Luzerne County, Pennsylvania
| Luzerne County, Pennsylvania | ||
|---|---|---|
| County | ||
| ||
 Topographical map of Luzerne County | ||
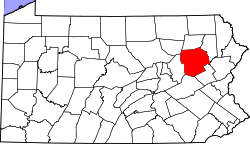 Location in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania | ||
| Country |
| |
| State |
| |
| Region | Northeastern Pennsylvania | |
| Metro area | Wyoming Valley | |
| Formed | September 25, 1786 | |
| Named for | Chevalier de la Luzerne | |
| County seat | Wilkes-Barre | |
| Largest city | Wilkes-Barre | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Council–manager | |
| • Council | ||
| • Council Chair | Tim McGinley (D) | |
| • Manager | C. David Pedri | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 906 sq mi (2,350 km2) | |
| • Land | 890 sq mi (2,300 km2) | |
| • Water | 16 sq mi (40 km2) | |
| Highest elevation | 2,460 ft (750 m) | |
| Lowest elevation | 512 ft (156 m) | |
| Population (2010) | ||
| • Total | 320,918 | |
| • Estimate (2017) | 317,343 | |
| • Density | 350/sq mi (140/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| Area code(s) | 570/272 | |
| Website |
www | |
Luzerne County is a county in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 906 square miles (2,350 km2), of which 890 square miles (2,300 km2) is land and 16 square miles (41 km2) is water. It is Northeastern Pennsylvania's second-largest county by total area. As of the 2010 census, the population was 320,918, making it the most populous county in the northeastern part of the state. The county seat and largest city is Wilkes-Barre.[1] Other populous communities include Hazleton, Kingston, Nanticoke, and Pittston. Luzerne County is included in the Scranton–Wilkes-Barre–Hazleton Metropolitan Statistical Area, which has a total population of 555,426 (as of 2017).
On September 25, 1786, Luzerne County was formed from part of Northumberland County. It was named after Chevalier de la Luzerne, a French soldier and diplomat during the 18th century. When it was founded, Luzerne County occupied a large portion of Northeastern Pennsylvania. From 1810 to 1878, it was divided into several smaller counties. The counties of Bradford, Lackawanna, Susquehanna, and Wyoming were all formed from parts of Luzerne County.[2][3]
The county gained prominence in the 19th and 20th centuries as an active anthracite coal mining region, drawing a large portion of its labor force from European immigrants. At its peak (in 1930), the county's population was 445,109. By the early 21st century, many factories and coal mines were closed. Like most counties in the Rust Belt, Luzerne witnessed population loss and urban decay.
History
The Luzerne County Historical Society maintains the storehouse for the collective memory of Luzerne County and its environs. It records and interprets the history, traditions, events, people, and cultures that have directed and molded life within the region.[4]
18th century
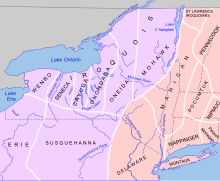
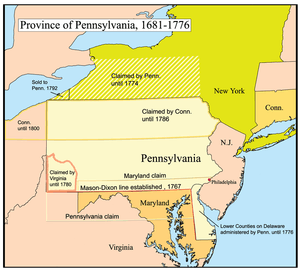

By the 1700s, the Wyoming Valley was inhabited by several Native American tribes (including the Susquehannock and the Delaware). In the mid-18th century, Connecticut settlers ventured into the valley. These were the first recorded Europeans in the region. Some came to conduct missionary work with the Native Americans, while others came to farm the fertile land near the Susquehanna River. Ultimately, the violence of the French and Indian War (the North American front of the Seven Years' War) drove these Connecticut settlers away.[5]
The British colonies of Pennsylvania and Connecticut claimed the Wyoming Valley as their own. King Charles II of England had granted the land to the Colony of Connecticut in 1662, and also to William Penn (the founder of Pennsylvania) in 1681. This led to a series of military skirmishes known as the Pennamite-Yankee Wars. By 1769, Yankee settlers from Connecticut returned to the valley and founded the town of Wilkes-Barre. However, they were not alone. Pennsylvanians (Pennamites) were also in the region. The armed bands of Pennsylvanians harassed the Connecticut settlers. While the land dispute continued, a much larger conflict began. The Thirteen Colonies were waging a war of independence against Great Britain (the mother country). Both Pennsylvania and Connecticut were loyal to the cause of American independence.
On June 30, 1778, British (Tory) forces, under the command of Colonel John Butler, arrived in the Wyoming Valley to confront the American settlers. The following day — July 1 — the American militia at Fort Wintermute (Wintermoot) surrendered. Several miles away, Fort Jenkins (a Patriot stockade in present-day West Pittston) also capitulated. It was later burned to the ground.[6]
On July 3, the British spotted the American militia near Forty Fort. Butler wanted to lure the Americans away from their fortifications. He ordered for Fort Wintermute to be set ablaze. The Patriots, believing it signified a British retreat, advanced rapidly. British soldiers, with the assistance of about 700 Native Americans, ambushed the oncoming American militia. In the end, nearly 300 Wyoming Valley settlers were killed in what would be known as the Wyoming Massacre. Today, in the Borough of Wyoming, a monument marks the gravesite of the victims from the battle.[7]
On July 4 — the following morning — the American colonel, Nathan Denison, agreed to surrender Forty Fort along with several other posts. A portion of Fort Pittston (located in present-day Pittston City) was destroyed when it surrendered to the British. Two years later, the Americans stormed the fortification and recaptured it. From then on, it was under Patriot control until the end of the war.[8]
In September 1778, revenge for the Wyoming defeat was taken by American Colonel Thomas Hartley. He and his 200 soldiers burned roughly one dozen Native American villages along the Susquehanna River (in both Pennsylvania and New York).[9]
Two years later, in September 1780, reports of British (Tory) activity in the region caused Captain Daniel Klader and a platoon of 40 to 50 Patriots (from Northampton County) to investigate. Captain Klader's men made it as far north as present-day Conyngham, when they were ambushed by the Seneca nation and the Tories. Eighteen of Klader's men were killed in what is now known as the Sugarloaf Massacre.[10]
The American Revolutionary War ended three years later (in 1783) with the signing of the Treaty of Paris. With the signing of the treaty, Great Britain finally recognized the sovereignty of the United States of America. Even though the War of Independence had concluded, the land dispute between Pennsylvania and Connecticut continued. Connecticut established its own county (by the name of Westmoreland) in the Wyoming Valley. However, Pennsylvania insisted that they owned the land. The Congress of the Confederation was asked to resolve the matter. With the Decree of Trenton, on December 30, 1782, the confederation government officially decided that the region belonged to Pennsylvania; the Wyoming Valley became part of Northumberland County.
