015-07-23.
- 南通博物苑. www.ntmuseum.com. Archived from the original on 2018-02-13. Retrieved 2018-02-13.
- "China Daily reference for First school of Embroidery, textile and drama". Archived from the original on 14 June 2015. Retrieved 12 June 2015.
- Archived August 15, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- 南通大学-英文版. English.ntu.edu.cn. Archived from the original on 2015-06-14. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
- 百年名校—江苏省南通中学. Ntzx.cn. Archived from the original on 2011-01-29. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
- 网站首页-江苏省南通第一中学. Jsntyz.edu.cn. Archived from the original on 2015-07-03. Retrieved 2015-07-02.
Further reading
- Qin Shao, Culturing Modernity: The Nantong Model, 1890–1930 (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2004).
- Bao, Mingwei & Wang, Jun (2002). Nantong Diqu Fangyan Yanjiu [A Study on the Dialects in Nantong Area]. Jiangsu Jiaoyu Press.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Nantong. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Nantong. |
- Government website of Nantong (available in Chinese, Japanese and English)
- Nantong comprehensive guide with open directory—Jiangsu.NET
- The Columbia Encyclopedia: Nantong—Brief facts about the city
- Nantong Science and Technology Commission—Brief description of the city and a list of cooperative projects available
- Historic US Army map of Nantong in 1942
- Zhiyan Gao, "nantong dialect phonological inventory"
