COVID-19 pandemic in Northern Cyprus
The COVID-19 pandemic was confirmed to have reached Northern Cyprus, officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (the Turkish-Cypriot-controlled de facto state comprising the north of the island), in March 2020.
| COVID-19 pandemic in the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus | |
|---|---|
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, China |
| Index case | Nicosia |
| Arrival date | 10 March 2020 (3 months, 2 weeks and 4 days) |
| Confirmed cases | 108[1] |
| Recovered | 104[2] |
Deaths | 4[3] |
| Government website | |
| Official website | |
Background
On 12 January 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed that a novel coronavirus was the cause of a respiratory illness in a cluster of people in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China, which was reported to the WHO on 31 December 2019.[4][5]
The case fatality ratio for COVID-19 has been much lower than SARS of 2003,[6][7] but the transmission has been significantly greater, with a significant total death toll.[8][6]
Timeline
March 2020
On 10 March 2020, Health Minister Ali Pilli announced the Northern Cyprus's first case of COVID-19, a 65-year-old tourist from Germany.[9]
On 12 March, the country's second case was confirmed, being the spouse of the German tourist who became the first person diagnosed with COVID-19.[10]
On 13 March, the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC) announced that five people have been tested positive for the coronavirus, up from two.[11]
On 17 March, the 2020 Northern Cypriot presidential election was delayed for 6 months due to the outbreak.[12]
On 24 March, over 840 German national tourists were sent back to Germany after being quarantined for 14 days.[13]
On 28 March, the first person died from COVID-19.
April 2020
North Cyprus announced a partial curfew until 10 April. The exception being for use of markets and acquisition of necessities. A full curfew is applied between 9pm and 6am until 10 April. Due to increase of cases, curfew states extended by the end of April. There is a suggestion that "curfew may continue until the end of the summer".
15 villages within the İskele/Karpaz district are under full curfew due to high number of cases.[14]
Turkish Cypriot authorities banned movement between districts, meaning no one will be allowed to travel from one district to another.
Three students out of 800 who came from UK and were under self isolated quarantine for 14 days, have tested positive.[15]
There have been no new reported cases of coronavirus infections for the past ten days and the last Covid-19 death in North Cyprus was on 13 April. Early medical intervention has meant 99 of those who tested positive for coronavirus in the TRNC have made a full recovery. As of 27 April, five people remained in hospital.
May 2020
On 7 May, It was noted that no active cases remained in TRNC.
The Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC) may be the first country in the world that does not have any new coronavirus case since 20 April, the country’s Foreign Ministry said on Saturday.
On 11 May, the last coronavirus patient has been discharged from hospital and there are no active cases left. [16]
Statistics
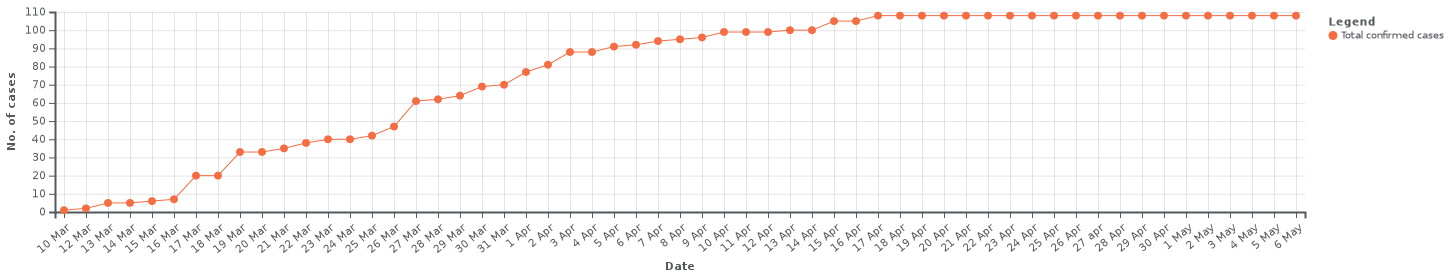
| Day | New cases | Cumulative cases | Active cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 March 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 12 March 2020 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 13 March 2020 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| 14 March 2020 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 15 March 2020 | 1 | 6 | 6 |
| 16 March 2020 | 1 | 7 | 6 |
| 17 March 2020 | 13 | 20 | 20 |
| 18 March 2020 | 0 | 20 | 20 |
| 19 March 2020 | 13 | 33[17] | 20 |
| 20 March 2020 | 0 | 33 | 20 |
| 21 March 2020 | 2 | 35[18] | 35 |
| 22 March 2020 | 3 | 38[19] | 38 |
| 23 March 2020 | 2 | 40[20] | 40 |
| 24 March 2020 | 0 | 40 | 42 |
| 25 March 2020 | 2 | 42[21] | 28 |
| 26 March 2020 | 5 | 47[22] | 32 |
| 27 March 2020 | 14 | 61[2][23] | 34 |
| 30 March 2020 | 8 | 69[24] | 39 |
| 31 March 2020 | 1 | 70[25] | 40 |
| 1 April 2020 | 7 | 77[26] | 46 |
| 2 April 2020 | 4 | 81 | 50 |
| 3 April 2020 | 7 | 88[27] | 57 |
| 4 April 2020 | 0 | 88 | 57 |
| 5 April 2020 | 3 | 91 | 53 |
| 6 April 2020 | 1 | 92 | 47 |
| 7 April 2020 | 2 | 94[28] | 47 |
| 8 April 2020 | 1 | 95 | 48 |
| 9 April 2020 | 1 | 96[29] | 49 |
| 10 April 2020 | 3 | 99 [30] | 52 |
| 11 April 2020 | 0 | 99[31] | 51 |
| 12 April 2020 | 0 | 99 | 39 |
| 13 April 2020 | 1 | 100 | 34 |
| 14 April 2020 | 0 | 100 | 30 |
| 15 April 2020 | 5 | 105 | 27 |
| 16 April 2020 | 0 | 105 | 21 |
| 17 April 2020 | 3 | 108 | 23 |
| 18 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 23 |
| 19 April 2020 | 1 | 109* | 21 |
| 20 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 19 |
| 21 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 19 |
| 22 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 17 |
| 23 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 17 |
| 24 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 17 |
| 25 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 12 |
| 26 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 12 |
| 27 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 5 |
| 28 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 5 |
| 29 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 3 |
| 30 April 2020 | 0 | 108 | 3 |
| 1 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 2 |
| 2 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 3 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 4 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 5 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 6 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 7 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 8 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 9 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 10 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 1 |
| 11 May 2020 | 0 | 108 | 0 [32] |
*19 April info suggested 1 new case giving a total of 109, but subsequent reports suggest an error of 1 case over-reported.
