Aguas Buenas, Puerto Rico
Aguas Buenas, commonly known as "La Ciudad de las Aguas Claras" (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈaɣwaz ˈβwenas]) or "The City of Clear (Good) Waters", is a municipality of Puerto Rico (U.S.) located in the Central Mountain Range, north of Cidra, south of Bayamón, Guaynabo and San Juan; east of Comerio; and north-west of Caguas. Aguas Buenas is spread over 9 wards and Aguas Buenas Pueblo (the downtown area and the administrative center of the city). It is part of the San Juan-Caguas-Guaynabo Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Aguas Buenas | |
|---|---|
Town and Municipality | |
 | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
| Nicknames: La Ciudad de las Aguas Claras, Los Mulos, El Oasis de Puerto Rico, Los Ñocos | |
| Anthem: "Yo Soy Aguas Buenas" | |
 Location of Aguas Buenas within Puerto Rico | |
| Coordinates: 18°15′25″N 66°06′11″W | |
| Commonwealth | |
| Founded | May 25, 1838 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Javier García Pérez (PNP) |
| • Senatorial dist. | 1 – San Juan |
| • Representative dist. | 5 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 30.12 sq mi (78.01 km2) |
| • Land | 30 sq mi (78 km2) |
| • Water | 0.004 sq mi (.01 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 28,659 |
| • Density | 950/sq mi (370/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Aguasbonenses |
| Time zone | UTC−4 (AST) |
| Zip code | 00703 |
| Major routes | |
| Website | http://legislaturaaguasbuenas.com/ |
History
Aguas Buenas was originally a sector of Caguas known as Aguabuena. In 1798, a group of residents started establishing their houses near some of the rivers in the area and started calling the sector Aguas Claras.
The quantity of residents incremented with time and on July 25, 1832, they organized a meeting and commissioned Francisco de Salas Torres and Ramón Díaz to do the necessary arrangements for the region to be declared a municipality. A resident, Julian López, offered part of his estate to be used for the construction of a town square, a church, the city hall, and the priest house.
The town was officially founded on May 25, 1838, and the name was changed to Aguas Buenas. Francisco de Salas Torres was declared the first mayor. Initially, the economy of the town relied on coffee plantations and commerce. At the end of the 19th century, the town's population was close to 7,000.
In 1906, mayor Don José E. Morales bought nearly six acres of terrain from Don Guillermo Díaz Delgado. In these lands, the sectors of La Pajilla, El Pueblito and El Guanábano were established, expanding the town's area.
Geography
The terrain is moderately mountainous located in the Cayey mountain range ("Sierra de Cayey"), part of the Cordillera Central in Puerto Rico. The highest peaks are La Peña, Santa Bárbara, La Tisa, and La Marquesa.[1]
Hurricane Maria
Hurricane Maria on September 20, 2017 triggered numerous landslides in Aguas Buenas with the significant amount of rainfall.[2][3] 1,000 homes in Aguas Buenas suffered significant damage as a result of the hurricane. A year after the hurricane struck, many older residents refused to leave their damaged homes and continued to live in their homes, without a reconstructed roof, but with a blue tarp for a roof.[4]
Water features
Several rivers flow through Aguas Buenas. Some of them are the Bayamón River, and several small rivers that are part of the Río Grande de Loíza, like Bairoa, Caguitas, and Cañas.
