Fort Caswell Historic District
Located in North Carolina on the Atlantic Coast, the Fort Caswell Historic District encompasses 2 sites, 43 buildings, and 23 structures; it was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2013.[2] The fort itself was occupied by various branches of the U.S. armed forces for most of the period between 1836 and 1945 and is now a part of the North Carolina Baptist Assembly, a Christian retreat, owned and operated by the Baptist State Convention of NC. It is accessible by the public to a limited extent per the conditions set forth by the Assembly’s Director. [3]
Fort Caswell Historic District | |
 Original Fort Caswell | |
  | |
| Location | 100 Caswell Beach Road, near Caswell Beach, North Carolina |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 33°53′28″N 78°01′41″W |
| Area | 760 acres (310 ha) |
| Built | 1838, 1898-ca. 1941 |
| Built by | U.S. Army Quartermaster Corps; Bernard, Simon |
| Architectural style | Colonial Revival, Queen Anne |
| NRHP reference No. | 13001025[1] |
| Added to NRHP | December 31, 2013 |
Geography
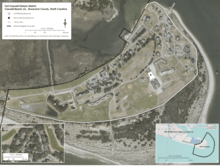
Sited on the eastern tip of Oak Island in Brunswick County, NC, the fort juts into the confluence of the Cape Fear River and the Atlantic Ocean. The district's boundaries also extend a little over 1/2 mile south into the Atlantic Ocean and east into the Cape Fear River in recognition of the fort's association with blockade runners during the Civil War and its role in hunting down German submarines during World War II. The rifle range site is located a little over two miles to the west-northwest of the fort in the Town of Caswell Beach. Typical of coastal southeastern North Carolina, the natural topography of the site is flat, roughly ten feet above sea level with a wide sandy beach along its southern boundary. Grass covers most of the area, with Yaupon Holly and Live Oaks trees liberally spread throughout the district.[4]
History

Named after former governor Richard Caswell, the original pentagonal fortification of brick walls and large earthworks was completed in 1836 at a cost of $473,402. With over 61 gun emplacements, it guarded the mouth of the Cape Fear River in defense of Wilmington, then an important port 20 miles upriver and, at the time, the state's largest city. In 1861, it was seized twice by a group called the "Cape Fear Minutemen", who were subsequently ordered by Governor John Willis Ellis to return it to the keeper of the fort, the only man stationed there by the U.S. Army at the time.[5] When the state finally seceded, the new Confederate Army made it, along with nearby Fort Fisher, one of the most elaborate defensive system in the world at that time. (Fort Fisher guarded the other inlet to the Cape Fear River). This system, along with swift blockade runners, kept Wilmington's port open longer than any other. No fewer than six plans were devised to capture the fort, but its imposing defenses and the Frying Pan Shoals just offshore deterred them; the Union Army then diverted its attention to Fort Fisher. After a massive Union assault captured Fort Fisher on January 15, 1865, orders came to spike Fort Caswell's guns, burn the barracks, and explode the magazines. On January 17, the magazines were ignited, exploding approximately 100,00 pounds of powder (reports at the time state that the blast could be heard as far as 100 miles away in Fayetteville). As a result of the explosion, one whole wall of the fort was destroyed. The loss of the Confederacy's last port was a major factor in Robert E. Lee's decision to surrender at Appomattox [5] The U.S. Army built a full military reservation on the site in the 1890s, complete with coastal artillery batteries, but abandoned it after World War I. Most of the buildings currently extant as well as the sea wall were built during this period. The discontiguous Fort Caswell Rifle Range site is also a World War I addition. From 1937-1941, the fort was unsuccessfully converted into a resort, with the gun emplacements used as swimming pools (two artesian wells produced hot mineral water to fill the pools). In 1941, the Navy purchased the fort for use as an anti-submarine base during World War II. The Baptist State Convention of North Carolina bought the property in 1949 as surplus for $86,000.
References
- "National Register of Historic Places Listings". Weekly List of Actions Taken: 12/30/13 through 1/03/14. National Park Service. 2014-01-10.
- "Fort Caswell NHRP" (PDF). NCDR.gov. Retrieved 2019-03-16.
- "Fort Caswell". FortCaswell.com. Retrieved 2019-01-30.
- "Fort Caswell Historic District" (PDF). NPS.gov. Retrieved 2019-02-25.
- Herring, Ethel & Williams, Carolee (1999). Fort Caswell in War and Peace. Oak Island, NC: NC Baptist Assembly. ISBN 0-9671897-1-3.
Further reading
- Lewis, Emanuel Raymond (1979). Seacoast Fortifications of the United States. Annapolis: Leeward Publications. ISBN 978-0-929521-11-4.
- Weaver II, John R. (2018). A Legacy in Brick and Stone: American Coastal Defense Forts of the Third System, 1816-1867, 2nd Ed. McLean, VA: Redoubt Press. ISBN 978-1-7323916-1-1.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)