Reaction
On 11 March 2020, Turkish Cypriot Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister Kudret Özersay said in a tweet that flights from Germany, France and Italy to Northern Cyprus would be suspended until 1 April 2020.[10]
All flights around the world to the North Cyprus and as well as Cross points from the southern part To north side of the island is banned.
On 12 March 2020, the Turkish republic of northern Cyprus government shut schools and banned mass gatherings as precautionary measures to prevent the spread of the coronavirus, which the World Health Organisation declared a pandemic.[10]
All educational activities from nursery to university degree suspended physical systems. Primary and middle schools turned into the digital system and will complete 2019-2020 semester by this way. North Cyprus have more than 20 institutions of higher education. 18 of them are universities and nearly 100,000 international students. All higher education services suspended and turned into the digital system.
See also
References
- "KUZEY KIBRIS COVID-19 GÜNLÜK TABLO". saglik.gov.ct.tr. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "KUZEY KIBRIS COVID-19 GÜNLÜK TABLO". saglik.gov.ct.tr. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "KUZEY KIBRIS COVID-19 GÜNLÜK TABLO". saglik.gov.ct.tr. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- Elsevier. "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- Reynolds, Matt (4 March 2020). "What is coronavirus and how close is it to becoming a pandemic?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Archived from the original on 5 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID); Guidance and information about high consequence infectious diseases and their management in England". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". www.wfsahq.org. Archived from the original on 12 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- "German tourist tests positive for virus in Northern Cyprus". 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020 – via athejakartapost.
- "Second coronavirus case in northern Cyprus". 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020 – via aa.com.tr.
- "Northern Cyprus confirms total of 5 coronavirus cases". 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020 – via aa.com.tr.
- "KKTC'de Cumhurbaşkanlığı seçimleri 6 ay erteleniyor". CNN Türk (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- DHA, Sefa KARAHASAN. "KKTC'de karantinadaki Almanlar ülkelerine dönüyor". www.hurriyet.com.tr. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "Turkish Cyprus declares curfew". Hurriyet Daily News. 31 March 2020. Archived from the original on 4 April 2020. Retrieved 4 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de Koronavirüs vaka sayısı 91 oldu". kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 7 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- "Last COVID-19 patient discharged in Northern Cyprus". aa.com/en. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- "KKTC'de Kovid-19 vaka sayısı 33'e yükseldi". www.aa.com.tr. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- Gazetesi, Gündem Kıbrıs. "SON DAKİKA! 1 yeni vaka daha görüldü". www.gundemkibris.com. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de corona virüs vaka sayısı 38'e yükseldi - Olay Gazetesi Bursa". Olay. 22 March 2020. Archived from the original on 22 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de korona virüsü vaka sayısı 40'a yükseldi". Timeturk.com. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "2 kişide daha koronavirüs testi pozitif çıktı". www.haberturk.com. Archived from the original on 25 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'deki Koronavirüs vaka sayısı 47'ye yükseldi". kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de koronavirüs vakalarında son durum". kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de Koronavirüs salgınına karşı geceleri tam sokağa çıkma yasağı". www.kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 1 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de 1 yeni Koronavirüs vakası daha". kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de 7 yeni Koronavirüs vakası daha! Vaka sayısı 77'ye çıktı". www.kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 4 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- "29 kişi ise tedavi edilerek taburcu oldu". www.haberturk.com (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 3 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de 2 yeni koronavirüs vakası!". kibrisgazetesi.com. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- "Lefke'de bir pozitif vaka!". KIBRIS POSTASI. Archived from the original on 12 April 2020. Retrieved 9 April 2020.
- "Ali Pilli: "3 yeni pozitif vaka daha görüldü"". Gundem Kibris. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "KKTC'de bugün yeni vaka yok!". Kıbrıs Gazetesi. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "KKTC Sağlık Bakanlığı > COVID-19 GENEL DURUM".