Barrios
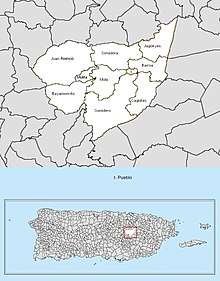
Like all municipalities of Puerto Rico, Aguas Buenas is subdivided into barrios. The municipal buildings, central square and large Catholic church are located in a small barrio referred to as "el pueblo", near the center of the municipality.[5][6][7][8]
Sectors
Barrios (which are like minor civil divisions)[9] in turn are further subdivided into smaller local populated place areas/units called sectores (sectors in English). The types of sectores may vary, from normally sector to urbanización to reparto to barriada to residencial, among others.[10][11][12]
Special Communities
Of the 742 places on the list of Comunidades Especiales de Puerto Rico, the following barrios, communities, sectors, or neighborhoods are in Aguas Buenas: Vázquez neighborhood, Las Parcelas in Bayamoncito barrio, Sonadora barrio, Cagüitas Centro, Pajilla sector in Centro Urbano, Jagüeyes Abajo, Las Corujas, and Parcelas Santa Clara in Sumidero barrio.[13]
Tourism
Some of the landmarks and places of interest in Aguas Buenas are located in its town square. Places of interest in Aguas Buenas include:
- Finca Artesanal
- La Charca Recreational Center
- Aguas Buenas Caves
- El Mirador Walkway
- Luis A. Ferré Plaza
- City Hall
- Lecture House
- Christ Redeemer House
- Jagüeyes Country Club
- Monte La Tiza
- Maximiliano Merced fire station
- Juan Nieves Cotto baseball park
- Holy Spirit parish
Culture
Sports
Aguas Buenas has an amateur baseball team called the Tigers.
Festivals and events
Several festivals and annual events are held in Aguas Buenas. The Salsa, Bomba & Plena Festival is held in the late summer, while the Fiestas Patronales are held in September 8. There's also an Agricultural Fest held in May and the "Festival Folklórico de Campo y Pueblo" in January. The annual Carnival is also held in March.
Demographics
The United States took control of Puerto Rico from Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish-American War under the terms of the Treaty of Paris of 1898 and conducted its first census of Puerto Rico, finding that the population of Aguas Buenas was 7,977.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1900 | 7,977 | — | |
| 1910 | 8,292 | 3.9% | |
| 1920 | 10,741 | 29.5% | |
| 1930 | 12,885 | 20.0% | |
| 1940 | 14,671 | 13.9% | |
| 1950 | 15,565 | 6.1% | |
| 1960 | 17,034 | 9.4% | |
| 1970 | 18,600 | 9.2% | |
| 1980 | 22,429 | 20.6% | |
| 1990 | 25,424 | 13.4% | |
| 2000 | 29,032 | 14.2% | |
| 2010 | 28,659 | −1.3% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[14] 1899 (shown as 1900)[15] 1910-1930[16] 1930-1950[17] 1960-2000[18] 2010[7] | |||
| Total Population | 28,659 |
|---|---|
| Population by Sex/Age[19] | |
| Male | 14,047 |
| Female | 14,612 |
| Under 18 | 7,185 |
| 18 & over | 21,474 |
| 20-24 | 1,962 |
| 25-34 | 3,953 |
| 35-49 | 5,572 |
| 50-64 | 5,352 |
| 65 & over | 3,787 |
| Population by Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic or Latino | 28,513 |
| Non Hispanic or Latino | 146 |
| Population by Race | |
| White | 20,770 |
| African American | 3,604 |
| Asian | 25 |
| American Indian and Alaska Native | 178 |
| Native Hawaiian and Pacific Islander | 5 |
| Other | 2,781 |
| Identified by two or more | 1,296 |
As of 2010, Aguas Buenas has a population of 28,659. Although that represents a decrease of 373 when compared to 2000, its population had steadily increased since 1930. That year, Aguas Buenas registered a population of 12,885.[20]
According to the 2010 Census, 72.5% of the population identifies themselves as White, and 12.6% as African-American. Also, according to the census, the population is equally divided by gender (49% are males, while 51% are females). Finally, 25% of the population is under 18 years old. The next biggest percentage of population (19.4%) is between 35 and 49 years old.[21]
Government
All municipalities in Puerto Rico are administered by a mayor, elected every four years. The current mayor of Aguas Buenas is Javier García Pérez, of the New Progressive Party (PNP). He was elected at the 2016 general elections. The city hall is located in front of the town square.
