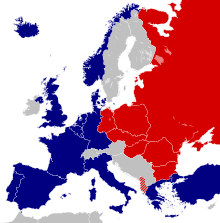
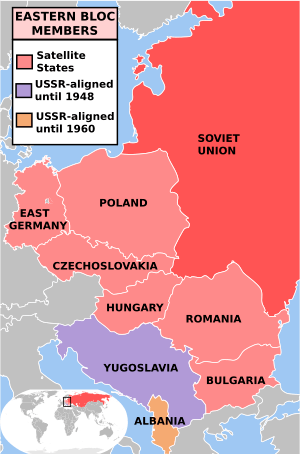
Warsaw Pact
| Russian: Договор о дружбе, сотрудничестве и взаимной помощи | |
 | |
.svg.png) Member states in 1990 (dark green) Former member states (light green) | |
| Formation | 14 May 1955 in Warsaw, Poland |
|---|---|
| Dissolved | 1 July 1991 |
| Type | Military alliance |
| Headquarters | Moscow, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union |
Membership |
(withdrew in 1968) |
| Petr Lushev (last) | |
| Vladimir Lobov (last) | |
The Warsaw Pact, formally known as the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance,[1] was a collective defence treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland among the Soviet Union and seven Soviet satellite states of Central and Eastern Europe in May 1955, during the Cold War. The Warsaw Pact was the military complement to the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (CoMEcon), the regional economic organization for the socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe. The Warsaw Pact was created in reaction to the integration of West Germany into NATO[2][3][4][5] in 1955 per the London and Paris Conferences of 1954,[6][7][8][9][10] but it is also considered to have been motivated by Soviet desires to maintain control over military forces in Central and Eastern Europe.[11]
The Warsaw Pact was established as a balance of power[12] or counterweight[13] to NATO; there was no direct confrontation between them. Instead, the conflict was fought on an ideological basis and in proxy wars. Both NATO and the Warsaw Pact led to the expansion of military forces and their integration into the respective blocs.[13] Its largest military engagement was the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968 (with the participation of all Pact nations except Albania, Romania and East Germany),[12] which, in part, resulted in Albania withdrawing from the pact less than a month later. The Pact began to unravel in its entirety with the spread of the Revolutions of 1989 through the Eastern Bloc, beginning with the Solidarity movement in Poland[14] and its electoral success in June 1989.
East Germany withdrew from the Pact following reunification with West Germany in 1990. On 25 February 1991, the Pact was declared at an end at a meeting of defence and foreign ministers from the six remaining member states in Hungary. The USSR itself was dissolved in December 1991, although most of the former Soviet republics formed the Collective Security Treaty Organization shortly thereafter. Throughout the following 20 years, the seven Warsaw Pact countries outside the USSR each joined NATO (East Germany through its reunification with West Germany; and the Czech Republic and Slovakia as separate countries), as did the three Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania) that had been part of the Soviet Union.
