COVID-19 pandemic in Louisiana
The first presumptive case relating to the COVID-19 pandemic in Louisiana was announced on March 9, 2020. Since the first confirmed case, the outbreak grew particularly fast relative to other states and countries. As of June 14, 2020, there have been 46,619 confirmed cases in Louisiana, and of those 2,901 people have died.[1] Confirmed cases have appeared in all 64 parishes, though the New Orleans metro area alone has seen the majority of positive tests and deaths.[1] Governor John Bel Edwards closed schools statewide on March 16, 2020, restricted most businesses to takeout and delivery only, postponed presidential primaries, and placed limitations on large gatherings.[2][3] On March 23, Edwards enacted a statewide stay-at-home order to encourage social distancing, and President Donald Trump issued a major disaster declaration, the fourth state to receive one.[2][4]
| COVID-19 pandemic in Louisiana | |
|---|---|
.jpg) A testing site in New Orleans | |
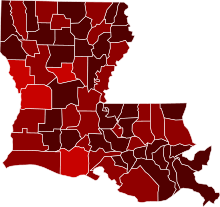 Map of the outbreak in Louisiana by confirmed infections per 100,000 people (as of June 26)
1,000+ confirmed infected
500–1,000 confirmed infected
100–500 confirmed infected
20–100 confirmed infected
0–20 confirmed infected | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Louisiana, U.S. |
| Index case | Orleans Parish |
| Arrival date | March 9, 2020 |
| Confirmed cases | 50,239 |
| Hospitalized cases | 630 (current) |
| Ventilator cases | 77 (current) |
| Recovered | 39,792 |
Deaths | 3,004 (confirmed) 113 (probable) |
| Government website | |
| LDH.LA.gov/Coronavirus | |
The rapid spread of COVID-19 in Louisiana likely originated in late February 2020, when over one million people visited New Orleans and the surrounding metropolitan area for Mardi Gras festivities.[5] Numerous "clusters" of confirmed cases have appeared at nursing homes across southern Louisiana, including an outbreak at Lambeth House in New Orleans that has infected over fifty and killed thirteen elderly residents as of March 30.[6][7] As the state has increased its capacity for testing, a University of Louisiana at Lafayette study estimated the growth rate in Louisiana was among the highest in the world, prompting serious concerns about the state's healthcare capacity to care for sick patients.[8] On March 24, only 29% of ICU beds were vacant statewide, and Edwards announced coronavirus patients would likely overwhelm hospitals in New Orleans by April 4.[9]
Since moving into phase two, Louisiana has seen a major spike in new confirmed cases bringing the total number of confirmed cases to 54,769 as of June 26, 2020. [10][11]
Timelines
March
March 9–10
On March 9, the state's first presumptive case of coronavirus was reported in the New Orleans metro region.[13][14] The patient is a veteran and resident of Jefferson Parish. On March 10, state officials confirmed 2 new cases also in the New Orleans area bringing the state's total to 3, with 3 additional presumptive cases sent to the CDC for confirmation. Mayor Latoya Cantrell and other city officials announced the cancellation of weekend parades as a precaution.[15]
March 11–13
On March 11, the total number of cases rose to 13, with 10 new, presumptive positive cases reported in 6 parishes, the first outside of the Orleans metro region and in the river parishes.[16] On March 12, Grambling State University announced travel restrictions to prevent the coronavirus from spreading.[17]
On March 13, Governor Edwards issued an order prohibiting gatherings of more than 250 people, and the closure of all K-12 public schools from March 16 to April 13,[18] as the number cases rose to 36.[1] Archbishop Gregory Aymond of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New Orleans announced that all Catholic schools would close from March 16 through April 13, following Governor John Bel Edwards' decision to close public schools in Louisiana. In addition, the Archbishop announced that all persons were dispensed from the obligation of attending Mass through April 13, though not going as far as suspending public Masses.[19]
March 14–16
Early March 14, the Louisiana Department of Health announced that the number of cases rose to 51.[20] That same evening, the number of cases rose to 77, with the first death being reported. That total includes 1 case where the resident is being treated in Louisiana but lives out of the state.[21]
On the morning of March 15, Governor John Bel Edwards announced that 14 additional positive cases had been confirmed in Louisiana, as well as the state's second death: a 53-year-old person from Orleans Parish with underlying medical conditions. This brought the total number of cases to 91.[22] Later that evening, another 12 cases were confirmed, bringing the total number of cases to 103.[1]
