Loyalist (American Revolution)
| Part of the Politics series on |
| Toryism |
|---|
 |
Loyalists were American colonists who stayed loyal to the British Crown during the American Revolutionary War, often called Tories, Royalists, or King's Men at the time. They were opposed by the Patriots, who supported the revolution, and called them "persons inimical to the liberties of America".[1] Prominent Loyalists repeatedly assured the British government that many thousands of them would spring to arms and fight for the crown. The British government acted in expectation of that, especially in the southern campaigns in 1780-81. In practice, the number of Loyalists in military service was far lower than expected since Britain could not effectively protect them except in those areas where Britain had military control. The British were often suspicious of them, not knowing whom they could fully trust in such a conflicted situation; they were often looked down upon. Patriots watched suspected Loyalists very closely and would not tolerate any organized Loyalist opposition. Many outspoken or militarily active Loyalists were forced to flee, especially to their stronghold of New York City. William Franklin, the royal governor of New Jersey and son of Patriot leader Benjamin Franklin, became the leader of the Loyalists after his release from a Patriot prison in 1778. He worked to build Loyalist military units to fight in the war, but the number of volunteers was much fewer than London expected.
When their cause was defeated, about 15 percent of the Loyalists (65,000–70,000 people) fled to other parts of the British Empire, to Britain itself, or to British North America (now Canada). The southern Loyalists moved mostly to Florida, which had remained loyal to the Crown, and to British Caribbean possessions, often bringing along their slaves. Northern Loyalists largely migrated to Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia. They called themselves United Empire Loyalists. Most were compensated with Canadian land or British cash distributed through formal claims procedures. Loyalists who left the US received £3 million or about 37 percent of their losses from the British government. Loyalists who stayed in the US were generally able to retain their property and become American citizens.[2] Historians have estimated that between 15 and 20 percent of the two million whites in the colonies in 1775 were Loyalists (300,000-400,000).[3]
Background
Families were often divided during the American Revolution, and many felt themselves to be both American and British, still owing a loyalty to the mother country. Maryland lawyer Daniel Dulaney the Younger opposed taxation without representation but would not break his oath to the King or take up arms against him. He wrote: "There may be a time when redress may not be obtained. Till then, I shall recommend a legal, orderly, and prudent resentment".[4] Most Americans hoped for a peaceful reconciliation but were forced to choose sides by the Patriots who took control nearly everywhere in the Thirteen Colonies in 1775-76.[5]
Motives for Loyalism
Yale historian Leonard Woods Larabee has identified eight characteristics of the Loyalists that made them essentially conservative and loyal to the king and Britain:[6]
- They were older, better established, and resisted radical change
- They felt that rebellion against the Crown—the legitimate government—was morally wrong.
- They were alienated when the Patriots resorted to violence, such as burning houses and tarring and feathering.
- They wanted to take a middle-of-the road position and were angry when forced by the Patriots to declare their opposition.
- They had a long-standing sentimental attachment to Britain (often with business and family links).
- They realized that independence was bound to come someday, but wanted to postpone the moment.
- They were cautious and afraid that chaos and mob rule would result.
- Some were pessimists who lacked the confidence in the future displayed by the Patriots. Others recalled the dreadful experiences of many Jacobite rebels after the failure of the last Jacobite rebellion as recently as 1745 who often lost their lands when the Hanoverian government won.[7][8][9]
Other motives of the Loyalists included:
- They felt a need for order and believed that Parliament was the legitimate authority.[10]
- In New York, powerful families had assembled colony-wide coalitions of supporters, Men long associated with the De Lancey faction went along when its leadership decided to support the crown.[11]
- They felt themselves to be weak or threatened within American society and in need of an outside defender such as the British Crown and Parliament.[12]
- They had been promised freedom from slavery by the British.[13][14][15]
- They felt that being a part of the British Empire was crucial in terms of commerce and their business operations.[16][17][18]
Loyalism and military operations
In the opening months of the Revolutionary War, the Patriots laid siege to Boston, where most of the British forces were stationed. Elsewhere there were few British troops and the Patriots seized control of all levels of government, as well as supplies of arms and gunpowder. Vocal Loyalists recruited people to their side, often with the encouragement and assistance of royal governors. In the South Carolina back country, Loyalist recruitment oustripped that of Patriots. A brief siege at Ninety Six, South Carolina in the fall of 1775 was followed by a rapid rise in Patriot recruiting, and a Snow Campaign involving thousands of partisan militia resulted in the arrest or flight of most of the back country Loyalist leadership. North Carolina back country Scots and former Regulators joined forces in early 1776, but they were broken as a force at the Battle of Moore's Creek Bridge.
By July 4, 1776, the Patriots had gained control of virtually all territory in the Thirteen Colonies and expelled all royal officials. No one who openly proclaimed their loyalty to the Crown was allowed to remain, so Loyalists fled or kept quiet. Some of those who remained later gave aid to invading British armies or joined uniformed Loyalist regiments.[19]
The British were forced out of Boston by March 17, 1776. They regrouped at Halifax and attacked New York in August, defeating George Washington's army at Long Island and capturing New York City and its vicinity, and they occupied the mouth of the Hudson River until 1783. British forces seized control of other cities, including Philadelphia (1777), Savannah, Georgia (1778–83), and Charleston, South Carolina (1780–82). But 90 percent of the colonial population lived outside the cities, with the effective result that Congress represented 80 to 90 percent of the population. The British removed their governors from colonies where the Patriots were in control, but Loyalist civilian government was re-established in coastal Georgia[20] from 1779 to 1782, despite presence of Patriot forces in the northern part of Georgia. Essentially, the British were only able to maintain power in areas where they had a strong military presence.
Numbers of Loyalists
Historian Robert Calhoon wrote in 2000, concerning the proportion of Loyalists to Patriots in the Thirteen Colonies:
Historians' best estimates put the proportion of adult white male loyalists somewhere between 15 and 20 percent. Approximately half the colonists of European ancestry tried to avoid involvement in the struggle—some of them deliberate pacifists, others recent immigrants, and many more simple apolitical folk. The patriots received active support from perhaps 40 to 45 percent of the white populace, and at most no more than a bare majority.[21]

Before Calhoon's work, estimates of the Loyalist share of the population were somewhat higher, at about one-third, but these estimates are now rejected as too high by most scholars.[22] In 1968 historian Paul H. Smith estimated there were about 400,000 Loyalists, or 16% of the white population of 2.25 million in 1780.[23][24]
Historian Robert Middlekauff summarized scholarly research on the nature of Loyalist support as follows:
The largest number of loyalists were found in the middle colonies: many tenant farmers of New York supported the king, for example, as did many of the Dutch in the colony and in New Jersey. The Germans in Pennsylvania tried to stay out of the Revolution, just as many Quakers did, and when that failed, clung to the familiar connection rather than embrace the new. Highland Scots in the Carolinas, a fair number of Anglican clergy and their parishioners in Connecticut and New York, a few Presbyterians in the southern colonies, and a large number of the Iroquois stayed loyal to the king.[25]

New York City and Long Island were the British military and political base of operations in North America from 1776 to 1783 and had a large concentration of Loyalists, many of whom were refugees from other states.[26]
According to Calhoon,[26] Loyalists tended to be older and wealthier, but there were also many Loyalists of humble means. Many active Church of England members became Loyalists. Some recent arrivals from Britain, especially those from Scotland, had a high Loyalist proportion. Loyalists in the southern colonies were suppressed by the local Patriots, who controlled local and state government. Many people—including former Regulators in North Carolina — refused to join the rebellion, as they had earlier protested against corruption by local authorities who later became Revolutionary leaders. The oppression by the local Whigs during the Regulation led to many of the residents of backcountry North Carolina sitting out the Revolution or siding with the Loyalists.[26]
In areas under Patriot control, Loyalists were subject to confiscation of property, and outspoken supporters of the king were threatened with public humiliation such as tarring and feathering, or physical attack. It is not known how many Loyalist civilians were harassed by the Patriots, but the treatment was a warning to other Loyalists not to take up arms. In September 1775, William Drayton and Loyalist leader Colonel Thomas Fletchall signed a treaty of neutrality in the interior community of Ninety Six, South Carolina.[27] For actively aiding the British army when it occupied Philadelphia, two residents of the city were tried for treason, convicted, and executed by returning Patriot forces.[28]
Slavery and Black Loyalists

As a result of the looming crisis in 1775 the Royal Governor of Virginia, Lord Dunmore, issued a proclamation that promised freedom to servants and slaves who were able to bear arms and join his Loyalist Ethiopian Regiment. Many of the slaves in the South joined the Loyalists with intentions of gaining freedom and escaping the South. About 800 did so; some helped rout the Virginia militia at the Battle of Kemp's Landing and fought in the Battle of Great Bridge on the Elizabeth River, wearing the motto "Liberty to Slaves", but this time they were defeated. The remains of their regiment were then involved in the evacuation of Norfolk, after which they served in the Chesapeake area. Eventually the camp that they had set up there suffered an outbreak of smallpox and other diseases. This took a heavy toll, putting many of them out of action for some time. There was a slave by the name of Boston King who joined the Loyalists and wound up catching smallpox. Boston King and other soldiers who were sick were relocated to a different part of the camp so that they did not contaminate the healthy soldiers. The survivors joined other British units and continued to serve throughout the war. Black colonials were often the first to come forward to volunteer and a total of 12,000 African Americans served with the British from 1775 to 1783. This factor had the effect of forcing the rebels to also offer freedom to those who would serve in the Continental Army; however, such promises were often reneged upon by both sides.[29]
Americans who gained their freedom by fighting for the British became known as Black Loyalists. The British honored the pledge of freedom in New York City through the efforts of General Guy Carleton who recorded the names of African Americans who had supported the British in a document called the Book of Negroes which granted freedom to slaves who had escaped and assisted the British. About 4,000 Black Loyalists went to the British colonies of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, where the British promised them land. They founded communities across the two provinces, many of which still exist today. Over 2,500 settled in Birchtown, Nova Scotia, instantly making it the largest free black community in North America. However, the inferior grants of land they were given and the prejudices of white Loyalists in nearby Shelburne who regularly harassed the settlement in events such as the Shelburne Riots in 1784, made life very difficult for the community.[30] In 1791 Britain's Sierra Leone Company offered to transport dissatisfied black Loyalists to the British colony of Sierra Leone in Africa, with the promise of better land and more equality. About 1,200 left Nova Scotia for Sierra Leone, where they named the capital Freetown.[30] After 1787 they became Sierra Leone's ruling elite. About 400 to 1,000 free blacks who joined the British side in the Revolution went to London and joined the free black community of about 10,000 there.
