Travel visa





A visa (from the Latin charta visa, meaning "paper that has been seen")[1] is a conditional authorization granted by a country to a foreigner, allowing them to enter, remain within, or to leave that country. Visas typically include limits on the duration of the foreigner's stay, territory within the country they may enter, the dates they may enter, the number of permitted visits or an individual's right to work in the country in question. Visas are associated with the request for permission to enter a country and thus are, in some countries, distinct from actual formal permission for an alien to enter and remain in the country. In each instance, a visa is subject to entry permission by an immigration official at the time of actual entry, and can be revoked at any time. A visa most commonly takes the form of a sticker endorsed in the applicant's passport or other travel document.
Historically, immigration officials were empowered to permit or reject entry of visitors on arrival at the frontiers. If permitted entry, the official would issue a visa, when required, which would be a stamp in a passport. Today, travellers wishing to enter another country must generally apply in advance for what is also called a visa, sometimes in person at a consular office, by mail or over the internet. The modern visa may be a sticker or a stamp in the passport, or may take the form of a separate document or an electronic record of the authorization, which the applicant can print before leaving home and produce on entry to the host country. Some countries do not require visitors to apply for a visa in advance for short visits.
Some countries require that their citizens, as well as foreign travellers, obtain an "exit visa" to be allowed to leave the country.[2] Uniquely, the Norwegian special territory of Svalbard is an entirely visa-free zone under the terms of the Svalbard Treaty.
Some countries—such as those in the Schengen Area—have agreements with other countries allowing each other's citizens to travel between them without visas. The World Tourism Organization announced that the number of tourists requiring a visa before travelling was at its lowest level ever in 2015.[3][4]
Overview
A visa generally gives non-citizens permission to appear at a foreign port of entry to apply for admission to a foreign country and to remain there within specified constraints, such as a time frame for entry, a limit on the time spent in the country, and a prohibition against employment. Many countries do not require a visa in some situations; this may be the result of treaties specifying reciprocal arrangements. The possession of a visa is not in itself a guarantee of entry into the country that issued it, and a visa can be revoked at any time.
A visa application in advance of arrival gives the country a chance to consider the applicant's circumstances, such as financial security, reason for travelling, and details of previous visits to the country. A visitor may also be required to undergo and pass security or health checks upon arrival at the port of entry.
History
In Western Europe in the late 19th century and early 20th century, passports and visas were not generally necessary for moving from one country to another. The relatively high speed and large movements of people traveling by train would have caused bottlenecks if regular passport controls had been used.[5] Passports and visas became usually necessary as travel documents only after World War I.[6]
Long before that, in ancient times, passports and visas were usually the same type of travel documents. In the modern world, visas have become separate secondary travel documents, with passports acting as the primary travel documents.
Conditions of issue
Some visas can be granted on arrival or by prior application at the country's embassy or consulate, or through a private visa service specialist who is specialized in the issuance of international travel documents. These agencies are authorized by the foreign authority, embassy, or consulate to represent international travellers who are unable or unwilling to travel to the embassy and apply in person. Private visa and passport services collect an additional fee for verifying customer applications, supporting documents, and submitting them to the appropriate authority. If there is no embassy or consulate in one's home country, then one would have to travel to a third country (or apply by post) and try to get a visa issued there. Alternatively, in such cases visas may be pre-arranged for collection on arrival at the border. The need or absence of need of a visa generally depends on the citizenship of the applicant, the intended duration of the stay, and the activities that the applicant may wish to undertake in the country he visits; these may delineate different formal categories of visas, with different issue conditions.
The issuing authority, usually a branch of the country's foreign ministry or department (e.g. U.S. State Department), and typically consular affairs officers, may request appropriate documentation from the applicant. This may include proof that the applicant is able to support himself in the host country (lodging, food), proof that the person hosting the applicant in his or her home really exists and has sufficient room for hosting the applicant, proof that the applicant has obtained health and evacuation insurance, etc. Some countries ask for proof of health status, especially for long-term visas; some countries deny such visas to persons with certain illnesses, such as AIDS. The exact conditions depend on the country and category of visa. Notable examples of countries requiring HIV tests of long-term residents are Russia[7] and Uzbekistan.[8] In Uzbekistan, however, the HIV test requirement is sometimes not strictly enforced.[8] Other countries require a medical test that includes an HIV test, even for a short-term tourism visa. For example, Cuban citizens and international exchange students require such a test approved by a medical authority to enter Chilean territory.
The issuing authority may also require applicants to attest that they have had no criminal convictions, or that they do not partake in certain activities (like prostitution or drug trafficking). Some countries will deny visas if the travellers' passports show evidence of citizenship of, or travel to, a country that is considered hostile by that country. For example, some Arabic-oriented countries will not issue visas to nationals of Israel and those whose passports bear evidence of visiting Israel.
Many countries frequently demand strong evidence of intent to return to the home country, if the visa is for a temporary stay, due to potential unwanted illegal immigration.
Types


Each country typically has a multitude of categories of visas with various names. The most common types and names of visas include:
By purpose
Transit visas
For passing through the country of issue to a destination outside that country. Validity of transit visas are usually limited by short terms such as several hours to ten days depending on the size of the country or the circumstances of a particular transit itinerary.
- Airside transit visa, required by some countries for passing through their airports even without going through passport control.
- Crew member, steward or driver visa, issued to persons employed or trained on aircraft, vessels, trains, trucks, buses and any other means of international transportation, or ships fishing in international waters.
Short-stay or visitor visas
For short visits to the visited country. Many countries differentiate between different reasons for these visits, such as:
- Private visa, for private visits by invitation from residents of the visited country.
- Tourist visa, for a limited period of leisure travel, no business activities allowed.
- Visa for medical reasons, for undertaking diagnostics or a course of treatment in the visited country's hospitals or other medical facilities.
- Business visa, for engaging in commerce in the country. These visas generally preclude permanent employment, for which a work visa would be required.
- Working holiday visa, for individuals traveling between nations offering a working holiday program, allowing young people to undertake temporary work while traveling.
- Athletic or artistic visa, issued to athletes and performing artists (and their supporting staff) performing at competitions, concerts, shows and other events.
- Cultural exchange visa, usually issued to athletes and performing artists participating in a cultural exchange program.
- Refugee visa, issued to persons fleeing the dangers of persecution, a war or a natural disaster.
- Pilgrimage visa: this type of visa is mainly issued to those intending to visit religious destinations, as for example in Saudi Arabia or Iran, and to take part in particular religious ceremonies. Such visas can usually be obtained relatively quickly and at low cost; those using them are usually permitted to travel only as a group, however. The best example is Hajj visas for Saudi Arabia.[9]
- Digital nomad visa, for digital nomads who want to temporarily reside in a country while performing remote work. Thailand launched its SMART Visa, targeted at high expertise foreigners and entrepreneurs to stay a longer time in Thailand, with online applications for the visa being planned for late 2018.[10] Estonia has also announced plans of a digital nomad visa, after the launch of its e-Residency program.[11]
Long-stay visas
Visas valid for longer but still finite stays:
- Student visa (F-1 in the United States), which allows its holder to study at an institution of higher learning in the issuing country. The F-2 visa allows the student's dependents to accompany them in the United States.
- Research visa, for students doing fieldwork in the host country.
- Temporary worker visa, for approved employment in the host country. These are generally more difficult to obtain but valid for longer periods of time than a business visa. Examples of these are the United States' H-1B and L-1 visas. Depending on a particular country, the status of temporary worker may or may not evolve into the status of permanent resident or to naturalization.
- Journalist visa, which some countries require of people in that occupation when traveling for their respective news organizations. Countries that insist on this include Cuba, China, Iran, Japan, North Korea, Saudi Arabia, the United States (I-visa) and Zimbabwe.