During the morning of March 16, the Louisiana Department of Health confirmed an additional 11 positive cases of COVID-19 in the state, bringing the total to 114.[23] Governor Edwards reported that the number of cases had risen to 136 by the afternoon and reported that a third person died due to the coronavirus.[24]
March 17
On March 17, Saint Patrick's Day, another 60 positive cases were added in Louisiana, bringing the cumulative total of positive cases to 196. The fourth death in the state was also reported by the Louisiana Department of Health: 80-year-old judge James Carriere, who became the second person to die of coronavirus in the Lambeth House retirement home in uptown New Orleans.[25]
Analysis of coronavirus data by New Orleans WVUE Fox 8 and the Michael I. Arnolt Center for Investigative Journalism at Indiana University determined that by March 17, Orleans Parish had the second-highest number of cases by county or parish per capita in the country, only behind Westchester County, New York. In addition, it was found that the New Orleans metropolitan area had the second-highest number of cases by metropolitan area per 100,000 people, behind the Seattle-Tacoma metropolitan area in Washington.[26]
Officials from the New Orleans Jazz and Heritage Festival announced that the festival, which was to be held for two weekends from late April to early May, would be postponed until the fall. Citing the restrictions set in place by the City of New Orleans and the State of Louisiana, organizers postponed the festival for the "health and safety of the community, [the] musicians, Festival fans, participants, sponsors, and staff" and recommended "everyone to follow the guidelines and protocols" from officials. Although no new exact dates were not announced for the festival, the tickets purchased will be honored in the fall.[27]
March 18–19
By March 18, the number of positive cases in Louisiana was over 200. Three new deaths were confirmed on March 18, bringing the total number of deaths in the state to 7. One of the three deaths confirmed that day in Louisiana was a 72-year-old man from Jefferson Parish, the first death outside of Orleans Parish.[28] The second of the three deaths confirmed on March 18 was 92-year-old psychiatrist Dr. Charles Rodney Smith, the third person who died in the Lambeth House retirement community in uptown New Orleans.[29] The Louisiana Department of Health also announced 84 additional positive cases on March 18, bringing the state's cumulative total of positive cases to 280, with 196 of them in Orleans Parish alone.[30]
Early on March 19, Governor Edwards announced that the number of cases had risen to 347, with the majority of cases concentrated in Orleans and Jefferson Parishes. West Baton Rouge, Lafayette, Plaquemines, and St. James Parishes all were confirmed to have their first cases that morning. St. James Parish also announced that their first case would also be Louisiana's eighth death, the first outside of New Orleans and Jefferson Parish.[31] The New Orleans Saints' head coach Sean Payton announced that he had tested positive, becoming the first member of an NFL organization to do so.[32] The evening update from the Louisiana Department of Health increased the number of positive cases to 392 and the number of deaths to 10. New positive cases were found in Assumption, Calcasieu, Iberia, Iberville, Livingston, Rapides, St. Landry, and Webster Parishes, increasing the number of parishes with cases from 17 to 25. One case was reported in Acadia Parish was but later reclassified by the LDH. The two new deaths were announced to be from New Orleans, increasing the number of deaths in the city-parish alone to 8. Governor Edwards also announced at a press conference that the number of residents who died at the Lambeth House in New Orleans had increased to 5.[29]
March 20–23
On March 20, the total number of cases has risen to 537. Jefferson Parish announced on March 20 that curbside recycling pickup would be suspended citing the safety of workers in the industry.[33] The Louisiana Department of Health increased the number of cases to 763 on March 21, also announcing 6 additional deaths, increasing the total number of deaths in Louisiana to 20. By that evening, over half of all Louisiana parishes had at least one case. The most cases were concentrated in Orleans Parish, which had 418 cases and 15 deaths. Jefferson Parish had the second-highest number of cases with 166, followed in third by St. Tammany Parish with 22 cases.[34][35]
