Sambhal
Sambhal (![]()
| Sambhal | |
|---|---|
| City | |
 Sambhal Location in Uttar Pradesh, India  Sambhal Sambhal (India) | |
| Coordinates: 28°35′N 78°33′E / 28.58°N 78.55°ECoordinates: 28°35′N 78°33′E / 28.58°N 78.55°E | |
| Country |
|
| State | Uttar Pradesh |
| District | Sambhal |
| Founded by | Prithviraj Chauhan |
| Government | |
| • MP | Satyapal Singh Saini (BJP) |
| • MLA | Iqbal Mehmood (SP) |
| • Chairman | Areefa Shakeel |
| Area | |
| • Total | 16 km2 (6 sq mi) |
| Elevation[1] | 203 m (666 ft) |
| Population (2014)[2] | |
| • Total | 220,813 (city only) |
| • Density | 11,433/km2 (29,610/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | Sambhali |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 244302 |
| Telephone code | (+91) (05923) |
| Vehicle registration | UP 38 |
| Website |
sambhal |
Sambhal city is famous for its unique kinds of horn and bone craft items which are manufactured in Sarai Tarin, 4 km away from Sambhal city (but included in Sambhal) which are being exported. The Sambhal headquarters are situated in Pawasa Sambhal.[3]
History
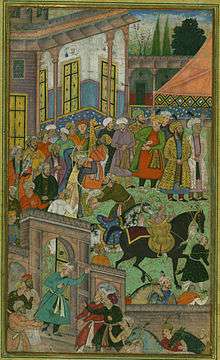
Sambhal has been an urban center for hundreds of years. it was a prominent town during the medieval period. The painting shown here is a folio from the Baburnama, and depicts an awards ceremony in Sultan Ibrahim Lodi's court before an expedition to Sambhal in the early 16th century. Sambhal is said to have flourished under the rule of Akbar but subsequently deteriorated in popularity when Akbar’s son Shah Jahan was made in charge of the city.[4][5]
Sambhal has a rich history and has been home to several rulers and emperors. It was found in Satyuga. At that time it was a very large city. From the Lodis to the Mughals, right from the 5th century BC and spanning up to the 16th century, Sambhal has been under the rule of one emperor or the other.
During the 5th century BC, Sambhal was home to the Panchal rulers and was subsequently a part of king Ashoka’s empire.
During the 12th century, Prithviraj Chauhan, Delhi’s last Hindu ruler is said to have engaged in two fierce battles here which were both fought against Ghazi Sayyad Salar Masud, who was the nephew of the ruler of the Ghazni empireMahmud Ghazni. Chauhan gained victory over the latter in the first war and vice versa is said to have occurred in the second war. There nevertheless is no circumstantial evidence to prove the same and is widely regarded as a legend.
Qutubuddin Aibak, the first Muslim sultan of Delhi, seized Sambhal and included it under his empire. That was in the early 14th Century and subsequently, Firoz Shah Tughlaq, another sultan of Delhi, raided the town of Sambhal as one of the Hindu rulers from there was responsible for the killing of several of his men. He, therefore, administered a Muslim rule in Sambhal to try and vanquish all of the Hindu ruler’s forces and enslave him for the rest of his life.
In the 15th century BC, Sikandar Lodi, the second ruler of the Lodi empire, declared Sambhal as one of the capitals of his vast empire and it remained that way for four long years.
Following the Siege of Sambhal Mughals took control. it was then the turn of the Mughals to stake a claim in the offerings of Sambhal as a place that was most suited to be the capital of their empire. Babar, the first Mughal ruler constructed the first Babri Masjid in Sambhal which is to date considered to be a historic monument. He, later on, made his son Humayun the governor of Sambhal and Humayun in turn passed on the reigns to his son Akbar. Sambhal is said to have flourished under the Akbar rule but subsequently deteriorated in popularity when Akbar’s son Shah Jahan was made in charge of the city.
Geography
Sambhal is part of the Sambhal district and Moradabad division Uttar Pradesh state. The Sambhal is the most important city of Sambhal district. The nearby districts from Sambhal are (clockwise from north) Amroha, Moradabad, Rampur, Badaun, Aligarh and Bulandshahr.
The nearest major metropolis is New Delhi. Sambhal lies 158.6 kilometres (98.5 mi) due east from New Delhi and lies 355 km north-west from the state capital Lucknow.
Politics
Sambhal City Has a Lok Sabha constituency and a Vidhan Sabha constituency.
Sambhal (Lok Sabha constituency) (Hindi: सम्भल लोकसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र) is one of the 80 Lok Sabha (parliamentary) constituencies in Uttar Pradesh state in northern India.
Sambhal (Assembly constituency) (Hindi: सम्भल विधानसभा निर्वाचन क्षेत्र) is one of the 403 constituency of the of Uttar Pradesh.