- Residence visa, granted to people obtaining long-term residence in the host country. In some countries, such as New Zealand, long-term residence is a necessary step to obtain the status of a permanent resident.
- Asylum visa, issued to people who have suffered or reasonably fear persecution in their own country due to their political activities or opinion, or features, or association with a social group; or were exiled from their own country.
Immigrant visas
Granted for those intending to immigrate to the issuing country (obtain the status of a permanent resident with a prospect of possible naturalization in the future):
- Spouse visa or partner visa, granted to the spouse, civil partner or de facto partner of a resident or citizen of a given country to enable the couple to settle in that country.
- Marriage visa, granted for a limited period before intended marriage or civil partnership based on a proven relationship with a citizen of the destination country. For example, a German woman wishing to marry an American man would obtain a Fiancée Visa (also known as a K-1 visa) to allow her to enter the United States. A K1 Fiancée Visa is valid for four months from the date of its approval.[12]
- Pensioner visa (also known as retiree visa or retirement visa), issued by a limited number of countries (Australia, Argentina, Thailand, Panama, etc.), to those who can demonstrate a foreign source of income and who do not intend to work in the issuing country. Age limits apply in some cases.
Official visas
These are granted to officials doing jobs for their governments, or otherwise representing their countries in the host country, such as the personnel of diplomatic missions.
- Diplomatic visas are normally only available to bearers of diplomatic passports.
- Courtesy visas are issued to representatives of foreign governments or international organizations who do not qualify for diplomatic status but do merit expedited, courteous treatment - an example of this is Australia's Special purpose visa.
By method of issue
Normally visa applications are made at and collected from a consulate, embassy or other diplomatic mission.
On-arrival visas
(Also known as Visa On Arrival, VOA), granted at a port of entry. This is distinct from not requiring a visa at all, as the visitor must still obtain the visa before they can even try to pass through immigration.
- Almost all countries will consider issuing a visa (or another document to the same effect) on arrival to a visitor arriving in unforeseen exceptional circumstances, for example:
- Under provisions of article 35 of the Schengen Visa Code, a visa may be issued at a border in situations such as the diversion of a flight causing air passengers in transit to pass through two or more airports instead of one. In 2010, Iceland's Eyjafjallajökull volcano erupted, causing significant disruption of air travel throughout Europe, and the EU responded by announcing that it would issue visas at land borders to stranded travelers.
- Under section 212(d)(4) of the Immigration and Naturalization Act, visa waivers can be issued to travelers arriving at American ports of entry in emergency situations or under other conditions.
- Certain international airports in Russia have consuls on-duty, who have the power to issue visas on the spot.
- Some countries issue visas on arrival to special categories of travelers, such as seafarers or air crew.
- Some countries issue them to regular visitors; there often are restrictions, for example:



Electronic visas
An electronic visa (e-Visa or eVisa) is stored in a computer and is linked to the passport number; no label, sticker or stamp is placed in the passport before travel. The application is done over the internet.























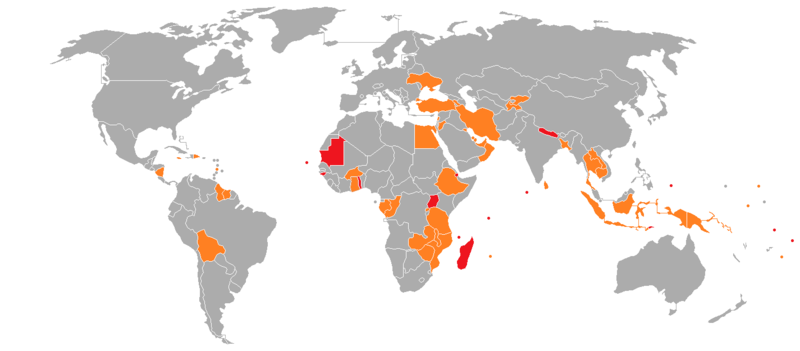
Authorities of Laos,[35] Madagascar,[36] Saudi Arabia,[37] South Africa,[38] Tunisia[39] and Uzbekistan[40] have announced plans to introduce electronic visas in 2018 or 2019.
These lists are not exhaustive. Some countries may have more detailed classifications of some of these categories reflecting the nuances of their respective geographies, social conditions, economies, international treaties, etc. Others, on the contrary, may combine some types into broader categories.
Electronic travel authorizations
A visa is an advance permission to visit a country, introduced for security reasons. Some countries demand an advance authorization obtained over the internet, which are not defined as visas.
- Canada requires all international visitors arriving by air who do not require a visa, except for United States nationals, to apply for an Electronic Travel Authorization (or eTA) before arrival.
- The United States has an internet system called Electronic System for Travel Authorization (or ESTA), but this is a security pre-screening only and does not technically qualify as a visa under US immigration law.
- The European Union is planning to adopt a system known as the European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS) for all non-EU citizens who are currently visa-exempt prior to their travel, to be implemented in 2020.[41]
Entry and duration period
Visas can also be single-entry, which means the visa is canceled as soon as the holder leaves the country; double-entry, or multiple-entry, which permits double or multiple entries into the country with the same visa. Countries may also issue re-entry permits that allow temporarily leaving the country without invalidating the visa. Even a business visa will normally not allow the holder to work in the host country without an additional work permit.
Once issued, a visa will typically have to be used within a certain period of time.
With some countries, the validity of a visa is not the same as the authorized period of stay. The visa validity then indicates the time period when entry is permitted into the country. For example, if a visa has been issued to begin on January 1 and to expire on March 30, and the typical authorized period of stay in a country is 90 days, then the 90-day authorized stay starts on the day the passenger enters the country (entrance has to be between January 1 and March 30). Thus, the latest day the traveler could conceivably stay in the issuing country is July 1 (if the traveler entered on March 30). This interpretation of visas is common in the Americas.
With other countries, a person may not stay beyond the period of validity of their visa, which is usually set within the period of validity of their passport. The visa may also limit the total number of days the visitor may spend in the applicable territory within the period of validity. This interpretation of visa periods is common in Europe.
Once in the country, the validity period of a visa or authorized stay can often be extended for a fee at the discretion of immigration authorities. Overstaying a period of authorized stay given by the immigration officers is considered illegal immigration even if the visa validity period isn't over (i.e., for multiple entry visas) and a form of being "out of status" and the offender may be fined, prosecuted, deported, or even blacklisted from entering the country again.
Entering a country without a valid visa or visa exemption may result in detention and removal (deportation or exclusion) from the country. Undertaking activities that are not authorized by the status of entry (for example, working while possessing a non-worker tourist status) can result in the individual being deemed deportable—commonly referred to as an illegal alien. Such violation is not a violation of a visa, despite the common misuse of the phrase, but a violation of status; hence the term "out of status".
Even having a visa does not guarantee entry to the host country. The border crossing authorities make the final determination to allow entry, and may even cancel a visa at the border if the alien cannot demonstrate to their satisfaction that they will abide by the status their visa grants them.
Some countries that do not require visas for short stays may require a long-stay visa for those who intend to apply for a residence permit. For example, the EU does not require a visa of citizens of many countries for stays under 90 days, but its member states require a long-stay visa of such citizens for longer stays.
Visa extensions
Many countries have a mechanism to allow the holder of a visa to apply to extend a visa. In Denmark, a visa holder can apply to the Danish Immigration Service for a Residence Permit after they have arrived in the country. In the United Kingdom, applications can be made to UK Visas and Immigration.
In certain circumstances, it is not possible for the holder of the visa to do this, either because the country does not have a mechanism to prolong visas or, most likely, because the holder of the visa is using a short stay visa to live in a country.
Visa run
Some foreign visitors sometimes engage in what is known as a visa run: leaving a country—usually to a neighboring country—for a short period just before the permitted length of stay expires, then return to the first country to get a new entry stamp in order to extend their stay ("reset the clock"). Despite the name, a visa run is usually done with a passport that can be used for an entry without a visa.