Loyalist women
While men were out fighting for the crown, women served at home protecting their land and property.[31] At the end of the war, many loyalist men left America for the shelter of England, leaving their wives and daughters to protect their land[31] The main punishment for Loyalist families was the expropriation of property, but married women were protected under "feme covert", which meant that they had no political identity and their legal rights were absorbed by their husbands.[31] This created an awkward dilemma for the confiscation committees: confiscating the land of such a woman would punish her for her husband's actions.[31] In fact, many women were punished in this way. Grace Growden Galloway[32] recorded the experience in her diary. Galloway's property was seized by the Rebels and she spent the rest of her life fighting to regain it.[31] It was returned to her heirs in 1783, after she and her husband had died.[31]
Loyalism in Canada

Rebel agents were active in Quebec (which was then frequently called "Canada", the name of the earlier French province) in the months leading to the outbreak of active hostilities. John Brown, an agent of the Boston Committee of Correspondence,[33] worked with Canadian merchant Thomas Walker and other rebel sympathisers during the winter of 1774–1775 to convince inhabitants to support the actions of the First Continental Congress. However, many of Quebec's inhabitants remained neutral, resisting service to either the British or the Americans.
Although some Canadians took up arms in support of the rebellion, the majority remained loyal to the King. French Canadians had been satisfied by the British government's Quebec Act of 1774, which offered religious and linguistic toleration; in general, they did not sympathize with a rebellion that they saw as being led by Protestants from New England, who were their commercial rivals and hereditary enemies. Most of the English-speaking settlers had arrived following the British conquest of Canada in 1759–1760, and were unlikely to support separation from Britain. The older British colonies, Newfoundland and Nova Scotia (including what is now New Brunswick) also remained loyal and contributed military forces in support of the Crown.
In late 1775 the Continental Army sent a force into Quebec, led by General Richard Montgomery and Colonel Benedict Arnold, with the goal of convincing the residents of Quebec to join the Revolution. Although only a minority of Canadians openly expressed loyalty to King George, about 1,500 militia fought for the King in the Siege of Fort St. Jean. In the region south of Montreal that was occupied by the Continentals, some inhabitants supported the rebellion and raised two regiments to join the Patriot forces.[34]
In Nova Scotia, there were many Yankee settlers originally from New England, and they generally supported the principles of the revolution. This element was declining in relative numbers and influence due to an influx of recent immigration from the British isles, and they remained neutral during the war, and the influx was greatest in Halifax.[35] Britain in any case built up powerful forces at the naval base of Halifax after the failure of Jonathan Eddy to capture Fort Cumberland in 1776.[36][37] Although the Continentals captured Montreal in November 1775, they were turned back a month later at Quebec City by a combination of the British military under Governor Guy Carleton, the difficult terrain and weather, and an indifferent local response. The Continental forces would be driven from Quebec in 1776, after the breakup of ice on the St. Lawrence River and the arrival of British transports in May and June. There would be no further serious attempt to challenge British control of present-day Canada until the War of 1812.
In 1777, 1,500 Loyalist militia took part in the Saratoga campaign in New York, and surrendered with General Burgoyne after the Battles of Saratoga in October. For the rest of the war, Quebec acted as a base for raiding expeditions, conducted primarily by Loyalists and Indians, against frontier communities.
Military service
The Loyalists rarely attempted any political organization. They were often passive unless regular British army units were in the area. The British, however, assumed a highly activist Loyalist community was ready to mobilize and planned much of their strategy around raising Loyalist regiments. The British provincial line, consisting of Americans enlisted on a regular army status, enrolled 19,000 Loyalists (50 units and 312 companies). The maximum strength of the Loyalist provincial line was 9,700 in December 1780.[38][39] In all about 19,000 at one time or another were soldiers or militia in British forces.[40] Loyalists from South Carolina fought for the British in the Battle of Camden. The British forces at the Battle of Monck's Corner and the Battle of Lenud's Ferry consisted entirely of Loyalists with the exception of the commanding officer (Banastre Tarleton).[41] Both white and black Loyalists fought for the British at the Battle of Kemp's Landing in Virginia.[42]
Emigration from the United States

Historian Maya Jasanoff estimated how many Loyalists departed the U.S. for British North America. She calculates 60,000 in total, including about 50,000 whites (Wallace Brown cites about 80,000 Loyalists in total permanently left the United States.[43]).[44] The majority of them — 36,000 - to New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, while about 6,600 went to Quebec and 2,000 to Prince Edward Island. 5,090 white Loyalists went to Florida, bringing along their slaves who numbered about 8,285 (421 whites and 2561 blacks returned to the States from Florida, David Lee Russell, The American Revolution in the Southern Colonies, 2000, p. 317, ISBN 0-7864-0783-2. When Florida was returned to Spain, however, very few Loyalists remained there while most left.[43]). 6,000 whites went to Jamaica and other Caribbean islands notable the Bahamas. About 13,000 went to Britain (including 5,000 free blacks). The total is 60-62,000 whites. A precise figure cannot be known because the records were incomplete and not accurate, and small numbers continued to leave after 1783. The 50,000 or-so white departures represented about 10% of the Loyalists (at 20-25% of the white population).[45] Loyalists (especially soldiers and former officials) could choose evacuation. Loyalists whose roots were not yet deeply embedded in the United States were more likely to leave; older people who had familial bonds and had acquired friends, property, and a degree of social respectability were more likely to remain in the US.[46] The vast majority of the half-million white Loyalists, about 20-25% of the total number of whites, remained in the U.S. Starting in the mid–1780s a small percentage of those who had left returned to the United States in particular as the anti-Tory laws were repealed (the last by 1788). The exiles amounted to about 2% of the total US population of 3 million at the end of the war in 1783.
