Guánica, Puerto Rico
Guánica (Spanish pronunciation: [ˈɡwanika]) is a town and municipality in southern Puerto Rico, bordering the Caribbean Sea, south of Sabana Grande, east of Lajas, and west of Yauco. It is part of the Yauco metropolitan statistical area.
Guánica | |
|---|---|
Town and Municipality | |
 | |
 Flag | |
| Nicknames: "Pueblo de la amistad", "El Pueblo de las Doce Calles", "Puerta de la Cultura" | |
| Anthem: "América es jardín del mundo" | |
 Location of Guánica in Puerto Rico | |
| Coordinates: 17°58′18″N 66°54′29″W | |
| Commonwealth | |
| Settled | 1508 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Santos Seda (PNP) |
| • Senatorial dist. | 5 - Ponce |
| • Representative dist. | 21 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 138.35 km2 (53.42 sq mi) |
| • Land | 96 km2 (37 sq mi) |
| • Water | 42.35 km2 (16.35 sq mi) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 19,427 |
| • Density | 140/km2 (360/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Guaniqueños |
| Time zone | UTC−4 (AST) |
| Zip code | 00653, 00647 |
| Major routes | |
| GNIS feature ID | 1610855[1] |
The town of Guánica, also known as Pueblo de Guánica, is the principal town of the municipality. The town's population in 2000 was 9,247 people among 3,808 housing units over a land area of 2.49 square miles (6.45 km2). The town is located on a deeply indented harbor of the same name. The harbor resembles a tropical fjord, narrow and bordered by rugged hills, barely a quarter-mile wide, but about two miles (3.2 km) from mouth to the town. The town is about 100 miles (160 km) and over two hours' driving distance from San Juan, the capital city of the island, and about 20 miles (30 km) west of Ponce, another principal city of the island.
Guánica's postal zip code is 00653 and telephone area codes are 787 and 939. The urban area of Ensenada has a separate postal zip code of 00647.
History
Settlement

Juan Ponce de Leon landed in the Guánica harbor on August 12, 1508 and founded a town called Guaynía, a word derived from the Taíno indigenous culture that possibly meant "Here is a place with water". The town, considered the capital of the island of Puerto Rico (which was at that time named Isla de San Juan Bautista), was destroyed during the indigenous uprising of 1511, and the area was abandoned by Europeans for some years, during which time San Juan (itself at first called Puerto Rico) became the capital of the island. The United States took control of Puerto Rico from Spain in the aftermath of the Spanish-American War under the terms of the Treaty of Paris of 1898. In 1899, the United States conducted its first census of Puerto Rico, finding that the population of Guánica barrio was 2,700.[2] The refounded town of Guánica was at first a barrio of the municipality of Yauco until Guánica was established as a separate municipality on March 13, 1914. Víctor Ángel Sallaberry Safini was Guánica's first mayor.
Invasion

On July 25, 1898, American forces (who included the young poet-writer Carl Sandburg led by General Nelson A. Miles) landed in Guánica as part of the course of the Puerto Rican Campaign in the Spanish–American War. This invasion led to Puerto Rico being acquired by the United States. The invasion, just one small part of the war between Spain and United States, occurred in Guánica due to its sheltered harbor and proximity to Ponce, besides being such an unexpected site for such an attack, which had been anticipated at the heavily fortified city of San Juan. The Gloucester was the first ship to set anchor in the Bay of Guánica. Twenty-eight sailors and Marines, under the command of lieutenants H. P. Huse and Wood, departed from the ship on rafts and landed on the beach. The Marines lowered the Spanish flag from the beach flagpole and replaced it with the American flag. They then proceeded to set up a machine gun nest and placed barbed wire around their perimeter. The first land skirmish in Puerto Rico between the Puerto Rican militia and the American forces occurred when Lt. Méndez López and his men attacked and opened fire on the Americans. During the small battle which followed, the Americans returned fire with their machine gun and the Gloucester began to bombard the Spanish position. Lt. Méndez López and three of his men were wounded and the militia unit was forced to retreat to the town of Yauco.[3][4] The invasion is commemorated by a contentious monument on the waterfront: along a broad paseo (el malecón), there is a large coral boulder marked by the carved words, "3rd Battalion, 1st U.S.V. Engineers, September 16, 1898." July 25 was subsequently commemorated in Puerto Rico as Occupation Day, later renamed Constitution Day (see Public holidays in Puerto Rico).
