Calamba, Laguna
| Calamba | ||
|---|---|---|
| Component City | ||
| City of Calamba | ||
 (From left, clockwise): Jose Rizal (monument), Calamba Church, Calamba Giant Water Pot | ||
| ||
Nickname(s):
| ||
| Motto(s): Mabuhay ang Calamba! | ||
 Map of Laguna with Calamba highlighted | ||
.svg.png) Calamba Location within the Philippines | ||
| Coordinates: 14°13′N 121°10′E / 14.22°N 121.17°ECoordinates: 14°13′N 121°10′E / 14.22°N 121.17°E | ||
| Country |
| |
| Region | Calabarzon (Region IV-A) | |
| Province | Laguna | |
| District | Legislative district of Calamba | |
| Founded | August 28, 1742 | |
| Cityhood | April 21, 2001 | |
| Barangays | 54 (see Barangays) | |
| Government [1] | ||
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod | |
| • Mayor | Justin Marc S.B. Chipeco | |
| • Vice Mayor | Roseller H. Rizal | |
| • Electorate | 268,283 voters (2016) | |
| Area [2] | ||
| • Total | 149.50 km2 (57.72 sq mi) | |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | ||
| • Total | 454,486 | |
| • Density | 3,000/km2 (7,900/sq mi) | |
| Demonym(s) |
Calambeño (Male), Calambeña (Female), Calambenean | |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) | |
| ZIP code | 4027, 4028, 4029 | |
| PSGC | 043405000 | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)49 | |
| Climate type | Tropical monsoon climate | |
| Income class | 1st city income class | |
| Revenue (₱) | 2,688,995,343.67 (2016) | |
| Native languages |
Tagalog Taglish Swardspeak | |
| Website |
www | |
Calamba, officially the City of Calamba, (Tagalog: Lungsod ng Calamba), or known simply as Calamba City is a 1st class city in the province of Laguna, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 454,486 people.[3]
It is the regional center of the Calabarzon region. It is situated 50 kilometres (31 mi) south of Manila, the city is known as the Resort Capital of the Philippines[4] because of its numerous hot spring resorts, which are mostly located in Barangay Pansol, Bucal and Bagong Kalsada.
According to the 2015 census, the city has a population of 454,486 people, making it the most populous local government unit in Laguna.[3] It is the 5th densest city in the province with more than 2,600 people per square kilometer after San Pedro, Biñan, Cabuyao and Santa Rosa. Based on the overall rankings of the 2014 Cities and Municipalities Index, the city ranked 18th in the overall competitiveness (cities ranking) and 1st among cities in the Calabarzon region. The city is known to be as the Calabarzon's Richest City following by Cabuyao City, because of its numerous factories according to the Region 4-A Calabarzon.[5][6]
The City of Calamba is the hometown of the Philippine national hero, Jose Rizal.
Etymology
The name of the city comes from a legend that during the early time of the Spanish period in the country, two "guardias civil" or soldiers were lost and passing through what is now Calamba. The soldiers met a young lady who came from a river carrying a jar of water and a clay stove. The soldiers unwittingly in Spanish language and in authoritative tone, to conceal the fact that they were lost, asked the local maiden the name of the place they were in. The lady, who speaks only her native language, naturally thought she was being interrogated about what she was carrying and nervously uttered "kalan-banga", meaning "clay stove" (kalan) and "water jar" (banga).[7] Because the Spaniards could not pronounce it properly, the town has been called Calamba supposedly since then. This legend is immortalized with a large concrete water jar erected in the city plaza with the names of the city's barangays written on its surface. It is now known as Calambanga and is considered the "World's Biggest Claypot".[8] This same jar is also found in the city's seal. The plaza was proposed by Dr. Agapito Alzona, then the town councilor to utilize the waste area where the old town market relocated from. The resolution was approved by the then town mayor Roman Lazaro and added additional P5,000 for the fence to the original P15,000 construction cost. It was completed in 1939.
History
The oldest part of Calamba is believed to be Barangay Sucol where its first settlers remained. With the arrival of Spaniards, the whole area was converted into a hacienda, then a part of Tabuco (now known as Cabuyao City). Calamba became an independent pueblo on August 28, 1742, and formed into the town of Calamba in 1770. In 1813, Calamba was placed in the hands of "encargados" by the Dominican Brothers, who divided into portions and sold the haciendas to the natives during the American regime.[7][9]
During the Japanese occupation in World War II, the city was the theater of a massacre during which the Imperial Japanese Army killed at least 2,000 civilians.[10] The St. John the Baptist Church, established in 1859, was burned by the Japanese during World War II. It was reconstructed by Fr. Eliseo Dimaculangan. It was the christening site of José Rizal. The original baptismal font has been preserved and refurbished.