After 1783 some former Loyalists (especially Germans from Pennsylvania) emigrated to Canada to take advantage of the British government's offer of free land. Many departed because they faced continuing hostility (in another migration more than 20,000 perhaps as many as 30,000 "Late Loyalists" arrived from the United States in the 1790s attracted by Lieutenant-Governor Simcoe's policy of land and low taxes, one-fifth those in the US and swearing an oath of allegiance to the King). They came mainly for economic, not political reasons.[47] Of the 30,000, 3,000 settled in the Eastern Townships of Quebec where they joined the 2,000 American Loyalists settlers who had arrived 7-8 years previously.
The 36,000 or so who went to Nova Scotia were not well-received by the 17,000 Nova Scotians, who were mostly descendants of New Englanders settled there before the Revolution.[48] "They [the Loyalists]", Colonel Thomas Dundas wrote in 1786, "have experienced every possible injury from the old inhabitants of Nova Scotia, who are even more disaffected towards the British Government than any of the new States ever were. This makes me much doubt their remaining long dependent."[49] In response, the colony of New Brunswick, until 1784 part of Nova Scotia, was created for the 14,000 who had settled in those parts. Of the 46,000 who went to Canada, 10,000 went to Quebec, especially what is now modern-day Ontario, the rest to Nova Scotia and PEI.
Realizing the importance of some type of consideration, on November 9, 1789, Lord Dorchester, the governor of Quebec, declared that it was his wish to "put the mark of Honour upon the Families who had adhered to the Unity of the Empire." As a result of Dorchester's statement, the printed militia rolls carried the notation:
Those Loyalists who have adhered to the Unity of the Empire, and joined the Royal Standard before the Treaty of Separation in the year 1783, and all their Children and their Descendants by either sex, are to be distinguished by the following Capitals, affixed to their names: U.E. Alluding to their great principle The Unity of the Empire.[50]
The postnominals "U.E." are rarely seen today, but the influence of the Loyalists on the evolution of Canada remains. Their ties to Britain and their antipathy to the United States provided the strength needed to keep Canada independent and distinct in North America. The Loyalists' basic distrust of republicanism and "mob rule" influenced Canada's gradual path to independence. The new British North American provinces of Upper Canada (the forerunner of Ontario) and New Brunswick were founded as places of refuge for the United Empire Loyalists.
In an interesting historical twist Peter Matthews, a son of Loyalists, participated in the Upper Canada Rebellion which sought relief from oligarchic British colonial government and pursued American-style Republicanism. He was arrested, tried and executed in Toronto, and later became heralded as a patriot to the movement which led to Canadian self governance.
The wealthiest and most prominent Loyalist exiles went to Great Britain to rebuild their careers; many received pensions. Many Southern Loyalists, taking along their slaves, went to the West Indies and the Bahamas, particularly to the Abaco Islands.
Many Loyalists brought their slaves with them to Canada (mostly to areas that later became Ontario and New Brunswick) where slavery was legal. An imperial law in 1790 assured prospective immigrants to Canada that their slaves would remain their property.[51]
Thousands of Iroquois and other Native Americans were expelled from New York and other states and resettled in Canada. The descendants of one such group of Iroquois, led by Joseph Brant (Thayendenegea), settled at Six Nations of the Grand River, the largest First Nations reserve in Canada. (The remainder, under the leadership of Cornplanter (John Abeel) and members of his family, stayed in New York.) A group of African-American Loyalists settled in Nova Scotia but emigrated again for Sierra Leone after facing discrimination there.
Benjamin Thompson (Count Rumford) was a Loyalist who fled to London when the war began. He became a scientist noted for pioneering thermodynamics and for his research on artillery ordnance. He expressed a desire to return to the United States in 1799 and was eagerly sought by the Americans (who needed help in fighting the Quasi-War with France). Rumford eventually decided to stay in London because he was engrossed with establishing the Royal Institution in England.[52]
Many of the Loyalists were forced to abandon substantial properties to America restoration of or compensation for these lost properties was a major issue during the negotiation of the Jay Treaty in 1794. The British Government eventually settled several thousand claims for more than 3.5 million Pounds Sterling, an enormous sum of money worth 500 million Pounds (by a factor of 141) in 2017 inflation adjusted.
Return of some expatriates
The great majority of Loyalists never left the United States; they stayed on and were allowed to be citizens of the new country. Some became nationally prominent leaders, including Samuel Seabury first Bishop of the Episcopal Church and Tench Coxe. There was a small, but significant trickle of returnees who found life in Nova Scotia and New Brunswick too difficult. Perhaps 10% of the refugees to New Brunswick returned to the States as did an unknown number from Nova Scotia, Christopher Moore, The Loyalists, Revolution, Exile, Settlement, 1984, pp. 244-252 ISBN 0-7710--6093-9. Some Massachusetts Tories settled in the Maine District. Nevertheless, the vast majority never returned (hundreds of thousand of their descendants did from 1870 to 1930 and beyond). Captain Benjamin Hallowell, who as Mandamus Councilor in Massachusetts served as the direct representative of the Crown, was considered by the insurgents as one of the most hated men in the Colony, but as a token of compensation when he returned from England in 1796, his son was allowed to regain the family house.[53]
Alexander Hamilton enlisted the help of the Tories (ex-Loyalists) in New York in 1782–85 to forge an alliance with moderate Whigs to wrest the State from the power of the Clinton faction. Moderate Whigs in other States who had not been in favor separation from Britain but preferred a negotiated settlement which would have maintained ties to the Mother Country mobilized to block radicals. Most States had rescinded anti-Tory laws but 1787, although the accusation of being a Tory was heard for another generation. Several hundred who had left for Florida returned to Georgia in 1783-84. South Carolina which had seen a bitter bloody internal civil war in 1780-82 adopted a policy of reconciliation that proved more moderate than any other state. About 4500 white Loyalists left when the war ended, but the majority remained behind. The state government successfully and quickly reincorporated the vast majority. During the war, pardons were offered to Loyalists who switched sides and joined the Patriot forces. Others were required to pay a 10% fine of the value of the property. The legislature named 232 Loyalists liable for confiscation of their property, but most appealed and were forgiven.[54] In Connecticut much to the disgust of the Radical Whigs the moderate Whigs were advertising in New York newspapers in 1782-83 that Tories who would make no trouble would be welcome on the grounds that their skills and money would help the State's economy. The Moderates prevailed. All anti-Tory laws were repealed in early 1783 except for the law relating to confiscated Tory estates: "...the problem of the loyalists after 1783 was resolved in their favor after the War of Indepedence ended." In 1787 the last of any discriminatory laws were rescinded, Oscar Zeichner, The Rebalitation of Loyalists in Connecticut, The New England Quarterly, Vol 11, no 2, 1938, pp. 308-330. Much to the disgust of the Whigs the Tories took control of the Delaware Legislature in the 1780s.