Pennsylvania ruled that the Connecticut settlers (Yankees) were not citizens of the Commonwealth. Therefore, they could not vote and were ordered to give up their property claims. In May 1784, armed men from Pennsylvania force-marched the Connecticut settlers away from the valley. By November, the Yankees returned with a greater force. They captured and destroyed Fort Dickinson in Wilkes-Barre. With that victory, a new state (which was separate from both Connecticut and Pennsylvania) was proposed. The new state was to be named Westmoreland. To ensure that they didn't lose the land, the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania worked out a compromise with the Connecticut (Yankee) settlers. The Yankee settlers would become citizens of Pennsylvania and their property claims would be restored (prior to the Decree of Trenton). As part of the compromise, Pennsylvania would establish a new county in Northeastern Pennsylvania. The Yankees agreed to the terms.[11]
On September 25, 1786, the Pennsylvania General Assembly passed a resolution which created Luzerne County. It was formed from a section of Northumberland County and named after Chevalier de la Luzerne, a French soldier and diplomat during the 18th century. Wilkes-Barre became the seat of government for the new territory. This resolution ended the idea of creating a new state. When it was founded, Luzerne County occupied a large portion of Northeastern Pennsylvania. The future counties of Bradford, Lackawanna, Susquehanna, and Wyoming were all part of the original Luzerne County.[2][3]
In the following years, elections were held, the courts were established, a courthouse was constructed, and a government was formed. In 1787, Lord Butler was elected the first sheriff of Luzerne County. A board of commissioners was also assembled to manage the county government. Some of the first county commissioners included Jesse Fell, Alexander Johnson, John Phillips, John Jenkins, and Thomas Wright (from 1794 to 1796).[12] The population of the new county grew rapidly. In 1790, fewer than 2,000 people resided within the Wyoming Valley. By 1800, that number increased to nearly 13,000.[13]
19th century


The county gained prominence in the 19th century as an active anthracite coal mining region. In 1791, German immigrant Philip Ginder stumbled across anthracite (or "hard coal") near Summit Hill. This resulted in the creation of the Lehigh Coal Mine Company. The company had a slow start because of the difficulty in igniting anthracite coal and the inability to transfer it to urban markets. In 1807, Brothers Abijah and John Smith were the first to successfully transport anthracite down the Susquehanna River on an ark. In 1808, Judge Jesse Fell of Wilkes-Barre discovered a solution to ignite anthracite with the usage of an iron grate; it allowed for the coal to light and burn easier. This invention increased the popularity of anthracite as a fuel source. This led to the expansion of the coal industry in Northeastern Pennsylvania. Throughout the 1800s, canals and railroads were constructed to aid in the mining and transportation of coal.[13]
As the mining industry grew, a large region north of the Wyoming Valley — close to the New York border — sought independence from Luzerne County. On February 21, 1810, the counties of Bradford — originally called Ontario — and Susquehanna were created from parts of Luzerne County. The two counties were officially formed in 1812.[14][15] Thirty years later, on April 4, 1842, Wyoming County — the region in and around present-day Tunkhannock — was also formed from a section of Luzerne County.[16]
The County of Luzerne witnessed a population boom as a result of the growing coal mining industry. Carbondale, with a population of nearly 5,000 residents, was incorporated as a city on March 15, 1851.[17] Scranton, with a population of nearly 35,000, was incorporated as a city on April 23, 1866.[18] And Wilkes-Barre, with a population of just over 10,000, was incorporated as a city in 1871.[19] By 1875, anthracite coal from Luzerne County alone represented half the anthracite produced in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania.[13]
Since 1839, the people in and around the cities of Scranton and Carbondale were seeking independence from Luzerne County. Wilkes-Barre was determined to preserve the integrity of the county; it did not want to lose its assets in the region. Decades later, in the 1870s, residents of the proposed territory were allowed to vote for independent status. Voters favored a new county by a proportion of 6 to 1, with Scranton residents providing considerable support. Lackawanna County was finally created from a portion of Luzerne County in 1878.[20]
Even through Luzerne County lost a vital region (the coal mining cities of Scranton and Carbondale), its boroughs and townships continued to grow. Hazleton (in 1891)[21] and Pittston (in 1894) were both incorporated as cities due to their expanding populations. Thousands of European immigrants poured into Luzerne County due to the booming coal industry. The growing population quickly attracted the attention of factory owners in New York City and Philadelphia. Dozens of factories throughout Luzerne County were established to take advantage of the ever-increasing pool of available labor.
With the build-up of industry in the region, tragedies became more frequent in the second half of the 19th century. The first major disaster occurred on September 6, 1869, when a mine fire killed 110 people in Avondale, an unincorporated community in Plymouth Township.[22] Another tragedy occurred on June 28, 1896, when the Newton Coal Company's Twin Shaft Mine in Pittston City caved-in and killed 58 miners.[23][24]
Towards the end of the 19th century, labor unrest and union activity intensified in the region. Miners protested poor working conditions and unfair pay. This revved up tensions throughout the county. One of the most notable and deadly confrontations occurred on September 10, 1897 (near Hazleton). Luzerne County Sheriff James Martin formed a posse and fired on a group of unarmed striking miners in what is now known as the Lattimer Massacre. Roughly nineteen people were killed and dozens more were wounded. Luzerne is infamous for being the last county whose sheriff legally formed a posse to restore order in a time of civil unrest.[25]
 The Wyoming Valley in the 1860s |
.jpg) Wilkes-Barre in 1872 |
.jpg) Hazleton in 1884 |
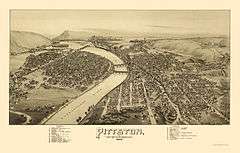 Pittston in 1892 |
20th century



.jpg)
At the beginning of the 20th century, Luzerne County was in the midst of an economic boom. Industry, which included manufacturing and coal mining, drew thousands of immigrants (mostly from Europe) to the region. However, there were several drawbacks to the industrial boom. Labor unrest, mining accidents, and child labor were just a few problems facing the county. Labor disputes led to miners striking in the late 1800s and early 1900s. The Great Strike of 1902 gained national attention when it threatened to shut down the winter fuel supply for major U.S. cities. At that time, residences were typically heated with anthracite (or "hard coal"). The United Mine Workers of America protested for higher wages, shorter workdays, and the recognition of their union. President Theodore Roosevelt became involved and set up a fact-finding commission that suspended the strike. The strike never resumed, as the miners received a ten percent wage increase and reduced workdays (from ten to nine hours). It was the first labor dispute in which the U.S. federal government intervened as a neutral arbitrator.[13]
Also, in the early 1900s, the anthracite coal mining industry — and its extensive use of child labor — was one of the industries targeted by the National Child Labor Committee and its hired photographer, Lewis Hine. Many of Hine's subjects were photographed in the mines and coal fields in and around Pittston and Wilkes-Barre. The impact of the Hine photographs led to the enactment of child labor laws across the country.[26]
Despite the better working conditions, industrial accidents were still commonplace. On December 6, 1915, an underground mine fire started in the Red Ash Coal Mine near the communities of Laurel Run and Georgetown. Hundreds of residents living near the mine fire were later relocated. The fire continued to burn well into the 21st century.[27] On June 5, 1919, another major mining accident occurred nearby. An explosion killed 92 miners at the Baltimore Colliery in Wilkes-Barre.[28]
Regardless of the industrial setbacks, the region continued to grow economically. In 1906, construction began on a new county courthouse in Wilkes-Barre.[29] Twenty years later (in 1926), Nanticoke, with a population of just over 22,000, was incorporated as a city.[30] It was the last city established in the county. By 1930, the county's population peaked at 445,109. It was obvious that industry was the driving force behind the expanding population. From the 1930s to the 1980s, Pittston City emerged as a national center for clothing manufacturing. Thousands of workers, mainly women, labored in many factories throughout the Greater Pittston area. Most were members of the International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union (ILGWU). It advocated for higher wages, improvements in workplace health and safety, and employee rights. The ILGWU was active in civic and political life throughout Pennsylvania.[31]
Railroad accidents were common throughout the United States in the 1800s and 1900s. In 1934, the right arm of Hughestown resident Harry Tompkins was crushed by an Erie Railroad train. This resulted in the U.S. Supreme Court case Erie Railroad Co. v. Tompkins, which laid the foundation for a large part of modern American civil procedure.[32]
As the United States entered the age of mass air transportation, Scranton and Wilkes-Barre (the largest cities in Northeast Pennsylvania) recognized the need for a large-scale airport. Despite the Great Depression and hard times affecting the local coal mining industry, a windfall multimillion-dollar opportunity to plan and build a regional airport was presented to the counties of Luzerne and Lackawanna through the federal government's Public Works Administration. It became apparent that a modern airport would be needed for the economic survival of the region. The site in and around Pittston Township was first surveyed in 1939 by the county commissioners of both counties.
In 1941, John B. McDade, president of the Heidelberg Coal Company and father of Congressman Joseph M. McDade, donated 122 acres on which part of the airport now sits. Most of the land was previously owned by various coal companies. By 1945, the two counties entered into a legal agreement to co-sponsor and operate the airport. Between 1945 and 1947, construction of the Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport took place in and around Pittston Township. Today, the airport is known as the "Gateway to Northeastern Pennsylvania and the Pocono Mountains." It is the fifth busiest airport in Pennsylvania.
