Ceiba, Puerto Rico
Ceiba (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈsejβa]) is both a small town and municipality in northeast Puerto Rico. It is named after the famous Ceiba tree. Ceiba is located in the north-east coast of the island, bordering the Atlantic Ocean, south of Fajardo, north of Naguabo and southeast of Río Grande. Located about one hour's driving distance from San Juan, Ceiba is spread over 7 barrios and Ceiba Pueblo (the downtown area and administrative center). It is part of the Fajardo Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Ceiba | |
|---|---|
Town and Municipality | |
 | |
 Flag | |
| Nicknames: "Los Come Sopas", "La Ciudad del Marlin", "Los Sin Sopa" | |
| Anthem: "Ceiba" | |
 Location of Ceiba in Puerto Rico | |
| Coordinates: 18°14′17″N 65°37′40″W | |
| Commonwealth | |
| Founded | April 7, 1838 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Angelo Cruz Ramos (PNP) |
| • Senatorial dist. | 8 - Carolina |
| • Representative dist. | 36 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 77.33 sq mi (200.28 km2) |
| • Land | 27.2 sq mi (70.5 km2) |
| • Water | 50.11 sq mi (129.78 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 13,631 |
| • Density | 180/sq mi (68/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | ceibeños |
| Time zone | UTC−4 (AST) |
| Zip code | 00735, 00742 |
| Major routes | |
Ceiba, situated near Fajardo, used to be home of an American military Naval base, the Roosevelt Roads Naval Station. Most of the units were relocated and the base was closed in 2004. Ex-governor Sila María Calderón suggested turning the property into a major international airport, to serve as a relief to Luis Muñoz Marín International Airport in San Juan, and to increase the number of international airlines that operate into Puerto Rico. She was met with skepticism about these plans from such groups as environmentalists, economists and others, but in 2008, José Aponte de la Torre Airport was inaugurated at the base's former site.
Locals are commonly known as "Los Come Sopa" (The Soup Eaters). Even though there is no official reason as to why they are called this, a few stories have been suggested. Among the tales is the belief that since the town did not have a local meat market people had to travel long distances in order to buy some meat and therefore mostly ate soup.
Ceiba is also known as "La Ciudad del Marlin" (The town of the Marlin).
History
Ceiba was founded on April 7, 1838 by Luis de la Cruz. Ceiba derives its name from an Indian word Seyba, which is the name for a famous tree that grows in the island, the Ceiba pentandra (Kapok).[1]
Ceiba was consolidated with Fajardo in the 1899 population count / census by the U.S.[2]
Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria on September 20, 2017 triggered numerous landslides in Ceiba with the significant amount of rainfall.[3][4]
Geography
Ceiba is home of the Ceiba Forest (787) which extends along the coastline between Ceiba and Fajardo. 95% of the forest is classified as mangrove. Various species of birds can be seen as well as turtles and manatees. Its rivers includes; Río Daguao, Río Demajagua and Río Fajardo.[1]
The municipality extends northwest into the seas between Fajardo and Culebra and thereby includes the reefs and islets named Arrecifes Hermanos and Arrecifes Barriles.[5] The reef are closest to the coastal barrio of Machos, but barrio boundaries are not defined in that area.[6]
Barrios

Like all municipalities of Puerto Rico, Ceiba is subdivided into barrios. The municipal buildings, central square and large Catholic church are located in a barrio referred to as "el pueblo", near the center of the municipality.[7][8][9][10]
Sectors
Barrios (which are like minor civil divisions)[11] in turn are further subdivided into smaller local populated place areas/units called sectores (sectors in English). The types of sectores may vary, from normally sector to urbanización to reparto to barriada to residencial, among others.[12][13][14]
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 5,973 | — | |
| 1930 | 7,275 | 21.8% | |
| 1940 | 7,021 | −3.5% | |
| 1950 | 9,199 | 31.0% | |
| 1960 | 9,075 | −1.3% | |
| 1970 | 10,312 | 13.6% | |
| 1980 | 14,944 | 44.9% | |
| 1990 | 17,145 | 14.7% | |
| 2000 | 18,004 | 5.0% | |
| 2010 | 13,631 | −24.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[17] 1920-1930[18] 1930-1950[19] 1960-2000[20] 2010[9] | |||
Tourism
Landmarks and places of interest
There are 60 beaches in Ceiba, including Los Machoes Beach.[21] Other places of interest include:
- Ceiba Historic Mural
- Medio Mundo Beach
- Roosevelt Roads Base (a former United States Navy installation which is now closed)
- The cellist Pablo Casals lived in Ceiba.
Culture
Festivals and events
- Enamorado (Lovers) Marathon - February
- Air Show - April 2/3
- Marlin Festival - May - June
- Fiestas Patronales-San Antonio de Padua (Patron Saint Festivities) - June
- Fiesta Nacional de la Raza (Race) - October
- Marathon Del Pavo - November
- Encendido Navideño - December
Sports
Former IBF world Jr. Middleweight boxing champion Carlos Santos hails from Ceiba. Ceiba also has an amateur AAA baseball team Los Marlins de Ceiba. Chi-Chi Rodriguez, Pro golfer is from Ceiba.
Religion
As in most towns of Puerto Rico it was founded on the Christian ideas and faith statements of the Roman Catholic Church which prevailed in previous centuries through Spaniard tradition. The town still maintains a central Roman Catholic church which can be found in the town square.
Economy
Manufacturing (plywood, apparel, hardware products).