Impact of the departure of Loyalist leaders
The departure of so many royal officials, rich merchants and landed gentry destroyed the hierarchical networks that had dominated most of the colonies. A major result was that a Patriot/Whig elite supplanted royal officials and affluent Tories.[55] In New York, the departure of key members of the De Lancey, De Peyster, Walton and Cruger families undercut the interlocking families that largely owned and controlled the Hudson Valley. Likewise in Pennsylvania, the departure of powerful families—Penn, Allen, Chew, Shippen—destroyed the cohesion of the old upper class there. Massachusetts passed an act banishing forty-six Boston merchants in 1778, including members of some of Boston's wealthiest families. The departure of families such as the Ervings, Winslows, Clarks, and Lloyds deprived Massachusetts of men who had hitherto been leaders of networks of family and clients. The bases of the men who replaced them were much different. One rich Patriot in Boston noted in 1779 that "fellows who would have cleaned my shoes five years ago, have amassed fortunes and are riding in chariots." New men became rich merchants but they shared a spirit of republican equality that replaced the former elitism.[56]
The Patriot reliance on Catholic France for military, financial and diplomatic aid led to a sharp drop in anti-Catholic rhetoric. Indeed the king replaced the pope as the demon Patriots had to fight against. Anti-Catholicism remained strong among Loyalists, some of whom went to Canada after the war most remained in the new nation. By the 1780s, Catholics were extended legal toleration in all of the New England states that previously had been so hostile. "In the midst of war and crisis, New Englanders gave up not only their allegiance to Britain but one of their most dearly held prejudices."[57]
Loyalists in art
- John Singleton Copley painted many prominent Loyalists and produced an oil-on-canvas depiction of a soldier wearing the uniform of the Royal Ethiopian Regiment (a regiment composed of black Loyalist soldiers) in The Death of Major Pierson (1784).[58]
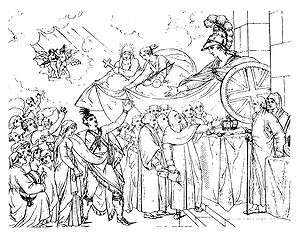
- Benjamin West characterized the ethnic and economic diversity of the Loyalists in his Reception of the American Loyalists by Great Britain in the Year 1783.[59] The original painting was lost, but a smaller version of it can be seen in the background of West's portrait of John Eardley Wilmot.[60]
- Gilbert Stuart painted a portrait of James DeLancey around 1785. It stays in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art, a bequest of his descendant George DeLancey Harris, Jr. of New York City &Annapolis Royal, NS.[61]
 John Copley's "The Death of Major Pierson"
John Copley's "The Death of Major Pierson" Benjamin West's "John Eardley Wilmot"
Benjamin West's "John Eardley Wilmot"
Loyalists in literature
- The Adventures of Jonathan Corncob, Loyal American Refugee (1787) by Jonathan Corncob. According to Maya Jasanoff, "traveling to London to file a claim served as the opening gambit" for this "picaresque novel about the American Revolution".[62][63][64]
- "Rip Van Winkle" (1819), short story by Washington Irving[65]
- The Spy: a Tale of the Neutral Ground (1821), novel by James Fenimore Cooper
- Oliver Wiswell (1940), a novel by Kenneth Roberts
- The Book of Negroes (2007) by Lawrence Hill
- The Fort (2010), novel by Bernard Cornwell
Notable Loyalists
A
- Samuel Adams (1730–1810), Vermont physician; not related to Samuel Adams, the Patriot leader in Boston
- Rev. H. Addison of Maryland, forbidden to ever live in his home state after the Revolution[66]
- Rev. John Agnew (d. 1812, New Brunswick), served a Church of England parish in Suffolk, Virginia[67]
- Samuel Aikens, land grant dated 2 June 1785 Guysborough, Nova Scotia, Canada
- Andrew Allen (1740–1825), Pennsylvanian Delegate to the Second Continental Congress
- Isaac Allen (d. 1806 age 65), Trenton, New Jersey attorney indicted for treason[68]
- William Allen (1704–1780), Chief Justice of Pennsylvania and former mayor of Philadelphia[69]
- Rev. Samuel Andrews (d. 1812 age 82), fled from his Patriot Church of England parishioners and died in New Brunswick[70]
- Samuel Andrews of North Carolina, major in the Loyal Militia[71]
- Brigadier General Benedict Arnold (January 14, 1741 [O.S. January 3, 1740/1741] – June 14, 1801), commissioned in 1780; originally a Patriot general
- Oliver Arnold, Connecticut native and Yale graduate; relocated to Sussex, New Brunswick where he served as the local vicar[72]
- John Askin (1739–1815), trader and land speculator at Detroit
B
- John Bacon (died 1783), New Jersey privateer and marauder who preyed on Patriots in and around the Pine Barrens and South East New Jersey
- Thomas Henry Barclay (1753–1830), New York City lawyer and later Governor of Nova Scotia
- Dr. Richard Bayley (1745–1801), New York physician and father of American-born saint Elizabeth Ann Seton
- Rev. John Beardsley (1732–1809), Anglican minister in Poughkeepsie, New York and Fishkill, New York who, in 1778, he served as chaplain to Beverley Robinson's Loyal American Regiment[73]
- Joseph Bettys, resident of the Town of Ballston, New York; hanged as a spy in 1782[74]
- Christopher Billopp (c. 1738 – March 29, 1827), Staten Island resident who commanded a Tory detachment
- Sampson Salter Blowers (March 10, 1742 – October 25, 1842), Boston, Massachusetts attorney
- Amos Botsford (1744–1812), Yale College graduate and judge
- Jonathan Boucher (1738–1804), Church of England priest in Maryland and Virginia and tutor to John Parke Custis, the stepson of George Washington[75][76]
- William Augustus Bowles (1763–1805), also known as Estajoca, served with the Maryland Loyalist Battalion and was a Maryland-born English adventurer and organizer of Native American attempts to create their own state outside of Euro-American control.[77][78][79]
- Joseph Brant Thayendenegea (1743–1807), Mohawk war leader
- Molly Brant (c.1736–1796), also known as Mary Brant, Konwatsi'tsiaienni, and Degonwadonti; influential Mohawk leader and sister of Joseph Brant
- Thomas Brown (1750–1825), LTC commanding King's Rangers in Georgia[80]
- Brigadier General Montfort Browne (fl. 1760–1780), commanding Prince of Wales American Regiment, 1777
- William Bull II (1710–1791), lieutenant governor of the province of South Carolina, 1759–1775
- Colonel John Butler (1728–1796), commanded Butler's Rangers in the Mohawk Valley[81]
- Walter Butler (1752–1781), Captain in Butler's Rangers; son of John Butler[82]
- Rev. Mather Byles (1706–1788), Harvard graduate and prominent Boston clergyman
C
- William Caldwell (c. 1750–1822), Scots-Irish who served in Butler's Rangers
- Benedict Swingate Calvert (ca. 1730 to 1732–1788), Judge of the Land Office, Maryland
- Elizabeth Calvert (1731 – 1788), wife and cousin of Loyalist politician Benedict Swingate Calvert
- Rev. John Camm (1718–1778), seventh president of the College of William and Mary
- Lt. Col. James Chalmers (d. 1806), Commander, First Battalion of Maryland Loyalists; author of anti-"Common Sense" pamphlet "Plain Truth" in 1776[83]
- Dr. Benjamin Church (1734–disappeared at sea 1778), Director Medical General Patriot Army and a Loyalist spy
- Richard Clarke (1711–1795), Boston merchant
- Christian Daniel Claus (1727–1787), commissioner of Indian affairs
- Col. Daniel Clary, Reg. Dutch Fork Militia, 96 Brigade, South Carolina 1773–1783
- Cheney Clow (1734–1788), Delaware plantation owner; served earlier as a British officer; involved in an act of hostility on April 18, 1778 which is known today as Cheney Clow's Rebellion
- Sir Isaac Coffin, 1st Baronet (1759–1839), Royal Navy officer and member of a prominent Massachusetts Loyalist family
- Nathaniel Coffin, Receiver-General of HM Customs of Boston at the time of the Boston Tea Party[84]
- John Connolly (c.1741–1813), planned with Lord Dunmore to raise a regiment of Loyalists and Indians in Canada called the Loyal Foresters and lead them to Virginia to help Dunmore put down the rebellion
- Myles Cooper (1735–1785), Church of England clergyman President of King's College in New York City[85]
- John Singleton Copley (1738–1815), innovative painter
- Brigadier General Robert Cunningham (died in Nassau in 1813 age 74), in 1780 in command of a garrison in South Carolina[86]
- William Cunningham (d. 1787, Nassau, Bahamas), earned the name ″Bloody Bill″ for his exploits against Backcountry South Carolina Patriots[87]