Demographics
As per provisional reports of the 2011 Census of India, the population of Sambhal city in 2011 was 221,334, of which 116,008 were male and 105,326 were female. Total literates in Sambhal city are 92,608 of which 51,382 are males while 41,226 are females. The average literacy rate in Sambhal city is 49.51 percent, of which male literacy was 52.27 percent and female 46.45 percent. The sex ratio of Sambhal city is 908 per 1,000 males and the child sex ratio of girls is 936 per 1,000 boys. Total children (0-6) in Sambhal city were 34,279 as per the records of Census India 2011. There were 17,702 boys and 16,577 girls. The children form 15.49% of the total population of Sambhal City.[6] Sambhal is a Muslim-majority area.
Festivals and culture
Although Sambhal is heavily populated by Muslims, the city is also much influenced by other cultures. It’s a place where Hindus and Muslims coexist peacefully. Many mosques are part of modern-day Sambhal, with some even dating back to the 14th and 15th century.

Eid ul Fitr, Eid Ul Azha, Eid Miladun Nabi, Diwali and Holi are major festivals observed in Sambhal.
Economy
Sambhal is the largest market of mentha (Menthenol) in Asia. There are many mint farms.
One of the main industry in sambhal is Bone crafted items, which are very popular on Horn-bone product nationally and internationally. The raw material used to craft the horns & bone of animals, which led the industry remains favorable natural balance. Horn-bone products are exported in national and international markets to be built. Thus a great deal of careful products are created, whose unique design, draw appearance and pattern consumer on your behalf. The craftsmen Careful known for producing the best decorative accessories globally.
SaraiTarin a major subcity in Sambhal famous for its handicraft industry. Decorated items of bone and horns are much popular in Europe.
In rural areas, agriculture is the main occupation.
Education
Most of schools in Sambhal are affiliated to the four main education boards. i.e. Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE Board), Uttar Pradesh Madhyamik Shiksha Parishad (UP Board), Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE Board) and UP Board OF Madarsa Education (Madarsa Board).
Higher Education
CBSE Board
- Saraswati Vidya Mandir Sambhal
- St.Mary's Secondary School, Sambhal
- Kainat International School
- Heritage Convent School
ICSE Board
- St. Amtul Public School
- Blooming Buds Co-Ed School
- Holy Suffah Public School
UP Board
- Al-Qadeer Higher Secondary School, Sambhal
- Hind Inter College, Sambhal
- S.B.S.J. Inter College, Sambhal
- A.M.H.R.S. Inter College, Sambhal
- Z.U. Inter College Sambhal
- Ummaid Rai Inter College
- T.H. Inter College
- B.D. Inter College
- Azad Girls Inter College
- Government Girl Inter College Sambhal (G.G.I.C. Sambhal)
- Braj Ratan Sunder Arya Kanya Inter College
- Faiz Girls Inter College
"computer centre" Janhit computer centre (harit gaur)
Degree Colleges
- Mahatma Gandhi Memorial Post Graduate College (MGMPG College Sambhal) [8]
- Government Degree College Sambhal(राजकीय स्नातकोत्तर महाविद्यालय सम्भल)[9]
- Ishrat Group Of Institutions Sambhal
- S.B.H. Aazad Girl's Degree College, Sambhal
- Hakim Rais Unani Medical College and Hospital
Islamic Madarsa
- Madrasa Sirajul Uloom Hilali Sarai Sambhal
- Anjuman Muavinul Islam Madarsa
- Madarsa Ahle Sunnat Ajmalul Uloom
- Madarsa Zainul Aabideen Sambhal
- Madrasa Hamidiya Ashrafiya
- Jeelani Arabic College
- Madrasa Khalil ul Uloom
Distance Learning
- Maulana Azad National Urdu University has A distance learning Center in Sambhal
- Aligarh Muslim University Has a distance learning Center in Madrasa Sirajul Uloom Hilali Sarai Sambhal.
IGNOU has a study center in Mahatma Gandhi Memorial Post Graduate College sambhal.
Tourism
Many mosques in Sambhal are more than 300 years old. There are many historical monuments in Sambhal:
- Shahi Jama Masjid, Sambhal
- Chakki Ka Paat
- Tota Maina Ki Kabr
- Manokamna Mandir
Transport
Sambhal is well connected to the major cities like Delhi, Moradabad, Aligarh, Bulandshahr, Gajraula and Badaun.
Sambhal has also a railway station known as Hatim Sarai Railway Station.
Media
Many newspapers are published in Sambhal in Hindi, Urdu and English Languages, such as:
- Dainik Jagran
- Amar Ujala
- Hindustan
- Inqalab
- Huqumat Express
Notable people
See also
References
- ↑ "Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh, India". latlong.net. Retrieved 11 August 2018.
- ↑ "Census of India Search details". censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 10 May 2015.
- ↑ http://m.indianexpress.com/news/shift-district-hq-to-sambal-residents/1001978/
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/520415/Sambhal
- ↑ Ain-i-Akbari, Vol II, Tr.H.S. Jarrett, Atlantic Publishers and Distributors, New Delhi, repr., 1989. p. 295.
- 1 2 "Census 2011 Sambhal Town". Census 2011. Retrieved 17 July 2017.
- ↑ http://www.censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2-vol2/data_files/India2/Table_2_PR_Cities_1Lakh_and_Above.pdf
- ↑ "Mahatma Gandhi Memorial College, Sambhal". Central Board Of Education.
- ↑ "Govt. Degree College, Sambhal, Uttar Pradesh".