Today

Guánica is a modern town that maintains roots and connections to a traditional past. Known as el pueblo de la amistad ('the town of friendship'), it is also occasionally referred to as el pueblo de las doce calles ('the town of the twelve streets'). The central part of town consists of five streets running north–south crossing seven other streets that run east–west, resulting in a compact grid of 24 square blocks, one of which is the town plaza. Facing the plaza is the Catholic Church, city hall, a school, and many shops; the plaza itself contains greenery, walks, and a music stand. In recent years this central area of the twelve streets has been extensively supplemented by suburbs in the south and west. Hills surround the town and harbor, including the 450-foot (140 m) hill to the east of town, itself topped by the tiny Fort Caprón. Two large factories, one producing fertilizer, partially distract the eye from the pleasant landscape, but both have been important to the economy of the town, at one time dominated by the sugar plantations of Central Guánica. The resort chain known as Club Med once attempted to set up a luxury resort on beaches east of the town, but withdrew due to local opposition which was apprehensive about both environmental and community degradation. East of the town some 200 acres (80.9 ha) of land, including three miles (4.8 km) of beach, have been intermittently for sale. It is a fishing village; commercial fishermen still ply their traditional trade beyond the harbor entrance. Copamarina Beach Resort & Spa offers beach access and a short boat ride to Giligan Island, which is a great spot to go snorkeling. The water is crystal clear and shallow, in which old pieces of coral and fish can be seen. People can walk from one island to another.
On January 6, 2020, a 5.8 magnitude earthquake was felt in Guánica and nearby municipalities, and several residences and cars were destroyed.[5] On January 7, 2020, a 6.4 magnitude earthquake hit.[6]
Geography

Guánica has mountains and a forest. The Guánica State Forest (Bosque Estatal de Guánica) is also the name of a small dry forest reserve east and west of the town, the largest remaining tract of tropical dry coastal forest in the world, and designated an international Biosphere Reserve in 1981. The park comprising much of the dry forest is known as el Bosque Seco de Guánica.[7][8]
Highway Route 116, the nearest principal road, heads west toward Lajas and east toward Ponce, passing through the island of Puerto Rico's driest area. The largely intact forest of the Guánica Dry Forest reserve hosts the greatest number of bird species found on the island, including several bird species seldom found anywhere else: the Puerto Rican lizard cuckoo, Puerto Rican woodpecker, the Puerto Rican nightjar, and the Puerto Rican emerald hummingbird. Other animals thought to be extinct in Puerto Rico have turned up in this forest. Many different types of cactus grow here, a stunning contrast to the lush Caribbean National Forest in the northeast part of the island, which is a tropical rainforest. The contrast is due to the mountain ridge Cordillera Central which separates Guánica from the northeast part of the island; while the northeast receives over 100 inches (2,500 mm) of precipitation each year, Guánica receives less than 30, and some regions of the forest reserve are said to receive only six inches.
The forest reserve of some 9,500 acres (38 km2) contains 36 miles (58 km) of trails through four different forest types: deciduous trees, a coastal region with tree-size milkweed and nine-foot-tall (2.7 m) prickly pear cactus, a mahogany forest, and twisted gumbo limbo trees. There are about 700 varieties of plants, including aroma (acacia) and guayacan (lignum vitae—Latin for 'wood of life'). One guayacan is about 500–700 years old. The squat melon cactus and other cacti can be found here along with 40 species of birds, including the guabairo (Puerto Rican nightjar), found nowhere else. Also in the area are a crested toad (Peltophryne lemur) and, sometimes on the beaches, green and leatherback turtles, though their eggs suffer severe predation from mongooses one time introduced to fight rats in sugar cane fields.