By the mid-20th century, anthracite production was declining at a steady rate. Consumers were gradually switching from coal to other forms of energy (e.g., oil, gas, and electricity). The Knox Mine Disaster was the final blow to the industry. On January 22, 1959, the Susquehanna River broke through the River Slope Mine in Port Griffith, Jenkins Township; it claimed the lives of twelve people. In the following months, two of the area's largest coal companies announced a full withdrawal from the anthracite business. Thousands of jobs were lost and the mining industry never recovered in Luzerne County.[33]
The Wyoming Valley witnessed historical flooding from the Susquehanna River in the past. In June 1972, Hurricane Agnes devastated much of the Eastern Seaboard (including Pennsylvania). The Susquehanna River rose to 40.9 feet and breached the levees of several communities in the Wyoming Valley. In Wilkes-Barre, hundreds were trapped in their homes; nearly nine feet of water inundated Public Square. At the historic cemetery in Forty Fort, 2,000 caskets were washed away, leaving body parts on porches, roofs, and in basements. In Luzerne County alone, 25,000 homes and businesses were either damaged or destroyed. Losses in the county totaled $1 billion.[34]
Luzerne County's economy was hit hard with the collapse of the mining industry and the devastating Agnes flood. To make matters worse, factories throughout the county were shutting down. They could not compete with lower labor costs elsewhere. By the end of the 20th century, Luzerne County was in the midst of a recession.
Following the Agnes flood (from the 1980s to 2000), two notable tragedies occurred in Luzerne County. The first took place on September 25, 1982, when George Banks killed thirteen people in a shooting rampage in Wilkes-Barre and Jenkins Township.[35] The second incident took place on May 21, 2000, when a plane crash in Bear Creek Township (near the intersection of Bear Creek Boulevard — PA Route 115 — and the Northeast Extension of the Pennsylvania Turnpike) killed the pilot as well as all nineteen passengers.[36]
21st century


Many factories and coal mines were closed by the early 21st century. Like most regions in the Rust Belt, Luzerne County witnessed population loss and urban decay. However, in recent years, the economy has grown moderately; warehousing has replaced manufacturing as the main industry.[37]
In the late 2000s, scandal, corruption, cronyism, patronage hiring, wasteful spending, higher property taxes, and out-of-control debt plagued the county.[38] The "kids for cash" scandal unfolded in 2008 over judicial kickbacks at the Luzerne County Court of Common Pleas in Wilkes-Barre. Two judges, President Judge Mark Ciavarella and Senior Judge Michael Conahan, were convicted of accepting money from Robert Mericle, builder of two private, for-profit youth centers for the detention of juveniles, in return for contracting with the facilities and imposing harsh adjudications on juveniles brought before their courts to increase the number of residents in the centers.[39]
In the following years, additional county officials faced criminal charges (e.g., a clerk of courts, a deputy chief clerk, a director of human resources). County Commissioner Greg Skrepenak resigned in 2009; he was ultimately sentenced to prison for accepting money from a developer who received government-backed financing. In May 2009, voters approved the creation of a government study commission. The commission proposed and wrote a home rule charter for Luzerne County. On November 2, 2010, the voters of Luzerne County held a referendum on the question of home rule. A total of 51,413 (55.25%) voted in favor of home rule, while another 41,639 (44.75%) voted against the move. This vote was the direct result of the corruption, wasteful spending, higher property taxes, and out-of-control debt facing the county.[40]
This referendum "starts a new chapter in Luzerne County history," remarked James Haggerty (the chairman of the commission that wrote and proposed the charter). The home rule charter would eliminate the positions of the three county commissioners; they would be replaced by an eleven-member county council (who will appoint and work alongside a county manager). The first election for the new government was scheduled for 2011 — which ended up becoming an eventful year for Luzerne County.
From March to June of that year, the Borough of Duryea received national attention for its role in the landmark Supreme Court case Borough of Duryea v. Guarnieri, in which the court stated that "a government employer's allegedly retaliatory actions against an employee do not give rise to liability under the Petition Clause unless the employee's petition relates to a matter of public concern."[41]
The second major event occurred in September 2011, when Luzerne County witnessed historical flooding from Tropical Storm Lee. The Susquehanna River reached a record high of 42.6 feet (13 meters) in Wilkes-Barre. The river topped the 40.9-foot (12.5 meters) level in flooding caused by Hurricane Agnes in 1972. However, unlike 1972, the levee system in Wilkes-Barre and several other communities held. Those municipalities without a levee system witnessed severe flooding.[42][43][44]
The third and final major event of 2011 occurred on November 8 — the first general election for the Luzerne County Council took place. In the end, six Democrats, four Republicans, and one independent politician were elected.
The home rule charter took effect on January 2, 2012. The Luzerne County Board of Commissioners was abolished and replaced with the new form of government (council–manager government). The last three commissioners were Chairwoman Maryanne Petrilla, Stephen A. Urban, and Thomas Cooney. The first eleven council members were sworn in that same day. According to the charter, the council chair is "recognized as head of the county government for ceremonial purposes."[45] The first council chair was Jim Bobeck.[46] During the first council meeting, Tom Pribula was appointed interim county manager.[47] Several weeks later, the council officially appointed the first permanent manager (Robert Lawton).[48]
Geography


According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 906 square miles (2,350 km2), of which 890 square miles (2,300 km2) is land and 16 square miles (41 km2), or 1.8%, is water.[49] The highest point in the county is Cherry Ridge in Fairmount Township. The ridge is 2,460 feet (750 m) above sea level.[50] The lowest point, of about 512 feet (156 m), can be found near Shickshinny.
Luzerne County consists of 76 independently governing municipalities (which includes 4 cities, 36 boroughs, and 36 townships). Wilkes-Barre is the largest city; it has a total area of 7.2 square miles (19 km2). Pittston, with a total area of 1.7 square miles (4.4 km2), is the smallest city. Harveys Lake is the largest borough; it has a total area of 6.2 square miles (16 km2). Jeddo, with a total area of 0.3 square miles (0.78 km2), is the smallest borough. Bear Creek is the largest township; it has a total area of 67.8 square miles (176 km2). Wilkes-Barre Township, with a total area of 2.9 square miles (7.5 km2), is the smallest.
The Wyoming Valley – also referred to as the Anthracite Valley Section of Pennsylvania – runs directly through Luzerne County. It extends from the northeastern border (with Lackawanna County) to the western border (with Columbia County). The valley is flat (at the Susquehanna Basin) and rises from 512 feet (156 m) to 2,000 feet (610 m) in some places. Bear Creek, on the eastern side of the valley, has a mean elevation of about 2,000 feet (610 m), while Shickshinny, on the Susquehanna Basin, is about 512 feet (156 m). The county is crossed by a series of east-to-west mountains (e.g., Buck Mountain, Nescopeck Mountain, Penobscot Knob, and Red Rock Mountain). They are all part of the Appalachian Mountain Range.
The Susquehanna River is the largest river in the county. There are several islands located within the river; for example, Scovell Island (near Pittston), Monocanock Island (near Wyoming), and Richard Island (near Wilkes-Barre). The Susquehanna drains most of the county (including Bowman Creek, Huntington Creek, the Lackawanna River, Nescopeck Creek, Solomon Creek, and many other streams). The Lehigh River, which forms part of Luzerne County's southeastern border, drains the easternmost region. Dozens of lakes and ponds are also scattered throughout the county (e.g., Harveys Lake, Lake Jean, Lake Louise, and Long Pond).
Luzerne County consists of several urban areas. The first is a contiguous quilt-work of former anthracite coal mining communities (including the cities of Pittston, Wilkes-Barre, and Nanticoke). It is located in the northeastern and central part of the county (in the Wyoming Valley). The second is Hazleton and it is located in the southern portion of the county. Other smaller urban areas – such as the Back Mountain and Mountain Top – are scattered throughout the region. Thick forests and small farming communities are located just outside the urban centers.