Nomenclature

In the Western Bloc, the Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance is often called the Warsaw Pact military alliance—abbreviated WAPA, Warpac and WP. Elsewhere, in the former member states, the Warsaw Treaty is known as:
- Albanian: Pakti i miqësisë, bashkëpunimit dhe i ndihmës së përbashkët
- Belarusian: Дагавор аб дружбе, супрацоўніцтве і ўзаемнай дапамозе
- Romanized Belarusian: Dagavor ab druzhe, supratsoŭnitstve i ŭzaemnaŭ dapamoze
- Bulgarian: Договор за дружба, сътрудничество и взаимопомощ
- Romanized Bulgarian: Dogovor za druzhba, satrudnichestvo i vzaimopomosht
- Czech: Smlouva o přátelství, spolupráci a vzájemné pomoci
- Slovak: Zmluva o priateľstve, spolupráci a vzájomnej pomoci
- German: Vertrag über Freundschaft, Zusammenarbeit und gegenseitigen Beistand
- Hungarian: Barátsági, együttműködési és kölcsönös segítségnyújtási szerződés
- Polish: Układ o przyjaźni, współpracy i pomocy wzajemnej
- Romanian: Tratatul de prietenie, cooperare și asistență mutuală
- Russian: Договор о дружбе, сотрудничестве и взаимной помощи
- Romanized Russian: Dogovor o druzhbe, sotrudnichestve i vzaimnoy pomoshchi
- Ukrainian: Договір про дружбу, співробітництво і взаємну допомогу
- Romanized Ukrainian: Dogovir pro druzhbu, spivrobitnitstvo i vzaêmnu dopomogu
Structure
The Warsaw Treaty's organization was two-fold: the Political Consultative Committee handled political matters, and the Combined Command of Pact Armed Forces controlled the assigned multi-national forces, with headquarters in Warsaw, Poland. Furthermore, the Supreme Commander of the Unified Armed Forces of the Warsaw Treaty Organization which commanded and controlled all the military forces of the member countries was also a First Deputy Minister of Defence of the USSR, and the Chief of Combined Staff of the Unified Armed Forces of the Warsaw Treaty Organization was also a First Deputy Chief of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the USSR. Therefore, although ostensibly an international collective security alliance, the USSR dominated the Warsaw Treaty armed forces.[15]
Strategy
The strategy behind the formation of the Warsaw Pact was driven by the desire of the Soviet Union to dominate Central and Eastern Europe. The Soviets wanted to keep their part of Europe and not let the Americans take it from them. This policy was driven by ideological and geostrategic reasons. Ideologically, the Soviet Union arrogated the right to define socialism and communism and act as the leader of the global socialist movement. A corollary to this idea was the necessity of intervention if a country appeared to be violating core socialist ideas and Communist Party functions, which was explicitly stated in the Brezhnev Doctrine.[16] Geostrategic principles also drove the Soviet Union with the desire to create a buffer zone to prevent invasion of its territory by Western European powers.
History
Beginnings

Before the creation of the Warsaw Pact, Czechoslovak leadership, fearful of a rearmed Germany, sought to create a security pact with East Germany and Poland.[9] These states protested strongly against the re-militarization of West Germany.[17] The Warsaw Pact was primarily put in place as a consequence of the rearming of West Germany inside NATO. Soviet leaders, like many European countries on both sides of the Iron Curtain, feared Germany being once again a military power and a direct threat. The terrible consequences of German militarism remained a fresh memory among the Soviets and Eastern Europeans.[3][4][18][19][20] As the Soviet Union already had bilateral treaties with all of its eastern satellites, the Pact has been long considered 'superfluous',[21] and because of the rushed way in which it was conceived, NATO officials labeled it as a 'cardboard castle'.[22] Previously, in March 1954, the USSR, fearing the restoration of German militarism in West Germany, requested admission to NATO.[23][24][25]
