Kufra (crater)
|
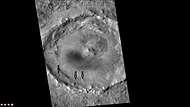
Kufra Crater Floor, as seen by HiRISE. Pits are thought to be caused by escaping water. | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 40°42′N 239°46′W / 40.7°N 239.77°WCoordinates: 40°42′N 239°46′W / 40.7°N 239.77°W |
| Diameter | 37.5 km |
| Eponym | Kufra, Libya |
Kufra is a crater in the Cebrenia quadrangle of Mars, located at 40.7° North and 239.77° West, the westernmost portion is inside Casius quadrangle. It is 37.5 kilometers in diameter and was named after a town in Libya.[1]
Nearby other craters are Rynok almost to the north, Chincoteague nearly to the east and Bacolor further south. To the south is Tinjar Vallis where the valley ends and west of the crater is the large Utopia Planitia where there are no major craters but some small craters.
Gullies
Gullies are visible on its wall. Martian gullies are small, incised networks of narrow channels and their associated downslope sediment deposits, found on the planet of Mars. They are named for their resemblance to terrestrial gullies. First discovered on images from Mars Global Surveyor, they occur on steep slopes, especially on the walls of craters. Usually, each gully has a dendritic alcove at its head, a fan-shaped apron at its base, and a single thread of incised channel linking the two, giving the whole gully an hourglass shape.[2] They are believed to be relatively young because they have few, if any craters. A subclass of gullies is also found cut into the faces of sand dunes which themselves considered to be quite young.
On the basis of their form, aspects, positions, and location amongst and apparent interaction with features thought to be rich in water ice, many researchers believed that the processes carving the gullies involve liquid water. However, this remains a topic of active research.
As soon as gullies were discovered,[2] researchers began to image many gullies over and over, looking for possible changes. By 2006, some changes were found.[3] Later, with further analysis it was determined that the changes could have occurred by dry granular flows rather than being driven by flowing water.[4][5][6] With continued observations many more changes were found in Gasa Crater and others.[7]
With more repeated observations, more and more changes have been found; since the changes occur in the winter and spring, experts are tending to believe that gullies were formed from dry ice. Before-and-after images demonstrated the timing of this activity coincided with seasonal carbon-dioxide frost and temperatures that would not have allowed for liquid water. When dry ice frost changes to a gas, it may lubricate dry material to flow especially on steep slopes.[8][9][10] In some years frost, perhaps as thick as 1 meter,
Images
 Kufra Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers.
Kufra Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers. Kufra Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers. Note: this is an enlargement of a previous photo.
Kufra Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Arrows indicate old glaciers. Note: this is an enlargement of a previous photo. Kufra Crater showing gullies, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Note: this is an enlargement of a previous photo.
Kufra Crater showing gullies, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Note: this is an enlargement of a previous photo.
See also
References
- ↑ http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/
- 1 2 Malin, M., Edgett, K. 2000. Evidence for recent groundwater seepage and surface runoff on Mars. Science 288, 2330–2335.
- ↑ Malin, M., K. Edgett, L. Posiolova, S. McColley, E. Dobrea. 2006. Present-day impact cratering rate and contemporary gully activity on Mars. Science 314, 1573_1577.
- ↑ Kolb, et al. 2010. Investigating gully flow emplacement mechanisms using apex slopes. Icarus 2008, 132-142.
- ↑ McEwen, A. et al. 2007. A closer look at water-related geological activity on Mars. Science 317, 1706-1708.
- ↑ Pelletier, J., et al. 2008. Recent bright gully deposits on Mars wet or dry flow? Geology 36, 211-214.
- ↑ NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. "NASA orbiter finds new gully channel on Mars." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 22 March 2014. www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/03/140322094409.htm
- ↑ http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.php?release=2014-226
- ↑ http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/ESP_032078_1420
- ↑ http://www.space.com/26534-mars-gullies-dry-ice.html