State parks and forests
- There are four state parks in Luzerne County:
- Frances Slocum State Park (northern Luzerne County)
- Lehigh Gorge State Park (eastern Luzerne County)
- Nescopeck State Park (southern Luzerne County)
- Ricketts Glen State Park (western Luzerne County)
- There is only one state forest in Luzerne County:
- Pinchot State Forest, which includes Moon Lake Park and Seven Tubs Recreation Area
- Other recreational areas:
Adjacent counties
- Carbon County (southeast)
- Columbia County (west)
- Lackawanna County (northeast)
- Monroe County (east)
- Schuylkill County (south)
- Sullivan County (northwest)
- Wyoming County (north)
_(8213883793).jpg) Adams Falls, Ricketts Glen State Park |
.jpg) Grand View Trail, Ricketts Glen State Park |
.jpg) Hayfields, Ricketts Glen State Park |
 Summit of Mount Yeager, Nescopeck State Park |
Climate

Luzerne County has a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dfa/Dfb) with four distinct seasons. Winters are cold with a January average of 25.8 °F (−3.4 °C).[52] The surrounding mountains have an influence on the climate (which includes both precipitation and temperature). This results in a wide array of weather conditions throughout the county.[53] On average, temperatures below 0 °F (−17.8 °C) are infrequent, occurring 3 days per year, and there are 36 days where the maximum temperature remains below 32 °F (0.0 °C).[53] In the Wilkes-Barre area, the average annual snowfall is 46.2 inches (117 cm) during the winter (in which severe snowstorms are rare).[53] However, when snowstorms do occur, they can disrupt normal routines for several days.[53] Summers are warm with a July average of 71.4 °F (21.9 °C).[52] In an average summer, temperatures exceeding 90 °F (32.2 °C) occur on 9 days and can occasionally exceed 100 °F (37.8 °C).[54] Spring and fall are unpredictable with temperatures ranging from cold to warm (although they are usually mild). On average, Wilkes-Barre receives 38.2 inches (970 mm) of precipitation each year, which is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year (though the summer months receive more precipitation).[54] Extreme temperatures range from −21 °F (−29.4 °C) on January 21, 1994, to 103 °F (39.4 °C) on July 9, 1936.[54] Wilkes-Barre averages 2,303 hours of sunshine per year, ranging from a low of 96 hours in December (or 33% of possible sunshine) to 286 hours in July (or 62% of possible sunshine).[55]
| Climate data for Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Int'l Airport, Pennsylvania (1981–2010 normals,[lower-alpha 1] extremes 1901–present[lower-alpha 2]) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 69 (21) |
76 (24) |
85 (29) |
93 (34) |
93 (34) |
99 (37) |
103 (39) |
102 (39) |
100 (38) |
91 (33) |
81 (27) |
71 (22) |
103 (39) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 55.4 (13) |
56.4 (13.6) |
69.6 (20.9) |
81.3 (27.4) |
86.6 (30.3) |
89.8 (32.1) |
91.8 (33.2) |
90.0 (32.2) |
85.7 (29.8) |
77.3 (25.2) |
68.7 (20.4) |
57.5 (14.2) |
93.4 (34.1) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 33.2 (0.7) |
36.8 (2.7) |
46.2 (7.9) |
59.1 (15.1) |
69.7 (20.9) |
77.7 (25.4) |
81.9 (27.7) |
79.9 (26.6) |
72.3 (22.4) |
60.7 (15.9) |
49.4 (9.7) |
37.5 (3.1) |
58.8 (14.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 18.5 (−7.5) |
20.7 (−6.3) |
27.6 (−2.4) |
38.2 (3.4) |
47.6 (8.7) |
56.5 (13.6) |
60.9 (16.1) |
59.5 (15.3) |
52.1 (11.2) |
41.1 (5.1) |
33.3 (0.7) |
23.8 (−4.6) |
40.1 (4.5) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −0.8 (−18.2) |
3.2 (−16) |
9.1 (−12.7) |
24.0 (−4.4) |
34.4 (1.3) |
43.1 (6.2) |
49.4 (9.7) |
47.1 (8.4) |
37.5 (3.1) |
28.3 (−2.1) |
18.9 (−7.3) |
5.9 (−14.5) |
−3.1 (−19.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −21 (−29) |
−19 (−28) |
−4 (−20) |
8 (−13) |
27 (−3) |
34 (1) |
43 (6) |
38 (3) |
29 (−2) |
19 (−7) |
6 (−14) |
−13 (−25) |
−21 (−29) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.37 (60.2) |
2.03 (51.6) |
2.55 (64.8) |
3.33 (84.6) |
3.52 (89.4) |
4.03 (102.4) |
3.79 (96.3) |
3.41 (86.6) |
4.07 (103.4) |
3.34 (84.8) |
3.14 (79.8) |
2.68 (68.1) |
38.26 (971.8) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 14.2 (36.1) |
9.3 (23.6) |
9.0 (22.9) |
3.3 (8.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0.1 (0.3) |
2.9 (7.4) |
7.4 (18.8) |
46.2 (117.3) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 12.0 | 11.0 | 11.8 | 12.3 | 13.2 | 12.8 | 11.2 | 11.3 | 10.2 | 10.7 | 11.2 | 11.5 | 139.2 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 9.3 | 7.7 | 5.0 | 1.7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 2.1 | 7.1 | 33.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70.1 | 67.5 | 63.3 | 60.4 | 64.6 | 70.5 | 71.1 | 73.8 | 75.2 | 71.6 | 71.8 | 72.5 | 69.4 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 130.3 | 143.7 | 185.7 | 210.5 | 246.9 | 269.7 | 285.7 | 257.2 | 200.2 | 173.3 | 104.3 | 95.9 | 2,303.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 44 | 48 | 50 | 53 | 55 | 60 | 62 | 60 | 54 | 50 | 35 | 33 | 52 |
| Source: NOAA (relative humidity 1964–1990, sun 1961–1990)[54][52][55] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 4,892 | — | |
| 1800 | 12,839 | 162.4% | |
| 1810 | 18,109 | 41.0% | |
| 1820 | 20,027 | 10.6% | |
| 1830 | 27,379 | 36.7% | |
| 1840 | 44,006 | 60.7% | |
| 1850 | 56,072 | 27.4% | |
| 1860 | 90,244 | 60.9% | |
| 1870 | 160,915 | 78.3% | |
| 1880 | 133,065 | −17.3% | |
| 1890 | 201,203 | 51.2% | |
| 1900 | 257,121 | 27.8% | |
| 1910 | 343,186 | 33.5% | |
| 1920 | 390,991 | 13.9% | |
| 1930 | 445,109 | 13.8% | |
| 1940 | 441,518 | −0.8% | |
| 1950 | 392,241 | −11.2% | |
| 1960 | 346,972 | −11.5% | |
| 1970 | 342,301 | −1.3% | |
| 1980 | 343,079 | 0.2% | |
| 1990 | 328,149 | −4.4% | |
| 2000 | 319,255 | −2.7% | |
| 2010 | 320,918 | 0.5% | |
| Est. 2017 | 317,343 | [57] | −1.1% |
| Sources:[58][59][60][61] | |||
As of the 2010 census, the county was 90.7% White, 3.4% Black or African American, 0.2% Native American, 1.0% Asian, 3.3% other race, and 1.5% were of two or more races. 6.7% of the population were of Hispanic or Latino ancestry.[62]
According to the census of 2000, there were 319,250 people, 130,687 households, and 84,293 families residing in the county. The population density was 358 people per square mile (138/km2). There were 144,686 housing units at an average density of 162 per square mile (63/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 96.63% White, 1.69% Black or African American, 0.09% Native American, 0.58% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.43% other race, and 0.57% from two or more races. 1.16% of the population were Hispanic or Latino. 22.2% were of Polish ancestry, 15.6% of Italian ancestry, 13.8% of Irish ancestry, 12.1% of German ancestry, and 5.3% of Slovak ancestry. Luzerne County is the only county in the United States with a plurality of citizens reporting Polish as their primary ancestry;[63] the plurality of Pennsylvanians report German or Pennsylvania Dutch.
There were 130,687 households, out of which 48.80% were married couples living together. 11.50% had a female householder with no husband present. 35.50% were non-families. 31.30% of all households were made up of individuals. 16% of those age 65 years and older lived alone. The average household size was 2.34 and the average family size was 2.95.
In the county, the population consisted of 21% under the age of 18, 8.10% from 18 to 24, 27.20% from 25 to 44, 24% from 45 to 64, and 19.70% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 41 years. For every 100 females, there were 93 males. For every 100 females (age 18 and over), there were 89.50 males.