Visa runs are frowned upon by immigration authorities, as such acts may signify that the foreigner wishes to reside permanently and might also work in that country, purposes that visitors are prohibited from engaging in and usually require an immigrant visa or a work visa. Immigration officers may deny re-entry to visitors suspected of engaging in prohibited activities, especially when they have done repeated visa runs and have no evidence of spending reasonable time in their home countries or countries where they have the right to reside and work.
To combat visa run, some countries have limits as to how long visitors can spend in the country without a visa, as well as how much time they may have to stay out before "resetting the clock". For example, Schengen countries impose a maximum limit for visitors of 90 days in a 180-day window. Some countries do not "reset the clock" when a visitor comes back after visiting a neighboring country. For example, the United States does not give visitors a new period of stay when they come back from visiting Canada, Mexico or the Caribbean; instead they are readmitted to the United States for the remaining days granted on their initial entry. Some other countries, e.g. Thailand, allow visitors who arrive by land from neighbouring countries a shorter length of stay than those who arrive by air.
In some cases, a visa run is necessary to activate new visas or change immigration status of a person, for example, leaving a country and back immediately to activate a newly issued work visa before a person can legally work in that country.
Visa refusal
In general, an applicant may be refused a visa if he or she does not meet the requirements for admission or entry under that country's immigration laws. More specifically, a visa may be denied or refused when the applicant:
- has committed fraud, deception or misrepresentation in his or her current application as well as in a previous application
- has obtained a criminal record, has been arrested, or has criminal charges pending
- is considered to be a threat to national security
- does not have a good moral character
- has previous visa/immigration violations (even if the violations didn't happen in the country the applicant is seeking a visa for)
- had their previous visa application(s) or application for immigration benefits refused and cannot prove that the reasons for the previous refusals no longer exist or are not applicable any more (even if the refusals didn't previously happen in the country the applicant is seeking a visa for)
- cannot prove to have strong ties to their current country of nationality or residence (for those who are applying for temporary or non-immigrant visas)
- intends to reside or work permanently in the country she/he will visit if not applying for an immigrant or work visa respectively
- fails to demonstrate intent to return (for non-immigrants)
- fails to provide sufficient evidence/documents to prove eligibility for the visa sought after
- does not have a legitimate reason for the journey
- does not have adequate means of financial support for themselves or family
- does not have adequate medical insurance, especially if engaging in high risk activities (e.g. rock climbing, skiing, etc)
- does not have travel arrangements (i.e. transport and lodging) in the destination country
- does not have health/travel insurance valid for the destination and the duration of stay
- has a sexually transmitted disease
- is a citizen of a country to which the destination country is hostile or at war with
- has previously visited, or intends to visit, a country to which the destination country is hostile
- has a communicable disease, such as tuberculosis or ebola
- has a passport that expires too soon
- didn't use a previously issued visa at all without a valid reason (e.g., a trip cancellation due to a family emergency)
Even if a traveler does not need a visa, the aforementioned criteria can also be used by border police to refuse the traveler entry into the country in question.
Visa policies
The main reasons states impose visa restrictions on foreign nationals are to curb illegal immigration, security concerns, and reciprocity for visa restrictions imposed on their own nationals. Typically, nations impose visa restrictions on citizens of poorer countries, along with politically unstable and undemocratic ones, as it is considered more likely that people from these countries will seek to illegally immigrate. Visa restrictions may also be imposed when nationals of another country are perceived as likelier to be terrorists or criminals, or by autocratic regimes that perceive foreign influence to be a threat to their rule.[42][43] According to Professor Eric Neumayer of the London School of Economics:
"The poorer, the less democratic and the more exposed to armed political conflict the target country is, the more likely that visa restrictions are in place against its passport holders. The same is true for countries whose nationals have been major perpetrators of terrorist acts in the past".[42]
Some countries apply the principle of reciprocity in their visa policy. A country's visa policy is called 'reciprocal' if it imposes visa requirement against citizens of all the countries that impose visa requirements against its own citizens. The opposite is rarely true: a country rarely lifts visa requirements against citizens of all the countries that also lift visa requirements against its own citizens, unless a prior bilateral agreement has been made.
A fee may be charged for issuing a visa; these are often also reciprocal—hence, if country A charges country B's citizens US$50 for a visa, country B will often also charge the same amount for country A's visitors. The fee charged may also be at the discretion of each embassy. A similar reciprocity often applies to the duration of the visa (the period in which one is permitted to request entry of the country) and the number of entries one can attempt with the visa. Other restrictions, such as requiring fingerprints and photographs, may also be reciprocated. Expedited processing of the visa application for some countries will generally incur additional charges.
Government authorities usually impose administrative entry restrictions on foreign citizens in three ways - countries whose nationals may enter without a visa, countries whose nationals may obtain a visa on arrival and countries whose nationals require a visa in advance. Nationals who require a visa in advance are usually advised to obtain them at a diplomatic mission of their destination country. Several countries allow nationals of countries that require a visa to obtain them online.
The following table lists visa policies of all countries by the number of foreign nationalities that may enter that country for tourism without a visa or by obtaining a visa on arrival with normal passport. It also notes countries that issue electronic visas to certain nationalities. Symbol "+" indicates a country that limits the visa-free regime negatively by only listing nationals who require a visa, thus the number represents the number of UN member states reduced by the number of nationals who require a visa and "+" stands for all possible non-UN member state nationals that might also not require a visa. "N/A" indicates countries that have contradictory information on its official websites or information supplied by the Government to IATA. Some countries that allow visa on arrival do so only at a limited number of entry points. Some countries such as the European Union member states have a qualitatively different visa regime between each other as it also includes freedom of movement.