On March 22, as cases grew to 837 cases statewide, the governor of Louisiana announced a statewide stay-at-home order effective until April 12.[36] The Louisiana Department of Health announced that new cases would only be updated once-a-day at 12:00 p.m. CT, moving from announcing cases two times a day at 9:30 a.m. and 5:30 p.m. CT as was done previously. This change went into effect mid-day on March 22, explaining the slowing of cases on that day as well, as the 40% increase of cases the next day. The number of cases in Louisiana grew to 1,172 on March 23. It was announced by the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of New Orleans that Archbishop Gregory Aymond had tested positive for coronavirus on March 23. The 70-year-old Archbishop stated that he had not been feeling well and was tested with his symptoms. He stated that he will continue to stream reflections on the crisis to Facebook and the Archdiocese's website.[37]
March 24
In a press conference, Governor Edwards said that of the 1,388 confirmed cases in the state, no one had yet recovered from the virus. In addition, 271 people are hospitalized with coronavirus in Louisiana, 94 of whom are on ventilators. According to the Governor, there were 923 ventilators across the state, with slightly over 10% of them being used for coronavirus patients in the state.[38]
Coastal Environmental Services, the contractor for St. Tammany Parish's recycling pickup, announced that they were suspending curbside recycling pickup throughout the parish on March 24. Trash pickup would continue normally and all recycle placed on the curb would be placed in the trash.[33]
Governor Edwards issued a request for a disaster declaration and federal aid in the state, projecting that New Orleans could exceed its hospital capacity by April 4.[39]
March 25
Governor Edwards warns that New Orleans may run out of ventilators by the first week of April. The state is distributing 100 ventilators and expects to soon have 200 more, but it will need another 600. The state has 1,795 cases and 65 deaths.[40]
March 27
Florida Governor Ron DeSantis (R) expands a previous order requiring airline travelers from New York City to self-quarantine for fourteen days to include people who enter from Louisiana via Interstate 10.[41]
March 31
Governor John Bel Edwards announces that the number of COVID-19 patients using ventilators has doubled in the past five days. The state also saw a one-day surge of more than 1,200 cases, bringing the state's total to over 5,200. 239 people have died, including 54 newly reported deaths. A statewide stay-at-home order through at least April 30.[42]
April

New Orleans has a death rate from COVID-19 that is twice that of New York City and four times that in Seattle. Health officials say obesity, diabetes, and hypertension are to blame.[43]
On April 4, an article stated that St. John the Baptist Parish had "the highest per capita coronavirus mortality rate in the nation."[44]
On April 13, LSU employees began mass producing personal protective equipment for essential medical personnel.[45]
As of April 22, there were over 2,400 cases of coronavirus and almost 500 deaths in adult residential care facilities, which includes nursing homes, across Louisiana.[46]
May
On May 5, sanitation workers in New Orleans went on strike over lack of protective equipment and hazard pay.[47]
On May 15, Governor Edwards lifted the Stay at Home order allowing businesses to re-open.[48]
On May 20, all city-parish public buildings re-opened with strict guidelines for protection.[49]
On May 21, the Louisiana Department of Health announced 1188 newly reported cases. Fully 62% (682) of those were from labs reporting for the first time, reflecting cases stretching as far back as 3/25/20.[50]
On May 26, the Louisiana Department of Health reported there have been 245 new positive cases and 11 new deaths.[51]
On May 27, Governor Edwards announced there are 13 cases and one death of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C) in children across the state. There is a correlation between children that have been exposed to COVID-19 and MIS-C.[52]
June
As of June 1st, Lafayette has experienced the highest seven day average of positive COVID cases since April. There had been 119 new cases over the past seven days. Multiple employees of the Borden Dairy processing plant and crawfish processing plants in Acadia parish have tested positive.[53]
On June 5, Governor Edwards announced that Louisiana will move into Phase 2 of the White House's guidelines of reopening. This means that businesses that had been operating at 25% capacity under Phase 1 can now operate at 50% capacity. Businesses that had previously been closed such as spas, tattoo parlors, event centers, and massage parlors will be allowed to open. Phase 2 will last at least 21 days at which the Governor will assess if the state can then move to Phase 3 or not.[54]
On June 19, the Louisiana Department of Health confirmed an outbreak of coronavirus infections in the Tigerland bars after receiving over 100 reports of positive cases from patrons and employees. Health officials urged anyone that visited Tigerland over the weekend to self-quarantine.[55]
On June 20, it was reported that 30 LSU football players tested positive for coronavirus and are now in quarantine. The football program reopened for voluntary workouts on June 9th and this is the first outbreak since then.[56]
