Mentougou District
Mentougou District (simplified Chinese: 门头沟区; traditional Chinese: 門頭溝區; pinyin: Méntóugōu Qū) is a district in western Beijing. Spanning 1,321 square kilometres (510 sq mi), with 266,591 inhabitants (2000 Census), it is subdivided into 4 subdistricts of the city proper of Beijing and 9 towns (1 of which is a suburb of the city proper of Beijing). It borders the Beijing districts of Changping to the northeast, Haidian and Shijingshan to the east, Fengtai to the southeast, and Fangshan to the south, as well as Hebei province to the west and northwest.
Mentougou 门头沟区 | |
|---|---|
District | |
 Tanzhe Temple's Entrance | |
| |
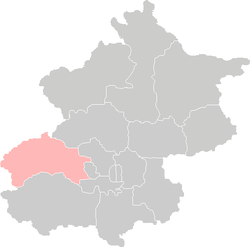 Location of Mentougou District in Beijing | |
| Coordinates (Mentougou government): 39°56′25″N 116°06′05″E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Municipality | Beijing |
| Township-level divisions | 4 subdistricts 9 towns |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,321 km2 (510 sq mi) |
| Population (2000) | |
| • Total | 266,591 |
| • Density | 200/km2 (520/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Area code(s) | 0010 |
It lies in the Western Hills of Beijing and is mountainous in terrain. In fact, the mountainous terrain—including a hundred or more peaks—occupy a stunning 93% of the entire area.
It is a treasure trove of natural resources, including coal, limestone, and granite. Mentougou also supplies Beijing with agricultural produce such as roses, wild jujubes, mushrooms, and Beijing white pears.
The district was purely a rural area well into the early 1990s and was not considered as part of Beijing by the urban population, and as of today, many parts of Mentougou remain quite rural. The 6th Ring Road cuts through the eastern, more urbanised section of Mentougou Precinct.
Mining is one of the key industrial activities. Around 10 medium and large mining companies once operated in Mentougou, but some of them have ceased operations as mineral deposits have been depleted. The first known mining activity in Mentougou was documented during the Ming Dynasty.
Tourism
Mentougou is gaining popularity as a tourist destination. Among its main sights are Jietai Temple, Tanzhe Temple, Longmen Gully (or Canyon), Mount Baihua, Mount Ling (the highest mountain in Beijing at 2,303 metres), Mount Miaofeng, and the village of Cuandixia.
Administrative divisions
There are 4 subdistricts and 6 towns with 3 towns of which carry the "area" (地区) label:[1][2]
| Name | Chinese (S) | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010)[3] | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dayu Subdistrict | 大峪街道 | Dàyù Jiēdào | 80,413 | 4.40 |
| Chengzi Subdistrict | 城子街道 | Chéngzi Jiēdào | 34,555 | 2.90 |
| Dongxinfang Subdistrict | 东辛房街道 | Dōngxīnfáng Jiēdào | 27,335 | 18.00 |
| Datai Subdistrict | 大台街道 | Dàtái Jiēdào | 11,296 | 81.00 |
| Wangping (town) Area | 王平(镇)地区 | Wángpíng (Zhèn) Dìqū | 6,513 | 46.00 |
| Yongding (town) Area | 永定(镇)地区 | Yǒngdìng (Zhèn) Dìqū | 42,446 | 68.60 |
| Longquan (town) Area | 龙泉(镇)地区 | Lóngquán (Zhèn) Dìqū | 32,149 | 49.00 |
| Tanzhesi town | 潭柘寺镇 | Tánzhèsì Zhèn | 8,672 | 73.20 |
| Junzhuang town | 军庄镇 | Jūnzhuāng Zhèn | 12,516 | 34.00 |
| Yanchi town | 雁翅镇 | Yànchì Zhèn | 6,587 | 239.00 |
| Zhaitang town | 斋堂镇 | Zhāitáng Zhèn | 10,817 | 392.40 |
| Qingshui town | 清水镇 | Qīngshuǐ Zhèn | 7,906 | 339.00 |
| Miaofengshan town | 妙峰山镇 | Miàofēngshān Zhèn | 9,271 | 110.00 |
See also
References
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Mentougou District. |
- These towns are officially classified as subdistricts, but as they coincide with the area of the same name, they are commonly named "areas" (地区)
- 2011年统计用区划代码和城乡划分代码:门头沟区 (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- Census Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China; Population and Employment Statistics Division of the National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China (2012). 中国2010人口普查分乡、镇、街道资料 (1 ed.). Beijing: China Statistics Print. ISBN 978-7-5037-6660-2.