Barrios
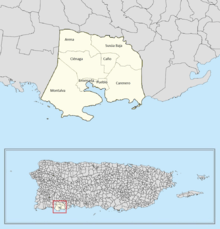
Like all municipalities of Puerto Rico, Guánica is subdivided into barrios. The municipal buildings, central square and large Catholic church are located in a small barrio referred to as "el pueblo".[9][10][11][12]
Sectors
Barrios (which are like minor civil divisions)[13] in turn are further subdivided into smaller local populated place areas/units called sectores (sectors in English). The types of sectores may vary, from normally sector to urbanización to reparto to barriada to residencial, among others.[14][15][16]
Special Communities
Of the 742 places on the list of Comunidades Especiales de Puerto Rico, the following barrios, communities, sectors, or neighborhoods are in Guánica: Esperanza neighborhood, Callejón Magüeyes, El Batey, El Tumbao, Ensenada, Fuig, La Luna, and Playa Santa.[17]
Tourism

Landmarks and places of interest
Guánica has 39 beaches, including Playa Santa.[18]
Other places of interest in Guánica include:
- Guánica Parador 1929 is a historic inn near the sugar mill[19]
- Azul Beach
- Ballena Bay
- Caprón Fortress
- Casa Alejada
- Cayo Aurora, Gilligan's Island
- Copamarina Beach Resort
- El Malecón (Boardwalk)
- Guiligan Island
- Guánica Bay
- Playa Manglillo is a beach near Playa Santa.
- Playa Santa Beach[20]
- Punta de Brea, a surf spot[21]
- Punta Jorobao
- Hacienda Santa Rita
- Serra Beach
- Central Guánica (Sugar Cane Refinery)
- Guánica State Forest, also called Guánica Dry Forest is a 9,000-acre forest[22]
- Mimi's Guest House, a small guest in the Guánica State Forest[23]
- Mary Lee's By the Sea[24]
- Guánica Lighthouse
Economy
Agriculture

- Salt and Sugarcane
Industry
- Manufacture (apparel)
Culture
Festivals and events
- Festival del Juey (Crab Festival) – June
- Patron Festivities – July
- July 25 Parade – July
- Juan Ponce de León Celebration – August
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1920 | 9,948 | — | |
| 1930 | 10,238 | 2.9% | |
| 1940 | 12,685 | 23.9% | |
| 1950 | 15,630 | 23.2% | |
| 1960 | 13,767 | −11.9% | |
| 1970 | 14,889 | 8.1% | |
| 1980 | 18,799 | 26.3% | |
| 1990 | 19,984 | 6.3% | |
| 2000 | 21,888 | 9.5% | |
| 2010 | 19,427 | −11.2% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census[25] 1920-1930[26] 1930-1950[27] 1960-2000[28] 2010[11] | |||
Uniformed mix of "Indio Taino, Africano y Espanol". No race segregation reported.
Government
Like all municipalities in Puerto Rico, Guánica is administered by a mayor. The current mayor is Santos Seda, from the New Progressive Party (PNP). Seda was elected at the 2012 general election.
The city belongs to the Puerto Rico Senatorial district V, which is represented by two senators. In 2012, Ramón Ruiz and Martín Vargas Morales, from the Popular Democratic Party, were elected as District Senators.[29]
Symbols
Flag
The five waves, blue and yellow represent the Guánica Bay, a fragment of the Official Shield of Guánica.
Coat of arms
Shield divided in four quarters. In the superior right side, it has a "bohio" (hut) under a crown that represents Cacique Agüeybaná, whose yucayeque (Indian territory) was in this region. In the superior left quarter, a lion representing Juan Ponce de León. The checkered strips over a silver-plated background in the inferior right side represent the shields of Don Cristóbal de Sotomayor, founder of the town of Tavara, the actual location of Guánica. The waved stripes represent the bay of this town. The branches surrounding the shield represent the sugar cane industry that was very important in this region.
Notable "Guaniqueños"
- Agüeybaná and Agüeybaná II, Taíno chiefs
- Rose Franco (b. 1932), first Puerto Rican woman Chief Warrant Officer in U.S. Marine Corps
- Primitivo Anglada – Activist in obtaining Guánica's municipal independence. First secretary of the Town Council.