Since 2011, the city belongs to the Puerto Rico Senatorial district I, which is represented by two Senators.[22] In 2012, José Nadal Power and Ramón Luis Nieves were elected as District Senators.[23]
Mayors
The following have been the Mayors of the Aguas Buenas Municipality, from its foundation to the present:
| Years | Mayor | Years | Mayor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1838-1841 | Francisco de Salas Torres | 1903-1904 | Jacobo Córdova |
| 1841 | Miguel Díaz | 1904-1909 | José E. Morales Díaz |
| 1841-1843 | José Mariano Benítez | 1909-1911 | Carlos Muñoz Díaz |
| 1843 | Miguel Díaz | 1911-1913 | José G. López Alvarado |
| 1842-1846 | José Manuel de la Vega | 1913-1917 | José E. Morales Díaz |
| 1846-1848 | Marcos Díaz | 1918-1927 | Enrique Lizardi |
| 1848-1850 | Manuel Otero | 1927 | José G. Sánchez |
| 1848-1856 | Manuel Otero | 1927-1929 | Alfredo Disdier Pacheco |
| 1856 | Valentín Pérez | 1929-1933 | José G. López Ferrer (Rafael) |
| 1856-1857 | Isidoro García | 1933-1937 | Rafael González López |
| 1857 | Valentín Pérez | 1937-1940 | Pedro G. López |
| 1857-1859 | José Tomás de Sarraga | 1940-1944 | Rafael González López PPD |
| 1859 | Valentín Pérez | 1944-1948 | Rafael Batalla Reyes PER |
| 1859 | Tomás Paz | 1948-1956 | Miran Carrasquillo Cartagena PPD |
| 1859 | Buenaventura de las Barcenas | 1956-1960 | Ramón López Batalla PPD |
| 1859 | Valentín Pérez | 1960-1964 | Ángel Rivera Rodríguez PPD |
| 1859-1862 | Manuel Boscana Guillermetty | 1965-1972 | Ángel T. Arroyo García PPD |
| 1860 | Valentín Pérez | 1972-1980 | Gregorio Torres Velásquez PPD |
| 1862 | Santiago Pereira | 1981-1988 | Gudelio Díaz Morales PPD |
| 1862-1867 | Juan Eugenio Vizcarrondo | 1989-1999 | Carlos Aponte Silva PNP |
| 1867-1898 | José Martínez Balasquides | 1999- 2004 | Buenaventura Dávila Roldán PNP |
| 1867-1898 | Agustin J. Díaz | 2004 – present | Luis Arroyo Chiqués PPD |
| 1898-1902 | Buenaventura Díaz | ||
| 1903 | Pío Rechani |
Symbols
Flag
The flag of Aguas Buenas features a blue triangle with the base at the hoist. The triangle has a solitary white star, like the national banner. A second triangle appears interposed with the first one, in yellow, with its point reaching the other end of the flag. The main field of the flag, under both triangles, is color green.
Coat of arms
The coat of arms features a four-paneled shield. The upper left panel shows the Virgin of Monserrate, while the upper right panel features a Taíno, a symbol of the original inhabitants of this region. At the bottom right panel, lies a cornucopia containing the native fruit of Aguas Buenas. This panel represents how the agriculture was the primary source of income for the town. In the lower left panel, there are four maracas and a güicharo, typical instruments of the "jibaros" of Aguas Buenas and Puerto Rico. The crown, as with other municipalities of Puerto Rico, consists of three towers.
Transportation
To reach the town of Aguas Buenas, visitors must take the Puerto Rico Highway 52 to the city of Caguas. From there, road #156 leads directly into the town square. Other roads lead to nearby towns like Comerío.
There are 13 bridges in Aguas Buenas.[24]
Education
There are around 14 public schools in Aguas Buenas. As with all other municipalities, education is handled by the Puerto Rico Department of Education. These are divided as follows:
Elementary Schools
- Dr. Gustavo Muñoz Díaz
- Ezequiel Ramos La Santa
- Jagüeyes Abajo
- José R. González
- Luis Santaella
- Luis T. Baliñas
- Mulitas Alvelo
- Ramón Luis Rivera/Juan Asencio
- Santa Clara
Junior High Schools
- Dr. Pedro Albizu Campos
- Luis Muñoz Marín
- Su Bayamoncito
- Su Sumidero
High Schools
- Josefa Pastrana
Anthem
Bajo el azul del cielo de mi patria
En el oriente de la Cordillera
Aguasbonenses forjando la historia
Defendiendo el honor de su bandera.
