Mackinac County, Michigan
Mackinac County is a county in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the population was 11,113.[3] The county seat is St. Ignace.[4] Formerly known as Michilimackinac County, in 1818 it was one of the first counties of the Michigan Territory, as it had long been a center of French and British colonial fur trading, a Catholic church and Protestant mission, and associated settlement.[1]
Mackinac County | |
|---|---|
_-_panoramio.jpg) | |
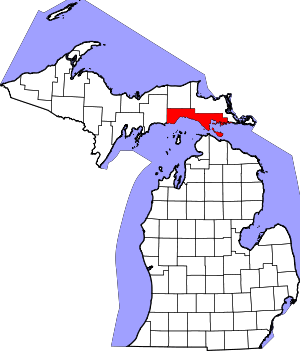 Location within the U.S. state of Michigan | |
 Michigan's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 46°01′N 85°01′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | October 26, 1818 organized 1849[1][2] |
| Named for | Straits of Mackinac |
| Seat | St. Ignace |
| Largest city | St. Ignace |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,101 sq mi (5,440 km2) |
| • Land | 1,022 sq mi (2,650 km2) |
| • Water | 1,079 sq mi (2,790 km2) 51%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 10,787 |
| • Density | 11/sq mi (4/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 1st |
| Website | www |
The county's name is believed to be shortened from "Michilimackinac", which referred to the Straits of Mackinac area as well as the French settlement at the tip of the lower peninsula.[1]
History
Michilimackinac County was created on October 26, 1818, by proclamation of territorial governor Lewis Cass. The county originally encompassed the Lower Peninsula of Michigan north of Macomb County and almost the entire present Upper Peninsula. As later counties were settled and organized, they were divided from this territory.
At the time of founding, the county seat was the community of Michilimackinac Island on Michilimackinac Island, later known as Mackinac Island, Michigan. This has been an important center for fur trading before the 1830s, when European demand declined. The county was organized in 1849 as Mackinac County. In 1882 the county seat was moved from Mackinac Island to St. Ignace, Michigan, which had been founded as a French Jesuit mission village during the colonial years.
Mackinac County is home to the Mackinac Bands of Chippewa and Ottawa Indians, a Native American tribe located in St. Ignace.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 2,101 square miles (5,440 km2), of which 1,022 square miles (2,650 km2) is land and 1,079 square miles (2,790 km2) (51%) is water.[5] Mackinac County lies at the boundary of Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.
St. Ignace is the northern terminus of the Mackinac Bridge. Mackinac Island is within the county.
Due to its sparse population, the county has no weather stations.
Adjacent counties
- Chippewa (northeast)
- Presque Isle County (southeast)
- Cheboygan County (south)
- Emmet County (south)
- Charlevoix County (southwest)
- Schoolcraft County (west)
- Luce County (northwest)
National protected area
- Hiawatha National Forest (part)
Transportation
Airports
The Mackinac County Airport (83D) in St. Ignace and Mackinac Island Airport (MCD) on Mackinac Island are located within Mackinac County. The nearest airports with scheduled commercial passenger service are Chippewa County International Airport (CIU) in Sault Ste. Marie and Pellston Regional Airport (PLN).[6]
Major highways
M-185 does not allow motor vehicles with the exception of emergency vehicles.
Ferry
Numerous companies operate ferries to Bois Blanc Island and Mackinac Island. Ferries to and from Mackinac Island sail from St. Ignace and Mackinaw City, while the Bois Blanc Island ferry sails from Cheboygan.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1830 | 877 | — | |
| 1840 | 923 | 5.2% | |
| 1850 | 3,598 | 289.8% | |
| 1860 | 1,938 | −46.1% | |
| 1870 | 1,716 | −11.5% | |
| 1880 | 2,902 | 69.1% | |
| 1890 | 7,830 | 169.8% | |
| 1900 | 7,703 | −1.6% | |
| 1910 | 9,249 | 20.1% | |
| 1920 | 8,026 | −13.2% | |
| 1930 | 8,783 | 9.4% | |
| 1940 | 9,438 | 7.5% | |
| 1950 | 9,287 | −1.6% | |
| 1960 | 10,853 | 16.9% | |
| 1970 | 9,660 | −11.0% | |
| 1980 | 10,178 | 5.4% | |
| 1990 | 10,674 | 4.9% | |
| 2000 | 11,943 | 11.9% | |
| 2010 | 11,113 | −6.9% | |
| Est. 2018 | 10,787 | [7] | −2.9% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[8] 1790-1960[9] 1900-1990[10] 1990-2000[11] 2010-2018[3] | |||
The 2010 census[12] ireported that Mackinac County had a population of 11,113. This was a decrease of 830 (-6.9%) from the 2000 United States Census. In 2010 there were 5,024 households and 3,219 families residing in the county. The population density was 11 per square mile (5/km²). There were 11,010 housing units at an average density of 11/sq mi (4/km²). 76.5% of the population were White, 17.3% Native American, 0.5% Black or African American, 0.2% Asian, 0.2% of some other race and 5.3% of two or more races. 1.1% were Hispanic or Latino (of any race). 18.5% were of German, 8.8% English, 8.0% French, French Canadian or Cajun, 7.6% Irish and 5.1% Polish ancestry.[13]
There were 5,024 households of which 20.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 51.3% were married couples living together, 8.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 35.9% were non-families. 31.0% of all households were made up of individuals and 14.3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.19 and the average family size was 2.7.