On June 22, Governor Edwards announced that Louisiana will stay in Phase 2 as there has been an uptick of cases, hospitalizations and deaths. Louisiana will remain in Phase 2 for an additional 28 days before reassessing.[57] Amid Governor Edwards extending Phase 2, Republic lawmakers are pushing to revoke the state's emergency declaration as they assert that people in their districts don't want to wear masks or adhere to governmental restrictions on social distancing at restaurants.[58]
The spike in coronavirus cases among young people is causing concerns about the availability of tests. Some health providers say the cases of infection are growing so quickly that they are having a hard time keeping up with demand. Dr. Kevin DiBenedetto, medical director for Premier Health, which is responsible for running urgent care clinics across the state, including Lake After Hours in Baton Rouge, LCMC Health Urgent Care in New Orleans and Lourdes Urgent Care in the Lafayette area says that the recent spike in cases "totally crushed" their supply of tests.[59]
On June 23, it was reported that Fred's bar in Tigerland would host a drive-thru coronavirus testing site for students and employees at nearby bars.[60]
Government response
Governor Edwards announced that schools would close until April 13.[61] Governor Edwards also signed an executive order on March 13 postponing all Louisiana elections in the months of April and May, including the Louisiana Democratic primary, until June and July, respectively.[62] The presidential primaries are expected to be held on June 20, 2020.[63]
Mayor of New Orleans LaToya Cantrell announced the closure of New Orleans' traffic and magistrate courts on March 15, beginning immediately and lasting for 30 days. The mayor also announced the closure of New Orleans Public Libraries beginning on March 16.[64] Also on March 15, Mayor Cantrell issued guidance surrounding bars and restaurants, directing full-service restaurants to close at 9:00 p.m. and restaurants to only seat 50 percent of their capacity to partake in physical distancing. In addition, quick-service or fast-casual restaurants can only partake in drive-thru service, but can extend their operating hours to 24 hours if needed. Bars and nightclubs are also required to serve up to 50 percent of their capacity, announce last call at 11:15 p.m., and be closed and vacated by midnight every night.[65]
Locally, Slidell Mayor Greg Cromer made a statement on March 14, re-stating the closure of public schools and the state of emergency that Governor Edwards announced previously. Mayor Cromer also announced the closing of the Slidell Cultural Center, the cancellation of the City of Slidell's Arts Evening cultural festival, and the rescheduling of the Bayou Jam Concert Series in Heritage Park. He reaffirmed that the Slidell Museum and Slidell Mardi Gras Museums would remain open.[66]
On March 16, Governor Edwards issued a state-wide executive order prohibiting public gatherings of more than 50 people, and ordering the closure of bars, bowling alleys, casino gaming (including casinos and video poker), fitness facilities, and movie theaters from March 17 through April 13. Restaurants were also restricted to takeout and delivery service only.[67][68][69]
On March 22, Governor Edwards announced a statewide stay-at-home order effective until April 12 in a press conference.[36] On March 31 the order was extended to at least April 30.[42]
On March 26, Mayor Cantrell criticized the Trump administration's early response to the pandemic, admitting that she would have canceled Mardi Gras festivities in New Orleans had she been provided with more sufficient information from federal authorities on potential risks. She explained that "we were not given a warning or even told, 'Look, you know what? Don't have Mardi Gras'", and that "if the federal government is not responding to or saying that we're potentially on the verge of having a crisis for the pandemic coming to the U.S. — that would change everything. But that wasn’t happening."[70][71]
Governor Edwards partnered with the Louisiana Department of Health on May 8 to develop a plan to hire 700 Louisiana residents as contact tracers, who interview and advise those who've tested positive for COVID-19 to ascertain who else in their lives may be at risk for contracting the virus. LDH Secretary, Dr. Courtney Phillips, acknowledged that this measure will only work if the people who are contacted by the tracers actually self-isolate.[72]
Impact on sports
On March 12, the National Basketball Association announced the season would be suspended for at least 30 days, affecting the New Orleans Pelicans.[73] The NCAA also cancelled all of its remaining tournaments for the academic year, including the 2020 NCAA Division I Women's Basketball Tournament — whose Women's Final Four was scheduled to be hosted by New Orleans.[74] The Louisiana High School Athletics Association canceled all events for the duration of the virus and likely the rest of semester and season.[75]
