Gaya, India
| Gaya | |
|---|---|
| City | |
 Vishnupad Temple in Gaya, contains footprints of Lord Vishnu | |
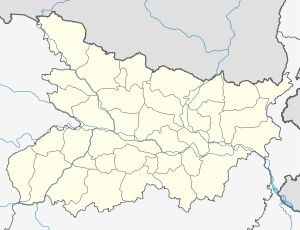 Gaya Location of Gaya in Bihar  Gaya Gaya (India) | |
| Coordinates: 24°45′N 85°01′E / 24.75°N 85.01°ECoordinates: 24°45′N 85°01′E / 24.75°N 85.01°E | |
| Country | India |
| State | Bihar |
| Region | Magadha |
| Division | Magadh Division |
| District | Gaya |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipal corporation |
| • Body | Gaya Nagar Nigam |
| • Mayor | Birendra Kumar |
| Area[1] | |
| • Total | 90.17 km2 (34.81 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 111 m (364 ft) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 470,839[2] |
| • Rank |
98th (India) 2nd (Bihar) |
| • Density | 9,482/km2 (24,560/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Gayaite, Gayavi [3] |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Hindi, Magahi, Urdu |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 823001 - 13 |
| Telephone code | 91-631 |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-BR |
| Vehicle registration | BR-02 |
| Railway Station | Gaya Junction |
| Airport | Gaya International Airport |
| Website |
www |
Gaya is of historical significance and is one of the major tourist attractions of the state of Bihar. Gaya is 100 kilometres (62 mi) south of Patna, the capital city of Bihar. It is the state's second-largest city, with a population of 470,839, and is the headquarters of Gaya district and Magadh division. The city is surrounded on three sides by small, rocky hills (Mangla-Gauri, Shringa-Sthan, Ram-Shila, and Brahmayoni), with the Phalgu River on its fourth (eastern) side.
Gaya is sanctified in the Jain, Hindu, and Buddhist religions. Gaya district is mentioned in the great epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata. It is the place where Rama, with Sita and Lakshmana, came to offer pind-daan for their father, Dasharath, and continues to be a major Hindu pilgrimage site for the pind-daan ritual. Bodh Gaya, where the Buddha is said to have reached enlightenment, is one of the four holy sites of Buddhism. The Mahabodhi Temple complex at Bodh Gaya is a World Heritage site.
Etymology
Gaya is named after the demon Gayasur (meaning "the demon Gaya"). According to Vayu Purana, Gaya was the name of a demon (Asura) whose body became pious after he performed strict penance and secured blessings from Lord Vishnu.[4] It was said that the body of Gayasura was transformed into the series of rocky hills that make up the landscape of Gaya.[5]
History

Ancient history
Gaya is an ancient city, with a documented history dating back to the 6th century BC when the sage Gautama Buddha attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya, 16 km (9.9 mi) from the modern city, and became the Buddha.[6]
Even before this time, Gaya was a place of pilgrimage for people from around the world. The fame of ancient Gaya derived from the account in the Ramayana of the god Rama coming here to the banks of Phalgu River (called the Niranjana), accompanied by his wife and younger brother, to offer pind-daan for their father Dasharatha, for the moksha of his soul.[7][8] In the Mahabharata, Gaya is referred to as Gayapuri.
Gaya flourished in the Maurya Empire (321–187 BC), which ruled from the city of Pataliputra (adjacent to modern Patna) over an area that extended beyond the Indian subcontinent. During this period, Gaya witnessed the rise and fall of many dynasties in the Magadha region, where it occupied an important place in cultural history over some 2,400 years between the 6th century BC and the 18th century AD.
The city's cultural significance began with the dynasty founded by Sisunaga, who exercised power over Patna and Gaya around 600 BC. Bimbisara, fifth king of the dynasty, who lived and ruled around 519 BC, had projected Gaya to the outer world. Having attained an important place in the history of civilization, the area experienced the influence of Gautama Buddha and Bhagwan Mahavir during the reign of Bimbisara. After a brief period under the Nanda dynasty (345–321 BC), Gaya and the entire Magadha region came under Mauryan rule. Mauryan Emperor Ashoka (272–232 BC) embraced and promoted Buddhism. He visited Gaya, and built the first temple at Bodh Gaya to commemorate the Buddha's attainment of supreme enlightenment.[9]
The period of Hindu revivalism began with the Gupta Empire during the 4th and 5th centuries AD. Samudragupta of Magadha brought Gaya into the limelight, making it the capital of Bihar district during the Gupta empire.