The median household income (in 2015 dollars) was $45,897. 15.1% of the population lives in poverty. 60.4% of those 16 years of age or older are in the civilian labor force. There are more white collar jobs in Luzerne County than blue collar jobs. In total, there are 91,801 white collar jobs and 62,813 blue collar jobs.[64] The mean travel time to work (for those 16 years of age or older) was 22.1 minutes. In terms of education, 88.9% (of those 25 years of age or older) are high school graduates or higher. 21.4% (of those 25 years of age or older) have a bachelor's degree or higher. In terms of healthcare, 10.8% (for those under the age of 65) are living with a disability. As of 2015, 25,317 veterans are living in Luzerne County.[65]
Languages
The two major languages spoken in Luzerne County are English and Spanish. 5.8% of the population speaks Spanish at home. Most of the Spanish speaking population can be found in and around the City of Hazleton.[66]
Religion
59.27% of the people in Luzerne County are religious, meaning they affiliate with a religion. 43.77% are Catholic; 0.28% are LDS (or The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints); 0.51% are Baptist; 0.55% are Episcopalian; 1.05% are Pentecostal; 3.11% are Lutheran; 4.40% are Methodist; 1.95% are Presbyterian; 2.33% are of some other Christian faith; 0.78% are Jewish; 0.00% are of an eastern faith; and 0.51% practice Islam.[67]
Government


Background
Luzerne County voters rejected home rule proposals in the past (once in 1974 and again in 2003). However, from 2008 to 2010, corruption plagued the county government. Three county judges, a county commissioner, a clerk of courts, a deputy chief clerk, and a director of human resources faced criminal charges. These events persuaded the voters of Luzerne County to adopt a new form of government. On Tuesday, November 2, 2010, a home rule charter was adopted by a margin of 51,413 to 41,639.[68][40]
The following year (in 2011), the first election for the new government was held. On Monday, January 2, 2012, the previous government (the board of county commissioners) was abolished and replaced with the new form of government (council–manager government). The first members of the Luzerne County Council were sworn in that same day. The council's highest-ranking officer is the chair; he or she is also the head of county government for ceremonial purposes. The first council chair was Jim Bobeck.[46] The assembly consists of eleven elected members. They appoint and work alongside a full-time manager. The manager runs an executive branch of county government. The first manager was Robert Lawton.[48]
County Council
The Luzerne County Council is the governing body of the county. The council meets at the Luzerne County Courthouse. There are eleven members on the assembly — eight Democrats and three Republicans. Each member is duly elected by the voters of the county. The chair is appointed by his or her fellow council members. The chair is both the highest-ranking officer on the council and the head of county government for ceremonial purposes.[45] He or she sets the agenda for the council and administers the meetings. When the group is not in session, the officer's duties often include acting as its representative to the outside world and its spokesperson. The current chair is Tim McGinley.[69]
| Council member | Time in office | Party | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tim McGinley | 2012–present | Democratic | Chair |
| Eugene Kelleher | 2012–present | Republican | Vice Chair |
| Edd Brominski | 2012–present | Democratic | |
| Harry Haas | 2012–present | Republican | |
| Linda McClosky Houck | 2012–present | Democratic | |
| Chris R. Perry | 2018–present | Republican | |
| Sheila Saidman | 2018–present | Democratic | |
| Robert Schnee | 2016–present | Democratic | |
| Stephen A. Urban | 2012–present | Democratic | |
| Matthew Vough | 2018–present | Democratic | |
| Jane Walsh Waitkus | 2016–present | Democratic |
| Chair | Time in office | Party | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jim Bobeck | 2012 | Democratic | |
| 2 | Tim McGinley | 2012–2014 | Democratic | |
| 3 | Rick Morelli | 2014–2015 | Republican | |
| 4 | Linda McClosky Houck | 2015–2018 | Democratic | First female chair |
| 5 | Tim McGinley | 2018–present | Democratic |
County Manager
The executive branch is headed by the Luzerne County Manager. The manager supervises the county's day-to-day operations. According to the home rule charter, he or she "shall serve at the pleasure of county council."[45] In other words, the council has the power to appoint and remove the manager.[71] Each ordinance, resolution, and policy established by county council should be faithfully executed by the county manager. The manager may make recommendations to the council; however, he or she does not have the authority to vote on or veto any legislation originating from the assembly.[45] The current manager is David Pedri.[72][73]
Other county officials
- Controller: Michelle Bednar
- Director of Human Resources: Angela Gavlick
- District Attorney: Stefanie J. Salavantis
- Chief Public Defender: Steven M. Greenwald
- Sheriff: Brian M. Szumski
 Luzerne County Courthouse |
 Luzerne County Courthouse (October 2009) |
 The Susquehanna River and the Wilkes-Barre skyline; the courthouse is in the background |
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 57.9% 78,688 | 38.6% 52,451 | 3.5% 4,762 |
| 2012 | 46.7% 58,325 | 51.5% 64,307 | 1.8% 2,213 |
| 2008 | 45.0% 61,127 | 53.3% 72,492 | 1.7% 2,349 |
| 2004 | 47.8% 64,953 | 51.2% 69,573 | 1.1% 1,502 |
| 2000 | 43.8% 52,328 | 52.0% 62,199 | 4.2% 5,059 |
| 1996 | 37.3% 43,577 | 51.5% 60,174 | 11.2% 13,066 |
| 1992 | 38.8% 49,285 | 44.5% 56,623 | 16.7% 21,238 |
| 1988 | 50.0% 59,059 | 49.6% 58,553 | 0.4% 480 |
| 1984 | 53.5% 69,169 | 45.2% 58,482 | 1.3% 1,640 |
| 1980 | 50.2% 67,822 | 44.4% 59,976 | 5.4% 7,282 |
| 1976 | 44.2% 60,058 | 54.9% 74,655 | 1.0% 1,296 |
| 1972 | 60.9% 81,358 | 38.3% 51,128 | 0.8% 1,120 |
| 1968 | 39.8% 57,044 | 55.1% 79,040 | 5.1% 7,296 |
| 1964 | 28.9% 43,895 | 70.0% 106,397 | 1.2% 1,779 |
| 1960 | 40.6% 70,711 | 59.1% 102,998 | 0.3% 562 |
| 1956 | 58.2% 92,458 | 41.0% 65,155 | 0.8% 1,207 |
| 1952 | 54.8% 88,967 | 44.7% 72,579 | 0.4% 715 |
| 1948 | 52.9% 71,674 | 45.6% 61,869 | 1.5% 2,068 |
| 1944 | 47.8% 67,984 | 51.8% 73,674 | 0.4% 541 |
| 1940 | 43.8% 79,685 | 55.9% 101,577 | 0.3% 622 |
| 1936 | 43.3% 81,572 | 55.7% 105,008 | 1.1% 1,997 |
| 1932 | 45.4% 52,672 | 52.6% 60,975 | 2.0% 2,281 |
| 1928 | 48.0% 67,872 | 51.9% 73,319 | 0.2% 220 |
| 1924 | 53.2% 46,475 | 23.4% 20,472 | 23.4% 20,449 |
| 1920 | 65.4% 49,419 | 31.1% 23,473 | 3.6% 2,683 |
| 1916 | 53.7% 25,348 | 42.4% 19,999 | 3.9% 1,832 |
| 1912 | 12.0% 4,970 | 32.6% 13,461 | 55.4% 22,907 |
| 1908 | 56.2% 24,594 | 39.7% 17,379 | 4.0% 1,760 |
| 1904 | 64.8% 27,809 | 31.5% 13,518 | 3.7% 1,568 |
| 1900 | 54.9% 21,793 | 41.5% 16,470 | 3.7% 1,454 |
| 1896 | 55.1% 22,718 | 42.0% 17,305 | 3.0% 1,225 |
| 1892 | 45.2% 14,118 | 50.4% 15,734 | 4.4% 1,377 |
| 1888 | 49.3% 15,543 | 48.2% 15,218 | 2.5% 797 |
As of November 2008, there were 187,849 registered voters in Luzerne County.[75]
- Democratic: 111,317 (59.26%)
- Republican: 61,085 (32.52%)
- Other Parties: 15,447 (8.22%)
During presidential elections, the county is considered a bellwether of the state. It voted for the presidential candidate who carried Pennsylvania in every election since 1936. While the Democratic Party has been historically dominant in county-level politics, on the statewide and national levels, Luzerne County leans toward the Democratic Party only slightly. During the 2000 U.S. presidential election, Democrat Al Gore won 52% of the vote to Republican George W. Bush's 44%. In 2004, it was much closer, with Democrat John Kerry winning 51% to Republican George Bush's 48%. Democrat Barack Obama carried the county twice (once in 2008, and again in 2012). During the 2016 presidential election, Republican Donald Trump won the county with 58% of the vote, the largest margin since President Richard Nixon in 1972. It was the first time a Republican presidential candidate carried the county since 1988.