18.7% of the population were under the age of 18, 5.5% from 18 to 24, 19.3% from 25 to 44, 34.0% from 45 to 64, and 22.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 49 years. The population was 50.5% male and 49.5% female.
The median household income was $39,055 and the median family income was $50,984. The per capita income was $22,195. About 10.5% of families and 14.1% of the population were below the poverty line, including 19.3% of those under age 18 and 6.2% of those age 65 or over.
Religion
Mackinac County is part of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Marquette.[14][15]
Government
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 60.9% 3,744 | 33.9% 2,085 | 5.1% 315 |
| 2012 | 55.5% 3,397 | 43.4% 2,652 | 1.1% 68 |
| 2008 | 51.0% 3,268 | 47.2% 3,027 | 1.8% 114 |
| 2004 | 56.2% 3,706 | 42.7% 2,819 | 1.1% 74 |
| 2000 | 54.8% 3,272 | 42.4% 2,533 | 2.8% 165 |
| 1996 | 39.6% 2,281 | 46.9% 2,700 | 13.6% 781 |
| 1992 | 38.1% 2,278 | 38.4% 2,293 | 23.5% 1,406 |
| 1988 | 59.7% 3,127 | 39.9% 2,093 | 0.4% 22 |
| 1984 | 64.9% 3,627 | 34.9% 1,949 | 0.3% 17 |
| 1980 | 52.2% 3,021 | 39.1% 2,262 | 8.7% 501 |
| 1976 | 55.2% 3,107 | 43.6% 2,452 | 1.2% 68 |
| 1972 | 60.7% 3,096 | 38.0% 1,937 | 1.4% 71 |
| 1968 | 54.8% 2,507 | 38.3% 1,751 | 7.0% 319 |
| 1964 | 41.7% 1,967 | 58.3% 2,748 | 0.0% 2 |
| 1960 | 59.9% 3,064 | 39.9% 2,042 | 0.2% 11 |
| 1956 | 68.0% 3,279 | 31.9% 1,540 | 0.1% 4 |
| 1952 | 70.2% 3,058 | 29.5% 1,285 | 0.3% 11 |
| 1948 | 64.9% 2,182 | 33.9% 1,138 | 1.3% 42 |
| 1944 | 60.1% 2,268 | 39.4% 1,488 | 0.5% 20 |
| 1940 | 55.4% 2,591 | 44.4% 2,075 | 0.3% 13 |
| 1936 | 45.7% 1,984 | 52.6% 2,286 | 1.8% 76 |
| 1932 | 36.6% 1,504 | 62.7% 2,578 | 0.7% 27 |
| 1928 | 57.9% 1,879 | 41.8% 1,355 | 0.3% 9 |
| 1924 | 51.6% 1,606 | 32.1% 998 | 16.3% 507 |
| 1920 | 62.9% 1,685 | 34.8% 932 | 2.4% 63 |
| 1916 | 53.4% 1,082 | 44.8% 908 | 1.8% 37 |
| 1912 | 34.6% 612 | 41.3% 730 | 24.1% 425 |
| 1908 | 58.9% 1,156 | 39.2% 769 | 1.9% 38 |
| 1904 | 69.2% 1,191 | 29.2% 503 | 1.6% 28 |
| 1900 | 61.7% 1,059 | 36.8% 632 | 1.5% 25 |
| 1896 | 48.7% 806 | 48.6% 804 | 2.7% 44 |
| 1892 | 35.4% 478 | 63.3% 855 | 1.3% 17 |
| 1888 | 40.2% 625 | 58.8% 913 | 1.0% 15 |
| 1884 | 46.1% 479 | 53.7% 558 | 0.3% 3 |
| 1880 | 32.9% 145 | 67.1% 296 | 0.0% 0 |
| 1876 | 26.6% 74 | 73.4% 204 | 0.0% 0 |
The county government operates the jail, maintains rural roads, operates the major local courts, keeps files of deeds and mortgages, maintains vital records, administers public health regulations, and participates with the state in the provision of welfare and other social services. The county board of commissioners controls the budget but has only limited authority to make laws or ordinances. In Michigan, most local government functions — police and fire, building and zoning, tax assessment, street maintenance, etc. — are the responsibility of individual cities and townships.