The Soviet request to join NATO arose in the aftermath of the Berlin Conference of January–February 1954. Soviet foreign minister Molotov made proposals to have Germany reunified[26] and elections for a pan-German government,[27] under conditions of withdrawal of the four powers' armies and German neutrality,[28] but all were refused by the other foreign ministers, Dulles (USA), Eden (UK) and Bidault (France).[29] Proposals for the reunification of Germany were nothing new: earlier on 20 March 1952, talks about a German reunification, initiated by the so-called 'Stalin Note', ended after the United Kingdom, France and the United States insisted that a unified Germany should not be neutral and should be free to join the European Defence Community and rearm. James Dunn (USA), who met in Paris with Eden, Adenauer and Robert Schuman (France), affirmed that "the object should be to avoid discussion with the Russians and to press on the European Defense Community".[30] According to John Gaddis "there was little inclination in Western capitals to explore this offer" from USSR.[31] While historian Rolf Steininger asserts that Adenauer's conviction that "neutralization means sovietization" was the main factor in the rejection of the Soviet proposals,[32] Adenauer also feared that German unification might have resulted in the end of the CDU's dominance in the West German Bundestag.[33]
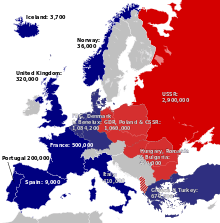
Consequently, Molotov, fearing that the EDC would be directed in the future against the USSR and "seeking to prevent the formation of groups of European States directed against other European States",[34] made a proposal for a General European Treaty on Collective Security in Europe "open to all European States without regard as to their social systems"[34] which would have included the unified Germany (thus making the EDC – perceived by the USSR as a threat – unusable). But Eden, Dulles and Bidault opposed the proposal.[35]
One month later, the proposed European Treaty was rejected not only by supporters of the EDC but also by Western opponents of the European Defence Community (like French Gaullist leader Palewski) who perceived it as "unacceptable in its present form because it excludes the USA from participation in the collective security system in Europe".[36] The Soviets then decided to make a new proposal to the governments of the USA, UK and France to accept the participation of the USA in the proposed General European Agreement.[36] And considering that another argument deployed against the Soviet proposal was that it was perceived by Western powers as "directed against the North Atlantic Pact and its liquidation",[36][37] the Soviets decided to declare their "readiness to examine jointly with other interested parties the question of the participation of the USSR in the North Atlantic bloc", specifying that "the admittance of the USA into the General European Agreement should not be conditional on the three Western powers agreeing to the USSR joining the North Atlantic Pact".[36]

Again all proposals, including the request to join NATO, were rejected by the UK, US and French governments shortly after.[25][38] Emblematic was the position of British General Hastings Ismay, a fierce supporter of NATO expansion. He opposed the request to join NATO made by the USSR in 1954[39] saying that "the Soviet request to join NATO is like an unrepentant burglar requesting to join the police force".[40]
In April 1954 Adenauer made his first visit to the USA meeting Nixon, Eisenhower and Dulles. Ratification of EDC was delaying but the US representatives made it clear to Adenauer that EDC would have to become a part of NATO.[41]
Memories of the Nazi occupation were still strong, and the rearmament of Germany was feared by France too.[4][42] On 30 August 1954 French Parliament rejected the EDC, thus ensuring its failure[43] and blocking a major objective of US policy towards Europe: to associate Germany militarily with the West.[44] The US Department of State started to elaborate alternatives: Germany would be invited to join NATO or, in the case of French obstructionism, strategies to circumvent a French veto would be implemented in order to obtain a German rearmament outside NATO.[45]
.jpg)
On 23 October 1954 – only nine years after Allies (UK, USA and USSR) defeated Nazi Germany ending World War II in Europe – the admission of the Federal Republic of Germany to the North Atlantic Pact was finally decided. The incorporation of West Germany into the organization on 9 May 1955 was described as "a decisive turning point in the history of our continent" by Halvard Lange, Foreign Affairs Minister of Norway at the time.[46] In November 1954, the USSR requested a new European Security Treaty,[47] in order to make a final attempt to not have a remilitarized West Germany potentially opposed to the Soviet Union, with no success.