The following table is current as of 1 March 2018. Source:[44]
| Country | Total (excl. electronic visas) |
Visa-free | Visa on arrival | Electronic visas | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | visa on arrival at Hamid Karzai International Airport for business visitors, journalists, athletes, airline staff | ||||
| 81 | 81 | ||||
| 7 | 8 | ||||
| 3 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 104 | 104 | All | |||
| 86 | 86 | 0 | |||
| 135 | 56 | 82 | |||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | All-1 | ||
| 23 | 9 | 15 | 93 | ||
| 121 | 120 | ||||
| 69 | 4 | 65 | 115 | ||
| 173 | 25 | All-20 | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 114 | 108 | ||||
| 91 | 22+79 | ||||
| 106 | 101 | ||||
| 198 | 54 | All | |||
| 3 | 3 | ||||
| 178 | 51 | 124+ | |||
| 100 | 97 | ||||
| 103 | 103 | ||||
| 92 | 93 | 4 | |||
| 62 | 55 | 7 | |||
| 69 | 18 | 52 | |||
| 6 | 6 | ||||
| 198 | 8 | All | All-1 | ||
| 5 | 6 | ||||
| 53 | 53 | ||||
| 197 | 19 | 178 | |||
| 15 | 16 | ||||
| 15 | 14 | 1 | |||
| 94 | 90 | ||||
| 16 | 13 | ||||
| 94 | 95 | All | |||
| 198 | 0 | All | |||
| 13 | 13 | 5 | |||
| 7 | 4 | 3 | |||
| 97 | 97 | ||||
| 21 | 21 | All | |||
| 178 | 20 | ||||
| 198 | 0 | All | |||
| 196 | All-2 | ||||
| 107 | 107 | ||||
| 186 | All-13 | 1 | |||
| 115 | 8 | 103 | 46 | ||
| 87 | 87 | ||||
| 9 | 8 | ||||
| 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 42 | 2 | 40 | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 108 | 107 | ||||
| 51 | 9 | 47 | All | ||
| 124 | 121 | 4 | |||
| 93 | 94 | ||||
| 54 | 20 | 34 | |||
| 101 | 103 | 14 | |||
| 87 | 86 | ||||
| 21 | 21 | ||||
| 198 | 14 | 180+ | All | ||
| 55 | 53 | any visitor as tourist can obtain visa on arrival | |||
| 194 | All-4 | ||||
| 84 | 84 | ||||
| 144 | 144 | 1 | |||
| 3 | 3 | 2 | 150 | Limited e-Tourist Visa locations. | |
| 169 | 168 | ||||
| 183 | 8 | 176+ | |||
| 7 | 1 | 6 | |||
| 87 | 55 | +31 EU/EEA/CH citizens. | |||
| 99 | 99 | ||||
| 122 | 93 | 23 | |||
| 66 | 66 | ||||
| 137 | 10 | 120 | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 61 | 61 | ||||
| 186 | 43 | 0 | All-16 | ||
| 72 | 68 | ||||
| 0 | |||||
| 111 | 117 | ||||
| 59 | 5 | 53 | 53 | ||
| 80 | 61 | 20 | All | ||
| 165 | 15 | All-30 | |||
| 102 | 7 | 79 | |||
| 71 | 71 | All | |||
| 15 | 15 | ||||
| 3 | 2 | ||||
| 192 | 81 | All-6 | |||
| 84 | 85 | ||||
| 197 | 0 | All-1 | |||
| 145 | 33 | 131 | |||
| 162 | 162 | 10 | |||
| 198 | 0 | All | |||
| 24 | 25 | ||||
| 86 | 33 | 55 | |||
| 198 | 9 | 185 | |||
| 182 | 111 | 66 | |||
| 67 | 65 | 3 | |||
| 198 | 194+ | ||||
| 69 | 69 | ||||
| 21 | 22 | ||||
| 94 | 95 | ||||
| 71 | 70 | ||||
| 198 | 8 | 186+ | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 8 | 8 | 102 | |||
| 53 | 52 | ||||
| 14 | 0 | 16 | |||
| 186 | 1 | 182+ | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 61 | 60 | ||||
| 161 | 92 | 74 | |||
| 19 | 19 | ||||
| 18 | 17 | 1 | |||
| 72 | 5 | 68 | |||
| 5 | 5 | ||||
| 196 | 34 | 158+ | |||
| 119 | 117 | ||||
| 71 | 0 | 70 | |||
| 64 | 57 | 5 | |||
| 100 | 98 | ||||
| 160 | 157 | ||||
| 90 | 5 | 80+4 | All-2 | Limited VOA locations. | |
| 44 | 48 | ||||
| 198 | 20 | 174+ | All | ||
| 116 | 102 | All | |||
| 143 | 95 | 54 | |||
| 190 | 0 | All-8 | |||
| 198 | All | ||||
| 57 | 45 | 0 | All | ||
| 4 | 4 | ||||
| 93 | 62 | 32 EU/EEA/CH citizens. | |||
| 124 | 125 | ||||
| 86 | 78 | ||||
| 198 | 34 | 160+ | |||
| 16 | 15 | ||||
| 163 | 160+ | ||||
| 76 | 30 | 47 | |||
| 198 | Limited VOA locations. | ||||
| 76 | 75 | ||||
| 5 | 0 | 6 | |||
| 179 | 3 | 172+ | 172+ | ||
| 8 | 32 | 2 | |||
| 70 | 28 | 50 | |||
| 93 | 96 | ||||
| 0 | |||||
| 81 | 9 | 81 | |||
| 176 | 6 | All-24 | |||
| 78 | 57 | 19 | |||
| 198 | 30 | All | Limited VOA locations. | ||
| 198 | 14 | 164+ | |||
| 68 | 31 | 37 | |||
| 104 | 101 | 2 | |||
| 96 | 96 | +11 for organized groups. | |||
| 159 | 78 | 0 | 43 | e-Visas can also be obtained on arrival for a higher cost. | |
| 1 | |||||
| 198 | 30 | 160+ | |||
| 198 | 33 | 161+ | All | ||
| 100 | 64 | 34 | |||
| 59 | 37 | 18 | |||
| 91 | 56 | 4 | +31 EU/EEA/CH citizens. | ||
| 44 | 42 | ||||
| 79 | 76 | ||||
| 16 | 16 | ||||
| 120 | 120 | ||||
| 70 | 71 | ||||
| 24 | 24 | 40 | |||
| 12 | 1 | 11 | |||
| 136 | 43 | 95 | All | ||
| 143 | 44 | 81 | All |
Visa exemption agreements
Possession of a valid visa is a condition for entry into many countries, and exemption schemes exist. In some cases visa-free entry may be granted to holders of diplomatic passports even as visas are required by normal passport holders (see: Passport).
Some countries have reciprocal agreements such that a visa is not needed under certain conditions, e.g., when the visit is for tourism and for a relatively short period. Such reciprocal agreements may stem from common membership in international organizations or a shared heritage:
- All citizens of European Union and EFTA member countries can travel to and stay in all other EU and EFTA countries without a visa. See Four Freedoms (European Union) and Citizenship of the European Union. Also See Brexit.
- The United States Visa Waiver Program allows citizens of 38 countries to travel to the United States without a visa (although a pre-trip entry permission, ESTA, is needed).[48]
- Any Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) citizen can enter and stay as long as required in any other GCC member state.
- All citizens of members of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), excluding those defined by law as undesirable aliens, may enter and stay without a visa in any member state for a maximum period of 90 days. The only requirement is a valid travel document and international vaccination certificates.[49]
- Nationals of the East African Community member states do not need visas for entry into any of the member states.[50][51][52]
- Some countries in the Commonwealth do not require tourist visas of citizens of other Commonwealth countries.
- Citizens of member states of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations do not require tourist visas to visit another member state, with the exception of Myanmar. Until 2009, Burmese citizens were required to have visas to enter all other ASEAN countries. Following the implementation of visa exemption agreements with the other ASEAN countries, in 2016 Burmese citizens are only required to have visas to enter Malaysia and Singapore. Myanmar and Singapore had agreed on a visa exemption scheme set to be implemented on 1 December 2016.[53] ASEAN citizens are entitled to use the Burmese visa on arrival facility.
- Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) member states mutually allow their citizens to enter visa-free, at least for short stays. There are exceptions between Tajikistan and Uzbekistan, and between Armenia and Azerbaijan.
- Nepal and India allow their citizens to enter, live and work in each other's countries due to the Indo-Nepal friendship treaty of 1951. Indians do not require a visa or passport to travel to Bhutan and are only required to obtain passes at the border checkpoints, whilst Bhutan nationals holding a valid Bhutanese passport are authorised to enter India without a visa.
- In the past, Qatar citizens did not require permission to enter the UAE, Saudi Arabia and other Gulf nations. That has now changed.
- Sometimes, citizens who hold a valid visa for America or another country, can enter another country.
Other countries may unilaterally grant visa-free entry to nationals of certain countries to facilitate tourism, promote business, or even to cut expenses on maintaining consular posts abroad.
Some of the considerations for a country to grant visa-free entry to another country include (but are not limited to):
- being a low security risk for the country potentially granting visa-free entry
- diplomatic relationship between two countries
- conditions in the visitor's home country as compared to the host country
- having a low risk of overstaying or violating visa terms in the country potentially granting visa-free entry
To have a smaller worldwide diplomatic staff, some countries rely on other country's (or countries') judgments when issuing visas. For example, Mexico allows citizens of all countries to enter without Mexican visas if they possess a valid American visa that has already been used. Costa Rica accepts valid visas of Schengen/EU countries, Canada, Japan, South Korea and the United States (if valid for at least 3 months on date of arrival). The ultimate example of such reliance is Andorra, which imposes no visa requirements of its own because it has no international airport and is inaccessible by land without passing through the territory of either France or Spain and is thus "protected" by the Schengen visa system.