- Miguel A. Morciglio – Member of the House of Representatives for District 24 (1961–64).
- Carmen Ramírez Vargas (Lolita Vargas) – Singer, actress, and educator.
- Rubén del Rosario – Educator, writer, and linguist.
- Víctor Sallaberry – First mayor elected by the people, in 1914.
- Pedro Santana Ronda – Writer, poet, and journalist. Was published in the weekly paper El Erizo.
- Domingo Suárez Cruz – Civic leader, political orator, and writer. Was keeper of the Guánica Lighthouse. The public library was named in his honor.
- María Heliodora Vargas – Educator and author of the poem «La bandera de los guaniqueños» ('The Flag of the Guaniqueños').
- Pedro Juan Vargas Mercado – Journalist and historian.
- Pedro Vargas Rodríguez – Secretary of the Separation Committee that achieved the emancipation of the municipality. Poet, orator, musician, writer, and journalist. Founded El Fósforo (1908) and Brisas del Caribe (1915), the first newspapers in Guánica.
Transportation
At one time during 1937, Guánica received domestic, commercial airline flights from San Juan on Puerto Rico's national airline, Puertorriquena de Aviacion.[30]
There are 25 bridges in Guánica.[31]
Gallery
 Playa Jaboncillo
Playa Jaboncillo Playa Jaboncillo and Bosque Seco in Guánica
Playa Jaboncillo and Bosque Seco in Guánica Fuerte Capron, Bosque Seco, Guánica
Fuerte Capron, Bosque Seco, Guánica Fuerte Capron, Bosque Seco, Guánica
Fuerte Capron, Bosque Seco, Guánica Facade of Fuerte Capron
Facade of Fuerte Capron Guánica boardwalk
Guánica boardwalk
Books
- Torres, Angel Luis, Walter Torres, and Miguel Canals. En el Bosque Seco de Guánica. San Juan, Puerto Rico: La Editorial Universidad de Puerto Rico (Colección San Pedrito), 1995. ISBN 0-8477-0207-3 – Children's picture book about a trip through the dry forest of Guánica with a sea turtle. (in Spanish)
- La Muerte de un Gigante: historia de la central guanica, autora Aria E. Ramos, La Muerte de Un Gigante: Historia de la Central Guanica y el poblado de Ensenada: Maria E. Ramos: 9781563281471: Amazon.com: Books
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Guánica, Puerto Rico. |
- List of Puerto Ricans
- History of Puerto Rico
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Guánica, Puerto Rico
- Did you know-Puerto Rico?
References
- "Guánica – Populated Place". Geographic Names Information System. USGS. Retrieved 2008-05-14.
- Joseph Prentiss Sanger; Henry Gannett; Walter Francis Willcox (1900). Informe sobre el censo de Puerto Rico, 1899, United States. War Dept. Porto Rico Census Office (in Spanish). Imprenta del gobierno. p. 165.
- Barnes, Mark R. "The American Army Moves on Puerto-Rico, Part 2". War in Puerto Rico. Spanish American War Centennial Website. Archived from the original on 2008-07-24. Retrieved 2008-08-02.
- "El desembarco en Guánica". 1898 La Guerra Hispano Americana en Puerto Rico (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 2010-04-21. Retrieved 2008-08-02.
- "Colapsan cinco residencias en la barriada Esperanza en Guánica por el temblor [Five residences in the Esperanza neighborhood of Guánica collapse as a result of the earthquake]". El Nuevo Dia. January 6, 2020.
- Rosa, Alejandra; Mazzei, Patricia (January 6, 2020). "Earthquake Strikes Puerto Rico, Toppling a Well-Known Natural Wonder" – via NYTimes.com.
- "Balneario Caña Gorda". drdpuertorico (in Spanish). Programa de Parques Nacionales de Puerto Rico. Archived from the original on 13 February 2019. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- "Guánica Municipality". enciclopediapr.org. Fundación Puertorriqueña de las Humanidades (FPH). Archived from the original on 2019-08-29. Retrieved 2019-03-20.