On 14 May 1955, the USSR and other seven European countries "reaffirming their desire for the establishment of a system of European collective security based on the participation of all European states irrespective of their social and political systems"[48] established the Warsaw Pact in response to the integration of the Federal Republic of Germany into NATO,[3][5] declaring that: "a remilitarized Western Germany and the integration of the latter in the North-Atlantic bloc [...] increase the danger of another war and constitutes a threat to the national security of the peaceable states; [...] in these circumstances the peaceable European states must take the necessary measures to safeguard their security".[48]
One of the founding members, East Germany was allowed to re-arm by the Soviet Union and the National People's Army was established as the armed forces of the country to counter the rearmament of West Germany and vice versa.[49]
Members

The eight member countries of the Warsaw Pact pledged the mutual defence of any member who would be attacked. Relations among the treaty signatories were based upon mutual non-intervention in the internal affairs of the member countries, respect for national sovereignty, and political independence. However, almost all governments of those member states were indirectly controlled by the Soviet Union.[50]
The founding signatories to the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance consisted of the following communist governments:
.svg.png)
.svg.png)



.svg.png)

![]()
During Cold War

For 36 years, NATO and the Warsaw Pact never directly waged war against each other in Europe; the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies implemented strategic policies aimed at the containment of each other in Europe, while working and fighting for influence within the wider Cold War on the international stage. These included the Korean War, Vietnam War, Bay of Pigs invasion, Dirty War, Cambodian–Vietnamese War and the others.[54][55]
In 1956, following the declaration of the Imre Nagy government of withdrawal of Hungary from the Warsaw Pact, Soviet troops entered the country and removed the government.[56] Soviet forces crushed the nationwide revolt, leading to the death of an estimated 2,500 Hungarian citizens.[57]
The multi-national Communist armed forces' sole joint action was the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968.[58] All member countries, with the exception of the Socialist Republic of Romania and the People's Republic of Albania, participated in the invasion.[59] The German Democratic Republic provided only minimal support, however.[59]
End of the Cold War
Beginning at the Cold War's conclusion, in late 1989, popular civil and political public discontent forced the Communist governments of the Warsaw Treaty countries from power, while independent national politics made feasible with the perestroika and glasnost induced institutional collapse of Communist government in the USSR.[60]
Between 1989 and 1991, Communist governments were overthrown in Albania, Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Romania, Bulgaria and the Soviet Union.
As the last acts of the Cold War were playing out, several Warsaw Pact states (Poland, Czechoslovakia and Hungary) participated in the U.S.-led coalition effort to liberate Kuwait in the Gulf War.
On 25 February 1991, the Warsaw Pact was declared disbanded at a meeting of defence and foreign ministers from remaining Pact countries meeting in Hungary.[61] On 1 July 1991, in Prague, the Czechoslovak President Václav Havel[62] formally ended the 1955 Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance and so disestablished the Warsaw Treaty after 36 years of military alliance with the USSR.[62][63] The USSR disestablished itself in December 1991.
Central and Eastern Europe after the Warsaw Treaty
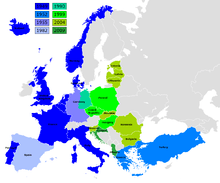
On 12 March 1999, the Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland joined NATO; Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania and Slovakia joined in March 2004; Albania joined on 1 April 2009.[64][65]
Russia and some other post-USSR states joined the Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) in 1992, or the Shanghai Five in 1996, which was renamed the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) after Uzbekistan's addition in 2001.[66]
In November 2005, the Polish government[67] opened its Warsaw Treaty archives to the Institute of National Remembrance, which published some 1,300 declassified documents in January 2006. Yet the Polish government reserved publication of 100 documents, pending their military declassification. Eventually, 30 of the reserved 100 documents were published; 70 remained secret and unpublished. Among the documents published is the Warsaw Treaty's nuclear war plan, Seven Days to the River Rhine – a short, swift counter-attack capturing Austria, Denmark, Germany and Netherlands east of River Rhine, using nuclear weapons, in self-defence, after a NATO first strike.[68] The plan originated as a 1979[69] field training exercise war game and metamorphosed into official Warsaw Treaty battle doctrine, until the late 1980s – which is why the Polish People's Republic was a nuclear weapons base,[70] first, to 178, then, to 250 tactical-range rockets, though these numbers may differ. Doctrinally, as a Soviet-style (offensive) battle plan, Seven Days to the River Rhine gave commanders few defensive-war strategies for fighting NATO in Warsaw Treaty territory.[68][71]
Gallery
- Badge Warsaw Pact. Union of peace and socialism
- Badge Warsaw Pact. Brothers in arms (1970)
- Badge A participant in joint exercises of Warsaw Pact "STIT" (1972)
- Badge 25 years Warsaw Pact (1980)
- Badge Air Forces Warsaw Pact
- Badge Warsaw Pact. The participants of the joint exercises in Bulgaria (1982)
- Jubilee badge 30 years of the Warsaw Pact (1985)
See also
- Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) – Modern military alliance between former Soviet states.