On March 19, New Orleans Saints head coach Sean Payton announced that he had tested positive for COVID-19. Payton stated in a tweet that he felt ill on March 15 and was tested the next day. He was the first NFL team member to be confirmed positive for the virus.[32]
On May 20, the National College Athletic Association debated and voted to end the moratorium on voluntary practices for football and men's and women's basketball[76] on college campuses.[77] This decision means that Louisiana State University student athletes can return to campus if they are able and adhere to local and state regulations.[78]
Southern University has altered its 2020 football schedule as a result of the coronavirus pandemic. Southern's opening game against Texas State University and subsequent home game against Florida A&M have both been canceled. There are five home games on the new schedule but no word has been given on if fans will be allowed in the stadium. The location of the famed Bayou Classic has been listed at TBD and could be moved from the traditional location of the Mercedes-Benz Superdome.[79]
Statistics
The University of Louisiana at Lafayette published a study finding that in the 14 days since its first case was reported, the growth rate of new COVID-19 cases in the state was 67.8%, exceeding New York's 66.1% growth in a similar period, and believed to be the fastest rate of cases in such a period in the world.[8] New Orleans has been noted for its high rate of cases; LSU associate professor Susanne Straif-Bourgeoi suggested that the city's Mardi Gras celebrations may have been a factor in its rapid spread—as they attract a large number of public gatherings and international tourism, and occurred before the wider scrutiny over the virus that emerged in March.[81]
The state's demographics have also influenced its rapid spread, including its sizable African American population (a group that has seen a disproportionate impact in other parts of the country as well). On April 6, numbers released by the Louisiana Department of Health revealed that approximately 70% of COVID-19 deaths in the state at that point were among African Americans. Although only accounting for 33% of the state's total population, the majority population in New Orleans is African American.[82][83][84] As of May 18, African Americans accounted for approximately 55% of total COVID-19 deaths, Caucasians accounted for almost 43%, with American Indians/Alaskan Indians, Asians, Native Hawaiians/Pacific Islanders, and Other/Unknown races accounting for less than 1% of total deaths each.[85] Industrialized parts of the state have seen particularly high numbers of deaths, including St. John the Baptist Parish (which has had the highest deaths per-capita in the country), and River Parishes between New Orleans and Baton Rouge colloquially known as "Cancer Alley".[86][87][88]
On June 24, health officials have announced that cases are on the rise among people under the age of 30. This can be linked to clusters of infections traced back to bars near LSU and graduation parties in New Orleans. The highest number of cases within any age group in the state is among the 18-29 age group and now accounts for 18% of all cases.[89]
| Parish [lower-alpha 1] | Cases [lower-alpha 2][lower-alpha 3] | Deaths [lower-alpha 3] | Recov. [lower-alpha 3][lower-alpha 4] | Pop. | Cases / 100k | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64 / 64 | 40,341 | 2,690 | 31,728 | 4,533,186 | 889.9 | |
| Acadia | 422 | 23 | – | 61,773 | 683.1 | |
| Allen | 184 | 10 | – | 25,764 | 714.2 | |
| Ascension | 827 | 56 | – | 107,215 | 771.3 | |
| Assumption | 252 | 14 | – | 23,421 | 1,076 | |
| Avoyelles | 130 | 9 | – | 42,073 | 309 | |
| Beauregard | 69 | 4 | – | 35,654 | 193.5 | |
| Bienville | 147 | 23 | – | 14,353 | 1,024.2 | |
| Bossier | 416 | 26 | – | 116,979 | 355.6 | |
| Caddo | 2,578 | 189 | – | 254,969 | 1,011.1 | |
| Calcasieu | 608 | 49 | – | 192,768 | 315.4 | |
| Caldwell | 58 | 0 | – | 10,132 | 572.4 | |
| Cameron | 6 | 0 | – | 6,839 | 87.7 | |
| Catahoula | 115 | 3 | – | 10,407 | 1,105 | |
| Claiborne | 66 | 10 | – | 17,195 | 383.8 | |
| Concordia | 88 | 5 | – | 20,822 | 422.6 | |
| DeSoto | 247 | 17 | – | 26,656 | 926.6 | |
| East Baton Rouge | 3,666 | 239 | – | 440,171 | 832.9 | |
| East Carroll | 159 | 0 | – | 7,759 | 2,049.2 | |
| East Feliciana | 197 | 30 | – | 20,267 | 972 | |
| Evangeline | 78 | 1 | – | 33,984 | 229.5 | |
| Franklin | 376 | 10 | – | 20,767 | 1,810.6 | |
| Grant | 29 | 1 | – | 22,309 | 130 | |
| Iberia | 410 | 38 | – | 73,240 | 559.8 | |
| Iberville | 577 | 41 | – | 33,387 | 1,728.2 | |
| Jackson | 106 | 13 | – | 16,274 | 651.3 | |
