Eastern Kentucky Coalfield
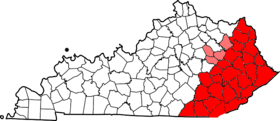
The Eastern Kentucky Coalfield is part of the Central Appalachian bituminous coalfield, including all or parts of 30 Kentucky counties and adjoining areas in Ohio, West Virginia, Virginia and Tennessee.[3] It covers an area from the Allegheny Mountains in the east across the Cumberland Plateau to the Pottsville Escarpment in the west. The region is known for its coal mining; most family farms in the region have disappeared since the introduction of surface mining in the 1940s and 1950s.
The Daniel Boone National Forest is located on rough but beautiful terrain along and east of the Pottsville Escarpment. There are many natural arches and sandstone cliffs that are excellent for rock climbing and rappeling. The Red River Gorge, part of the National Forest, is known worldwide in rock climbing circles.
The Sheltowee Trace Trail runs 420–430 km north and south through the region.
During the American Civil War most of this region leaned toward the Union due to its makeup at the time of mostly small farmers, but more than 2,000 men from this area formed the 5th. Kentucky Vol. Inf., known as the Army of Eastern Kentucky, under Gen. Humphrey Marshall, C.S.A. During the Great Depression, New Deal programs and the organizing of the United Mine Workers of America made many of the eastern counties Democratic.
Eastern Kentucky has a rich musical heritage. A large number of nationally acclaimed country music singers and musicians are from the area. These include: Loretta Lynn, Crystal Gayle, The Judds, Ricky Skaggs, Keith Whitley, Patty Loveless, Dwight Yoakam, Tom T. Hall, Billy Ray Cyrus, Jean Ritchie, Sturgill Simpson and George S. Davis.
As of the 1980s, the only counties in the United States where over half of the population cited "English" as their only ancestry group were in the hills of eastern Kentucky (and made up virtually every county in this region).[4] In the 1980 census, 1,267,079 Kentuckians out of a total population of 2,554,359 cited that they were of English ancestry, making them 49 percent of the state at that time. Large numbers of people of Scots and Scots-Irish ancestry settled the area as well.[5]
Geography
The Eastern Kentucky Coalfield covers 31 counties with a combined land area of 13,370 sq mi (34,628 km²), or about 33.1 percent of the state's land area. Its 2000 census population was 734,194 inhabitants, or about 18.2 percent of the state's population. The largest city, Ashland, has a population of 21,981. Other cities of significance in the region include Pikeville, Corbin, and Middlesboro. The state's highest point, Black Mountain, is located in the southeastern part of the region in Harlan County.
Counties
Major cities

The following list consists of Eastern Kentucky cities with populations over 4,000 according to the U.S. Census estimates released in 2016:[9]
| Rank | City | Population 2016 | County |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ashland | 21,038 | Boyd |
| 2 | Middlesboro | 9,626 | Bell |
| 3 | London | 8,157 | Laurel |
| 4 | Morehead | 7,758 | Rowan |
| 5 | Corbin | 7,398 | Whitley and Knox |
| 6 | Flatwoods | 7,311 | Greenup |
| 7 | Mount Sterling | 7,242 | Montgomery |
| 8 | Pikeville | 7,106 | Pike |
| 9 | Williamsburg | 5,313 | Whitley |
| 10 | Hazard | 5,300 | Perry |
| 11 | Paintsville | 4,203 | Johnson |
| 12 | Grayson | 4,043 | Carter |
Protected areas
.jpg)
Historical parks
State resort parks
State recreational parks

Other
Economy
The region's economy is centered around the vast amount of natural resources available, which includes coal, timber, natural gas, and oil. Recently, tourism has become a leading industry in the region, due to the region's unique cultural history and the creation of state parks.