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) – Modern Eurasian political, economic and military organization.
References
- ↑ "Text of Warsaw Pact" (PDF). United Nations Treaty Collection. Retrieved 22 August 2013.
- ↑ Yost, David S. (1998). NATO Transformed: The Alliance's New Roles in International Security. Washington, DC: U.S. Institute of Peace Press. p. 31. ISBN 1-878379-81-X.
- 1 2 3 "Formation of Nato and Warsaw Pact". History Channel. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- 1 2 3 "The Warsaw Pact is formed". History Channel. Retrieved 22 December 2015.
- 1 2 "In reaction to West Germany's NATO accession, the Soviet Union and its Eastern European client states formed the Warsaw Pact in 1955." Citation from: NATO website. "A short history of NATO". nato.int. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- ↑ Broadhurst, Arlene Idol (1982). The Future of European Alliance Systems. Boulder, Colorado: Westview Press. p. 137. ISBN 0-86531-413-6.
- ↑ Christopher Cook, Dictionary of Historical Terms (1983)
- ↑ The Columbia Enclopedia, fifth edition (1993) p. 2926
- 1 2 The Warsaw Pact Reconsidered: International Relations in Eastern Europe, 1955–1969 Laurien Crump Routledge, p. 21–22, 11.02.2015
- ↑ The Oder-Neisse Line: The United States, Poland, and Germany in the Cold War Debra J. Allen page 158 "Treaties approving Bonn's participation in NATO were ratified in May 1955...shortly thereafter Soviet Union...created the Warsaw Pact to counter the perceived threat of NATO"
- ↑ "Warsaw Pact: Wartime Status-Instruments of Soviet Control". Wilson Center. Retrieved 5 October 2013.
- 1 2 Amos Yoder (1993). Communism in Transition: The End of the Soviet Empires. Taylor & Francis. p. 58. ISBN 978-0-8448-1738-5.
- 1 2 Bob Reinalda (11 September 2009). Routledge History of International Organizations: From 1815 to the Present Day. Routledge. p. 369. ISBN 978-1-134-02405-6.
- ↑ Cover Story: The Holy Alliance By Carl Bernstein Sunday, June 24, 2001
- ↑ Fes'kov, V. I.; Kalashnikov, K. A.; Golikov, V. I. (2004). Sovetskai͡a Armii͡a v gody "kholodnoĭ voĭny," 1945–1991 [The Soviet Army in the Cold War Years (1945–1991)]. Tomsk: Tomsk University Publisher. p. 6. ISBN 5-7511-1819-7.
- ↑ ' 'The Review of Politics Volume' ', 34, No. 2 (April 1972), pp. 190–209
- ↑ Europa Antoni Czubiński Wydawn. Poznańskie, 1998, p. 298
- ↑ World Politics: The Menu for Choice page 87 Bruce Russett, Harvey Starr, David Kinsella – 2009 The Warsaw Pact was established in 1955 as a response to West Germany's entry into NATO; German militarism was still a recent memory among the Soviets and East Europeans.
- ↑ "When the Federal Republic of Germany entered NATO in early May 1955, the Soviets feared the consequences of a strengthened NATO and a rearmed West Germany". Citation from:United States Department of State, Office of the Historian. "The Warsaw Treaty Organization, 1955". Office of the Historian. history.state.gov. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- ↑ "1955: After objecting to Germany's admission into NATO, the Soviet Union joins Albania, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Hungary, Poland and Romania in forming the Warsaw Pact.". See chronology in:"Fast facts about NATO". CBC News. 6 April 2009. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ↑ The Warsaw Pact Reconsidered: International Relations in Eastern Europe, 1955–1969 Laurien Crump Routledge, pp. 17, 11.02.2015
- ↑ The Warsaw Pact Reconsidered: International Relations in Eastern Europe, 1955–1969 Laurien Crump Routledge, p. 1, 11.02.2015
- ↑ "Soviet Union request to join NATO" (PDF). Nato.int. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ "1954: Soviet Union suggests it should join NATO to preserve peace in Europe. U.S. and U.K. reject this". See chronology in:"Fast facts about NATO". CBC News. 6 April 2009. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- 1 2 "Proposal of Soviet adherence to NATO as reported in the Foreign Relations of the United States Collection". UWDC FRUS Library. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, pp. 197,201.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, p. 202.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, pp. 197–198, 203, 212.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, pp. 211–212, 216.