| Jefferson Davis | 78 | 7 | – | 31,594 | 246.9 | |
| Jefferson | 7,652 | 451 | – | 432,552 | 1,769 | |
| Lafayette | 793 | 26 | – | 221,578 | 357.9 | |
| Lafourche | 827 | 72 | – | 96,318 | 858.6 | |
| LaSalle | 52 | 0 | – | 14,890 | 349.2 | |
| Lincoln | 160 | 14 | – | 46,735 | 342.4 | |
| Livingston | 428 | 29 | – | 128,026 | 334.3 | |
| Madison | 101 | 0 | – | 12,093 | 835.2 | |
| Morehouse | 122 | 5 | – | 27,979 | 436 | |
| Natchitoches | 171 | 13 | – | 39,566 | 432.2 | |
| Orleans | 7,141 | 507 | – | 343,829 | 2,076.9 | |
| Ouachita | 1,264 | 41 | – | 153,720 | 822.3 | |
| Plaquemines | 213 | 17 | – | 23,042 | 924.4 | |
| Pointe Coupee | 199 | 24 | – | 22,802 | 872.7 | |
| Rapides | 800 | 28 | – | 131,613 | 607.8 | |
| Red River | 50 | 7 | – | 9,091 | 550 | |
| Richland | 138 | 3 | – | 20,725 | 665.9 | |
| Sabine | 47 | 0 | – | 24,233 | 194 | |
| St. Bernard | 539 | 22 | – | 35,897 | 1,501.5 | |
| St. Charles | 642 | 44 | – | 52,780 | 1,216.4 | |
| St. Helena | 51 | 1 | – | 11,203 | 455.2 | |
| St. James | 294 | 25 | – | 22,102 | 1,330.2 | |
| St. John the Baptist | 862 | 79 | – | 45,924 | 1,877 | |
| St. Landry | 263 | 54 | – | 83,384 | 315.4 | |
| St. Martin | 300 | 23 | – | 52,160 | 575.2 | |
| St. Mary | 321 | 30 | – | 54,650 | 587.4 | |
| St. Tammany | 1,764 | 158 | – | 233,740 | 754.7 | |
| Tangipahoa | 868 | 35 | – | 121,097 | 716.8 | |
| Tensas | 12 | 0 | – | 5,066 | 236.9 | |
| Terrebonne | 686 | 51 | – | 111,860 | 613.3 | |
| Union | 324 | 17 | – | 22,721 | 1,426 | |
| Vermilion | 55 | 3 | – | 57,999 | 94.8 | |
| Vernon | 26 | 3 | – | 52,334 | 49.7 | |
| Washington | 433 | 38 | – | 47,168 | 918 | |
| Webster | 147 | 7 | – | 41,207 | 356.7 | |
| West Baton Rouge | 175 | 30 | – | 23,788 | 735.7 | |
| West Carroll | 64 | 0 | – | 11,604 | 551.5 | |
| West Feliciana | 211 | 13 | – | 15,625 | 1,350.4 | |
| Winn | 173 | 2 | – | 15,313 | 1,129.8 | |
| Under Investigation | 84 | 0 | – | – | – | |
| Updated Jun 1, 2020 Data is publicly reported by Louisiana Department of Health[90] | ||||||
| ||||||
See also
- Timeline of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States
- COVID-19 pandemic in the United States – for impact on the country
- COVID-19 pandemic – for impact on other countries
References
- "Coronavirus (COVID-19) | Department of Health | State of Louisiana". ldh.la.gov. Retrieved 2020-03-13.
- "Gov. Edwards Issues Statewide Stay at Home Order to Further Fight the Spread of COVID-19 in Louisiana". Louisiana Office of the Governor. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- Corasaniti, Nick; Mazzei, Patricia. "Louisiana Postpones April Primary as 4 More States Prepare to Vote on Tuesday". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- Coleman, Justine. "Trump approves major disaster declaration in Louisiana for coronavirus pandemic". The Hill. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- Finch, Chris. "Gov. Edwards: Mardi Gras caused many cases of coronavirus in New Orleans area". FOX 8. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- Umholtz, Katelyn. "Coronavirus death toll at Lambeth House in New Orleans at 13; more cases reported". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-31.
- Simerman, John. "At coronavirus-stricken Lambeth House, halls 'feel like they're full of ghosts' as death toll rises". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-31.
- Daigle, Adam. "Coronavirus cases grew faster in Louisiana than anywhere else in the world: UL study". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- GALLO, ANDREA; SLEDGE, MATT; WOODRUFF, EMILY; KARLIN, SAM. "'It's like a war zone': Fighting coronavirus, limited ICU beds, bracing for chaos in New Orleans". NOLA.com. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- "Health Department reports 1,356 new COVID-19 cases | Department of Health | State of Louisiana". ldh.la.gov. Retrieved 2020-06-25.
- WBRZ. "La. reports more than 1,300 new coronavirus cases Friday; hospitalizations increase again". WBRZ. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- "Coronavirus (COVID-19)". Louisiana Department of Health. Retrieved 2020-06-17.
- report, Staff. "First case of 'presumptive' coronavirus confirmed in Louisiana". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- Team, WDSU Digital (2020-03-09). "Louisiana governor confirms first presumptive case of coronavirus". WDSU. Archived from the original on 2020-03-10. Retrieved 2020-03-09.
- "Coronavirus cases in Louisiana jump to six; three more positive tests for New Orleans residents | Coronavirus | nola.com". nola.com. Retrieved March 12, 2020.
- Deslatte, Melinda. "Louisiana declares public health emergency for coronavirus". Stamford Advocate. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- "Grambling State issues travel restrictions to prevent coronavirus spread". thenewsstar.com. Retrieved March 13, 2020.