Calgon Carbon constructed the Big Sandy Plant near Ashland in 1961 and it has since became the world's largest producer of granular activated carbon. The facility produces in over 100 million pounds of granular activated carbon annually.[10]
Persistent poverty
Most of the counties in the Eastern Kentucky Coalfield are classified as "persistent poverty counties". The definition of a persistent poverty county by the Economic Research Service of the United States Department of Agriculture is that 20 percent or more of the total county population has been living in poverty since the 1980 census.[11]
A June 2014 article in The New York Times identified six counties in the Kentucky Coal Field as among the "hardest places to live in the United States." The lowest-ranking counties were Breathitt, Clay, Jackson, Lee, Leslie, and Magoffin. They ranked among the bottom ten counties nationwide. The factors which accounted for the low ranking of those six counties were unemployment, prevalence of disabilities, obesity, income, and education.[12] The Times declared Clay County the hardest place to live in the U.S.[13]
Appalachian Regional Commission
The Appalachian Regional Commission was formed in 1965 to aid economic development in the Appalachian region, which was lagging far behind the rest of the nation on most economic indicators. The Appalachian region currently defined by the Commission includes 420 counties in 13 states, including all counties in Kentucky's Eastern Coalfield. The Commission gives each county one of five possible economic designations—distressed, at-risk, transitional, competitive, or attainment—with "distressed" counties being the most economically endangered and "attainment" counties being the most economically prosperous. These designations are based primarily on three indicators—three-year average unemployment rate, market income per capita, and poverty rate.[14]
From 2012 to 2014, "Appalachian" Kentucky—which includes all of the Eastern Coalfield and several counties in South Central Kentucky and a few in the eastern part of the Bluegrass region—had a three-year average unemployment rate of 9.8%, compared with 7.6% statewide and 7.2% nationwide.[14] In 2014, Appalachian Kentucky had a per capita market income of $18,889, compared with $28,332 statewide and $38,117 nationwide. From 2010 to 2014, Appalachian Kentucky had an average poverty rate of 25.4%—the highest of any of the ARC regions—, compared to 18.9% statewide and 15.6% nationwide. Twenty-five Eastern Mountain Coal Field counties—Bell, Breathitt, Carter, Clay, Elliott, Floyd, Harlan, Jackson, Johnson, Knott, Knox, Lawrence, Lee, Leslie, Letcher, Magoffin, Martin, McCreary, Menifee, Morgan, Owsley, Powell, Rowan, Whitley, and Wolfe—were designated "distressed," while four - Laurel, Montgomery, Perry, and Pike — were designated "at-risk." Two Eastern Coalfield counties were designated "transitional" — Boyd and Greenup. No counties in the Eastern Coalfields region were given the "attainment" designation or were designated "competitive."
The following table illustrates the economic status of each county.
| County | Population (2010) | Unemployment Rate (2012-14)[14] | Per Capita Market Income (2014)[14] |
Poverty Rate (2010–14)[14] | Status (2017)[14] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bell | 28,691 | 11.9% | $14,644 | 32.7% | Distressed |
| Boyd | 49,542 | 8.6% | $24,337 | 19.1% | Transitional |
| Breathitt | 13,878 | 13.7% | $14,386 | 31.5% | Distressed |
| Carter | 27,720 | 12.0% | $18,014 | 18.7% | Distressed |
| Clay | 21,730 | 13.3% | $11,531 | 35.7% | Distressed |
| Elliott | 7,852 | 13.5% | $10,529 | 39.6% | Distressed |
| Floyd | 39,451 | 11.7% | $18,473 | 29.5% | Distressed |
| Greenup | 36,910 | 9.3% | $23,879 | 18.0% | Transitional |
| Harlan | 29,278 | 15.4% | $13,620 | 32.1% | Distressed |
| Jackson | 13,494 | 15.4% | $13,496 | 31.7% | Distressed |
| Johnson | 23,356 | 10.1% | $19,008 | 25.3% | Distressed |
| Knott | 16,346 | 13.5% | $14,271 | 26.5% | Distressed |
| Knox | 31,883 | 11.9% | $15,549 | 33.8% | Distressed |
| Laurel | 58,849 | 9.2% | $21,051 | 23.3% | At-Risk |
| Lawrence | 15,860 | 10.5% | $15,399 | 23.5% | Distressed |
| Lee | 7,887 | 11.7% | $11,750 | 33.4% | Distressed |
| Leslie | 11,310 | 15.0% | $15,357 | 23.9% | Distressed |
| Letcher | 24,519 | 14.2% | $15,955 | 24.5% | Distressed |
| Magoffin | 13,333 | 16.3% | $11,139 | 26.8% | Distressed |
| Martin | 12,929 | 9.4% | $14,826 | 33.9% | Distressed |
| McCreary | 18,306 | 12.4% | $9,763 | 37.7% | Distressed |
| Menifee | 6,306 | 11.2% | $15,656 | 28.8% | Distressed |
| Montgomery | 26,499 | 8.2% | $23,093 | 25.2% | At-Risk |
| Morgan | 13,923 | 10.3% | $13,451 | 29.7% | Distressed |
| Owsley | 4,755 | 11.9% | $10,528 | 39.2% | Distressed |
| Perry | 28,712 | 12.3% | $20,131 | 26.6% | Distressed |
| Pike | 68,736 | 10.6% | $21,285 | 24.1% | At-Risk |
| Powell | 12,613 | 10.1% | $18,403 | 27.5% | Distressed |
| Rowan | 23,333 | 7.8% | $18,642 | 26.0% | At-Risk |
| Whitley | 35,637 | 10.0% | $17,321 | 24.1% | Distressed |
| Wolfe | 7,355 | 13.3% | $10,532 | 44.3% | Distressed |
Health
Most of the counties in the Eastern Kentucky Coalfield rank in the lowest ten percent of U.S. counties in average life expectancy. Both men and women have average life spans that are several years less than the average life span in the United States. Moreover, many counties have seen a decline in the life expectancy of men and/or women since 1985. Factors influencing the health of residents include a high prevalence of smoking and obesity and a low level of physical activity.[15]
Post-secondary education


Public universities
Private colleges and universities
Community and technical colleges
Notable residents
- Hylo Brown, bluegrass and country music singer, born in River.
