Yūbari, Hokkaido
| Yūbari 夕張市 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City | |||
|
From top left: Yubari melon, Mount Yubari, Yubari River, Coal Mine Museum in Yubari, Yubari Melon Castle, Yubari Film Festival site | |||
| |||
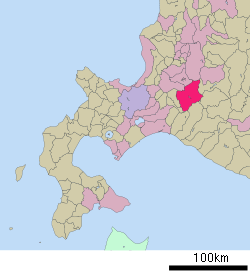 Location of Yūbari in Hokkaido (Sorachi Subprefecture) | |||
 Yūbari Location in Japan | |||
| Coordinates: 43°3′N 141°58′E / 43.050°N 141.967°ECoordinates: 43°3′N 141°58′E / 43.050°N 141.967°E | |||
| Country | Japan | ||
| Region | Hokkaido | ||
| Prefecture | Hokkaido (Sorachi Subprefecture) | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Naomichi Suzuki (since May 2011) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 763.20 km2 (294.67 sq mi) | ||
| Population (April 30, 2017) | |||
| • Total | 8,612 | ||
| • Density | 11/km2 (29/sq mi) | ||
| Symbols | |||
| • Tree | Sakura | ||
| • Flower | Azalea | ||
| Time zone | UTC+9 (JST) | ||
| City hall address |
4-2 Honchō, Yūbari-shi, Hokkaido 068-0492 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Yūbari (夕張市 Yūbari-shi) is a city located in Sorachi Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan.
As of April 30, 2017, the city has an estimated population of 8,612, with 5,030 households.[1] The total area is 763.20 km². Hemmed in by mountains Yūbari stretches for 25 kilometers along a mountain valley.
The city is famous for the Yubari Melon and the Yubari International Fantastic Film Festival, which skipped a show in 2007 due to the city's financial crisis.[2]
History
The city was founded on April 1, 1943 as a coal mining town. When the mines were operating Yūbari had as many as 120,000 people. With the closing of the mines in the 1980s, an attempt was made to convert the economic base to tourism. Subsidies were obtained from the central government and huge debts incurred for the building of tourist attractions, but few visitors came. In 2007 the city was in the news due to bankruptcy and the refusal of the national government to bail it out. City services had been severely cut and its white elephant amusement park and museums were up for sale.[3] The amusement park has begun to be demolished as of June 2008.[4]
Roughly half of Yūbari's government officials resigned in March 2007 as part of an attempt to streamline the local fiscal situation. The majority of officials stepping down who responded to a survey conducted by Mainichi Shimbun say they "feel no sense of responsibility" for the city's financial problems.[5]
Geography
- Mountain : Mount Yūbari
- River : Yūbari River
Education
High School
- Hokkaido Yubari High School
- Hokkaido Yubari Special High School
Junior High School
- Yubari Junior High School
Elementary School
- Yubari Elementary High School
Transportation
Rail
The central train station is Yūbari Station on the Sekishō Line, operated by JR Hokkaido.
- Sekishō Line (Main Line) : Takinoue - Tomisato - Shin-Yūbari - (Kaede Passing Loop)
- Sekishō Line (Yūbari Branch Line) : Shin-Yūbari - Numanosawa - Minami-Shimizusawa - Shimizusawa - Shikanotani - Yūbari
Road
- Dōtō Expressway : Yūbari IC
Bus
- Hokkaido Chuo Bus
- Yubari Tetsudo
Sister city
See also
References
- ↑ "Official website of Yūbari City" (in Japanese). Japan: Yūbari City. Retrieved 14 May 2017.
- ↑ Petersson, Torbjörn (2009-01-31). "Yubari - övergiven stad". Dagens Nyheter (in Swedish). Retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ↑ "Tokyo Cuts Aid, and Hinterland Withers in Japan", article by Norimitsu Onish in the New York Times, January 27, 2007
- ↑ asahi.com: In Yubari, even less amusement now, June 6, 2008 Archived June 7, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Most high-ranking officials of bankrupt municipal gov't feel no sense of responsibility, Mainichi Daily News, March 7, 2007.
Further reading
- Kazama Kensuke. Kazama Kensuke shashinshū: Yūbari (風間健介写真集:夕張) / Kensuke Kazama Photographic Collection: Yubari. Sapporo: Jyuryousya, 2005. ISBN 4-902269-14-7. A collection of Kensuke Kazama's black-and-white photographs of Yūbari and its mines after their closure. All text and captions in both Japanese and English.
- Toda Reiko. Yūbari tankōbushi (夕張炭坑節, Song of the Yūbari mines). Tokyo: Shobunsha, 1985. ISBN 4-7949-7009-9. Black-and-white photo documentary of the last five hundred days of mining in Yūbari, a period during which a disaster occurred.(in Japanese)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yubari, Hokkaido. |
- Official Website (in Japanese)