In 750 AD, Gaya became a part of the Pala Empire, under the rule of its founder, Gopala. It is believed that the present temple of Bodh Gaya was built during the reign of Gopala's son, Dharmapala.
In the 12th century AD, Gaya was invaded by Muhammad Bakhtiyar Khilji of the Ghaznavid Empire. By 1557, it had become part of the Mughal Empire, and remained under its power until the Battle of Buxar and the beginning of British rule in 1764. Gaya, along with other parts of the country, gained its independence in 1947.
Modern history
As attested by Francis Buchanan-Hamilton in the early nineteenth century, the city was divided into two areas: a sacred area in the southern part of the city, called Gaya; and the larger secular area, which may have been known by the Muslim community as Allahabad. During the British rule, the commercial and administrative area of the secular zone was formally named Saheb Ganj by British policy reformer Thomas Law, who was a district officer in Gaya in the late nineteenth century.[10]
Swami Sahajanand Saraswati, founder of the All India Kisan Sabha peasant movement in 1936, established an ashram at Neyamatpur, Gaya, which later became the centre of the freedom struggle in Bihar. Many prominent leaders of the Indian National Congress visited frequently to meet Yadunandan (Jadunandan) Sharma when he was leader of Kisan Sabha, residing in the ashram set up by Swamiji. Yadunandan Sharma became the leader of the peasants of Gaya district and second-in-command to Swami Sahajanand Saraswati.
Gaya played a significant role in the Indian Independence Movement. From 26 to 31 December 1922, the 37th session of the Indian National Congress was held in Gaya[11] under the presidency of Deshbandhu Chittaranjan Das. It was attended by prominent leaders and luminaries of the Independence Movement, including Mohandas K. Gandhi, Dr. Rajendra Prasad, Dr. Anugrah Narayan Sinha, Sardar Patel, Maulana Azad, Jawaharlal Nehru and Sri Krishna Sinha.[12]
Gaya is the birthplace of eminent nationalist Bihar Vibhuti, Dr. Anugrah Narayan Sinha, Bihar's first deputy Chief Minister and Finance Minister. Former Bihar Chief Minister Satyendra Narayan Sinha also hailed from Gaya. Shri Ishwar Chaudhary, a member of the Fifth, Sixth and Ninth Lok Sabhas from 1971 to 1979 and from 1989 to 1991, represented the Gaya constituency of Bihar.
Administration
Until 1864, Gaya was a part of the district of Behar and Ramgarh (now in the state of Jharkhand). It became a district of Bihar in its own right on 3 October 1865.[13] In May 1981, the Bihar state government created the Magadh division, comprising the district of Gaya, along with Nawada, Aurangabad and Jehanabad, all of which had originally been sub-divisions when Gaya district was created.[4] Aurangabad and Nawada were partitioned from the territory of Gaya in 1976; and Jehanabad in 1988.[14] Gaya district occupies an area of 4,976 km2 (1,921 mile2).[4]
Culture
Pilgrimage
The city of Gaya is a holy place of Hinduism, with a great number of Hindu deities represented in the engravings, paintings and carvings of its shrines. Of particular importance are the sites in the city associated with Vishnu, in particular the Phalgu River and the shrine Vishnupad Mandir, or Vishnupada, which is marked by a large footprint of Lord Vishnu engraved in a basalt block.[10] Gaya is the location at which Rama, with Sita and Lakshmana, offered pind-daan for his father, Dasharatha. Gaya has since remained a site of key importance for the performance of the pind-daan ritual.[7][8]
Nearby Bodh Gaya ("Buddha Gaya"), so named to distinguish it from the Hindu town centre of Gaya, is one of the four holiest sites of Buddhism and the site where the Buddha attained enlightenment.[9][10]
World Heritage site at Bodh Gaya
The Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya was listed as a World Heritage site by the World Heritage Committee of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) at its 26th session, on 26 June 2002.[9]
The 50-metre-high (160 ft) Mahabodhi Temple central to the complex was first built by the emperor Ashoka in the 3rd century AD. The main part of the present structure dates from the 5th–6th centuries AD. It is one of the earliest and best-preserved Buddhist temples built entirely of brick dating from the later Gupta period. The Bodhi Tree (Ficus religiosa), the most important of the sacred places within the complex, is reputedly a descendant of the original tree under which Siddhārtha Gautama attained enlightenment and became the Buddha.[9] Marking this seminal moment, Bodh Gaya is one of the four holiest pilgrimage sites of Buddhism, with Lumbini, Sarnath and Kushinagar.[15]