- ↑ Steininger, Rolf (1991). The German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and the Problem of Reunification. Columbia Univ Press. p. 56.
- ↑ Gaddis, John (1997). We Know Now: Rethinking Cold War History. Clarendon Press. p. 126.
- ↑ Steininger, Rolf (1991). The German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and the Problem of Reunification. Columbia Univ Press. p. 80.
- ↑ Steininger, Rolf (1991). The German Question: The Stalin Note of 1952 and the Problem of Reunification. Columbia Univ Press. p. 103.
- 1 2 "Draft general European Treaty on collective security in Europe — Molotov proposal (Berlin, 10 February 1954)" (PDF). CVCE. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, p. 214.
- 1 2 3 4 "MOLOTOV'S PROPOSAL THAT THE USSR JOIN NATO, MARCH 1954". Wilson Center. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ Molotov 1954a, p. 216,.
- ↑ "Final text of tripartite reply to Soviet note" (PDF). Nato website. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ Ian Traynor. "Soviets tried to join Nato in 1954". the Guardian.
- ↑ "Memo by Lord Ismay, Secretary General of NATO" (PDF). Nato.int. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ Adenauer 1966a, p. 662.
- ↑ "The refusal to ratify the EDC Treaty". CVCE. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ "Debates in the French National Assembly on 30 August 1954". CVCE. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ "US positions on alternatives to EDC". United States Department of State / FRUS collection. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ "US positions on german rearmament outside NATO". United States Department of State / FRUS collection. Retrieved 1 August 2013.
- ↑ "West Germany accepted into Nato". BBC News. 9 May 1955. Retrieved 17 January 2012.
- ↑ "Indivisible Germany: Illusion or Reality?" James H. Wolfe Springer Science & Business Media, 06.12.2012 page 73
- 1 2 "Text of the Warsaw Security Pact (see preamble)". Avalon Project. Retrieved 31 July 2013.
- ↑ "No shooting please, we're German". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ "How the Russians Used the Warsaw Pact". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "The Warsaw Pact is formed - May 14, 1955 - HISTORY.com". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- 1 2 Mastny, Vojtech; Byrne, Malcolm (1 January 2005). "A Cardboard Castle?: An Inside History of the Warsaw Pact, 1955-1991". Central European University Press. Retrieved 23 August 2018 – via Google Books.
- ↑ Reuters (3 March 1990). "Soviet Troops to Leave Mongolia in 2 Years". Retrieved 23 August 2018 – via LA Times.
- ↑ "America Wasn't the Only Foreign Power in the Vietnam War". 2 October 2013. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ "Crisis Points of the Cold War - Boundless World History". courses.lumenlearning.com. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ "The Hungarian Uprising of 1956 - History Learning Site". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ CNN, Matthew Percival,. "Recalling the Hungarian revolution, 60 years on". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ "Soviets Invade Czechoslovakia - Aug 20, 1968 - HISTORY.com". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- 1 2 Nosowska, Agnieszka. "Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia". www.enrs.eu. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ The New Fontana Dictionary of Modern Thought, third edition, 1999, pp. 637–8
- ↑ "Warsaw Pact and Comecon To Dissolve This Week". Csmonitor.com. 26 February 1991. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
- 1 2 Greenhouse, Steven. "DEATH KNELL RINGS FOR WARSAW PACT". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ Havel, Václav (2007). To the Castle and Back. Trans. Paul Wilson. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-307-26641-5.