Cityhood
After a process of more than seven years, Calamba became the second component city of the Laguna by virtue of Republic Act No. 9024, "An Act Converting the Municipality of Calamba, Province of Laguna into a Component City to be known as the City of Calamba." R.A. 9024 was signed into law by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo on March 5, 2001, at the Malacañan Palace. The Commission on Elections (COMELEC) then set the plebiscite for Calamba's cityhood on April 21, 2001 where 15,056 residents participated. 3,413 or 22.67% voted "No" while the remaining 77.33% voted "Yes" to Calamba's conversion into a component city.[11]
Events leading to Cityhood

As early as 1994, the town's Sangguniang Bayan approved Resolution No. 60, Series of 1994 requesting the Senate of the Philippines thru its president and the House of Representatives thru its speaker to co-sponsor a bill for Calamba's conversion into a city. It was only after two years that another resolution, Resolution No. 115 was passed requesting then Congressman Joaquin M. Chipeco Jr, to co-sponsor a bill for Calamba's cityhood and requesting the Sangguniang Panlalawigan for their comments and recommendations regarding the matter. Another two years passed before House Bill No. 986 and Senate bill Nos. 1630 and 1791 were filed in the House of Representatives by Congressman Chipeco and Senate of the Philippines by Senators Franklin M. Drilon and Sergio Osmeña III, respectively.
It was only in the year 2000 that the motion for Calamba's cityhood was fast tracked. Then Mayor Severino J. Lajara requested favorable endorsement of House Bill No. 986 from the Sangguniang Panlalawigan on January 3, 2000. The Sangguniang Bayan also endorsed House Bill No. 986 and Senate Bill Nos. 1630 and 1791 and also requested favorable endorsement from the Sangguniang Panlalawigan on the same month. A month passed and Mayor Lajara sent a follow-up letter to then Vice Governor Teresita "Ningning" Lazaro on updates regarding the matter.
On March 8, the House Committee on Local Government approved House Bill No. 986 on 2nd reading at a hearing held at Hotel Rembrandt, Quezon City. The same House Committee conducted a public hearing on House Bill No. 986 at the Calamba Elementary School (Central II) gymnasium on March 23, approving the House Bill in principle. House Bill 986 was deliberated in April by the House of Representatives in plenary session and approved as House Bill No. 10661, which was then filed with the Senate of the Philippines in June.
The year 2001 came and brought about approval on 2nd reading of Senate Bill Nos. 1630 and 1791 and House Bill No. 10661 in a hearing held on February 5 at the Ambrocio Padilla Hall, Senate of the Philippines. Three days later, February 8, Senate Bill Nos. 1630 and 1791 and House Bill No. 10661 was deliberated in Plenary Session and was approved as Republic Act No. 9024.[11]
Calabarzon Regional Government Center
Calamba City was declared the regional center of the Calabarzon region by then President Gloria Arroyo by virtue of Executive Order No. 246, dated October 28, 2003.[12]
Geography
Calamba lies on the northern slopes of Mount Makiling, a dormant volcano. The southern terminus of the South Luzon Expressway is in Calamba and this geographic position makes the city a gateway to the southern provinces of Luzon. The highway at the end of the South Luzon Expressway leads east to the other towns of Laguna and south towards the provinces of Batangas and Quezon.
Calamba City is bordered by Cabuyao City to the north, Los Baños to the east, by the province of Batangas to the south, specifically the municipalities of Santo Tomas, Tanauan City and Talisay, and by the province of Cavite to the west, with Tagaytay City and Silang. Laguna de Bay the country's largest lake, forms the city's northeast border. The provincial capital, Santa Cruz, is located 37 kilometres (23 mi) by road to the east.
Calamba covers a total land area of 14,950 hectares (36,900 acres), making it is the 2nd largest city in Laguna province in terms of land area after San Pablo City.
Land Uses
| Classification[13] | Land Area (hectares) |
|---|---|
| Urban Redevelopment Zone | 2,080 |
| Growth Management Zone 1 | 4,199 |
| Growth Management Zone 2 | 2,460 |
| Upland Conservation Zone | 3,401.22 |
| Forest Buffer Zone | 333 |
| Makiling Forest Reservation Zone | 579.78 |
| Agricultural Development Zone | 1,427 |
| Shoreland Area | - |
| Total Land Area | 14,480 |
| Urban Expansion Area | 8,562.7 has |
Barangays
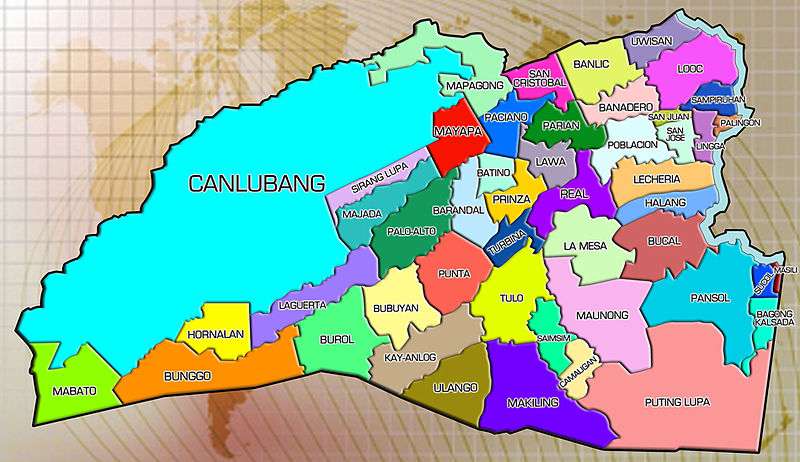
Calamba City is politically subdivided into 54 barangays, the smallest administrative unit in the city.[14]
- ‡ Urbanized Barangay
- ± Independent Barangay
- † Poblacion
- ∗ Industrial & Component Barangay
- Common Barangay
| Barangays of Calamba City | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Barangay | Land Area (hectares) | Population (2010) | Population (2007) | Classification | Zoning Classification |