The various structures on the site have undergone a number of restorations over the centuries. Ongoing maintenance and management is required to protect the complex which, as a major pilgrimage site, is under pressure due to large numbers of visitors.[15] The site is under the responsibility of the state government of Bihar, and is managed by the Bodhgaya Temple Management Committee (BTMC) and Advisory Board under the Bodh Gaya Temple Act, 1949.[16]
Climate
As Gaya is surrounded by hills on three sides and river on the fourth side, the climate of Gaya is seasonable. Climate is characterised by relatively high temperatures and evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year. The Köppen Climate Classification sub-type for this climate is "Cfa" (humid subtropical).[17]
| Climate data for Gaya, India | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 24 (75) |
27 (80) |
33 (92) |
39 (102) |
41 (105) |
38 (101) |
33 (92) |
32 (90) |
33 (91) |
32 (89) |
29 (84) |
25 (77) |
32 (90) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10 (50) |
13 (55) |
18 (64) |
23 (74) |
27 (80) |
28 (82) |
26 (79) |
26 (78) |
25 (77) |
22 (71) |
14 (58) |
10 (50) |
20 (68) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 20 (0.8) |
20 (0.8) |
13 (0.5) |
8 (0.3) |
20 (0.8) |
137 (5.4) |
315 (12.4) |
328 (12.9) |
206 (8.1) |
53 (2.1) |
10 (0.4) |
3 (0.1) |
1,130 (44.5) |
| Source: Weatherbase[18] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Gaya is the second-largest contributor to the economy of Bihar, after Patna. Agriculture is the leading economic activity of the district. The main crops grown are rice, wheat, potatoes, and lentils. Livestock raised include cattle, buffaloes, goats and pigs. Gaya has a large number of household industries, producing incense sticks (atagarbatti), local sweets tilkut (made with sesame seed) and lai (made with poppy seed), stone-work, hand weaving, power-loom weaving, textiles and garments, small-scale manufactured goods, and plastic products. Small-scale industries also include agricultural services, metalworking, machinery and equipment production and repair services.[4] The main vegetable market in the city is the Kedarnath Market. Commercial activities are located along its main roads; the city also has a large number of informal shops.[19] As Gaya is an important centre of religious tourism, accommodation is widely available.[20] Bodh Gaya's largest hotel is the Maha Bodhi Hotel, Resort & Convention Centre; the Sambodhi Retreat, a resort of Bihar and Jharkhand, is also in the town.
In January 2015, Gaya was chosen as one of twelve heritage cities to benefit from the Government of India's four-year Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana (HRIDAY) scheme for urban planning, economic growth and heritage conservation projects.[21] The scheme is due to complete in November 2018.[22]
Demographics
In the 2011 census, the Gaya Urban Agglomeration had a population of 474,093.[24] The Gaya Urban Agglomeration encompasses the Gaya Municipal Corporation, Kaler (Out Growth), and Paharpur (Census Town).[25] the Gaya Municipal Corporation had a total population of 468,614,[26] of whom 247,572 were male and 221,042 were female. The population below 5 years was 59,669. The sex ratio was 986 women to 1000 men. The literacy rate for the population aged 7 and over was 85.74%.[27]
Transport
Gaya is connected to the rest of India by roads, rail and airways. The Grand Chord section of the Indian Railways passes through Gaya.
Local transport
There are many city buses and taxis providing services across the city and Bodh Gaya. Tangas, auto rickshaws, and cycle rickshaws also ply the city and Bodh Gaya. The main bus stands are Government Bus Stand, Sikaria More Bus Stand, Gaurkashni Bus Stand (Manpur),and Delha Bus Stand. Local transport is reliable, and auto rickshaws are available for various destinations in the city. The Gaya–Patna railway line plays a major role in transporting people from the town to the state capital.
Roadways
Gaya has a road network providing good connectivity with the state of Bihar and other parts of the country.[28] Regular direct bus services run from Gaya to Patna, Bhagalpur, Munger, Nalanda, Rajgir, Varanasi, Ranchi, Jamshedpur, Hazaribagh, Durgapur, Asansol, Kolkata and Dhanbad. In 2011, A/C Mercedes-Benz luxury services were introduced by Bihar State Road Transport Corporation for Muzaffarpur, Patna, Munger, Bhagalpur, Motihari, Hazaribagh, Koderma, and Ramgarh.