In recent years, Luzerne County has witnessed mixed results in U.S. senate elections. In 2000, 2004, and 2016, the Republican candidates for U.S. senate won the county. However, Democratic candidates for U.S. senate carried the county in 2006 (with 60.6% of the vote), 2010, and 2012.
Democratic candidates for Pennsylvania governor won Luzerne County in 2002, 2006 (with 67.5% of the vote), and 2014. In recent years, the county voted for a Republican gubernatorial candidate only once (in 2010).
United States Senate
United States House of Representatives
State Senate
State House of Representatives
- Tarah Toohil, R, Pennsylvania's 116th Representative District
- Karen Boback, R, Pennsylvania's 117th Representative District
- Michael B. Carroll, D, Pennsylvania's 118th Representative District
- Gerald Mullery, D, Pennsylvania's 119th Representative District
- Aaron Kaufer, R, Pennsylvania's 120th Representative District
- Eddie Day Pashinski, D, Pennsylvania's 121st Representative District
Public safety

There are many fire and police departments scattered throughout Luzerne County.[76] Each individual community (city, borough, and township) determines the boundaries of each department. The firefighters provide fire protection for its citizens. Most fire departments are headed by a fire chief and are staffed by a combination of career and volunteer firefighters.
The police provide full-time protection to its citizens, visitors, businesses, and public property. Most departments are headed by a chief of police and operate out of their local municipal building. The Luzerne County Sheriff's Office operates out of Wilkes-Barre's Luzerne County Courthouse. The sheriff is an official who is responsible for keeping the peace and enforcing the law throughout the county.[77] After Luzerne County adopted a home rule charter, the office of sheriff became an appointed position (and was no longer an elected one). The Pennsylvania State Police also have a presence in the county. Troop P operates out of the northern half of Luzerne County and is headquartered in Wyoming. Troop N operates out of the southern portion of the county and is headquartered in Hazleton.
Healthcare
.jpg)
Hospitals
- First Hospital in Kingston, an affiliate of Commonwealth Health
- Geisinger South Wilkes Barre Hospital (GSWB), formerly Mercy Hospital
- Geisinger Wyoming Valley Medical Center (GWV) in Plains Township
- Hazleton General Hospital (Lehigh Valley Hospital)
- Nanticoke Special Care Hospital, an affiliate of Commonwealth Health
- VA Medical Center in Wilkes-Barre
- Wilkes-Barre General Hospital, an affiliate of Commonwealth Health
Education


Public school districts
- Berwick Area School District (also in Columbia County)
- Crestwood School District
- Dallas School District
- Greater Nanticoke Area School District
- Hanover Area School District
- Hazleton Area School District (also in Carbon and Schuylkill Counties)
- Lake-Lehman School District (also in Wyoming County)
- Northwest Area School District
- Pittston Area School District
- Wilkes-Barre Area School District
- Wyoming Area School District (also in Wyoming County)
- Wyoming Valley West School District
Charter schools
- Bear Creek Community Charter School, Bear Creek Township
Public vocational technical schools
Private schools
- Graham Academy, Kingston
- Holy Cross High School, located in Lackawanna County; it serves Luzerne County residents
- Holy Redeemer High School, Wilkes-Barre
- Jenny Lynn Ferraro Academy, Kingston
- Milford E. Barnes Junior School, Wilkes-Barre
- MMI Preparatory School, Freeland
- New Story School, Wyoming
- Wilkes-Barre Academy, Wilkes-Barre
- Wyoming Seminary, Forty Fort and Kingston[78]
Colleges and universities
- Geisinger Commonwealth School of Medicine, Wilkes-Barre
- King's College, Wilkes-Barre
- Luzerne County Community College, Nanticoke
- McCann School of Business & Technology, Wilkes-Barre
- Misericordia University, Dallas
- Penn State Hazleton, Hazleton
- Penn State Wilkes-Barre, Lehman Township
- Wilkes University, Wilkes-Barre
Libraries
The Luzerne County Library System includes the following locations:[79][80]
- Back Mountain Memorial Library, Back Mountain
- Hazleton Area Public Library, Hazleton
- Hoyt Library, Kingston
- Marian Sutherland Kirby Library, Mountain Top
- Mill Memorial Library, Nanticoke
- Osterhout Free Library, Wilkes-Barre
- Pittston Memorial Library, Pittston
- Plymouth Public Library, Plymouth
- West Pittston Library, West Pittston
- Wyoming Free Library, Wyoming
Culture



Local attractions
- Bear Creek Village Historic District, Bear Creek Village
- Bittenbender Covered Bridge, Huntington Township
- Dorothy Dickson Darte Center for the Performing Arts, located on the campus of Wilkes University (in Wilkes-Barre)[81]
- Eckley Miners' Village, Foster Township
- F.M. Kirby Center for the Performing Arts, Wilkes-Barre[82]
- Frederick Stegmaier Mansion, Wilkes-Barre[83]
- Giants Despair Hillclimb, Laurel Run
- Kingston Armory, Kingston
- Little Theatre of Wilkes-Barre, Wilkes-Barre[84]
- Luzerne County Convention and Visitors Bureau, Wilkes-Barre
- Luzerne County Museum, Wilkes-Barre[85]
- Mohegan Sun Arena at Casey Plaza, Wilkes-Barre Township
- Mohegan Sun at Pocono Downs, Plains Township
- Public Square, Wilkes-Barre
- River Street Historic District, Wilkes-Barre
- Stegmaier Brewery, Wilkes-Barre
- Swetland Homestead, Wyoming
- Wilkes-Barre station, Wilkes-Barre
- Wyoming Monument, Wyoming
- Wyoming Valley Mall, Wilkes-Barre Township
Media
The Scranton/Wilkes-Barre area is the 55th-largest U.S. television market.[86] Local television stations[87] include: WNEP-TV (ABC affiliate), WBRE-TV (NBC affiliate), WYOU-TV (CBS affiliate), WVIA-TV (PBS affiliate), WOLF-TV (FOX affiliate), WQMY (MyNetworkTV affiliate), WSWB (CW affiliate), WQPX (Ion Television affiliate), and WYLN-LP (Youtoo TV affiliate).
Times Leader and The Citizens' Voice are the two largest daily newspapers in the Wilkes-Barre area. Wilkes-Barre's radio market is ranked No. 69 by Arbitron's ranking system. There are news, adult alternative, and music radio stations which are receivable in the area.