- ↑ https://www.nato.int/docu/comm/1999/9904-wsh/pres-eng/03acce.pdf
- ↑ https://www.nato.int/docu/update/2004/03-march/e0329a.htm
- ↑ 宋薇. "SCO from the Uzbekistan perspective: Expectations and reality - Opinion - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ "Here's how the USSR planned to conquer Europe in an all-out nuclear war". 29 October 2016. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- 1 2 Catcher, Redd (11 July 2013). "DECODED: The Cold War in Europe 1945-1995 : Nuclear War in the West: Seven Days to the River Rhine". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ Mizokami, Kyle (2 July 2016). "Revealed: How the Warsaw Pact Planned to Win World War Three in Europe". Retrieved 23 August 2018.
- ↑ http://eastviewpress.com/Files/SS_FROM%20THE%20ARCHIVES_No.%202_2012.pdf
- ↑ "7 Days to the Rhine". 2 January 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2018.
Works cited
- Adenauer, Konrad (1966a). Memorie 1945–1953 (in Italian). Arnoldo Mondadori Editore.
- Molotov, Vyacheslav (1954a). La conferenza di Berlino (in Italian). Ed. di cultura sociale.

Further reading
- Faringdon, Hugh. Confrontation: the strategic geography of NATO and the Warsaw Pact. (London: Routledge & Kegan Paul, 1986.)
- Heuser, Beatrice (1998). "Victory in a Nuclear War? A Comparison of NATO and WTO War Aims and Strategies". Contemporary European History. 7 (3): 311–327. doi:10.1017/S0960777300004264.
- Mackintosh, Malcolm. The evolution of the Warsaw Pact (International Institute for Strategic Studies, 1969)
- Kramer, Mark N. "Civil-military relations in the Warsaw Pact, The East European component," International Affairs, Vol. 61, No. 1, Winter 1984–85.
- Lewis, William Julian (1982). The Warsaw Pact: Arms, Doctrine, and Strategy. Cambridge, Mass.: Institute for Foreign Policy Analysis. ISBN 978-0-07-031746-8.
- Mastny, Vojtech; Byrne, Malcolm (2005). A Cardboard Castle ?: An Inside History of the Warsaw Pact, 1955–1991. Budapest: Central European University Press. ISBN 978-963-7326-07-3.
- A. James McAdams, "East Germany and Detente." Cambridge University Press, 1985.
- McAdams, A. James. "Germany Divided: From the Wall to Reunification." Princeton University Press, 1992 and 1993.
Other languages
- Umbach, Frank (2005). Das rote Bündnis: Entwicklung und Zerfall des Warschauer Paktes 1955 bis 1991 (in German). Berlin: Ch. Links Verlag. ISBN 978-3-86153-362-7.
- Wahl, Alfred (2007). La seconda vita del nazismo nella Germania del dopoguerra (in Italian). Torino: Lindau. ISBN 978-88-7180-662-4. – Original Ed.: Wahl, Alfred (2006). La seconde histoire du nazisme dans l'Allemagne fédérale depuis 1945 (in French). Paris: Armand Colin. ISBN 2-200-26844-0.
Memoirs
- Adenauer, Konrad (1966b). Konrad Adenauer Memoirs 1945–53. Henry Regnery Company.
- Molotov, Vyacheslav (1954b). Statements at Berlin Conference of Foreign Ministers of U.S.S.R., France, Great Britain and U.S.A., January 25 – February 18, 1954. Foreign Languages Publishing House.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Warsaw Pact. |
- "What was the Warsaw Pact?". North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
- The Woodrow Wilson Center Cold War International History Project's Warsaw Pact Document Collection
- Parallel History Project on Cooperative Security
- Library of Congress / Federal Research Division / Country Studies / Area Handbook Series / Soviet Union / Appendix C: The Warsaw Pact (1989)
- Map of Russia and the Warsaw Pact (omniatlas.com)
- Map of Europe and the Warsaw Pact (omniatlas.com)
- The Warsaw Pact, 1955–1968. by Hugh Collins Embry. Contain extensive documentation of the Pacts first 13 years.