The Grand Trunk Road from Kolkata to Delhi passes some 30 km (19 mi) from Gaya. This road, known as National Highway 2 before 2010,[29] is now called National Highway 19. It connects Gaya to Patna, Ranchi, Jamshedpur, Bokaro, Rourkela, Durgapur, Kolkata (495 km), Varanasi (252 km), Allahabad, Kanpur, Delhi, Amritsar, and to the Pakistani cities of Lahore and Peshawar. Gaya is connected to Patna (105 km) by National Highway 22 (formerly NH 83), and to Nawada, Rajgir (78 km) and Bihar Sharif by NH 120. Construction work began in 2014 on the road from Patna to Dobhi via Gaya and Gaya to Bihar Sharif to create a four-lane highway with additional road and bridge infrastructure. Completion of the project, originally due in April 2018, has been delayed.[30]
Railways
Gaya Junction railway station is a junction station serving the city. Gaya Junction was the only station in Bihar and Jharkhand in the list of 66 stations to be built to international standards drawn up by Minister of Railways Mamata Banerjee. Gaya falls under the jurisdiction of the Mughalsarai railway division of the East Central Railway zone. The Grand Chord rail line that connects Howrah and New Delhi passes through Gaya. It lies between Mughalsarai Junction on the Delhi side and Dhanbad Junction on the Howrah side. It is located at 24°48′13″N 84°59′57″E / 24.80361°N 84.99917°E.[31] It has an elevation of 117 metres (384 ft).[32][33]
Airport
Situated between Gaya (7 km) and Bodh Gaya (11 km), Gaya Airport is the largest airport by area, and one of two operating international airports in the states of Bihar and Jharkhand. It is the second-busiest airport in Bihar, after Patna's Jay Prakash Narayan Airport. Gaya airport mainly operates seasonal flights for Buddhist pilgrims to Bodh Gaya from Colombo, Sri Lanka; Bangkok, Thailand; Singapore, and Paro, Bhutan. With flights to Jeddah in Saudi Arabia, it also caters for for Muslim pilgrims underaking the Hajj to Mecca. There are also regular domestic flights to Varanasi, Kolkata and Delhi. The Airports Authority of India has plans to develop Gaya Airport as a stand-by to the Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport in Kolkata.[34]
Education
Gaya has a number of English-language schools which provide primary and secondary education, including DAV Public School, Creane Memorial High School, Elegant Public School, Gyan Bharti Public School, Nazareth Academy, and Takshila School.[35]
Magadh University was established in 1962 in Bodh Gaya. The Central University of South Bihar, established in 2009, has its campus in the Gaya village of Panchanpur. Other tertiary education institutions include Anugraha Memorial College, Anugrah Narayan Magadh Medical College and Hospital, Gaya College, Mirza Ghalib College, and Gaya College of Engineering.[36] A new National Importance Management College, the Indian Institute of Management Bodh Gaya, was established in 2015. Pending completion of its permanent campus, this college is operating from the campus of Magadh University.[37]
Universities
Colleges
- Gaya College
- Jagjivan College
- Mirza Ghalib College
Engineering colleges
- Gaya College of Engineering
- Buddha Institute of Technology[38]
Medical college
Independent tertiary institutions
Schools
- Nazareth Academy
- DAV Public School
- Creane Memorial High School
- Elegant Public School
- Gyan Bharti Public School
- Takshila School
- Secondary Delhi Public School
- British English School
See also
References
- ↑ "City Development Plan for Gaya: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY" (PDF). Urban Development and Housing Department, Government of Bihar. p. 4. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 September 2014. Retrieved 8 October 2012.
- ↑ "UA/Cities 1 lakh and above" (PDF). Government of India. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2011.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 16 August 2016. Retrieved 12 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 MSME-Development Institute, Ministry of MSME, Government of India (2011). "Brief Industrial Profile of Gaya District – Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises" (PDF). Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "The Hare Krsnas - Battles of Vishnu Avatars - Gayasur". Harekrsna.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ↑ World Heritage Committee (June 29, 2002). "World Heritage Scanned Nomination - Site Name: Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya" (PDF). www.whc.unesco.org. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- 1 2 Griffith, Ralph T. H. (1870–1874). The Rámayán of Válmíki Translated into English Verse (PDF). London: Trübner & Co.; Benares: E. J. Lazarus and Co. p. 761.
- 1 2 Bhalla, Prem D (2006). "Chapter N6-N7: What is the importance of pind daan for the deceased?; What is the purpose of the Shraddh ceremony?". Hindu Rites, Rituals, Customs and Traditions: A to Z on the Hindu Way of Life. Pustak Mahal. pp. 314–319. ISBN 978-8-122-30902-7. Retrieved September 28, 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 "Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya, Description". www.whc.unesco.org. UNESCO World Heritage Centre. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- 1 2 3 Vidyarthi, Lalita Prasad (1978). "Chapter 1: The Sacred Centres of Gaya". The Sacred Complex in Hindu Gaya (2nd ed.). Concept Publishing Company. pp. 1–29. ISBN 978-1-234-56789-7. Retrieved September 28, 2018.