Visa-free travel between countries also occurs in all cases where passports (or passport-replacing documents such as laissez-passer) are not needed for such travel. (For examples of passport-free travel, see International travel without passports.)
As of 2016, the Visa Restrictions Index ranks the German passport as the one with the most visa exemptions by other nations, allowing holders of this passport to visit 177 countries without obtaining a visa in advance of arrival.
Common visas
Normally, visas are valid for entry only into the country that issued the visa. Countries that are members of regional organizations or party to regional agreements may, however, issue visas valid for entry into some or all of the member states of the organization or agreement:
- The Schengen Visa is a visa for the Schengen Area, which consists of most of the European Economic Area, plus several other adjacent countries. The visa allows visitors to stay in the Schengen Area for up to 90 days within a 180-day period. The visa is valid for tourism, family visits, and business.
- The Central American Single Visa (Visa Única Centroamericana) is a visa for Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua. It was implemented by the CA-4 agreement. It allows citizens of those four countries free access to other member countries. It also allows visitors to any member country to enter another member country without having to obtain another visa.
Possible common visa schemes
These are potentially new common visas:
- The ASEAN common visa scheme is considered when the labor union goes into effect in 2016 (being delayed a year); Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar are opting in earlier, however. After talk arose of a CLMV common visa,[54] with Thailand being omitted, Thailand initiated and begun implementation of a trial common visa with Cambodia, but cited security risks as the major hurdle. The trial run was delayed,[55] but Thailand implemented a single visa scheme with Cambodia beginning on December 27, 2012, on a trial basis.[56]
- A Gulf Cooperation Council single visa has been recommended as a study submitted to the council.[57]
- The Pacific Alliance, that currently consists of Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru, offer a common visa for tourism purposes only in order to make it easier for nationals from countries outside of the alliance to travel through these countries by not having to apply for multiple visas.[58]
- An East African Single Tourist Visa is under consideration by the relevant sectoral authorities under the East African Community (EAC) integration program. If approved the visa will be valid for all five partner states in the EAC (Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda and Burundi). Under the proposal for the visa, any new East African single visa can be issued by any partner state's embassy. The visa proposal followed an appeal by the tourist boards of the partner states for a common visa to accelerate promotion of the region as a single tourist destination and the EAC Secretariat wants it approved before November's World Travel Fair (or World Travel Market) in London.[59] When approved by the East African council of ministers, tourists could apply for one country's entry visa, which would then be applicable in all regional member states as a single entry requirement initiative.[60] This is considered also by COMESA.
- The SADC UNIVISA (or Univisa) has been in development since Southern African Development Community (SADC) members signed a Protocol on the Development of Tourism in 1998. The Protocol outlined the Univisa as an objective so as to enable the international and regional entry and travel of visitors to occur as smoothly as possible. It was expected to become operational by the end of 2002.[61] Its introduction was delayed and a new implementation date, the end of 2006, was announced.[62] The univisa was originally intended to only be available, initially, to visitors from selected "source markets" including Australia, the Benelux countries, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Portugal, Spain, the United Kingdom and the United States.[61] It is now expected that when the Univisa is implemented, it will apply to non-SADC international (long-haul) tourists traveling to and within the region and that it will encourage multi - destination travel within the region. It is also anticipated that the univisa will enlargen tourist market for transfrontier parks by lowering the boundaries between neighboring countries in the parks. The visa is expected to be valid for all the countries with trans frontier parks (Botswana, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa and Zimbabwe) and some other SADC countries (Angola and Swaziland).[63] As of 2017, universal visa is implemented by Zambia and Zimbabwe. Nationals of 65 countries and territories are eligible for visa on arrival that is valid for both countries. This visa is branded KAZA Uni-visa programme after Kavango–Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area (KAZA). It is expected that other SADC countries will join the programme in the future.[64]
Previous common visa schemes
These schemes no longer operate.
- The CARICOM Visa was introduced in late 2006 and allowed visitors to travel between 10 CARICOM member states (Antigua & Barbuda, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, St. Kitts & Nevis, St. Lucia, St. Vincent & the Grenadines and Trinidad and Tobago). These ten member countries had agreed to form a "Single Domestic Space" in which travelers would only have their passport stamped and have to submit completed, standardized entry and departure forms at the first port and country of entry. The CARICOM Visa was applicable to the nationals of all countries except CARICOM member states (other than Haiti) and associate member states, Canada, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, South Africa, the United Kingdom, the United States of America and the overseas countries, territories or departments of these countries. The CARICOM Visa could be obtained from the Embassies/Consulates of Barbados, Jamaica and Trinidad & Tobago and in countries that have no CARICOM representatives, the applications forms could be obtained from the embassies and consulates of the United Kingdom. The common visa was only intended for the duration of the 2007 Cricket World Cup and was discontinued on May 15, 2007. Discussions are ongoing into instituting a revised CARICOM visa on a permanent basis in the future.
- A predecessor of the Schengen common visa was the Benelux visa. Visas issued by Belgium, Netherlands and Luxemburg were valid for all the three countries.
Exit visas
Europe
During the Fascist period in Italy, an exit visa was required from 1922 to 1943. Nazi Germany required exit visas from 1933 to 1945.[65] The Soviet Union and its Warsaw Pact allies required exit visas both for emigration and for those who wanted to leave the USSR for a shorter period.
Some countries, including the Czech Republic,[66] require that an alien who needs a visa on entry be in possession of a valid visa upon exit. To satisfy this formal requirement, exit visas sometimes need to be issued. Russia requires an exit visa if a visitor stays past the expiration date of their visa. They must then extend their visa or apply for an exit visa and are not allowed to leave the country until they show a valid visa or have a permissible excuse for overstaying their visa (e.g., a note from a doctor or a hospital explaining an illness, missed flight, lost or stolen visa). In some cases, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs can issue a Return-Home certificate that is valid for ten days from the embassy of the visitor's native country, thus eliminating the need for an exit visa.
A foreign citizen granted a temporary residence permit in Russia needs a temporary resident visa to take a trip abroad (valid for both exit and return). It is also colloquially called an exit visa. Not all foreign citizens are subject to that requirement. Citizens of Germany, for example, do not require this exit visa.
Asia
Saudi Arabia and Qatar have an exit visa requirement, particularly for foreign workers. This is part of the kafala system, also present in Lebanon, United Arab Emirates, Iraq, Kuwait, and Oman. Consequently, at the end of a foreign worker's employment period, the worker must secure clearance from their employer stating that the worker has satisfactorily fulfilled the terms of their employment contract or that the worker's services are no longer needed. The exit visa can also be withheld if there are pending court charges that need to be settled or penalties that have to be meted out.
Nepal requires citizens emigrating to the United States on an H-1B visa to present an exit permit issued by the Ministry of Labour. This document is called a work permit and needs to be presented to immigration to leave the country.[67]
Uzbekistan was the last remaining former USSR state that required an exit visa, which was valid for a two-year period. The practice was abolished in 2016.[68] There has been explicit UN complaint about this practice.[69]
The DPRK (North Korea) requires that its citizens obtain an exit visa stating the traveller's destination country and time to be spent abroad before leaving the country. Additionally, DPRK authorities also require that their citizens obtain a re-entry visa from a DPRK embassy or mission abroad before being allowed back into the DPRK.
The government of the People's Republic of China requires its citizens to obtain a Two-way Permit, issued by the PRC authorities, prior to their visit to the Chinese dependencies of Hong Kong or Macau. The Two-way Permit is a de facto exit visa for Hong Kong- or Macau-bound trips for PRC citizens.