- June Buchanan (1887–1988), educator who worked with Alice Spencer Geddes Lloyd (see below). Co-founder of Caney Junior College, now Alice Lloyd College. Lived in Knott County from 1919 until her death.
- Earle Combs (1899–1976), Hall of Fame MLB center fielder for the New York Yankees. Born in Pebworth, a community in Owsley County.[16]
- Tim Couch, former NFL quarterback. Born and raised in Hyden.
- Billy Ray Cyrus (born 1961), American country music singer, songwriter and actor. Born in Flatwoods.
- Richie Farmer (born 1969), basketball standout for the University of Kentucky and politician (Kentucky Commissioner of Agriculture, 2003–2011). Born and raised in Manchester.
- Jim Ford, singer-songwriter, born in Johnson County.
- Mary Elliott Flanery, first woman elected to a state legislature south of the Mason–Dixon line.
- Crystal Gayle, country singer and younger sister of Loretta Lynn; both raised in Van Lear.
- Eula Hall, Founder of the Mud Creek Clinic.
- Roscoe Holcomb, American musician who lived the majority of his life in Daisy.
- Silas House (born 1971), author. Born and raised in Laurel County; also lived in Leslie County during his childhood.
- The Judds, a country music duo of mother Naomi (born 1946) and daughter Wynonna (born 1964). Born in Ashland.
- Ashley Judd (born 1968), actress; daughter of Naomi Judd and half-sister of Wynonna Judd. Born in Ashland.
- Alice Spencer Geddes Lloyd (1876–1962), social reformer who founded 100 elementary schools in the region as well as co-founding the college that now bears her name. Lived in Knott County from 1915 until her death.
- Patty Loveless, country music singer. Born in Pikeville.
- Loretta Lynn, country singer, raised in Van Lear.
- John Pelphrey (born 1968), basketball standout for the University of Kentucky (and teammate of Farmer); former head basketball coach at the University of Arkansas, and current assistant at the University of Florida. Born in Paintsville.
- Francis Gary Powers (August 17, 1929 – August 1, 1977) was an American pilot whose CIA U-2 spy plane was shot down while over the Soviet Union, causing the 1960 U-2 incident. Born in Jenkins.
- Venus Ramey, Miss America, 1944. Born in Ashland.
- Jeff Sheppard (born 1974), University of Kentucky basketball star (1998 NCAA Tournament Most Outstanding Player) and former player in the NBA and several European leagues. Has lived in London since he retired from play.
- Benjamin F. Stapleton, Mayor of Denver, Colorado between (1923–1931) and (1935–1947). Born in Paintsville.
- Gary Stewart, Country music singer and musician, 1944–2003, born in Jenkins.
- Jesse Stuart, author and former poet laureate of Kentucky
- Dwight Yoakam (born 1956), singer-songwriter, actor and film director. Born in Pikeville.
- Sturgill Simpson, Outlaw Country Music singer-songwriter born in Jackson in 1978
See also
References
- ↑ "Wayback Machine". archive.org. 28 March 2008. Archived from the original on 28 March 2008. Retrieved 7 May 2018.
- ↑ "National Digital Newspaper Program: The Kentucky Edition, More about KY-NDNP: regions". Uky.edu. November 6, 2007. Archived from the original on October 1, 2013. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ↑ Eastern Mountain Coal Fields Archived 2013-10-01 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved on 2010-1-30
- ↑ James Paul Allen and Eugene James Turner, We the People: An Atlas of America's Ethnic Diversity (Macmillan, 1988), 41.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2012-02-24. Retrieved 2012-02-10.
- ↑ "EPA County FIPS Code Listing". EPA. Archived from the original on 2004-09-22. Retrieved 2007-04-09.
- 1 2 3 4 National Association of Counties. "NACo – Find a county". Archived from the original on 2007-07-11. Retrieved 2007-07-22.
- ↑ "Montgomery County, Kentucky Genealogy". Kentucky Comprehensive Genealogy Database. Archived from the original on 2008-10-13. Retrieved 2007-01-26.
- ↑ Annual Estimates of the Resident Population: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2016 Population Estimates Archived August 31, 2015, at the Wayback Machine. U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved 2015-08-13
- ↑ Calgon Carbon Big Sandy Plant Retrieved 2014-03-21.
- ↑ "Geography of Poverty", "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-02-17. Retrieved 2017-02-17. , accessed 17 February 2017
- ↑ Lowrey, Annie (2014-06-29). "What's the Matter With Eastern Kentucky?". NYtimes.com. Archived from the original on 2017-12-01.
- ↑ Flippen, Alan (June 26, 2014), "Where Are the Hardest Places to Live in the U.S.?" The New York Times.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 County Economic Status, Fiscal Year 2017: Appalachian Kentucky Archived 2017-05-14 at the Wayback Machine.. ARC. Retrieved: 2017-07-14.
- ↑ "Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation", "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2017-02-24. Retrieved 2017-02-17. , accessed 17 February 2017
- ↑ Earle Combs / Baseball Legend