Bonestell (crater)
|
Bonestell, as seen by HiRISE. Scale bar is 1000 meters long. | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°22′N 30°34′W / 42.37°N 30.57°WCoordinates: 42°22′N 30°34′W / 42.37°N 30.57°W |
| Diameter | 42.4 km |
| Eponym | Chesley Bonestell, a famous American space artist (1888-1986) |
Bonestell is a crater in the Northern hemisphere in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle of Mars, located at 42.37° North and 30.57° West.[1] It is 42.4 km in diameter and was named after Chesley Bonestell, a famous American space artist (1888-1986), whose drawings inspired many young people to study sciences.[2]
Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them. In contrast, volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits. As craters get larger (greater than 10 km in diameter) they usually have a central peak.[3] The peak is caused by a rebound of the crater floor following the impact.[4] If one measures the diameter of a crater, the original depth can be estimated with various ratios. Because of this relationship, researchers have found that many Martian craters contain a great deal of material; much of it is believed to be ice deposited when the climate was different.[5] Sometimes craters expose layers that were buried. Rocks from deep underground are tossed onto the surface. Hence, craters can show us what lies deep under the surface.
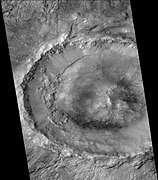 Bonestell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).
Bonestell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter).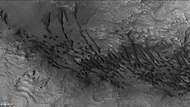 Field of dunes on floor of Bonestell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous photo.
Field of dunes on floor of Bonestell Crater, as seen by CTX camera (on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter). Note: this is an enlargement of the previous photo.
See also
References
- ↑ https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/images/mc4_2014.pdf
- ↑ Bonestell. Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, retrieved June 19, 2011
- ↑ http://www.lpi.usra.edu/publications/slidesets/stones/
- ↑ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ↑ Garvin, J., et al. 2002. Global geometric properities of martian impact craters. Lunar Planet Sci. 33. Abstract @1255.