Singapore operates an Exit Permit scheme in order to enforce the national service obligations of its male citizens and permanent residents.[70] Requirements vary according to age and status:[71]
| Status | Time overseas | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-enlistment: 13 – 16.5 years of age | 3+ months | Exit permit |
| 2+ years | Exit permit + bond | |
| Pre-enlistment: 16.5 years of age and older | 3+ months | Registration, exit permit + bond[72] |
| Full-time National Service | 3+ months | Exit permit |
| Operationally-ready National Service | 14+ days | Overseas notification |
| 6+ months | National service unit approval + exit permit | |
| Regular servicemen | 3+ months | Exit permit, where Minimum Term of Engagement is not complete |
| 6+ months | Exit permit |
Taiwan[73] and South Korea, two countries currently enforcing conscription, require draftees to register with local immigration office before short-term international travels and studies.
The Americas
The government of Cuba announced in October 2012 its plans to remove exit visa requirements to be effective January 14, 2013, albeit with some exceptions.[74]
Guatemala requires any foreigner who is a permanent resident to apply for a multiple 5-year exit visa.
United States of America
The United States of America does not require exit visas. Since October 1, 2007, however, the U.S. government requires all foreign and U.S. nationals departing the United States by air to hold a valid passport (or certain specific passport-replacing documents). Even though travelers might not require a passport to enter a certain country, they will require a valid passport booklet (booklet only, U.S. Passport Card not accepted) to depart the United States in order to satisfy the U.S. immigration authorities.[75] Exemptions to this requirement to hold a valid passport include:
- U.S. Permanent Resident/Resident Alien Card (Form I-551);
- U.S. Military ID Cards when traveling on official orders;
- U.S. Merchant Mariner Card;
- NEXUS Card;
- U.S. Travel Document:
- Refugee Travel Document (Form I-571); or
- Permit to Re-Enter (Form I-327)
- Emergency Travel Document (e.g. Consular Letter) issued by a Foreign Embassy or Consulate specifically for the purpose of travel to the bearer's home country.
- Nationals of Mexico holding one of the following documents:
- (expired) "Matricula Consular"; or
- Birth Certificate with consular registration; or
- Certificate of Nationality issued by a Mexican consulate abroad; or
- Certificate of Military Duty (Cartilla Militar); or
- Voter's Certificate (Credencial IFE or Credencial para Votar).
In addition, green card holders and certain other aliens must obtain a certificate of compliance (also known as a "sailing permit" or "departure permit") from the Internal Revenue Service proving that they are up-to-date with their US income tax obligations, before they may leave the country.[76] While the requirement has been in effect since 1921, it has not been stringently enforced, but the House Ways and Means Committee has recently considered it as a way to increase tax revenues.[77]
Visa restrictions
Henley & Partners
Henley & Partners annually compiles their Passport Index, which ranks passports according to the lack of visas required of their bearers. The index is based on the International Air Transport Association database.[78] The HPI consists of a ranking of passports according to how many other territories can be reached 'visa-free' (defined below). All distinct destination countries and territories in the IATA database are considered. However, since not all territories issue passports, there are far fewer passports to be ranked than destinations against which queries are made.[79]
World Tourism Organization
The World Tourism Organization in its Visa Openness Report concluded that the 30 countries whose citizens were least affected by visa restrictions in 2015 were (based on the data compiled by the UNWTO, based on information from national official institutions):[80]
| Rank | Country | Mobility index (out of 215 with no visa weighted by 1, visa on arrival weighted by 0.7, eVisa by 0.5 and traditional visa weighted by 0) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 160 | |
| 8 | 159 | |
| 14 | 158 | |
| 21 | 157 | |
| 24 | 156 | |
| 26 | 155 | |
| 29 | 154 |
The world average score in 2015 was 89, among advanced economies the average score was 154 and among emerging economies, 73 (Brazil scored 144, Russia 93, Indonesia 57, India 50 and China 46).
Non-visa restrictions
Passport validity length
In the absence of specific bilateral agreements, countries requiring passports to be valid at least 6 months on arrival include Afghanistan, Algeria, Anguilla, Bahrain,[81] Bhutan, Botswana, British Virgin Islands, Brunei, Cambodia, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Cayman Islands, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Costa Rica, Côte d'Ivoire, Curaçao, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Equatorial Guinea, Fiji, Gabon, Guinea Bissau, Guyana, Haiti, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel,[82] Jordan, Kenya, Kiribati, Kuwait, Laos, Madagascar, Malaysia, Maldives, Marshall Islands, Mongolia, Myanmar, Namibia, Nepal, Nicaragua, Nigeria, Oman, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Philippines, Rwanda, Samoa, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Solomon Islands, Somalia, Sri Lanka, Sudan, Suriname, Tanzania, Thailand, Timor-Leste, Tokelau, Tonga, Tuvalu, Uganda, United Arab Emirates, Vanuatu, Venezuela and Vietnam.[83]
Turkey requires passports to be valid for at least 150 days upon entry.
Countries requiring passports valid for at least 4 months on arrival include Micronesia and Zambia.
Countries requiring passports valid for at least 3 months beyond the period of intended stay include European Union countries (except the Republic of Ireland and the United Kingdom), Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland (and always excepting EU/EEA/Swiss nationals), Azerbaijan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Nauru, Moldova, New Zealand and 3 months validity on arrival in Albania, Honduras, Macedonia, Panama, Qatar and Senegal.
Bermuda requires passports to be valid for at least 45 days upon entry.
Countries that require a passport validity of at least one month beyond the period of intended stay include Eritrea, Hong Kong, Lebanon, Macau and South Africa.
Other countries require either a passport valid on arrival or a passport valid throughout the period of the intended stay. Some countries have bilateral agreements with other countries to shorten the period of passport validity required for each other's citizens[84][85] or even accept passports that have already expired (but not been cancelled).[86]
Blank passport pages
Many countries require a minimum number of blank pages in the passport being presented, generally one or two pages.[87] Endorsement pages, which often appear after the visa pages, are not counted as being available.
Vaccination
Many African countries, including Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Republic of the Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Rwanda, São Tomé and Príncipe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Uganda, and Zambia, require all incoming passengers to have a current International Certificate of Vaccination.
Some other countries require vaccination only if the passenger is coming from an infected area or has recently visited one.[88]
Israeli stamps

Kuwait,[89] Lebanon,[90] Libya,[91] Saudi Arabia,[92] Sudan,[93] Syria[94] and Yemen[95] do not allow entry to people with passport stamps from Israel or whose passports have either a used or an unused Israeli visa, or where there is evidence of previous travel to Israel such as entry or exit stamps from neighbouring border posts in transit countries such as Jordan and Egypt.
To circumvent this Arab League boycott of Israel, the Israeli immigration services have now mostly ceased to stamp foreign nationals' passports on either entry to or exit from Israel. Since 15 January 2013, Israel no longer stamps foreign passports at Ben Gurion Airport, giving passengers a card instead that reads: "Since January 2013 a pilot scheme has been introduced whereby visitors are given an entry card instead of an entry stamp on arrival. You should keep this card with your passport until you leave. This is evidence of your legal entry into Israel and may be required, particularly at any crossing points into the Occupied Palestinian Territories." [96] Passports are still (as of 22 June 2017) stamped at Erez when travelling into and out of Gaza. Also, passports are still stamped (as of 22 June 2017) at the Jordan Valley/Sheikh Hussein and Yitzhak Rabin/Arava land borders with Jordan.
Iran refuses admission to holders of passports containing an Israeli visa or stamp that is less than 12 months old.
Armenian ethnicity
Due to a state of war existing between Armenia and Azerbaijan, the government of Azerbaijan not only bans entry of citizens from Armenia, but also all citizens and nationals of any other country who are of Armenian descent, to the Republic of Azerbaijan[97][98] (although there have been exceptions, notably for Armenia's participation at the 2015 European Games held in Azerbaijan).