D
- James De Lancey (1746–1804), of Westchester County, New York, led a Loyalist unit known as "De Lancey's Cowboys" and was known as the "Outlaw of the Bronx"
- Brigadier General Oliver De Lancey (1718–1785), commanded De Lancey's Brigade 1776[88]
- Stephen De Lancey (1738–1809), Loyalist lawyer and political figure in New York state and Nova Scotia
- Abraham DePeyster, Officer of King's American Regiment[89]
- Colonel Arent DePeyster (1736–1822), Officer of the 8th Regiment of Foot
- Colonel Andrew Deveaux (1758–1812), Colonel in South Carolina Loyalist militia[90]
- Doan Outlaws, fallen Pennsylvania Quaker family of British spies and bandits[91]
- Margaret Green Draper (1727–ca. 1804), Boston printer and journalist; one of the first American women to run an independent business; United Empire Loyalist; supported the British
E
- Sir Robert Eden, 1st Baronet, of Maryland (ca. 1741–1784), Provincial Governor of Maryland and last Royal Governor of Maryland[92]
- Samuel Ogden Edison, grandfather of Thomas Edison
- Jacob Ellegood (1742–1801), Virginia-born farmer who became a political figure in early New Brunswick
F
- Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron (1693–1781), of Virginia; the only British peer resident in Colonial America[93]
- David Fanning (1755–1825), commander of militia in North Carolina, and later Member of the Legislative Assembly of New Brunswick, 1791–1801
- Edmund Fanning (1739–1818), commanded militia in the War of the Regulation and Loyalist militia in the American Revolution; later Lieutenant Governor of Nova Scotia and Saint John's Island[94]
- David Farnsworth (d. 1778), British agent hanged for his participation in a plot to undermine the American economy by distributing counterfeit currency
- Elizabeth Graeme Fergusson, Loyalist who wrote poems lamenting her husband's desertion of her; these shared the grief of herself and other women left behind
- William Franklin (ca. 1730–1813), Governor of New Jersey; son of Benjamin Franklin
- Rebecca Franks (1760–1823), prominent member of Loyalist society in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania during the American Revolution
- Shaddrick Furman, a Virginia free black; guide and information source for British troops; upon his capture by Patriots, he was beaten and blinded; received a pension of £18 per year for life from the Loyalist Claims Commission[95]
G
- Grace Growden Galloway (1727–1783), Loyalist who documented her fight for property rights
- Joseph Galloway (1731–1803), Member of the Pennsylvania Provincial Assembly[96]
- Micajah Ganey (1756–1830), Loyalist leader of the Pee Dee defeated by Francis Marion[97]
- Alexander Garden (1720–1791), Scottish-born naturalist who lived in Charles Town, South Carolina until fleeing to London in 1783
- Dr. Silvester Gardiner (1708–1786), Massachusetts physician, visionary land developer; in 1774 added his name to a letter addressed to Massachusetts Royal Governor Thomas Hutchinson, affirming his allegiance to the Loyalist cause
- David George (ca. 1743–1810), African-American Baptist preacher and a Black Loyalist from the American South who escaped to British lines in Savannah, Georgia; later accepted transport to Nova Scotia and land there; eventually resettled in Freetown, Sierra Leone
- Abraham Gesner (1756–1851), served with the King's Orange Rangers during the American Revolution; purchased a commission of major in the British Army
- Simon Girty (1741–1818), British liaison with the Indians
- Harrison Gray (1711–1794), wealthy merchant; Treasurer and Receiver-General for the Province of Massachusetts Bay
- Joseph Gray (1729–1803), Boston, Massachusetts Loyalist and progenitor of noted Canadian family[98]
H
- John Hamilton (died 1816), commander of the Royal North Carolina Regiment, later British consul in Norfolk, Virginia[99]
- Reuben Hankinson, Ensign, First New Jersey Volunteers, September 1780[100]
- Harpe brothers, North Carolina bandits and allegedly America's first serial killers
- Joseph Harris, runaway mulatto slave of Henry King, of Hampton, Virginia; smuggled supplies for the British[101]
- John Howe (1754–1835), printer of the Massachusetts Gazette and Boston Weekly News-Letter[102]
- Thomas Hutchinson (1711–1780), last royal Governor of Massachusetts
I
- Charles Inglis (1734–1816), first Bishop of the Anglican Diocese of Nova Scotia[103]
- Ralph Inman (1713–1788), Boston, Massachusetts merchant[104]
J
- Samuel Jarvis (1720–1780), Stamford, Connecticut official forced out of office due to his Loyalism; father of William Jarvis
- William Jarvis (1756–1817), New Yorker who served in the Queen's Rangers
- Edward Jessup (1735–1816), Colonel of Jessup's Loyal Rangers near Albany, New York; and his brothers Ebenezer and Joseph
- Sir John Johnson (1741–1820), commander of the King's Royal Regiment of New York
- Capt. Joseph Jones, while serving under Micajah Ganey's command, led a band of raiders who hanged Patriot Col. Abel Kolb in front of his wife and children, although they had just promised him his safety as a prisoner of war[105][106]
- Thomas Jones (1731–1792), Recorder of New York City, 1769–1773; historian who authored History of New York During the Revolutionary War and of the Leading Events in the Other Colonies at That Period; fled to Britain and died in Hoddesdon, Hertfordshire
K
- Boston King (ca. 1760–1802), Black Loyalist; settled in Nova Scotia and later emigrated to Sierra Leone, where he helped found Freetown and became the first Methodist missionary to African indigenous people
L
- John Lawrence (1708/9–1791), surveyor who ran the Lawrence Line between East and West Jersey; jailed, despite his age, for espousing support of the Crown[107]
- Elisha Leavitt (1714–1790), Hingham, Massachusetts merchant and landowner
- Nicholas Lechmere, Newport, Rhode Island Officer of the Customs[108]
- Sir Egerton Leigh, 1st Baronet (1733–1781), South Carolina colonial official[109]
- Daniel Leonard (1740–1829), son of a Taunton, Massachusetts Patriot; later served as the Chief Justice of the Bermudas[110]
- John Lovell, Headmaster of the Boston Latin School[111]
- Isaac Low (1735–1791), delegate for New York to the First Continental Congress in 1774 and to New York Provincial Congress; first President of the New York Chamber of Commerce[112]
- Gabriel Ludlow, New York merchant
- George Ludlow, New York judge
M
- David Mathews, Princeton University graduate and Mayor of New York City; subsequent administrator of Cape Breton, Nova Scotia
- William McCormick (1742–1815), North Carolina merchant[113]
- Colonel Alexander McKee (ca. 1735–1799), liaison between the British and the Shawnees
- Benjamin Milliken, founder of Ellsworth Maine, mill and ship owner
- James Moody, Lieutenant, First New Jersey Volunteers, March 1781[114]
- Benjamin Moore (1748–1816), Assistant Rector of Trinity Church, New York City; his son Clement composed "A Visit from St. Nicholas", which later became famous as "'Twas the Night Before Christmas"[115]
- John Murray, Representative to the Great and General Court of the Province of Massachusetts Bay
N
- Peter Nagle, Continental soldier sentenced to death in 1777 for attempting to join the Loyalist forces[116]
O
- Rev. Jonathan Odell (1737–1818), New Jersey Anglican clergyman and Loyalist poet
- David Ogden (1707–1800), New Jersey Council member and Judge of the Supreme Court; brother to Robert Ogden[117]
- Robert Ogden, Speaker of the New Jersey House of Assembly; member of the Stamp Act Congress[118]
- Peter Oliver (1713–1791), Massachusetts judge briefly satirized in "McFingal"[119]
P
- William Parker (d. 1781 age 77), Portsmouth, New Hampshire Judge of the Superior Court[120]
- Richard Pearis (1725–1794), Indian trader and pioneer settler of Upstate South Carolina
- Frederick Philipse III (1720–1786), militia colonel and politician in New York; last lord of Philipsburg Manor
- Josiah Phillips (d. 1778), led a band of Tories, commissioned by Lord Dunmore, who upon capture was executed[121]
R
- John Randolph (1727–1784), King's Attorney for Virginia[122]
- Anna Rawle, Loyalist who used letter-diaries to spy and transfer information about rebels in Pennsylvania to Loyalists in New York
- James Rivington (1734–1802), Loyalist editor of Rivington Gazette; Patriot spy
- Colonel Beverley Robinson (1723–1792), of New York, Loyal American Regiment[123][124]