| 1 | Bagong Kalsada | 157.8 | 3,306 | 2,090 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 2 | Bañadero | 190.0 | 7,116 | 5,309 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 3 | Banlic | 274.9 | 12,780 | 12,626 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 4 | Barandal | 189.3 | 4,625 | 2,994 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 5 | Barangay 1 (Poblacion) | 29.2 | 6,569 | 6,415 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 6 | Barangay 2 (Poblacion) | 17.1 | 8,005 | 6,764 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 7 | Barangay 3 (Poblacion) | 29.8 | 4,408 | 5,111 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 8 | Barangay 4 (Poblacion) | 4.5 | 3,237 | 2,989 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 9 | Barangay 5 (Poblacion) | 25.6 | 6,285 | 5,406 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 10 | Barangay 6 (Poblacion) | 42.3 | 2,447 | 2,309 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 11 | Barangay 7 (Poblacion) | 81.8 | 2,519 | 2,706 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 12 | Batino | 110.5 | 1,249 | 1,295 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 13 | Bubuyan | 196.0 | 1,666 | 1,466 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 14 | Bucal | 265.0 | 11,346 | 12,171 | Urban | Upland Conservation Zone Urban Redevelopment Zone Agricultural Development Zone |
| 15 | Bunggo | 556.6 | 3,809 | 3,650 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 16 | Burol | 258.2 | 1,783 | 1,722 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 17 | Camaligan | 106.5 | 978 | 918 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 2 |
| 18 | Canlubang | 3,912.0 | 54,655 | 54,602 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 1 & 2 |
| 19 | Halang | 166.7 | 6,829 | 6,442 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone Agricultural Development Zone |
| 20 | Hornalan | 22.0 | 1,397 | 1,302 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 21 | Kay-Anlog | 272.0 | 2,665 | 2,195 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 2 |
| 22 | La Mesa | 294.1 | 11,836 | 11,961 | Urban | Upland Conservation Zone Urban Redevelopment Zone Growth Management Zone |
| 23 | Laguerta | 314.9 | 1,766 | 1,752 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 24 | Lawa | 146.6 | 9,169 | 6,132 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 25 | Lecheria | 157.5 | 8,391 | 6,722 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone Agricultural Development Zone |
| 26 | Lingga | 45.0 | 5,817 | 6,322 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 27 | Looc | 179.1 | 14,524 | 12,444 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 28 | Mabato | 273.1 | 705 | 702 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 29 | Majada Labas | 180.2 | 5,172 | 2,090 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 30 | Makiling | 465.7 | 7,510 | 7,100 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 & 2 |
| 31 | Mapagong | 320.8 | 4,942 | 3,618 | Rural | Urban Redevelopment Zone Agricultural Development Zone Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 32 | Masili | 32.1 | 3,585 | 2,859 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 33 | Maunong | 399.2 | 2,105 | 1,917 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone Growth Management Zone 1 & 2 |
| 34 | Mayapa | 116.3 | 21,826 | 21,968 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 35 | Milagrosa | 209.4 | 5,308 | 5,568 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 1 & 2 |
| 36 | Paciano Rizal | 126.8 | 11,958 | 11,733 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 2 |
| 37 | Palingon | 15.3 | 6,403 | 5,093 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 38 | Palo-Alto | 273.7 | 10,628 | 7,270 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 39 | Pansol | 528.2 | 10,868 | 9,980 | Urban | Upland Conservation Zone Urban Redevelopment Zone Forest Buffer Zone Agricultural Development Zone |
| 40 | Parian | 112.0 | 20,248 | 19,587 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 41 | Prinza | 95.3 | 3,996 | 2,737 | Rural | Urban Redevelopment Zone Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 42 | Punta | 331.0 | 3,511 | 2,615 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 & 2 |
| 43 | Putting Lupa | 542.0 | 1,720 | 2,383 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone Growth Management Zone 2 Forest Buffer Zone |
| 44 | Real | 132.9 | 13,805 | 13,375 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 45 | Saimsim | 194.5 | 5,504 | 4,634 | Rural | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 46 | Sampiruhan | 81.0 | 8,144 | 6,788 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
| 47 | San Cristobal | 119.0 | 12,584 | 13,453 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 48 | San Jose | 89.6 | 4,203 | 4,299 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 49 | San Juan | 15.3 | 4,780 | 4,309 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 50 | Sirang Lupa | 198.4 | 8,225 | 6,683 | Urban | Growth Management Zone 1 |
| 51 | Sucol | 31.6 | 4,765 | 4,300 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 52 | Turbina | 51.5 | 4,475 | 3,677 | Urban | Urban Redevelopment Zone |
| 53 | Ulango | 227.6 | 858 | 845 | Rural | Upland Conservation Zone |
| 54 | Uwisan | 78.0 | 2,358 | 2,367 | Urban | Agricultural Development Zone |
Climate
Calamba has a tropical monsoon climate (type Am), with a short dry season and a longer rainy season. The dry season lasts only from January to April, and the rest of the year is characterized by high levels of rainfall.