- Picó, Rafael; Buitrago de Santiago, Zayda; Berrios, Hector H. Nueva geografía de Puerto Rico: física, económica, y social, por Rafael Picó. Con la colaboración de Zayda Buitrago de Santiago y Héctor H. Berrios. San Juan Editorial Universitaria, Universidad de Puerto Rico,1969. Archived from the original on 2018-12-26. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- Gwillim Law (20 May 2015). Administrative Subdivisions of Countries: A Comprehensive World Reference, 1900 through 1998. McFarland. p. 300. ISBN 978-1-4766-0447-3. Retrieved 25 December 2018.
- Puerto Rico:2010:population and housing unit counts.pdf (PDF). U.S. Dept. of Commerce Economics and Statistics Administration U.S. Census Bureau. 2010. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-02-20. Retrieved 2019-01-04.
- "Map of Guánica at the Wayback Machine" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-03-24. Retrieved 2018-12-29.
- "US Census Barrio-Pueblo definition". factfinder.com. US Census. Archived from the original on 13 May 2017. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- "Agencia: Oficina del Coordinador General para el Financiamiento Socioeconómico y la Autogestión (Proposed 2016 Budget)". Puerto Rico Budgets (in Spanish). Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza: Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (first ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "Leyes del 2001". Lex Juris Puerto Rico (in Spanish). Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- Rivera Quintero, Marcia (2014), El vuelo de la esperanza:Proyecto de las Comunidades Especiales Puerto Rico, 1997-2004 (Primera edición ed.), San Juan, Puerto Rico Fundación Sila M. Calderón, p. 273, ISBN 978-0-9820806-1-0
- "Las 1,200 playas de Puerto Rico [The 1200 beaches of Puerto Rico]". Primera Hora (in Spanish). April 14, 2017. Archived from the original on December 12, 2019. Retrieved December 12, 2019.
- "Historic Hotels and Resorts in Puerto Rico". Discover Puerto Rico. Archived from the original on 2019-07-17. Retrieved 2019-06-25.
- "Playa Santa in Guanica | Puerto Rico Day Trips Travel Guide". www.puertoricodaytrips.com. Archived from the original on 2019-03-06. Retrieved 2019-06-25.
- "Punta de Brea - Surfing in Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico - WannaSurf, surf spots atlas, surfing photos, maps, GPS location". Wanna Surf.
- "Guanica Dry Forest Reserve | Puerto Rico Day Trips Travel Guide". Puerto Rico Day Trips. Archived from the original on 2019-07-05. Retrieved 2019-07-05.
- "MIMI'S GUEST HOUSE - Prices & Reviews (Puerto Rico/Guanica)". Trip Advisor. Archived from the original on 2019-07-05. Retrieved 2019-07-05.
- "Mary Lee's by the Sea in Guanica - Hotel | Frommer's". Frommers.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 3-Population of Municipalities: 1930 1920 and 1910" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 17, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- "Table 4-Area and Population of Municipalities Urban and Rural: 1930 to 1950" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2015. Retrieved September 21, 2014.
- "Table 2 Population and Housing Units: 1960 to 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved September 21, 2017.
- Elecciones Generales 2012: Escrutinio General Archived 2013-01-15 at the Wayback Machine on CEEPUR
- "Aerovias NPR - Aerovias Nacionales Puerto Rico". Time Table Images. Retrieved 19 April 2018.
- "Guánica Bridges". National Bridge Inventory Data. US Dept. of Transportation. Archived from the original on 21 February 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2019.
External links
- Visit the Guanica dry forest
- World Wildlife Fund, ed. (2001). "Puerto Rican dry forests". WildWorld Ecoregion Profile. National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on 2010-03-08.
- Gilligan's Island Photos and information, Guanica, Puerto Rico
- Bosque Seco de Guánica (in Spanish)
- El Bosque Estatal de Guánica (in Spanish)
- Mapa del Bosque Seco
- Welcome to Puerto Rico! Guánica
![]()