- Lieutenant-Colonel Robert Rogers (1731–1795), commander of Rogers' Rangers/Queen's Rangers to 1777 (now The Queen's York Rangers (1st American Regiment) (RCAC)), innovator of ranging tactics
S
- Peggy Shippen (1760–1804), Philadelphia socialite and second wife of Benedict Arnold
- John Graves Simcoe (1752–1806), commander of Queen's Rangers from 1777 (now The Queen's York Rangers (1st American Regiment) (RCAC)); founding Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada (today the Province of Ontario, Canada)
- James Simpson (1737–1815), Attorney General of Colonial South Carolina; buried in the Temple Church, London[125][126]
- Philip Skene (1725–1810), colonial New York "patroon" and British officer, of Scottish birth
- Brigadier Cortlandt Skinner (1727–1799), commanded New Jersey Volunteers, September 4, 1776
- Lieutenant-Colonel William Stark (1724–1776), of New Hampshire; brother of John Stark, a major general in the Continental Army
- George H. Steuart (1700–1784), planter; Judge of the Land Office, Maryland
- Duncan Stewart (d. 1793), New London, Connecticut Royal Collector of the Customs[127]
- Joel Stone (1749–1833), Connecticut merchant who helped Loyalists escape to British-controlled part of the Colonies, including David Mathews
T
- John Taylor, Captain, First New Jersey Volunteers, January 1781
- Sir Benjamin Thompson (Count Rumford) (1753–1814), of Massachusetts, Royal official and scientist
- Consider Tiffany (1732–1796), Connecticut storekeeper and sergeant during the French and Indian War[128]
- William Tryon (1729–1788), Royal Governor of North Carolina[129]
V
- Philip Van Cortlandt (1739–1814), New York-born Major of the Third Battalion of New Jersey Volunteers[130]
- Peter van Schaack (March 1747 – 17 September 1832), New York lawyer
- John Vardill (July 5, 1749 – January 16, 1811), New York City-born British spy, clergyman, educator, pamphleteer, playwright, and poet
W
- Sir John Wentworth, 1st Baronet (1737–1820), last Royal Governor of New Hampshire at the time of the American Revolution; Lieutenant-Governor of Nova Scotia[131]
- Robert Winthrop (1764–1832), descendant of John Winthrop; Vice Admiral in the British Navy, residing in England[132]
- Charles Woodmason (ca. 1720–1789), Church of England missionary in South Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland, diarist, poet, and corresponding member of the Royal Society of Arts, London.[133][134] He authored an article published (under the pseudonym "Sylvanus") in the South Carolina Gazette and Country-Journal on March 28, 1769 chiding the local Patriot leaders for hypocrisy and asked pointedly how they could justly complain of "No taxation without representation!" regarding Acts of Parliament, while these very same powerful men denied the Carolina Backcountry any representation in South Carolina's Assembly, yet expected them to pay taxes passed by that body.[135]
- Gov. James Wright (1716–1785), last Royal Governor of Georgia, buried in Westminster Abbey
X, Y, Z
- John Joachim Zubly (1724–1781), Reformed minister and delegate from Georgia to the Continental Congress[136]
See also
- American Revolution - Nova Scotia theatre
- Loyalists in the American Revolution
- Expulsion of the Loyalists
- List of places named for Loyalists (American Revolution)
- Frederick Haldimand (1718–1791) while serving in Canada amassed a huge collection filling 115 microfilm reels of documents, letters, etc. reflecting the Loyalist experience in Canada. A partial finding aid to this collection may be found on the Queens University Archives website.
- Godfrey–Milliken Bill, proposed Canadian law demanding compensation from the U.S. for Loyalist claims after U.S. independence.
- Lorenzo Sabine (1803–1877), early historian and chronicler of the Loyalist experience
- Martin v. Hunter's Lessee
- Maryland Loyalists Battalion
- Tory
- Treaty of Paris (1783)
- United Empire Loyalist
References
- ↑ Barbara Smith (2013). The Freedoms We Lost: Consent and Resistance in Revolutionary America. New Press. p. 142.
- ↑ Jack P. Greene and J. R. Pole, eds, A Companion to the American Revolution (2004) pp. 246, 399, 641–2
- ↑ Calhoon, "Loyalism and neutrality", p. 235; Middlekauff (2005) pp. 563–564; Thomas B. Allen, Tories: Fighting for the King in America's First Civil War (2010) p. xx
- ↑ Andrews, p.284
- ↑ Jassanoff, ch 1
- ↑ Leonard Woods Larabee, Conservatism in Early American History (1948) pp 164–65
- ↑ See also N. E. H. Hull, Peter C. Hoffer and Steven L. Allen, "Choosing Sides: A Quantitative Study of the Personality Determinants of Loyalist and Revolutionary Political Affiliation in New York," Journal of American History, (1978) 65#2 pp. 344–366 in JSTOR
- ↑ Edwin G. Burrows and Michael Wallace, "The American Revolution: The Ideology and Psychology of National Liberation," Perspectives in American History, (1972) vol. 6 pp 167–306
- ↑ Mark Jodoin. Shadow Soldiers of the American Revolution: Loyalist Tales from New York to Canada. 2009. ISBN 978-1-59629-726-5. The History Press, Charleston, SC.
- ↑ Hull, Hoffer and Allen, "Choosing Sides (1978), p, 352
- ↑ Hull, Hoffer and Allen, "Choosing Sides (1978), pp 347, 354, 365
- ↑ Wilson, Bruce G. "Loyalists".
- ↑ "Loyalists During the American Revolutionary War: What Happened to Them?". Bright Hub Education.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2013-05-15. Retrieved 2013-03-11.
- ↑ "Lord Dunmore's Ethiopian Regiment - The Black Past: Remembered and Reclaimed". www.blackpast.org.
- ↑ lindann8 (16 October 2012). "Patriots loyalists powerpoint 2".
- ↑ "Loyalists". George Washington's Mount Vernon.
- ↑ "The Loyalists".
- ↑ Calhoun (1973)
- ↑ Georgia Encyclopædia.
- ↑ Robert M. Calhoon, in 'A companion to the American Revolution' (2000); p 235.
- ↑ John Adams has sometimes been cited as having claimed, in an 1813 letter, that one-third of Americans supported the revolution and one-third were against. However, the passage in question actually refers to the French Revolution of 1789. Robert D. Marcus (1971). The American Scene: Varieties of American History. p. 147. See also "Only 1/3 of Americans Supported the American Revolution?", by William Marina. 6-28-2004. Retrieved on July 14, 2008.
- ↑ Ray Raphael (2012). A People's History of the American Revolution. The New Press. p. 393.
- ↑ Paul H. Smith, "The American Loyalists: Notes on Their Organization and Numerical Strength," William and Mary Quarterly (1968) 25#2 pp. 259–277 in JSTOR
- ↑ Middlekauff, Robert. The Glorious Cause: The American Revolution, 1763–1789 (1985), p 550.
- 1 2 3 Calhoon (1973)
- ↑ See online NPS.gov
- ↑ Louis P. Masur (1989). Rites of Execution: Capital Punishment and the Transformation of American Culture, 1776-1865. Oxford UP. p. 75.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-11-17. Retrieved 2007-10-17.
- 1 2
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Tillman, Kacy Dowd (2016). "Women Left Behind: Female Loyalism, Coverture, and Grace Growden Galloway's Empire of Self". Women's Narratives of the Early Americas and the Formation of Empire. New York City, NY: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 142, 143, .
- ↑ Baxter, Beverly (1978). "Grace Growden Galloway". Frontiers: A Journal of Women Studies. 62.
- ↑ Aptheker, Herbert (1960). The American Revolution, 1763–1783. International Publishers Co. p. 169. ISBN 0-7178-0005-9.
- ↑ Mason Wade, The French Canadians (1955) 1:67–9.
- ↑ George Rawlyck, A People Highly Favoured Of God. The Nova Scotia Yankees. And the American Revolution (Toronto: 1972)
- ↑ Philip Buckner and John G Reid, eds. The Atlantic Region to Confederation: A History (1995) pp 168–170
- ↑ J.B. Brebner, The Neutral Yankees of Nova Scotia (1937)
- ↑ Smith 264–7.
- ↑ Calhoon 502.
- ↑ Smith, p 267
- ↑ Wilson, David. The Southern Strategy (University of South Carolina Press. 2005.)
- ↑ Selby, John E; Higginbotham, Don (2007)
- 1 2 Brown, Wallace (1968). "The American Farmer during the Revolution: Rebel or Loyalist?". Agricultural History. 42 (4): 331.
- ↑ However Philip Ranlet estimates that only 20,000 adult white Loyalists went to Canada. "How Many American Loyalists Left the United States?." Historian 76.2 (2014): 278-307.
- ↑ Maya Jasanoff (2012). Liberty's Exiles: American Loyalists in the Revolutionary World. Random House. p. 357.
- ↑ Lohrenz (1998)
- ↑ The Canadian Encyclopedia, "Loyalists"; and Liberty's Exiles, Maya Jasanoff, pp. 206–208.