- "Gov. Edwards Signs Proclamation Aimed to Slow the Spread of COVID-19 in Louisiana | Office of Governor John Bel Edwards". gov.louisiana.gov. Retrieved 2020-03-13.
- "Archbishop Aymond addresses Archdiocese of New Orleans regarding coronavirus". WGNO. 2020-03-13. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "LDH confirms 51 presumptive positive COVID-19 cases in Louisiana as of Saturday morning". WGNO. 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- "Gov. Edwards confirms first death in state due to COVID-19". WGNO. 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- "State of Louisiana Reports Second COVID-19 Related Death | Office of Governor John Bel Edwards". gov.louisiana.gov. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "Louisiana Coronavirus Updates: 114 cases statewide, 79 in Orleans Parish". WWL. Retrieved 2020-03-16.
- writer, KATELYN UMHOLTZ | Staff. "Louisiana's third coronavirus death takes life of Lambeth House resident". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-16.
- writer, RAMON ANTONIO VARGAS | Staff. "'He put in a hard fight': Ex-lawyer, judge James Carriere dies from Lambeth House coronavirus outbreak". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- Zurik, Lee; Lillich, Cody. "Zurik: New Orleans continues to be one of the nation's COVID-19 hot spots, analysis shows". Fox8. Retrieved 2020-03-28.
- "Jazz Fest 2020 postponed". WGNO. 2020-03-18. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "LDH announces seventh COVID-19 related death, first in Jefferson Parish". WGNO. 2020-03-18. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "Louisiana Coronavirus Updates: State has 392 cases, 10 deaths". WWL. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "Evening update: 7 deaths, 280 cases of coronavirus in Louisiana". WGNO. 2020-03-18. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "COVID-19 snapshot: How New Orleans and Louisiana compare to the rest of the country". WGNO. 2020-03-19. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "Saints coach Payton tests positive for coronavirus". ESPN.com. 2020-03-19. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- "Curbside recycling suspended in St. Tammany, Jefferson parishes". WWL. Retrieved 2020-03-24.
- "LDH reports 763 coronavirus cases in Louisiana as of Saturday afternoon". WGNO. 2020-03-21. Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- "Coronavirus (COVID-19) | Department of Health | State of Louisiana". 2020-03-22. Archived from the original on 2020-03-22. Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- Karlin, Sam (22 March 2020). "Louisiana issues statewide stay-at-home order to combat coronavirus spread". The Advocate. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- "New Orleans Archbishop Aymond says he has coronavirus". WWL. Retrieved 2020-03-24.
- "271 people hospitalized in Louisiana due to coronavirus". WWL. Retrieved 2020-03-24.
- Karlin, Sam. "New Orleans on track to run out of health care capacity by 1st week of April, John Bel Edwards says". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- Peter Sullivan (25 March 2020). "Louisiana governor warns New Orleans could run out of ventilators by early April". The Hill.
- Florida coronavirus cases pass 4000: state border checkpoints begin, vacation rentals halted by James Call, USA TODAY NETWORK-Florida Capital Bureau, 29 Mar 2020
- Coronavirus: Number of Louisiana patients on ventilators doubles in five days The Independent, 31 Mar 2020
- Why is New Orleans' coronavirus death rate twice New York's? Obesity is a factor By Brad Brooks, Reuters, 2 Apr 2020
- Goldberg, Dan; Ollstein, Alice Miranda (2020-03-04). "Virus hot spots in South poised for disproportionate suffering". POLITICO. Retrieved 2020-04-04.
- Gremillion, Nick. "Gov. Edwards to tour PPE distribution facility at PMAC". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- writer, FAIMON A. ROBERTS III | Staff. "Coronavirus death toll in Louisiana adult residential care facilities nears 500; more than 2,400 total cases". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "New Orleans sanitation workers protesting". WDSU. May 5, 2020. Retrieved May 11, 2020.
- "Can This Business Open? | Office of Governor John Bel Edwards". gov.louisiana.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- Chrisman, Spencer. "Baton Rouge government buildings reopening with new guidelines". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- Hillburn, Greg. "Louisiana coronavirus: Backlog blamed for startling case spike". Monroe News-Star. Retrieved 21 May 2020.
- "ONE-STOP-SHOP: Press conferences, stats, links related to COVID-19". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-05-27.
- Hunter, Nick Gremillion, Scottie. "Gov. Edwards: 13 cases of MIS-C, 1 death in La". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-05-27.
- "Lafayette Parish sees surge in COVID-19 stats; multiple cases discovered at Borden Dairy facility". WBRZ. Retrieved 2020-06-04.
- Gremillion, Nick. "La. will move to Phase 2 of reopening June 5". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-06-05.