Azerbaijan also strictly bans any visit by foreign citizens to the separatist region of Nagorno-Karabakh[99] (the de facto independent Republic of Artsakh), its surrounding territories and the Azerbaijani exclaves of Karki, Yuxarı Əskipara, Barxudarlı and Sofulu which are de jure part of Azerbaijan but under control of Armenia, without the prior consent of the government of Azerbaijan. Foreign citizens who enter these occupied territories will be permanently banned from entering the Republic of Azerbaijan[100] and will be included in their "list of personae non gratae".[101] As of April 2018 the list contains 710 persons.
Upon request, the authorities of the largely unrecognized Republic of Artsakh may attach their visa and/or stamps to a separate piece of paper in order to avoid detection of travel to their country.
Criminal record
Some countries (for example: Australia, Canada, Fiji, New Zealand and the United States [102]) routinely deny entry to non-citizens who have a criminal record.
Persona non grata
The government of a country can declare a diplomat persona non grata, banning their entry into that country. In non-diplomatic use, the authorities of a country may also declare a foreigner persona non grata permanently or temporarily, usually because of unlawful activity. Attempts to enter the Gaza strip by sea may attract a 10-year ban on entering Israel.[103]
Fingerprinting
Several countries mandate that all travellers, or all foreign travellers, be fingerprinted on arrival and will refuse admission to or even arrest those travellers that refuse to comply. In some countries, such as the United States, this may apply even to transit passengers who merely wish to quickly change planes rather than go landside.[104]
Fingerprinting countries include Afghanistan,[105][106] Argentina,[107] Brunei, Cambodia,[108] China when entering through Shenzhen airport,[109] Ethiopia,[110] Ghana, India, Japan,[111][112] Malaysia upon entry and departure,[113] Paraguay, Saudi Arabia,[114] Singapore, South Korea,[115] and Taiwan.[116]
Additionally, the United Arab Emirates conducts iris scanning on visitors who need to apply for a visa.[117][118]
See also
References
- ↑ "Online Etymology Dictionary".
- ↑ B. S. Prakash (2006-05-31). "Only an exit visa". Retrieved 2008-05-10.
- ↑ "Visa requirements for tourism eased around the world: UN agency". 15 January 2016.
- ↑ "Visa Openness Report 2015 January 2016".
- ↑ "History of passports - Passport Canada". 2013-06-03. Archived from the original on 2013-06-03. Retrieved 2018-06-26.
- ↑ Benedictus, Leo (2006-11-17). "A brief history of the passport". the Guardian. Retrieved 2018-06-26.
- ↑ Canada, Gouvernement du Canada, Affaires étrangères et Commerce international. "International.gc.ca".
- 1 2 Canada, Gouvernement du Canada, Affaires étrangères et Commerce international. "Affaires mondiales Canada - international.gc.ca".
- ↑ "Ministry of foreign affairs of Saudi Arabia - Pilgrimage visa".
- ↑ "Thailand 4-Year Smart Visa arrives next month- Few Digital Nomads should be covered – Moving Nomads". movingnomads.com. Retrieved 2018-03-01.
- ↑ "Estonia plans its Digital Nomad Visa - Enterprise Times". Enterprise Times. 2018-02-27. Retrieved 2018-03-01.
- ↑ "404 - Page Not Found". www.travel.state.gov.
- ↑
- ↑ "Republic of Armenia Electronic Visa System". e-Visa. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "The Electronic Visa System of Azerbaijan Republic". evisa.gov.az.
- ↑ "Bahrain Visa Online Application". Evisa.gov.bh. Retrieved 2014-06-30.
- ↑ "Brazil Visa Information In eVisa - Home Page". www.vfsglobal.com.
- ↑ "eVisa". Archived from the original on 2014-07-28.
- ↑ "What is an Electronic Travel Authorization?". Government of Canada. Retrieved 2017-09-29.
- ↑
- ↑ "Ethiopian eVISA". www.evisa.gov.et.
- 1 2 "National Web Portal On Immigration".
- ↑ "Energie – SNEDAI GROUPE". www.snedai.com.
- ↑ "evisa.go.ke - Republic of Kenya Electronic Visa System". evisa.go.ke.
- ↑ "Kuwait e-Visa".
- ↑ "Official Government Website". Myanmar E visa. Archived from the original on 2013-10-19. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑
- ↑ "VISA". Migration.gov.rw. 2013-09-10. Archived from the original on 2013-10-16. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "Main Page". evisa.gov.kn.
- ↑ Submission of Application for Visa Electronically (SAVE), Government of Singapore
- ↑ "Online Visa Application". Department of Immigration and Emigration of Sri Lanka. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- ↑ "From Rep. of Turkey Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Archived from the original on 2013-10-05. Retrieved 2013-10-03.
- ↑ "Electronic Visa Application System".
- ↑ "Uganda e-Visa". visas.immigration.go.ug.
- ↑ Le Laos veut lancer un e-visa d'ici début 2019
- ↑ eVisa Madagascar
- ↑ Saudi Arabia to introduce tourist visas and online application in 2018
- ↑
- ↑ Manager, African (11 July 2017). "Le visa électronique fait son apparition fin 2017/début 2018 - African Manager".
- ↑ "Узбекистан отменяет визы для граждан семи стран". gazeta.uz. 3 February 2018. Retrieved 7 April 2018.
- ↑ "European Travel Information and Authorisation System (ETIAS) - Think Tank". www.europarl.europa.eu. Retrieved 2018-03-15.
- 1 2 "Eprints.lse.ac.uk" (PDF).
- ↑ "Study Finds Global Visa Curbs Increasingly Restrictive, Imbalanced".
- ↑ "Country information (visa section)". Timatic. International Air Transport Association (IATA) through Olympic Air.
- ↑ "Visa Information".
- ↑ "Indian Tourist Visa On Arrival". Retrieved 7 January 2015.
- ↑ Encompasses Schengen member states - Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland as well as Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus and Romania and countries without border controls - Monaco, San Marino, Vatican and a country accessible only via Schengen area - Andorra.
- ↑ "Esta.cbp.dhs.gov".
- ↑ "ECOWAS Official Site".
- ↑ "Tanzanian Embassy in France".
- ↑ "Ugandan Visa".
- ↑ "Kenyahighcommission.net".
- ↑ "Myanmar, Singapore agree on visa exemption to boost tourism". Bangkok Post. 2016-06-08. Retrieved 2016-08-05.
- ↑ "CLMV bloc inks tourism pact, mulls over single tourist visa - TTG Asia - Leader in Hotel, Airlines, Tourism and Travel Trade News". TTG Asia. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "Thailand-Cambodia joint visa delayed | Bangkok Post: news". Bangkok Post. 2012-11-23. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ IANS – Thu, Dec 27, 2012 (2012-12-27). "Thai-Cambodia single visa for visitors - Yahoo News Maktoob". En-maktoob.news.yahoo.com. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "Single GCC tourism visa will boost visitor numbers — study". GulfNews.com. 2012-11-18. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "México, Colombia, Chile y Perú crean la visa Alianza del Pacífico – CNN en Español: Ultimas Noticias de Estados Unidos, Latinoamérica y el Mundo, Opinión y Videos - CNN.com Blogs". Cnnespanol.cnn.com. Retrieved 2013-10-22.
- ↑ "Single East African visa for tourists coming in November". Archived from the original on 2008-05-31.
- ↑ "East Africa geared for single tourist entry visa program". Archived from the original on 2009-03-05.
- 1 2 "SA teams vs local schools".
- ↑ "Southern African Migration Project (SAMP)".
- ↑ "Single visa proposed for southern Africa for 2010". sagoodnews.co.za. Archived from the original on September 24, 2006.
- ↑ "Zim, Zambia revive Kaza Uni-Visa - The Chronicle". www.chronicle.co.zw.
- ↑ "Encarta.msn.com".
- ↑ Act on the status of aliens in Czech Republic, §20
- ↑ "Department of Labour - Government Of Nepal".