- ↑ Neil MacKinnon, This Unfriendly Soil: The Loyalist Experience in Nova Scotia, 1783–1791 (1989)
- ↑ S.D. Clark, Movements of Political Protest in Canada, 1640–1840 (1959), pp. 150–51
- ↑ Boudreau, Claire; Cogné, Daniel; Vachon, Auguste (1998). Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress of Genealogical and Heraldic Sciences in Ottawa from August 18 to 23, 1996. University of Ottawa Press. p. 202.
|access-date=requires|url=(help) - ↑ Patrick Bode, "Upper Canada, 1793: Simcoe and the Slaves." Beaver 1993 73(3): 17–19
- ↑ Bradley 1974
- ↑ "Jamaica Plain Historical Society - 'Colonial Era' Editor - - Capt Benjamin Hallowell Homestead". www.jphs.org. Archived from the original on 2008-09-04.
- ↑ Rebecca Brannon, From Revolution to Reunion: The Reintegration of the South Carolina Loyalists (Univ of South Carolina Press, 2016).
- ↑ The Forging of the New Nation, 1781-1789, Robert B. Morris, 1987, p. 163.
- ↑ Gordon S. Wood (1992). The Radicalism of the American Revolution. Random House. pp. 176–177.
- ↑ Francis Cogliano, No King, No Popery: Anti-Catholicism in Revolutionary New England (1995) pp 154-55, quote p 155. online
- ↑ "Black Loyalists in New Brunswick, 1783-1854: 'The Death of Major Peirson', John Singleton Copley". atlanticportal.hil.unb.ca.
- ↑ Allen, Thomas. "Tories: Fighting for the King in America's First Civil War". www.toriesfightingfortheking.com.
- ↑ "Black Loyalists in New Brunswick, 1783-1854: 'John Eardley Wilmot' by Benjamin West". atlanticportal.hil.unb.ca.
- ↑ "Gilbert Stuart - James DeLancey". The Metropolitan Museum of Art.
- ↑ Maya Jasanoff (2011), p, 386, n. 67.
- ↑ Davidson, Cathy N. (30 September 2004). "Revolution and the Word: The Rise of the Novel in America". Oxford University Press, USA – via Google Books.
- ↑ Perrin, Noel (8 June 1988). "A Reader's Delight". UPNE – via Google Books.
- ↑ "Rip Van Winkle Summary - eNotes.com". eNotes.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 154.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 154–155.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 159.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 157–158.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 165.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 165-166.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 184.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 222-223.
- ↑ Stone, William Leete (1838). Life of Joseph Brant, Thayendanegea. New York: George Dearborn & Co. pp. 210–-214. Retrieved December 11, 2015.
- ↑ Anne Y. Zimmer. Jonathan Boucher, loyalist in exile. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University Press, 1978.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 240–241.
- ↑ Maya Jasanoff (2011), pp. xiv–xv,234–242, 321–323, 348.
- ↑ J. Leitch Wright. William Augusutus Bowles: Director General of the Creek Nation. Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 1967.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 245-246.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 260–265.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 278–280.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 280.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 301.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 323–324.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 335.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 346–347.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 348-349.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 363–366.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 372–374.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 377–378.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 381–383.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 402.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 408–412.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 417–418.
- ↑ Jasanoff (2011), pp. 127–128, 138.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 453–457.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 458.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 489–490.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 511-512.
- ↑ "Hankinson Online: An Online Resource for Hankinson Genealogy". www.hankinsononline.com.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 519.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 548–550.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, pp. 563-565.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 566.
- ↑ Alexander Gregg. History of the Old Cheraws. New York: Richardson and Co., 1867, pp. 359–364.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 1, p. 595.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 2.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 8.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 9–10.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 10–12.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 29–30.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 32–33.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 55.
- ↑ "Historical Biographies, Nova Scotia, 1800-1867". www.blupete.com.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 88-100.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 118.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 123-126.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 123.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 128-129.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 148.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 184-185.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 208–209.
- ↑ Maya Jasanoff (2011), pp. xi, 34–36, 93–94, 123–125, 131, 134, 143, 313.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 221–225.
- ↑ An exercise in futility: the pre-Revolutionary career and influence of loyalist James Simpson by James Riley Hill, III. M. A. Thesis. University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, 1992. viii, 109 leaves ; 28 cm. OCLC 30807526
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 302.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, p. 331.
- ↑ Connecticut Births and Christenings 1649-1906. Consider Tiffany, 15 Mar 1732; citing; FHL microfilm.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 364–366.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 376–377.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 410–413.
- ↑ Stark, James. The loyalists of Massachusetts and the other side of the American Revolution. Boston, 1910, pages 426-429.
- ↑ Richard J. Hooker, ed. The Carolina Backcountry on the Eve of the Revolution: The Journal and Other Writings of Charles Woodmason, Anglican Itinerant. 1953.
- ↑ Joseph R. Gainey. "Rev. Charles Woodmason (c. 1720–1789): Author, Loyalist, Missionary, and Psalmodist." West Gallery: The Newsletter of the West Gallery Music Association, Issue No. 59 (Autumn 2011), pp. 18–25.
- ↑ South Carolina Gazette and Country-Journal in the March 28, 1769 issue (much abridged and heavily edited). The complete text is in Hooker, pp. 260–263.
- ↑ Sabine (1864), Vol. 2, pp. 466–468.
Further reading
- Allen, Thomas B. Tories: Fighting for the King in America's First Civil War. New York: HarperCollins, 2010. 496 pp. ISBN 9780061241819
- Andrews, Matthew Page, History of Maryland, Doubleday, New York (1929)
- Bailyn, Bernard. The Ideological Origins of the American Revolution (2nd ed. 1992) pp 230–319.
- ———. The Ordeal of Thomas Hutchinson: Loyalism and the Destruction of the First British Empire (1974), full scale biography of the most prominent Loyalist
- Brown, Wallace. The King's Friends: The Composition and Motives of the American Loyalist Claimants (1966).
- Calhoon, Robert M. "Loyalism and neutrality" in Jack P. Greene and J.R. Pole, eds., The Blackwell Encyclopedia of the American Revolution (1991); reprinted in Greene, Jack P.; Pole, J. R. (2008). A Companion to the American Revolution. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 235–47.
- Calhoon, Robert M. The Loyalists in Revolutionary America, 1760–1781 (1973), the most detailed scholarly study
- Calhoon, Robert M., Timothy M. Barnes and George A. Rawlyk, eds. Loyalists and Community in North America (1994).
- Chopra, Ruma. "Enduring Patterns of Loyalist Study: Definitions and Contours" History Compass (2013) 11#11 pp 983–993, DOI: 10.1111/hic3.12105
- Chopra, Ruma. Choosing Sides: Loyalists in Revolutionary America (2015)
- Doré, Gilbert. "Why The Loyalists Lost," Early America Review (Winter 2000) online, focus on ideology
- Jasanoff, Maya. Liberty's Exiles: American Loyalists in the Revolutionary World (2011), excellent comprehensive treatment and winner of the 2011 National Book Critics Circle Award for Non-Fiction and 2012 George Washington Book Prize
- Jensen, Merrill. The New Nation: A History of the United States during the Confederation, 1781–1789 1950; detailed discussion of return of Loyalists, popular anger at their return; repeal of wartime laws against them
- Kermes, Stephanie. "'I Wish for Nothing More Ardent upon Earth, than to See My Friends and Country Again': The Return of Massachusetts Loyalists." Historical Journal of Massachusetts 2002 30(1): 30–49. ISSN 0276-8313
- Kerber, Linda. Women of the Republic: Intellect and Ideology in Revolutionary America (1997)
- Knowles, Norman. Inventing the Loyalists: The Ontario Loyalist Tradition and the Creation of Usable Pasts (1997) explores the identities and loyalties of those who moved to Canada.
- Lambert, Robert Stansbury. South Carolina Loyalists in the American Revolution (2nd ed. Clemson University Digital Press, 2011). full text online free 273 pp
- Middlekauff, Robert. "The Glorious Cause: The American Revolution, 1763–1789." (2005 edition)
- Moore, Christopher. The Loyalist: Revolution Exile Settlement. Toronto: McClelland and Stewart (1994).
- Mason, Keith. "The American Loyalist Diaspora and the Reconfiguration of the British Atlantic World." In Empire and Nation: The American Revolution and the Atlantic World, ed. Eliga H. Gould and Peter S. Onuf (2005).