- writer, DAVID J. MITCHELL | Staff. "Tigerland coronavirus cluster: If you recently visited, you should self-quarantine, state says". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- writer, BROOKS KUBENA | Staff. "LSU football players test positive for coronavirus, and 30 are reportedly in quarantine". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- WBRZ. "La. reports more than 900 new coronavirus cases, more patients in hospitals Thursday". WBRZ. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- writer, SAM KARLIN | Staff. "As coronavirus spreads and Phase 2 continues, GOP lawmakers threaten to revoke emergency". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- writers, ANDREA GALLO AND BLAKE PATERSON | Staff. "Why coronavirus spike in Baton Rouge among young adults is causing a big problem for testing". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- writer, BLAKE PATERSON | Staff. "After coronavirus cluster linked to Tigerland, Fred's to host drive-thru testing for students". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- "Latest: Louisiana now has 36 coronavirus cases; schools will close until April 13". WDSU. 2020-03-13. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- "Gov. Edwards Signs Executive Order Postponing Louisiana's Primary Election | Office of Governor John Bel Edwards". gov.louisiana.gov. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- Pramuk, Jacob (2020-03-13). "Louisiana postpones Democratic primary over coronavirus, the first state to do so". CNBC. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- "Public Libraries, Municipal and Traffic Court closed; City Hall to have limited access". NOLA Ready – The City of New Orleans. 2020-03-15. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "Mayor Cantrell Issues Guidance To Bars and Restaurants In Response To Covid-19 Outbreak". NOLA Ready – The City of New Orleans. 2020-03-15. Retrieved 2020-03-15.
- "Slidell Mayor issues statement on coronavirus". WGNO. 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- Karlin, Sam. "Louisiana steps up restrictions on bars, gyms; state warns people will die as coronavirus spreads". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- "Executive Order – Office of Governor John Bel Edwards" (PDF). Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- "Gov. Edwards orders all restaurants, movie theaters, bars to close amid Coronavirus threat". Fox8Live.com. 2020-03-16. Retrieved 2020-03-16.
- "'We were not given a warning': New Orleans mayor says federal inaction informed Mardi Gras decision ahead of covid-19 outbreak". Washington Post. 2020-03-26. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- "New Orleans would have canceled Mardi Gras if feds had taken coronavirus more seriously, Mayor says". WWL. Tegna, Inc. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- "State of Louisiana Will Hire Hundreds of Louisianans as Contact Tracers to Fight the Spread of COVID-19 | Office of Governor John Bel Edwards". gov.louisiana.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "Silver: NBA hiatus likely to last 'at least' 30 days". ESPN.com. March 12, 2020. Retrieved March 13, 2020.
- NCAA cancels remaining winter and spring championships NCAA, March 12, 2020
- "High school basketball state tournaments, postseason showcases canceled amid coronavirus concerns – MaxPreps". MaxPreps.com. 2020-03-15. Retrieved 2020-03-20.
- "NCAA Approves On-Campus Training For Football, Basketball Athletes". SI.com. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- Writer, STEVE MEGARGEE AP Sports. "NCAA weighs end to moratorium amid push to offer fall sports". WAFB. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "NCAA Votes To End On-Campus Moratorium, SEC Decision Could See LSU Athletes Return to Campus". SI.com. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- report, Staff. "Southern football releases new 2020 schedule, confirms two canceled games". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- "Orleans Parish COVID-19 Dashboard". City of New Orleans. June 27, 2020. Based on Louisiana Department of Health data.
- "New Orleans has some of the highest coronavirus infection rates in the U.S. – yet it's overlooked". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-03-25.
- "Death rate soars in New Orleans coronavirus 'disaster' that could define city for generations". USA Today. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- "Coronavirus disparity in Louisiana: About 70% of the victims are black, but why?". NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- Zanolli, Lauren (2020-04-08). "Data from US south shows African Americans hit hardest by Covid-19". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- "Louisiana Coronavirus COVID-19 | Department of Health | State of Louisiana". ldh.la.gov. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- Russel, Gordon. "Here's why these 13 Louisiana parishes have some of the highest coronavirus death rates in the U.S." NOLA.com. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- Eligon, John (2020-04-07). "Black Americans Face Alarming Rates of Coronavirus Infection in Some States". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- Levenson, Eric. "Why black Americans are at higher risk for coronavirus". CNN. Retrieved 2020-04-09.
- writer, ANDREA GALLO | Staff. "Louisiana young adults are catching coronavirus at higher rates. Experts say 'think of other people'". The Advocate. Retrieved 2020-06-26.
- "Louisiana Coronavirus COVID-19". Louisiana Department of Health. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to COVID-19 pandemic in Louisiana. |