- ↑ Indian National Congress (1923). "Report of the Thirty-Seventh Indian National Congress held at Gaya on the 26th, 27th, 29th , 30th and 31st December 1922" (PDF). Retrieved September 26, 2018.
- ↑ Roy, Evelyn (1923). "Politics in Gaya" (PDF). The Communist International, Organ of the Executive Committee of the Communist International, English Edition. London, England. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "Gaya celebrates 154th establishment day".
- ↑ Law, Gwillim (2011-09-25). "Districts of India". Statoids. Archived from the original on 2011-10-17. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
- 1 2 Lambah, Abha Narain; Dorje, Nangze (2017). "Chapter 13: Challenges of managing a living Buddhist site: Mahabodhi Temple, Bodh Gaya, India". In Wijesuriya, Gamini; Lee, Sujeong. ICCROM-CHA Conservation Forum Series: First ICCROM-CHA International Forum on Conservation Asian Buddhist Heritage: Conserving the Sacred (PDF). ICCROM, International Centre for the Study of the Preservation and Restoration of Cultural Property. pp. 103–111. ISBN 978-92-9077-240-8. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "The Bodh Gaya Temple Act, 1949 (Bihar Act of 17 of 1949), (as modified up to the 8th February, 1955)" (PDF). www.bodhgayatemple.com. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "Climate Summary for Gaya, India". Weatherbase.com. Archived from the original on 23 March 2016. Retrieved 7 January 2016.
- ↑ "Weatherbase.com". Weatherbase. 2013. Archived from the original on 3 April 2015. Retrieved on 31 July 2013.
- ↑ Udyog Mitra, Department of Industries (2011). "Bihar – Economic Profile Gaya" (PDF). www.udyogmitrabihar.in. Government of Bihar. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ Geary, David (2017). "Buddhist Circuits and Spiritual Tourism (in Chapter 5: A Master Plan for World Heritage)". The Rebirth of Bodh Gaya: Buddhism and the Making of a World Heritage Site. University of Washington Press. p. 159. ISBN 978-0-295-74238-0.
- ↑ HRIDAY National Project Management Unit, National Institute of Urban Affairs, Ministry of Urban Development Government of India (January 21, 2015). "Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana" (PDF). www.hridayindia.in. Retrieved September 26, 2018.
- ↑ HRIDAY National Project Management Unit, National Institute of Urban Affairs. "HRIDAY-Rejuvenating the Soul of Urban India-Heritage City Development and Augmentation Yojana". www.hridayindia.in. Retrieved September 26, 2018.
- ↑ "Gaya City Census 2011 data". Census 2011 India. Archived from the original on 7 May 2017. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- ↑ "Urban Agglomerations/Cities having population 1 lakh and above" (PDF). Provisional Population Totals, Census of India 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ↑ "Constituents of urban Agglomerations Having Population 1 Lakh & above" (PDF). Provisional Population Totals, Census of India 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 June 2016. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ↑ "Gaya, District in Bihar - The population development of Gaya". Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 13 July 2016.
- ↑ "Cities having population 1 lakh and above" (PDF). Provisional Population Totals, Census of India 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 May 2012. Retrieved 16 April 2012.
- ↑ Egis India Consulting Engineers Private Limited. "City Development Plan (2010-30) Gaya: Executive Summary" (PDF). www.urban.bih.nic.in. Urban Development and Housing Department Government of Biha. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "Rationalisation of Numbering Systems of National Highways" (PDF). New Delhi: Department of Road Transport and Highways. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ Qadir, Abdul (April 25, 2018). "Dobhi-Patna road project delayed". The Times of India. India. Retrieved September 28, 2018.
- ↑ "Gaya Junction". Wikimapia. Archived from the original on 10 February 2013. Retrieved 1 December 2011.
- ↑ "Trains at Gaya". India Rail Info. Archived from the original on 8 December 2011. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- ↑ "Ghanbad Junction Railway Station Details". indiantrains.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- ↑ Airports Authority of India. "Gaya Airport". www.aai.aero. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "List of Schools in Gaya, Bihar". www.targetstudy.com. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ "List of All Colleges In Gaya, Bihar". www.indcareer.com. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ Indian Institute of Management Bodh Gaya. "Indian Institute of Management Bodh Gaya". www.udyogmitrabihar.in. Retrieved September 27, 2018.
- ↑ http://bodhgayabit.org/en/home/
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gaya, India. |
- Entry on Gaya in the Buddhist Dictionary of Pali Proper Names
- Suttas spoken by Gautama Buddha concerning Gaya: (more)

- Official website of the Shashika Cab Gaya.