| Climate data for Calamba (averages 1982-2012) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29.3 (84.7) |
30.3 (86.5) |
31.9 (89.4) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.5 (92.3) |
32.4 (90.3) |
31.4 (88.5) |
31 (88) |
31.1 (88) |
30.9 (87.6) |
30.3 (86.5) |
29.3 (84.7) |
31.2 (88.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.4 (77.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
27 (81) |
28.5 (83.3) |
28.9 (84) |
28.2 (82.8) |
27.5 (81.5) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
25.7 (78.3) |
27.1 (80.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21.5 (70.7) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.2 (72) |
23.5 (74.3) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24 (75) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.6 (74.5) |
23.5 (74.3) |
23.3 (73.9) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.2 (72) |
23 (73.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 54 (2.13) |
26 (1.02) |
29 (1.14) |
36 (1.42) |
160 (6.3) |
199 (7.83) |
290 (11.42) |
265 (10.43) |
245 (9.65) |
248 (9.76) |
141 (5.55) |
79 (3.11) |
1,772 (69.76) |
| Source: Climate-data.org[15] | |||||||||||||
City government
| City Mayor of Calamba City, Laguna
Alkalde ng Lungsod ng Calamba (in Tagalog) | |
|---|---|
| Style | (Mr.) Mayor, Mayor |
| Residence | New Calamba City Hall Building, Brgy. Real, Calamba City, Laguna |
| Appointer | Elected via popular vote |
| Term length | 3 years (maximum of three consecutive terms) |
| Inaugural holder | Mateo Elojorde |
| Formation | 1901 |
Like other cities in the Philippines, Calamba City is governed by a city mayor and city vice mayor who are elected to three-year terms. The city mayor is the executive head who leads the city's departments in the execution of city ordinances and in the delivery of public services. The city vice mayor heads a legislative council that is composed of 12 members: 10 councilors and two ex-officio offices: one for the Sangguniang Kabataan Federation President, representing the youth sector, and one for the Association of Barangay Chairmen President as the barangay sectoral representative. The council is in charge of creating the city's policies in the form of ordinances and resolutions.
By virtue of Republic Act no. 11078, Calamba has been separated from the 2nd District of Laguna to form its own, the Lone District of the City of Calamba[16].
Government officials
The 2016 local elections in Calamba City, held on May 9, 2016, replaced some members of the city government, primarily on the members of the city council. The mayor and vice mayor ran unopposed.
Elected officials for the 2016–2019 term are:
| Position | Name | Party | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mayor | Justin Marc SB. Chipeco | Nacionalista | |
| Vice Mayor | Roseller H. Rizal | Nacionalista | |
| Councilors | Edgardo H. Catindig | Nacionalista | |
| Moises E. Morales | Nacionalista | ||
| Saturnino Lajara | Nacionalista | ||
| Maria Virgina G. Alcasid | Nacionalista | ||
| Charisse Anne C. Hernandez | Liberal | ||
| Peewee P. Perez | Nacionalista | ||
| Angelito Lazaro Jr. | Independent | ||
| Dyan DV. Espiridion | Independent | ||
| Johnny Lazaro | Liberal | ||
| Santiago O. Atienza | Nacionalista | ||
| Ex Officio City Council Members | |||
| ABC President | Larry Dimayuga (Canlubang) | Nonpartisan | |
| SK President | Kenneth delas Llagas | Nonpartisan | |
List of mayors of Calamba
The then Mayors and political leaders of Calamba are:[9]
- Mateo Elejorde (1901–1904)
- Isidoro Cailles (1904–1907)
- Ramon Santos (1907–1910)
- Rafael Pabalan (1910–1917)
- Roman D. Lazaro (1919–1922/1931-1934) (1937-1941/1945-1946)
- Felipe Belarmino (1922–1931)
- Eduardo A. Barretto (1934–1937)
- Enrique G. Shinyo (1942)
- Artemio M. Elepano (1943-1944)
- Exequiel Geneciran (1944–1945)
- Severino Q. Arambulo (1946-1947/1956-1959) (1968–1971)
- Sisenando V. Rizal Sr. (1948-1951/1952-1954)
- Pantaleon Alihan (1954–1955)
- Taciano V. Rizal (1960-1963/1964-1967) (1972–1975)
- Eduardo T. Yu Jr. (1975–1980)
- Salvador E. Delmo (1980–1986)
- Apolonio A. Elazegui (1986–1987)
- Victoriano Chipeco (1987-1988)
- Jesus Miguel Yulo (1987–1994)
- Severino J. Lajara (1994–2004)
- Joaquin M. Chipeco Jr. (2004 to 2013)
- Justin Marc SB Chipeco (2013 to present)
Official Seal of Calamba City

The seal of the City of Calamba has evolved and has been modified throughout the years. From being a municipality to a component city, a new seal was necessary to symbolize the new thrust of Calamba. In a citywide seal-making contest, Reyjon de Guzman emerged as winner, for his work best symbolized the ideals, pride and achievements of the city. Each color, shape, number and object has its own meaning relative to what is Calamba in the past, present and future.[17]
- Shield Shape – The shield shape in the center, with a slight circular bottom, flat top and curved edges at the top corners project solidity and congruence.