- Nelson, William H. The American Tory (1961)
- Norton, Mary Beth. The British-Americans: The Loyalist Exiles in England, 1774–1789. Boston, MA: Little, Brown, 1972.
- ———. Liberty's Daughters: The Revolutionary Experience of American Women, 1750–1800 (1996)
- ———. "The Problem of the Loyalist—and the Problems of Loyalist Historians," Reviews in American History June 1974 v.2 #2 pp 226–231
- Peck, Epaphroditus; The Loyalists of Connecticut Yale University Press, (1934) online
- Potter, Janice. The Liberty We Seek: Loyalist Ideology in Colonial New York and Massachusetts (1983).
- Quarles, Benjamin; Black Mosaic: Essays in Afro-American History and Historiography University of Massachusetts Press. (1988)
- Ranlet, Philip. "How Many American Loyalists Left the United States?." Historian 76.2 (2014): 278-307; estimates that only 20,000 adult white Loyalists went to Canada.
- Ryerson, Egerton. The Loyalists of America and Their Times: From 1620 to 1816. 2 volumes. Second edition. 1880.
- Smith, Paul H. "The American Loyalists: Notes on Their Organization and Numerical Strength," William and Mary Quarterly 25 (1968): 259–77. in JSTOR
- Van Tyne, Claude Halstead. The Loyalists in the American Revolution (1902) online
- Wade, Mason. The French Canadians: 1760–1945 (1955) 2 vol.
Compiled volumes of biographical sketches
- Palmer, Gregory. Biographical Sketches of Loyalists of the American Revolution. Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc., 1983. 998 pp. ISBN 9780313281020
- Sabine, Lorenzo. The American Loyalists, or Biographical Sketches of Adherents to the British Crown in The War of the Revolution; Alphabetically Arranged; with a Preliminary Historical Essay. Boston, MA: Charles C. Little and James Brown, 1847. Google Book vi, 733 pp.
- ———. Biographical Sketches of Loyalists of the American Revolution, with an Historical Essay. 2 volumes. Boston, MA: Little, Brown and Company, 1864. Google Book Volume 1—vi, 608 pp. Google Book Volume 2—600 pp.
Studies of individual Loyalists

- Gainey, Joseph R. "Rev. Charles Woodmason (c. 1720–1789): Author, Loyalist, Missionary, and Psalmodist." West Gallery: The Newsletter of the West Gallery Music Association ( ISSN 0960-4227), Issue No. 59 (Autumn 2011), pp. 18–25. This undocumented article is the first publication to identify Woodmason's parents, background, baptism, marriage, and burial dates and places and contains much previously unavailable information.
- Hill, James Riley, III. An exercise in futility: the pre-Revolutionary career and influence of loyalist James Simpson. M. A. Thesis. University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, 1992. viii, 109 leaves ; 28 cm. OCLC 30807526
- Hooker, Richard J., ed. The Carolina Backcountry on the Eve of the Revolution: The Journal and Other Writings of Charles Woodmason, Anglican Itinerant. 1953. ISBN 978-0-8078-4035-1
- Lohrenz, Otto; "The Advantage of Rank and Status: Thomas Price, a Loyalist Parson of Revolutionary Virginia." The Historian. 60#3 (1998) pp 561+. online
- Randall, Willard Sterne. A Little Revenge: Benjamin Franklin & His Son Little, Brown & Co, 1984.
- Skemp, Sheila. William Franklin: Son of a Patriot, Servant of a King Oxford University Press, 1990.
- Wright, J. Leitch. William Augusutus Bowles: Director General of the Creek Nation. Athens, GA: University of Georgia Press, 1967.
- Zimmer, Anne Y. Jonathan Boucher, loyalist in exile. Detroit, MI: Wayne State University Press, 1978.
Primary sources and guides to manuscripts and the literature
- Allen, Robert S. Loyalist Literature: An Annotated Bibliographic Guide to the Writings on the Loyalists of the American Revolution. Issue 2 of Dundurn Canadian historical document series, 1982. ISBN 9780919670617
- Brown, Wallace. "Loyalist Historiography." Acadiensis, Vol. 4, No. 1 (Autumn 1974), pp. 133–138. Link to downloadable pdf of this article.
- ———. "The View at Two Hundred Years: The Loyalists of the American Revolution", Proceedings of the American Antiquarian Society, Vol. 80, Part 1 (April 1970), pp. 25–47.
- Crary, Catherine S., ed. Price of Loyalty: Tory Writings from the Revolutionary Era (1973)
- Egerton, Hugh Edward, ed. The Royal commission on the losses and services of American loyalists, 1783 to 1785, being the notes of Mr. Daniel Parker Coke, M. P., one of the commissioners during that period. Oxford: The Roxburghe Club, 1915. Link to downloadable pdf
- Galloway, Joseph. The claim of the American loyalists: reviewed and maintained upon incontrovertible principles of law and justice. G. and T. Wilkie, 1788. Downloadable Google Book pdf 138 pages
- Guide to The Loyalist Collection website, Harriet Irving Library, Fredericton campus, University of New Brunswick, Canada
- Guide to the New York Public Library Loyalist Collection (19 pdfs)
- Palmer, Gregory S. A Bibliography of Loyalist Source Material in the United States, Canada, and Great Britain. Westport, CT, 1982.
- The Particular Case of the Georgia Loyalists: in Addition to the General Case and Claim of the American Loyalists, which was Lately Published by Order of Their Agents. February, 1783. n.p.:n.p., 1783. 16 pp. Google Book pdf
External links
- American Loyalists
- The American Loyalists: Or, Biographical Sketches of Adherents to the ... (1847) by Lorenzo Sabine. Complete text of the first of two editions (the second appeared in 1864 in two volumes) of Sabine's magnum opus in pdf format.
- Benjamin Franklin to Baron Francis Maseres, June 26, 1785 (Opinion of Benjamin Franklin on persons who called themselves "Loyalists", whom he judged better called "Royalists")
- Bibliography of the Loyalist Participation in the American Revolution compiled by the United States Army Center of Military History
- "Black Loyalists: Our History, Our People"
- Haldimand Collection The main source for historians in the study of the settlement of the American Loyalists in Canada. More than 20,000 letters and documents, now fully indexed, and free on the Web.
- Story of Loyalist Privateer "Vengence"
- James Chalmers and "Plain Truth" (A Loyalist Answers Thomas Paine)
- The Loyalist Declaration of Independence published in The Royal Gazette (New York) on November 17, 1781 (Transcription provided by Bruce Wallace and posted on The On-Line Institute for Advanced Loyalist Studies.)
- The Loyalist Link: The Forest and The Sea – Port Roseway Loyalists
- Loyalist Page – Cyndi's List
- The Loyalist Research Network (LRN) This website focuses on Canadian Loyalists, but, the links and bibliographies are extremely helpful to all serious Loyalist researchers.
- Maryland
- The On-Line Institute for Advanced Loyalist Studies
- "Remembering Black Loyalists, Black Communities in Nova Scotia"
- "Salem Loyalists-unpublished letters" THE NEW-ENGLAND HISTORICAL AND GEUEALOGICAL REGISTER AND ANTIQUARIAN JOURNAL 1872 pp.243-248
- "A Short History of the United Empire Loyalists" Ann Mackenzie
- South Carolina
- Lambert, Robert Stansbury (2011). South Carolina Loyalists in the American Revolution (2nd ed.). Clemson, SC: Clemson University Digital Press. External link in
|title=(help) Originally published in 1987. 272 pages, available online in PDF format. - United Empire Loyalists' Association of Canada (UELAC)
- Virginia
- “What is a Loyalist? The American Revolution as civil war” by Prof. Edward Larkin published in www.common-place.org, Vol. 8, No. 1 (October 2007).
- Why Were Some of Our Ancestors Tories?
Videos
- a lecture by Maya Jasanoff. "An Imperial Disaster? The Loyalist Diaspora after the American Revolution". youtube.
- Thomas B. Allen. "Video discussing his book". Tories: Fighting for the King in America's First Civil War.
- Thomas B. Allen. "Lecture on his book at the Library of Congress". Tories: Fighting for the King in America's First Civil War.
- YaleCourses YouTube (March 18, 2011). "Who Were the Loyalists? (Youtube video)". The American Revolution (HIST 116), Session 9 (of 25).