Transportation
José Aponte de la Torre Airport offers commercial (mostly domestic) flights on four airlines; it also houses an MD-82 jet donated by American Airlines to local air mechanics students.
There are 29 bridges in Ceiba.[22]
Notable people
People who were born in, residents of, or otherwise closely associated with Ceiba include:
- Carlos Santos - former IBF Junior Middleweight Champion of the World.
- Luis Vigoreaux - radio and television show host, announcer, comedian and producer. Luis Vigoreaux was found murdered on January 17, 1983. His wife Lydia Echevarria arranged his murder.
- Domingo Quiñones - although born in Perth Amboy, New Jersey; Domingo Quiñones moved to Ceiba at the early age of 4 and lived there until the age of 14.
- Pablo Casals - built his home in Ceiba at the age of 80; the place was known as "El Pesebre".
- Rogelio Figueroa Garcia - was born in Naguabo, Puerto Rico; however, was raised in Parcelas Aguas Claras (Barrio El Corcho) in Ceiba. He is a Puerto Rican engineer, a politician, and the co-founder of the Puerto Ricans for Puerto Rico (PPR) political party.
- McJoe Arroyo - IBF Super Flyweight world boxing champion
- Jaron Brown - is a wide receiver for the Seattle Seahawks. He was born in Ceiba, PR.
Government
All municipalities in Puerto Rico are administered by a mayor, elected every four years. The current mayor of Ceiba is Angelo Cruz Ramos, of the New Progressive Party (PNP). He was elected at the 2012 general elections.
The city belongs to the Puerto Rico Senatorial district VIII, which is represented by two Senators. In 2012, Pedro A. Rodríguez and Luis Daniel Rivera were elected as District Senators.[23]
Symbols
Flag
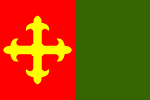
Ceiba's flag derives its design and colors from the municipal coat of arms. This maintains the same symbolism given to the coat of arms. It is made of two vertical lines of the same width, red in the left side and green on the right. The red side depicts a yellow cross.
Shield
It depicts a shield with golden field with a Ceiba tree in the middle. In the upper part of the shield it has a red horizontal line with a golden cross in the middle and two golden flowers in each side. The cross symbolizes the Christian faith as well as a recognition to Don Luis de la Cruz who founded the town. The golden flowers represent sugar cane flowers. Above the shield there is a golden Spanish fort.
See also
- List of Puerto Ricans
- History of Puerto Rico
- Roosevelt Roads Naval Station
- Did you know-Puerto Rico?
References
- "Ceiba Municipality". enciclopediapr.org. Fundación Puertorriqueña de las Humanidades (FPH). Archived from the original on 2019-06-23. Retrieved 2019-03-20.
- Joseph Prentiss Sanger; Henry Gannett; Walter Francis Willcox (1900). Informe sobre el censo de Puerto Rico, 1899, United States. War Dept. Porto Rico Census Office (in Spanish). Imprenta del gobierno. p. 41.
- "Preliminary Locations of Landslide Impacts from Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico". USGS Landslide Hazards Program. USGS. Archived from the original on 2019-03-03. Retrieved 2019-03-03.
- "Preliminary Locations of Landslide Impacts from Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico" (PDF). USGS Landslide Hazards Program. USGS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-03-03. Retrieved 2019-03-03.
- Census 2000 map of Ceiba Municipio
- Census 2000 map of Machos barrio
- Picó, Rafael; Buitrago de Santiago, Zayda; Berrios, Hector H. Nueva geografía de Puerto Rico: física, económica, y social, por Rafael Picó. Con la colaboración de Zayda Buitrago de Santiago y Héctor H. Berrios. San Juan Editorial Universitaria, Universidad de Puerto Rico,1969. Archived from the original on 2018-12-26. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- Gwillim Law (20 May 2015). Administrative Subdivisions of Countries: A Comprehensive World Reference, 1900 through 1998. McFarland. p. 300. ISBN 978-1-4766-0447-3. Retrieved 25 December 2018.
- Puerto Rico:2010:population and housing unit counts.pdf (PDF). U.S. Dept. of Commerce Economics and Statistics Administration U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- "Map of Ceiba at the Wayback Machine" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-03-24. Retrieved 2018-12-29.
- "US Census Barrio-Pueblo definition". factfinder.com. US Census. Archived from the original on 13 May 2017. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- "Agencia: Oficina del Coordinador General para el Financiamiento Socioeconómico y la Autogestión (Proposed 2016 Budget)". Puerto Rico Budgets (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza: Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (first ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "Leyes del 2001". Lex Juris Puerto Rico (in Spanish). Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza: Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (1st ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, p. 273, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "Comunidades Especiales de Puerto Rico" (in Spanish). 8 August 2011. Archived from the original on 24 June 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 3-Population of Municipalities: 1930 1920 and 1910" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 17, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 4-Area and Population of Municipalities Urban and Rural: 1930 to 1950" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2015. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Table 2 Population and Housing Units: 1960 to 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Las 1,200 playas de Puerto Rico [The 1200 beaches of Puerto Rico]". Primera Hora (in Spanish). April 14, 2017. Archived from the original on December 12, 2019. Retrieved December 12, 2019.
- "Ceiba Bridges". National Bridge Inventory Data. US Dept. of Transportation. Archived from the original on 20 February 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
- Elecciones Generales 2012: Escrutinio General Archived 2012-12-03 at the Wayback Machine on CEEPUR