- Banga shaped twined with Dr. Jose Rizal's image – The historical ambience is depicted in this twin image. The abstract represents the influence of Dr. Jose Rizal and the Banga in the history of the City of Calamba.
- Numbers – the engraved "1742" mentions the year when Calamba was founded and seceded from the town of Cabuyao, while "2001" was identified as the year of Calamba's cityhood.
- Objects – the mountain in the background and the water current at the bottom part relate to land and water resources of the city pertain to the vast natural resources of Mount Makiling and the aquatic benefits of Laguna de Bay. The water beneath Mt. Makiling shows that Calamba City touches a body of water notably Laguna de Bay, the largest lake in the country, and that's why Calamba City is also known as the "City by the Lake". The silhouette image of rice field on the left and the industrial buildings on the right symbolizing Calamba City's rapid modernization, urbanization, and industrialization. With both signs located beside each other, it shows everyone that nature and progress can efficiently coexist in Calamba City.
- Colors - Except for silver grey and metallic gold, all others are similar with the national seal. However, additional meanings are attached to each.
- Metallic Gold – This represents the radiating image of Dr. Jose Rizal and Banga that reflects in the minds and deeds of Calambeños.
- Red – This symbolizes the burning patriotism of residents as exemplified by Rizal.
- Blue – As land and water represent wealth and prosperity, the color blue signifies productivity and tranquility of the constituents.
- Silver Grey – This represents the transformation of development from an agricultural pueblo in the 1700s to an agro-industrial town in the 1900s and finally to an industrial city.
- White – This projects purity, transparency, efficiency and prudence pertaining to governance.
- Calamba City has a golden edge etched at the upper half with the words Lungsod ng Calamba depicting Calamba City as a Philippine component city. Laguna at the bottom part means that Calamba City is still part of Laguna province.
Demographics
| Population census of Calamba | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
| 1903 | 8,058 | — |
| 1918 | 18,062 | +5.53% |
| 1939 | 32,363 | +2.82% |
| 1948 | 36,586 | +1.37% |
| 1960 | 57,715 | +3.87% |
| 1970 | 82,714 | +3.66% |
| 1975 | 97,432 | +3.34% |
| 1980 | 121,175 | +4.46% |
| 1990 | 173,453 | +3.65% |
| 1995 | 218,951 | +4.46% |
| 2000 | 281,146 | +5.51% |
| 2007 | 360,281 | +3.48% |
| 2010 | 389,377 | +2.87% |
| 2015 | 454,486 | +2.99% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3] [18] [19] [20] | ||
The population of Calamba City is fast-growing with an intercensal growth rate of 5% from 1995 to 2000, repeated and more in subsequent decades (except for 2007 to 2010 census).
100,000
200,000
300,000
400,000
500,000
1990
1,160/km2 1995
1,460/km2 2000
1,900/km2 2007
2,400/km2 2010
2,600/km2 2015
3,000/km2 |
According to the 2015 census, Calamba has a population of 454,486 inhabitants, making it the most populated town in Laguna province, followed by Santa Rosa, Biñan City, San Pedro City, Cabuyao City, and San Pablo. Calamba City is the 24th most populated city in the Philippines.
Calamba is predominantly Roman Catholic (84.22%), followed by Members Church of God International (MCGI or ADD)(4.5%), Protestants (3.43%), Iglesia Ni Cristo (3.14%), and Islam (0.26%).[7]
Economy
Calamba City is known today as the "Richest City in Calabarzon", (according to the 2014 Commission on Audit Annual Audit Report), as it registered a total income of ₱2,501,048,126.00.[21] Calamba is also considered as one of the "Next Wave Cities" for outsourcing firms.[22]
The major income sources comes from manufacturing and economic plants, tourism, agriculture and services. There are many manufacturing and economic plants located in upland barangays like Canlubang, Real, La Mesa, Milagrosa, Makiling, Punta, Barandal, Batino and Prinza.