- ↑ "Uzbekistan: Journalist Alo Hojayev is denied exit visa". 2007-05-02. Archived from the original on 2008-06-05. Retrieved 2010-04-29.
- ↑ "NGO REPORT On the implementation of the ICCPR" (PDF). April 2009. Retrieved 2010-04-29. Freedom of Movement (article 12): "Exit visas and propiska violate not only international law such as the ICCPR, but also the Constitution of the Republic of Uzbekistan"
- ↑ "Enlistment Act". s. 32, No. 25 of 1970.
- ↑ "National Service: Exit permit requirements". ecitizen.gov.sg.
- ↑ Amount equal to SGD 75,000 or 50% of the parents' combined annual income (whichever is greater), covered by a banker's guarantee.
- ↑ "內政部役政署役男線上申請短期出境". www.ris.gov.tw.
- ↑ Cuba to end exit permits for foreign travel 16 October 2012
- ↑ "Page 7 of IATA document accessed 5 December 2015 at" (PDF).
- ↑ "11. Departing Aliens and the Sailing or Departure Permit". Publication 519: U.S. Tax Guide for Aliens (PDF). Internal Revenue Service. 2015. pp. 50–52.
- ↑ "IRS may step up focus on 'sailing permits'". Grant Thornton. October 23, 2014.
- ↑ "Global Ranking - Visa Restriction Index 2017" (PDF). Henley & Partners. Retrieved 14 March 2017.
- ↑ Kalin, Christian H. Global Residence and Citizenship Handbook (5 ed.). Ideos Publications. pp. 147–148. ISBN 978-3-9524052-7-7.
- ↑ "Visa Openness Report 2016" (PDF). World Tourism Organization. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 January 2016. Retrieved 17 January 2016.
- ↑ ]https://www.evisa.gov.bh/VisaBhr5En.html]
- ↑
- ↑ Timatic
- ↑ "Foreign Affairs Manual, 9 FAM 403.9-3(B)(2) f". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ↑ "How long should my passport be valid when traveling to the United States?" (PDF). U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 10 October 2017.
- ↑ "Countries whose citizens are allowed to enter Turkey with their expired passports". Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Republic of Turkey. Archived from the original on 8 October 2015. Retrieved 6 July 2018.
Countries whose citizens are allowed to enter Turkey with their expired passports: 1. Germany – Passports expired within the last year / ID’s expired within the last year, 2. Belgium - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 3. France - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 4. Spain - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 5. Switzerland - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 6. Luxemburg - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 7. Portugal - Passports expired within the last 5 years, 8. Bulgaria – Valid ordinary passport
- ↑ "Country Information". Bureau of Consular Affairs, U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 11 September 2017.
- ↑ Country list - Yellow fever vaccination requirements and recommendations; and malaria situation; and other vaccination requirement
- ↑ "Travel Report - Kuwait". Voyage.gc.ca. 2012-11-16. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ↑ Travel Advice for Lebanon - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade Archived 2008-12-24 at the Wayback Machine. and Lebanese Ministry of Tourism Archived 2009-03-27 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Travel Advice for Libya - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Smartraveller.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2013-06-22. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ↑ Michael Freund, Canada defends Saudi policy of shunning tourists who visited Israel, 2008-12-07, Jerusalem Post
- ↑ "Travel Advice for Sudan - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Smartraveller.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2013-07-05. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ↑ Travel Advice for Syria - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade Archived 2008-12-19 at the Wayback Machine. and Syrian Ministry of Tourism
- ↑ "Travel Advice for Yemen - Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade". Smartraveller.gov.au. Archived from the original on 2011-08-20. Retrieved 2013-07-01.
- ↑ "Israel travel advice - GOV.UK". www.gov.uk. Retrieved 2015-12-17.
- ↑ Azerbaijan Country Page Archived 2009-03-08 at the Wayback Machine.. NCSJ: Advocates on behalf of Jews in Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic States & Eurasia. Accessed 23 May 2010.
- ↑ Azerbaijan doesn't allow Armenians in the country - Panarmenian.net
- ↑ "Azerbaijan Country Page of the NCSJ (advocates on behalf of Jews in Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic States & Eurasia) accessed 23 May 2010". Archived from the original on 8 March 2009. Retrieved 2010-05-26.
- ↑ "Warning for the foreign nationals wishing to travel to the occupied territories of the Republic of Azerbaijan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Azerbaijan. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ↑ "List of foreign citizens illegally visited occupied territories of the Republic of Azerbaijan". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Azerbaijan. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ↑ Government of Canada -- Overcome criminal convictions
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-04-13. Retrieved 2014-04-10.
- ↑ Calder, Simon (24 April 2017). "Airline lobbying for a relaxation of draconian rules for London-Auckland travellers". The Independent. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
Travellers heading west from the UK to New Zealand may soon be able to avoid the onerous requirement to clear US border control during the refuelling stop at Los Angeles airport (LAX). Unlike almost every other country in the world, the US insists on a full immigration check even for travellers who simply intend to re-board their plane to continue onwards to a foreign destination. Air New Zealand, which flies daily from Heathrow via Los Angeles to Auckland, says there are currently “strict requirements for travellers” in transit at LAX. Through passengers to Auckland on flight NZ1 or Heathrow on NZ2 must apply in advance for an ESTA (online visa) even though they have no intention of staying in the US. They also have to undergo screening by the Transportation Security Administration.
- ↑ "How to enter Afghanistan. The Entry Requirements for Afghanistan - CountryReports". Countryreports.org.
- ↑ Nordland, Rod (19 November 2011). "In Afghanistan, Big Plans to Gather Biometric Data". Nytimes.com.
- ↑ "Argentina strengthens migratory control". Archived from the original on 2 December 2013.
- ↑ "Cambodia Foreign Entry Requirements". Us-passport-information.com.
- ↑ "China to require fingerprints of all foreign visitors as new security step". Boing Boing. 8 Feb 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
The fingerprinting of foreigners will be introduced at Shenzhen airport in the south from Friday, and it will then be gradually rolled out at other entry points around the country, the ministry said in a statement. All foreign passport holders aged 14-70 will have to give their fingerprints, it said, without saying if other biometric data would also be collected. The ministry said the regulation would strengthen immigration controls and increase efficiency.
- ↑ "Äthiopien: Reise- und Sicherheitshinweise". Auswaertiges-amt.de.
- ↑ "Japan fingerprints foreigners as anti-terror move". 20 November 2016. Retrieved 3 March 2017 – via Reuters.
- ↑ "Anger as Japan moves to fingerprint foreigners - World". Theage.com.au.
- ↑ "Malaysia". CountryReports. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- ↑ "Saudi Arabia mandates fingerprints and biometrics for foreigners - SecureIDNews". secureidnews.com. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ↑ F_161. "S Korea to scan fingerprints of suspicious foreign visitors - People's Daily Online". peopledaily.com.cn. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ↑ "404 - Page Not Found". travel.state.gov. Archived from the original on 20 June 2013.
- ↑ "Iris Scan Implemented at Doha International Airport". Archived from the original on 8 January 2012.
- ↑ "Iris Scanner Could Replace Emirates ID In UAE". SimplyDXB. 11 June 2017. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
The breach of privacy is probably the biggest threat to the biometric technique of iris recognition. Secondly, a device error can false reject or false accept the identity which can also have some heinous consequences. Lastly, the method isn’t the most cost-effective one. It is complex and therefore expensive. Furthermore, the maintenance of devices and data can also be relatively burdensome. However, thanks to the oil money and spending ability of Dubai, they are economically equipped to effectively embrace this system.
Further reading
- United States Department of State, "Report of the Visa Office", Visa Office, Immigrant Visa Control and Reporting Division
- United States Department of State, Nonimmigrant Visa Statistics
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Visas. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Visa. |
- Travel visa at Curlie (based on DMOZ)