Sports
| Team name | League | Sport | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wilkes-Barre/Scranton Penguins | AHL | Ice Hockey | Mohegan Sun Arena |
| Scranton/Wilkes-Barre RailRiders | IL | Baseball | PNC Field |
Transportation
.jpg)
Highways
Railroads
Airports
- Hazleton Municipal Airport
- Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport
- Wilkes-Barre Wyoming Valley Airport
 Interstate 80 in southern Luzerne County |
.jpg) Specialist Dale J. Kridlo Bridge (U.S. Route 11) |
 North Cross Valley Expressway (PA 309) |
Communities




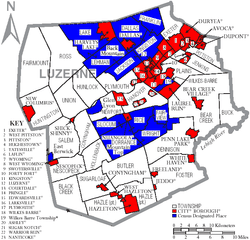
Luzerne County contains the second highest number of independently governing municipalities in the state of Pennsylvania, with 76; only Allegheny County has more.[88] Under Pennsylvania law, there are four types of incorporated municipalities: cities, boroughs, townships, and, in the case of Bloomsburg, towns. The following cities, boroughs, and townships are located in Luzerne County:
Cities
- Hazleton
- Nanticoke
- Pittston
- Wilkes-Barre (county seat)
Boroughs
- Ashley
- Avoca
- Bear Creek Village
- Conyngham
- Courtdale
- Dallas
- Dupont
- Duryea
- Edwardsville
- Exeter
- Forty Fort
- Freeland
- Harveys Lake
- Hughestown
- Jeddo
- Kingston
- Laflin
- Larksville
- Laurel Run
- Luzerne
- Nescopeck
- New Columbus
- Nuangola
- Penn Lake Park
- Plymouth
- Pringle
- Shickshinny
- Sugar Notch
- Swoyersville
- Warrior Run
- West Hazleton
- West Pittston
- West Wyoming
- White Haven
- Wyoming
- Yatesville
Townships
Census-designated places
Census-designated places are geographical areas designated by the U.S. Census Bureau for the purposes of compiling demographic data. They are not actual jurisdictions under Pennsylvania law.
Other places
Population ranking
The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2010 census of Luzerne County.[89]
† county seat
| Rank | City/Borough/Township | Municipal type | Population (2010 census)
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | † Wilkes-Barre | City | 41,498 |
| 2 | Hazleton | City | 25,340 |
| 3 | Kingston | Borough | 13,182 |
| 4 | Hanover Township | Township | 11,076 |
| 5 | Nanticoke | City | 10,465 |
| 6 | Plains Township | Township | 9,961 |
| 7 | Hazle Township | Township | 9,549 |
| 8 | Butler Township | Township | 9,221 |
| 9 | Dallas Township | Township | 8,994 |
| 10 | Pittston | City | 7,739 |
| 11 | Kingston Township | Township | 6,999 |
| 12 | Plymouth | Borough | 5,951 |
| 13 | Exeter | Borough | 5,652 |
| 14 | Wright Township | Township | 5,651 |
| 15 | Newport Township | Township | 5,374 |
| 16 | Swoyersville | Borough | 5,062 |
| 17 | Duryea | Borough | 4,917 |
| 18 | West Pittston | Borough | 4,868 |
| 19 | Edwardsville | Borough | 4,816 |
| 20 | Jackson Township | Township | 4,646 |
| 21 | West Hazleton | Borough | 4,594 |
| 22 | Fairview Township | Township | 4,520 |
| 23 | Larksville | Borough | 4,480 |
| 24 | Jenkins Township | Township | 4,442 |
| 25 | Salem Township | Township | 4,254 |
| 26 | Forty Fort | Borough | 4,214 |
| 27 | Sugarloaf Township | Township | 4,211 |
| 28 | Freeland | Borough | 3,531 |
| 29 | Lehman Township | Township | 3,508 |
| 30 | Foster Township | Township | 3,467 |
| 31 | Pittston Township | Township | 3,368 |
| 32 | Rice Township | Township | 3,335 |
| 33 | Wyoming | Borough | 3,073 |
| 34 | Wilkes-Barre Township | Township | 2,967 |
| 35 | Ross Township | Township | 2,937 |
| 36 | Luzerne | Borough | 2,845 |
| 37 | Dallas | Borough | 2,804 |
| 38 | Harveys Lake | Borough | 2,791 |
| 39 | Ashley | Borough | 2,790 |
| 40 | Bear Creek Township | Township | 2,774 |
| 41 | West Wyoming | Borough | 2,725 |
| 42 | Dupont | Borough | 2,711 |
| 43 | Avoca | Borough | 2,661 |
| 44 | Hunlock Township | Township | 2,443 |
| 45 | Exeter Township | Township | 2,378 |
| 46 | Huntington Township | Township | 2,244 |
| 47 | Dorrance Township | Township | 2,188 |
| 48 | Lake Township | Township | 2,049 |
| 49 | Union Township | Township | 2,042 |
| 50 | Black Creek Township | Township | 2,016 |
| 51 | Conyngham | Borough | 1,914 |
| 52 | Plymouth Township | Township | 1,812 |
| 53 | Franklin Township | Township | 1,757 |
| 54 | Nescopeck | Borough | 1,583 |
| 55 | Laflin | Borough | 1,487 |
| 56 | Conyngham Township | Township | 1,453 |
| 57 | Hughestown | Borough | 1,392 |
| 58 | Fairmount Township | Township | 1,276 |
| 59 | Hollenback Township | Township | 1,196 |
| 60 | Nescopeck Township | Township | 1,155 |
| 61 | Dennison Township | Township | 1,125 |
| 62 | Slocum Township | Township | 1,115 |
| 63 | White Haven | Borough | 1,097 |
| 64 | Sugar Notch | Borough | 989 |
| 65 | Pringle | Borough | 979 |
| 66 | Shickshinny | Borough | 838 |
| 67 | Courtdale | Borough | 732 |
| 68 | Nuangola | Borough | 679 |
| 69 | Yatesville | Borough | 607 |
| 70 | Warrior Run | Borough | 584 |
| 71 | Laurel Run | Borough | 500 |
| 72 | Buck Township | Township | 435 |
| 73 | Penn Lake Park | Borough | 308 |
| 74 | Bear Creek Village | Borough | 257 |
| 75 | New Columbus | Borough | 227 |
| 76 | Jeddo | Borough | 98 |
Notable people
See also
Notes
- ↑ Mean monthly maxima and minima (i.e. the expected highest and lowest temperature readings at any point during the year or given month) calculated based on data at said location from 1981 to 2010.
- ↑ Official records for Avoca/Wilkes-Barre–Scranton kept at downtown Scranton from January 1901 to 17 April 1955 and at Wilkes-Barre/Scranton International Airport since 18 April 1955.[56]
References
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- 1 2 Tice, Joyce M. "History of Bradford County PA, 1770–1878 by David Craft – Chapter 9". www.joycetice.com.
- 1 2 "Wyoming County Historical Society". pawchs.org.
- ↑ "Home". archive.org. February 5, 2007. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007.
- ↑ Fisher, Sydney George (1896). The Making of Pennsylvania. Philadelphia, PA: J. B. Lippincott Company.
- ↑ Baillie, William. "The Wyoming Massacre and Columbia County". Columbia County Historical and Genealogical Society. Archived from the original on April 28, 2003. Retrieved September 12, 2012.
- ↑ Jenkins, Steuben (July 3, 1878). Historical Address at the Wyoming Monument (Speech). 100th Anniversary of the Battle and Massacre of Wyoming. Retrieved 2 July 2013.
- ↑ Hayden, Horace Edwin (1895). The Massacre of Wyoming: The Acts of Congress for the Defense of the Wyoming Valley, Pennsylvania, 1776–1778. Wyoming Historical and Geological Society. p. 57.
- ↑ "The American Revolution". 1759–1796 Guardhouse of the Great Lakes. Old Fort Niagara. Archived from the original on October 12, 2006. Retrieved 2007-11-18.
- ↑ Rogan H. Moore (2000), The Bloodstained Field: A History of the Sugarloaf Massacre, September 11, 1780 , p. 19
- ↑ "Second Yankee-Pennamite War". Luzerne County. Luzerne County. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ↑ "History of Luzerne County Pennsylvania 1893". Usgwarchives.net. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- 1 2 3 4 "Luzerne County : History of Luzerne County". www.luzernecounty.org.
- ↑ Bradford County History Archived July 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine., Bradford County, Pennsylvania. Accessed August 21, 2007
- ↑ "Township Incorporations, 1790 to 1853". Susquehanna County Historical Society. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015. Retrieved 9 March 2013.
- ↑ "Wyoming County | WyomingHistory". Wycopa.org. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ Hollister, Horace (1885). History of the Lackawanna Valley. Lippincott. p. 488.