De sol a sol sembrando nuestros frutos
El orgullo labrado en nuestra tierra
La siega de un futuro va anunciando
El brillo de la solitaria estrella.
Que se levanta en medio del combate
Por negarse a ser solo una quimera
Raices firmes que en el pecho laten
Afirmando la patria y la conciencia.
Aguas Buenas, estirpe de valientes
Pedazo del terruño borinqueño
Un pueblo que se une en la conquista
De lo que es ser un buen puertoriqueñio.
Yo soy Aguas Buenas!
Notable "Aguasbonenses"
- Victor Hernández Cruz – Poet
- Gustavo Muñoz Díaz – Dramatist
- Jacobo Córdova Chirino (1901–1955) – Journalist & Humorist
- José Arsenio Torres – Professor
- Luis Rechani Agrait (1902–1997) – Dramatist
- Pio Rechani – Journalist
- Rafael Nicolau – Journalist
- Josefa Pastrana Lopez (1899–1958) – Professor
- Joyce Giraud – Actress
References
- "Aguas Buenas Municipality". enciclopediapr.org. Fundación Puertorriqueña de las Humanidades (FPH). Archived from the original on 14 February 2019. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- "Preliminary Locations of Landslide Impacts from Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico". USGS Landslide Hazards Program. USGS. Archived from the original on 2019-03-03. Retrieved 2019-03-03.
- "Preliminary Locations of Landslide Impacts from Hurricane Maria, Puerto Rico" (PDF). USGS Landslide Hazards Program. USGS. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-03-03. Retrieved 2019-03-03.
- "Aguas Buenas: la vida atrapada en azul [Aguas Buenas: Life trapped in blue]". El Nuevo Día. Archived from the original on 2019-12-12. Retrieved 2019-12-12.
- Picó, Rafael; Buitrago de Santiago, Zayda; Berrios, Hector H. Nueva geografía de Puerto Rico: física, económica, y social, por Rafael Picó. Con la colaboración de Zayda Buitrago de Santiago y Héctor H. Berrios. San Juan Editorial Universitaria, Universidad de Puerto Rico,1969. Archived from the original on 2018-12-26. Retrieved 2019-01-05.
- Gwillim Law (20 May 2015). Administrative Subdivisions of Countries: A Comprehensive World Reference, 1900 through 1998. McFarland. p. 300. ISBN 978-1-4766-0447-3. Retrieved 25 December 2018.
- Puerto Rico:2010:population and housing unit counts.pdf (PDF). U.S. Dept. of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration, U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved 2019-01-05.
- "Map of Aguas Buenas" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-07-30. Retrieved 2018-12-28.
- "US Census Barrio-Pueblo definition". factfinder.com. US Census. Archived from the original on 13 May 2017. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- "Agencia: Oficina del Coordinador General para el Financiamiento Socioeconómico y la Autogestión (Proposed 2016 Budget)". Puerto Rico Budgets (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza: Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (first ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "Leyes del 2001". Lex Juris Puerto Rico (in Spanish). Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza:Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (Primera edición ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, p. 273, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Report of the Census of Porto Rico 1899". War Department, Office Director Census of Porto Rico. Archived from the original on July 16, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 3-Population of Municipalities: 1930, 1920, and 1910" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 17, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 4-Area and Population of Municipalities, Urban and Rural: 1930 to 1950" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2015. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Table 2 Population and Housing Units: 1960 to 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "2010 US Census Population Data for Aguas Buenas, PR". US Census 2010. U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 13 December 2012. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- "Población de Puerto Rico por Municipios: 1930-2000". CEEPUR. Archived from the original on 2013-03-21.
- "2010 Census Interactive Population Search: Aguas Buenas, Puerto Rico". US Census 2010. Archived from the original on 2013-07-27.
- Distribución de Distritos Senatoriales de Puerto Rico Archived 2011-11-16 at the Wayback Machine on ElectionsPuertoRico
- Elecciones Generales 2012: Escrutinio General Archived 2013-01-15 at the Wayback Machine on CEEPUR
- "Aguas Buenas Bridges". National Bridge Inventory Data. US Dept. of Transportation. Archived from the original on 20 February 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2019.