Elected officials
- Prosecuting Attorney: J. Stuart Spencer
- Sheriff: Scott Strait
- County Clerk: Mary Kay Tamlyn
- County Treasurer: Nora A. Massey
- Register of Deeds: Deborah Holle
- County Surveyor: Jeffrey M. Davis
Historical markers
There are 34 official state historical markers in the County:[19]
- Across the Peninsula
- American Fur Company Store
- Battlefield of 1814
- Biddle House
- Bois Blanc Island
- British Cannon
- British Landing
- Early Missionary Bark Chapel
- Epoufette
- Fort de Buade
- Fort Holmes
- Grand Hotel
- Gros Cap Island & St. Helena Island
- Historic Fort Mackinac
- Indian Dormitory
- Island House (Mackinac Island)
- Lake Michigan
- Lake View Hotel
- Little Stone Church
- Mackinac Conference
- Mackinac Island
- Mackinac Straits
- Market Street
- Mission Church
- Mission House
- Northernmost Point of Lake Michigan
- Old Agency House
- Round Island Lighthouse
- Sainte Anne Church
- St. Ignace
- St. Ignace Mission
- Skull Cave
- Trinity Church (Mackinac Island)
- Wawashkamo Golf Club[20]
Media
Newspapers
- The Mackinac Island Town Crier is the weekly seasonal newspaper of Mackinac Island.
- The St. Ignace News is the weekly newspaper for the Upper Peninsula area of the Mackinac Straits.
Television
The following television stations can be received in St. Ignace:
Radio
The following stations can be heard in St. Ignace:
FM
| Call sign | Frequency | City broadcast from |
|---|---|---|
| WIAB | 88.5 | Mackinaw City |
| WYPV | 94.5 | Mackinaw City |
| WLXT | 96.3 | Petoskey |
| WWMK | 106.3 | Cheboygan |
| WKLZ | 98.9 | Petoskey |
| WCBY - W264CF | 100.7 | St.Ignace, Michigan |
| WMKC | 102.9 | Indian River |
| WCMW | 103.9 | Harbor Springs |
| WKHQ | 105.9 | Petoskey |
AM
| Call sign | Frequency | City broadcast from |
|---|---|---|
| WTCM | 580 | Traverse City |
| WARD | 750 | Petoskey |
| WIDG | 940 | St. Ignace |
| WJML | 1100 | Petoskey |
| WCBY | 1240 | Cheboygan |
Attractions
- Beaches
- Garlyn Zoo
- Lake Michigan
Communities

Cities
- Mackinac Island
- St. Ignace (county seat)
Civil townships
Unincorporated communities
- Allenville
- Brevort
- Cedarville
- Curtis
- Engadine
- Epoufette
- Evergreen Shores
- Garnet
- Gould City
- Gros Cap
- Hessel
- Millecoquins
- Moran
- Naubinway
- Pointe Aux Pins
- Rexton
Indian reservations
- The Sault Tribe of Chippewa Indians, which is headquartered in Sault Ste. Marie in Chippewa County to the north, occupies two small territories within Mackinac County. One is located in St. Ignace Township about 3 miles (4.8 km) north of the city of St. Ignace on the shores of Lake Huron. The other portion is located in rural northwest Clark Township.[21]
See also
- List of Michigan State Historic Sites in Mackinac County, Michigan
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Mackinac County, Michigan
References
- "Bibliography on Mackinac County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- "Mackinac Early History". Archived from the original on July 21, 2013. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 6, 2011. Retrieved August 28, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on November 13, 2013. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- "Pellston Regional Airport Serving Northern Michigan Emmet County". pellstonairport.com.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 16, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 27, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". Retrieved July 6, 2013.
- "American FactFinder"
- Floline Media LLC. "Diocese of Marquette :: home". dioceseofmarquette.org. Archived from the original on 2012-12-01. Retrieved 2007-12-29.
- David M. Cheney. "Marquette (Diocese) [Catholic-Hierarchy]". catholic-hierarchy.org.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 10 April 2018.
- http://www.mackinaccounty.net/departments/
- Michigan Bar Journal. State Bar of Michigan. April 2015. p. 107.
- "Michigan Historical Markers". michmarkers.com. Archived from the original on 2014-07-17. Retrieved 2008-02-02.
- "Wawashkamo Golf Club Mackinac Island". Wawashkamo Golf Club Mackinac Island.
- United States Census Bureau. "Michigan County Subdivision Outline Map" (PDF). Retrieved April 18, 2019.
Bibliography
- "Bibliography on Mackinac County". Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University. Retrieved July 20, 2013.
- Wood, Edwin Orin (1918). Historic Mackinac : the historical, picturesque and legendary features of the Mackinac country : illustrated from sketches, drawings, maps and photographs, with an original map of Mackinac Island, made especially for this work: in two volumes. 1. New York: Macmillan. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
- Wood, Edwin Orin (1918). Historic Mackinac : the historical, picturesque and legendary features of the Mackinac country : illustrated from sketches, drawings, maps and photographs, with an original map of Mackinac Island, made especially for this work: in two volumes. 2. New York: Macmillan. Retrieved April 20, 2014.
.jpg)