- ↑ David Craft (1891). History of Scranton, Penn: With Full Outline of the Natural Advantages, Accounts of the Indian Tribes, Early Settlements, Connecticut's Claim to the Wyoming Valley, the Trenton Decree, Down to the Present Time. H. W. Crew. pp. 18–. Retrieved 19 March 2013.
- ↑ "History of Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania". u-s-history.com.
- ↑ Henry C. Bradsby, History of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, Volume 1, 1893, Pages 232-233
- ↑ Administrator. "History – Life – Life". www.hazletoncity.org.
- ↑ Cheryl A. Kashuba (September 6, 2009). "Avondale mine disaster claimed 110 lives". The Times-Tribune. Retrieved April 23, 2010.
- ↑ "Twin Shaft Disaster Marker". Hmdb.org. August 19, 2008. Retrieved July 21, 2009.
- ↑ "GenDisasters ... Genealogy in Tragedy, Disasters, Fires, Floods – Events That Touched Our Ancestors' Lives". www.gendisasters.com. Archived from the original on November 21, 2008.
- ↑ Novak, Michael. The Guns of Lattimer. Reprint ed. New York: Transaction Publishers, 1996; ISBN 1-56000-764-8
- ↑ Troncale, Anthony T. "About Lewis Wickes Hine". New York Public Library. Archived from the original on 2007-03-08. Retrieved 2007-05-22.
- ↑ Glenn B. Stracher, ed. (January 1, 2007), Geology of Coal Fires: Case Studies from Around the World, ISBN 9780813741185, retrieved January 30, 2014
- ↑ "New York Times "FLAME IN TUNNEL KILLS 84, BURNS 42: Spreads Like Blanket Over Miners."". June 6, 1919.
- ↑ "National Historic Landmarks & National Register of Historic Places in Pennsylvania" (Searchable database). CRGIS: Cultural Resources Geographic Information System. Note: This includes Gary F. Lamont (n.d.). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory Nomination Form: Luzerne County Courthouse" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-03-13.
- ↑ "history". www.nanticokecity.com.
- ↑ Tyler, Gus (1995). Look for the Union Label: A History of the International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union. Armonk, NY: M. E. Sharpe.
- ↑ Lavietes, Stuart (September 17, 2002). "Aaron Danzig, 89, Who Argued Landmark Case on Court Power". The New York Times.
Erie Railroad Co. v. Tompkins, the landmark 1938 Supreme Court case that limited the power of the federal courts
- ↑ David Pencek (1998). "Knox Mine Disaster". Times Leader. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ↑ Bill O'Boyle (June 22, 2009). "Agnes now a flood of memories". Times Leader. Archived from the original on January 2, 2014. Retrieved March 6, 2012.
- ↑ "Banks named in 8 more murder indictments". The Reading Eagle. Associated Press. 30 September 1982. Retrieved 2011-03-26.
- ↑ "CNN Transcript - WorldView: NTSB Begins Investigation Into Charter Plane Crash in Pennsylvania Which Killed All 19 Onboard - May 21, 2000". Cnn.com. 2000-05-21. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ On Money By ADAM DAVIDSON JULY 6, 2016 (2016-07-06). "Blaming Trade and Voting Trump in the Rust Belt - The New York Times". Nytimes.com. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ Voters say 'yes' to home rule – News. Standard Speaker (2010-11-03). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ↑ Frank, Thomas (April 1, 2009). "Thomas Frank Says 'Kids for Cash' Incentivizes the Prison Industry". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- 1 2 "Election Results Archive". Luzerne County. Archived from the original on January 11, 2018. Retrieved January 19, 2018.
- ↑ "BOROUGH OF DURYEA, PENNSYLVANIA, et al.,<linebreak> PETITIONERS v. CHARLES J. GUARNIERI". Legal Information Institute, Cornell University Law School. 20 June 2011. Retrieved 26 August 2013.
- ↑ Mandatory Evacuation of Wyoming Valley by 4 p.m., Times-Leader, September 8, 2011
- ↑ Eckert, Paul (September 9, 2011). "UPDATE 3-Pennsylvania hit by huge flooding, towns submerged". Reuters.
- ↑ Luzerne officials issue mandatory evacuation in footprint of Agnes flood, Times Tribune, September 8, 2011
- 1 2 3 4 "Home Rule Charter". Luzerne County. Retrieved 2018-03-02.
- 1 2 "Luzerne County Council members sworn in – The Times Leader reports". YouTube. 2012-01-02. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ System Administrator. "Luzerne County's manager search - News - Citizens' Voice". Citizensvoice.com. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- 1 2 "Luzerne County Manager Robert Lawton Resigns". pahomepage.com. November 26, 2015.
- ↑ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Pennsylvania County High Points". Peakbagger.com. 2004-11-01. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ Susquehanna Warrior Trail, PA – Google Maps. Maps.google.com (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- 1 2 3 "Station Name: PA WILKES-BARRE INTL AP". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2016-09-11.
- 1 2 3 4 "Local Climatological Data–Annual Summary with Comparative Data: Wilkes–Barre/Scranton" (PDF). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved September 30, 2015.
- 1 2 3 4 "NowData - NOAA Online Weather Data". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Retrieved 2017-02-25.
- 1 2 "NOAA". NOAA.
- ↑ ThreadEx
- ↑ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved October 10, 2018.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
- ↑ Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 24, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved March 9, 2015.
- ↑ Census data, USA Today
- ↑ US Census Bureau. "2011 American Community Survey 1-Year Estimates." American FactFinder <http://factfinder2.census.gov>.
- ↑ "Luzerne County Demographics & Statistics â€" Employment, Education, Income Averages, Crime in Luzerne County â€" Point2 Homes". Point2homes.com. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ "Luzerne County Pennsylvania QuickFacts from the U.S. Census Bureau". Census.gov. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ↑ "Languages in Luzerne County, Pennsylvania (County)". Statistical Atlas. 2015-04-17. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ "Luzerne County, Pennsylvania Religion". Bestplaces.net. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ Voters say 'yes' to home rule - News. Standard Speaker (2010-11-03). Retrieved on 2013-07-23.
- ↑ "Tim McGinley appointed new Luzerne County Council chair". Times Leader. 2018-01-02. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "Council". Luzerne County. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ Administrator, System. "Luzerne County's manager search". citizensvoice.com.
- ↑ "County Manager Open Position". Luzerne County. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ "County Manager". Luzerne County. 2013-10-29. Retrieved 2017-02-22.
- ↑ David Leip. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "Home". www.dos.state.pa.us.
- ↑ "Luzerne County : Police and Fire Departments". www.luzernecounty.org.
- ↑ "Definition of SHERIFF". www.merriam-webster.com.
- ↑ Pennsylvania Department of Education (2011). "Licensed, Private Academic Schools in Pennsylvania". Archived from the original on April 29, 2011.
- ↑ "Member Libraries | Luzerne County Library System". www.luzernelibraries.org. Retrieved 2018-01-25.
- ↑ "Luzerne County : Library Locations". www.luzernecounty.org. Retrieved 2018-01-25.
- ↑ "Wilkes Division of Performing Arts". Wilkes University. Archived from the original on April 1, 2014. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
- ↑ "The F.M. Kirby Center for the Performing Arts". Kirbycenter.org. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
- ↑ "The Frederick Stegmaier Mansion". Stegmaiermansion.com. 2011-05-26. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Little Theatre of Wilkes-Barre". Ltwb.org. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
- ↑ Luzerne County Historical Society. "Welcome to the Luzerne County Historical Society website | NEPA Luzerne County Pennsylvania history". Luzernehistory.org. Retrieved May 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Nielsen Local Television Market Universe Estimates" (PDF). Nielsen. Retrieved 2015-05-26.
- ↑ "Wilkes Barre – Scranton Television Stations". Station Index. Retrieved 2011-08-29.
- ↑ "Pennsylvania Municipalities Information". Pamunicipalitiesinfo.com. Retrieved August 16, 2012.
- ↑ "2010 Census". Census.gov. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. |
- Official Luzerne County website
- "Luzerne County Library System". Archived from the original on February 12, 2008.
- Tournepa.com: Luzerne County Convention and Visitors Bureau
- The Luzerne Foundation — the county's Community Foundation.
- Luzerne County Community College website