Income
| Year | Total Income (COA)[23] | Growth % | Total Income (BLGF)[24] | Growth % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2002 | ₱810,569,652.58 | ₱809,806,000.00 | ||
| 2003 | ₱847,402,297.32 | ₱1,046,621,000.00 | ||
| 2004 | ₱872,473,683.19 | ₱921,272,904.23 | ||
| 2005 | ₱1,035,488,459.60 | ₱1,094,639,552.79 | ||
| 2006 | ₱1,110,330,981.73 | ₱1,110,330,981.73 | ||
| 2007 | ₱1,161,438,445.76 | ₱1,162,050,643.28 | ||
| 2008 | ₱1,338,299,724.69 | ₱1,338,769,422.02 | ||
| 2009 | ₱1,580,699,818.00 | ₱1,586,541,340.26 | ||
| 2010 | ₱1,634,025,898.00 | ₱1,699,391,678.99 | ||
| 2011 | ₱1,952,122,303.00 | ₱1,887,800,323.68 | ||
| 2012 | ₱2,023,350,771.00 | ₱2,023,350,600.11 | ||
| 2013 | ₱2,191,286,734.00 | |||
| 2014 | ₱2,501,048,126.00 |
Banking
As of December 31, 2013, there are 83 banking offices operating in the city that offers banking services to businesses and residents according to Philippine Deposit Insurance Corporation. Calamba is the top city in Calabarzon with total deposits amounting to 29,632,884 in thousand pesos from 374,122 accounts.[25]
Industries and manufacturing
The city is a haven for industries. Considered as the heart of Calabarzon due to the number of companies housed in its area, Calamba City is one of the premiere industrial hubs outside of Metro Manila. Some of the industrial parks located in the city are:[26]
- Allegis IT Park (Brgy. Milagrosa)
- Calamba Premiere International Park (Brgy. Batino, Barandal and Prinza)
- Canlubang Industrial Estate (Brgy. Canlubang)
- Carmelray Industrial Park 1 (Brgy. Canlubang)
- Carmelray Industrial Park 2 (Brgy. Milagrosa & Punta)
- Carmelray International Business Park (Brgy. Canlubang)
- Filinvest Technology Park (Brgy. Punta, Burol & Bubuyan)
- Light Industry and Science Park of the Philippines II (Brgy. Real & Lamesa)
- NYK-TDG IT Park (Brgy. Canlubang)
- SMPIC Special Economic Zone (Brgy. Paciano Rizal)
- YTMI Realty Special Economic Zone (Brgy. Makiling)
Food processing plants in Calamba like Zenith Foods Corp. (central commissary of Jollibee Foods Corporation), where its sauces and food products (i.e. burger, pies, fries, etc.) are first made before distributing to Jollibee outlets is currently the most advanced food processing plant in the Philippines and one of the best in Asia. Other food and beverage processing plants in Calamba are Rebisco, RC Cola, Monde-M.Y. San Corporation and Zest-O Corporation.
Some of the semiconductor companies are also located in Calamba. To name a few, they are Samsung Electronics Philippines, Continental Temic Electronics Philippines, Toshiba Storage Device Philippines Inc., ST Microelectronics (formerly Philips Electronics), Fuji Electric Philippines, NEC Tokin Electronics, NEC Toppan Circuit Solutions and Austriamicrosystems Phils.
Automobile manufacturer that have plants located in Calamba City are Asian Transmission Corporation and Suzuki Philippines Inc.
Avon, the leading global beauty company has a manufacturing plant (Avon Products Manufacturing) located at Calamba Premiere International Park.
Information technology
Calamba City is also considered as one of the "Next Wave Cities" for outsourcing firms and call centers, among them are Accenture and SPi Technologies.
Commerce and trade
Aside from the Crossing area in Barangay Uno, Barangays Real and Parian are also bustling with business structures, including SM City Calamba, Walter Mart Calamba and Liana's Discount Center Calamba.
Notable shopping centers and travel agencies in Calamba also include Southern Sky Travel Tours (Calamba Headquarters), Walter Mart Makiling, SM Savemore Parian, Puregold Halang, Puregold Calamba Crossing, Checkpoint Mall, and iMall Canlubang among others.
Tourism
.jpg)



Calamba is the location of José Rizal's birthplace, Rizal Shrine, found in the poblacion (city proper), and St. John the Baptish Parish Church, the location of Rizal's baptism. A park built to commemorate José Rizal, Rizal Park (or the Plaza) hosts a 22 feet (6.7 m) tall statue of Rizal, with the number symbolizing the 22 languages and dialects used by Rizal. The statue sits on top of a 15-step podium, symbolizing one decade since Rizal was born. The monument was once cited as the tallest Jose Rizal Monument in the World,[27] until a monument of Rizal was built in Santa Cruz, Laguna for the Palarong Pambansa 2014. The monument was inaugurated by President Benigno Aquino III in preparation for the National Hero's sesquicentennial birth anniversary on June 19, 2011.
Other tourist attractions include the Calamba Claypot (Banga or Calambanga), a large pot that is the namesake of the city, Republ1c Wakepark, a water sports park in the Nuvali mixed-use residential development in Canlubang, and Calamba Island, an island
For its proximity to Mount Makiling, Calamba also hosts hot spring resorts, concentrated Pansol, Bucal and Bagong Kalsada.
Festivals
The Buhayani Festival, the official festival of the City of Calamba was the brainchild of Mayor Justin Marc SB. Chipeco during his first year as Mayor in 2013. Mayor Timmy wanted the city to have a festival that will best characterize its culture, progress and tourism potential. He wanted to capitalize on the city’s historical heritage as the birthplace of Philippine National Hero, Dr. Jose P. Rizal. Thus, the Buhayani Festival was born.
The term “BUHAYANI” was coined by joining two Filipino words, “buhay” meaning life or the state of being alive and lively and “bayani” or hero. The festival’s tagline “Buhay ng Bayani, Buháy na Bayani” literally translates to “Life of the Hero”pertaining to the life of our famous kababayan, Dr. Jose Rizal and “Living Hero”which refers to the common man who has the capacity and potential to become everyday heroes in their own small ways.
“We want everyone who revere our kababayan, Dr. Jose Rizal to come to Calamba and join us in honouring him on his birthday and in celebrating the modern Rizal in us. We want to make our National Hero modern and relevant in today’s challenging times and we want to celebrate the spirit of heroism that lives in each Filipino, not just in us Calambeños,” Mayor Chipeco was quoted saying.
Different activities were lined up for this year’s Buhayani Festival—Kuwentong Bayani for selected Grade 5 students, Talinong Rizal Quiz Bee, Buhayani Football Cup, Independence Day Job Fair, SayawIndak Street Dancing Competition, Marching Band Competition, Baile de Gala, Hawig Rizal (Rizal Look-a-Like), Buhayani Eye Care Mission and a whole lot more. Highlighting this year’s celebration is the Morning Program wherein Philippine National Police Chief, Director General Ronald “Bato” Dela Rosa is the Guest of Honor and Speaker. A special wreath-laying ceremony shall also commence at the Museo ni Rizal sa Calamba after a simultaneous floral offering at five different Rizal monuments around the city.
“Jose Rizal is not just the pride of Calamba, he is the pride of the entire country as he was the Greatest Malay to have lived. His works, teachings and ideals have inspired and will continue to inspire us as we strive to live up to his ideals of nationalism and love of country. In the Buhayani Festival, we celebrate an ideal and an advocacy that through this festival, we can rekindle the fire of patriotism and heroism in the hearts of every Filipino. Come to Calamba--retrace history’s footsteps, rediscover the richness and uniqueness of our heritage, fire up our Filipino pride and be inspired to share and spread what you have experienced and be part of the force that will bring about a renewed love of country in every Filipino,” Mayor Chipeco challenged.
Infrastructure
Transportation
Tricycles, buses, and jeepneys, are popular modes of transportation in Calamba. There is also a PNR station in the city, namely as the Calamba railway station that will serve as a terminal for commuters going to Manila.
Road Systems
The only expressway on Calamba is the South Luzon Expressway(SLEX), which passes through the city with 3 exits. SLEX is part of AH26 up to Calamba Exit.
Main national highways includes the Maharlika Highway (Daang Maharlika) or National Highway, which passes through the city and curves toward Santo Tomas in Batangas, Calamba-Sta. Cruz-Famy Road (also called "National Highway") links Calamba with Los Baños and Santa Cruz.
Other arterial roads includes Chipeco Avenue and Extension, which passes near the city hall, Calamba-Tagaytay Road, a road leading to Tagaytay via the Tagaytay Highlands, and Mayapa–Canlubang Cadre Road, a spur of Maharlika Highway serving Canlubang and Canlubang/Mayapa Exit (Exit 47)[28]
Proposed expressways includes Calamba-Los Baños Expressway, which spurs from SLEX Extension (Calamba Exit), traverses along Laguna de Bay and ends on a national highway at Bay, and Laguna Lakeshore Expressway Dike, an expressway and dike that will run on the coast of Laguna de Bay. The projects will cost an estimated ₱5.9 billion ($131.11 million) and ₱18.59 billion ($413 million).[29]
Health care

There are 9 private and 1 government-run hospitals in Calamba. Some of the health centers in the city are the Calamba Medical Center, Calamba Doctors' Hospital, Pamana Golden Care Hospital, St. John the Baptist Hospital, San Jose Hospital and Trauma Center, St. Marks Hospital Medical Center, Holy Angel General Hospital, CH Garcia Medical and Diagnostic Center, Dr. Jose Rizal Memorial Hospital, and Jose Yulo Foundation Canlubang Industrial Hospital...
Utilities and communication
Communication concerns are managed by different agencies found in the city: postal affairs rests on the Philippine Postal Corp. with three operating offices located in Barangays. Canlubang, Mayapa and the main office located at the back of City Hall. Telecommunications as well as internet connections are under the three major telecom companies such as PLDT, Globe Telecom, Smart Communications and Sun Cellular for Digitel. Aside from these, print and radio services are also present, with Calambalita DZLN-AM and DZJV– a local radio station catering to the whole Calabarzon area.
A major part of the city is currently served by MERALCO, with two substations of the company located in Brgys Mayapa and Brgy 1 facilitate the flow of power throughout the entire city. All the 54 barangays are equipped with electricity, with only a few barangays such as part of Canlubang, Pansol, Bucal and Lecheria under NAPOCOR.
A big part of the City is served by the Calamba Water District, providing water to 23,655 households, 1,238 commercial establishments and 53 public buildings. Most of the city's water supply comes from the faucet community water system.
Education
Calamba has a literacy rate of 98.9%. As of 2007, there are 120 elementary schools, 51 of which are public and 69 private. There are 50 secondary schools, 16 public and 34 private. Post-secondary education include 17 universities and colleges, and 9 technical and vocational schools.[7]
The city has four NCAA affiliate schools/branches, namely as the Colegio de San Juan de Letran, Lyceum of the Philippines University, San Sebastian College – Recoletos and University of Perpetual Help System DALTA.
Some private schools that are also located in Calamba are City College of Calamba, Don Bosco College, Canlubang, Calamba Institute, Laguna College of Business and Arts, Saint Benilde International School, Asian Computer College, Inc., Active Community Contributor Calamba Churchitute, Inc. and Philippine Women's University Saint John Colleges. In Nuvali Calamba, there are two other schools located which are the Miriam College and Xavier School. In the near future, Everest Academy, a renowned Catholic and international school will also open its second campus in Nuvali.
The City College of Calamba is the only public college in the city.
Media
AM stations
- DZ__ 585 kHz (Laguna College of Business and Arts) (TBA)
- DZJV 1458 kHz (ZOE Broadcasting Network)
Gallery
 SLEX Calamba Mayapa Exit
SLEX Calamba Mayapa Exit Checkpoint, captured at Paseo De Calamba in Paciano Rizal
Checkpoint, captured at Paseo De Calamba in Paciano Rizal- Rizal Shrine Calamba
 Jose Rizal monument in Jose Rizal Plaza
Jose Rizal monument in Jose Rizal Plaza- Stop Light in Halang
 Republ1c Wakepark Canlubang
Republ1c Wakepark Canlubang Calamba Claypot or Kalan-Banga
Calamba Claypot or Kalan-Banga Laguna de Bay in Bucal
Laguna de Bay in Bucal- Maharlika Highway, Turbina
- City College of Calamba
- Pansol
 I-Mall in Canlubang
I-Mall in Canlubang- Barangay Makiling
- St. John the Baptist Parish Church
Notable people
- José Rizal, Philippine national hero, nationalist and reformist
- Paciano Rizal, military general and revolutionary, and the older brother of José Rizal
- Vicente Lim, World War II Brigadier General
- Palito, Filipino comedian and actor
- Ronnie Alcano, professional pool player
- Thea Tolentino, actress, Protégé: The Battle For The Big Artista Break winner
- Jeric Gonzales, actor, Protégé: The Battle For The Big Artista Break winner
- Sam Mangubat, Filipino singer, 2nd placer of Tawag ng Tanghalan
Sister cities
Locals
International


See also

References
- ↑ "City". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 30 May 2013.
- ↑ "Province: Laguna". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Census of Population (2015). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- ↑ "laguna.com.ph - This website is for sale! - bitcoin,ethereum Resources and Information". laguna.com.ph.
- ↑ "Overall Rankings (2014) - Cities and Municipalities Competitiveness Index". Archived from the original on August 22, 2014. Retrieved August 26, 2014.
- ↑ "2014 Cities and Municipalities Competitiveness Index" (PDF). National Econonmic Research and Business Assistance Center - CALABARZON.
- 1 2 3 4 "City profile". About the City. Official Website of the City of Calamba. Archived from the original on June 3, 2014. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ↑ "Calamba City's Giant Claypot". Going Around Asia. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
- 1 2 "Political History". City Government. Official Website of the City of Calamba. Archived from the original on October 23, 2012. Retrieved November 12, 2012.
- ↑ Jintaro Ishida, The Remains of War, 2001, p.238, citing the Barangay Real Memorial.
- 1 2 Cityhood of Calamba http://www.calambacity.gov.ph/About-the-City/Cityhood-of-Calamba/ Archived December 8, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Executive Order No. 246, s. 2003". Official Gazette of the Republic of the Philippines. Retrieved January 15, 2013.
- ↑ "City Profile". Archived from the original on June 3, 2014.
- ↑ "Barangay Names". Archived from the original on May 13, 2014.
- ↑ "Climate: Calamba - Climate graph, Temperature graph, Climate table". Climate-data.org. Retrieved August 15, 2018.
- ↑ Placido, Darel (25 September 2018). "Aklan split into two legislative districts, Calamba City becomes lone". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved 25 September 2018.
- ↑ The Official Seal http://www.calambacity.gov.ph/About-the-City/The-Official-Seal/ Archived December 7, 2013, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- ↑ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- ↑ "Province of Laguna". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- ↑ "Commission on Audit - Cities". www.coa.gov.ph. Retrieved May 19, 2016.
- ↑ "List of 'next wave' cities for outsourcing firms released".
- ↑ COA AAR
- ↑ Local Government Unit (LGUs) Financial Data
- ↑ http://www.pdic.gov.ph/files/BSDStats/DDD_PBS_ProvinceMunicipality.htm
- ↑ "Operating Economic Zones". Archived from the original on October 25, 2014.
- ↑ News, ABS-CBN. "Rizal's birthplace now home to his tallest monument".
- ↑ "DPWH Road Data | Laguna 2nd". Department of Public Works and Highways Website. DPWH. Archived from the original on January 10, 2014. Retrieved April 30, 2013.
- ↑ Rogelio L. Singson (November 18, 2010). "PPP Road Projects" (PDF). Public Private Partnership Center. Retrieved March 1, 2013.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Calamba. |
- The Official Website of Calamba City
- Calamba City Business Directory Website
- Official Website of the Tourism Department of Calamba City
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Local Governance Performance Management System
- Visit Laguna - Tourist Spot in Laguna, Things to do in Laguna