Ulster County, New York
| Ulster County, New York | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| County of New York State | |||
| County of Ulster | |||
 | |||
| |||
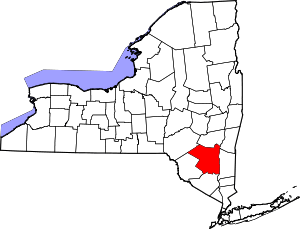 Location in the U.S. state of New York | |||
 New York's location in the U.S. | |||
| Founded | 1683 | ||
| Named for | Ulster | ||
| Seat | Kingston | ||
| Largest city | Kingston | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 1,161 sq mi (3,007 km2) | ||
| • Land | 1,124 sq mi (2,911 km2) | ||
| • Water | 37 sq mi (96 km2), 3.1% | ||
| Population | |||
| • (2010) | 182,493 | ||
| • Density | 162/sq mi (63/km2) | ||
| Congressional district | 19th | ||
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC−5/−4 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Ulster County is a county located in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2010 census, the population was 182,493.[1] The county seat is Kingston.[2] The county is named after the Irish province of Ulster.
Ulster County comprises the Kingston, New York Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is also included in the New York–Newark, NY–NJ–CT–PA Combined Statistical Area. It is located in the Mid-Hudson Region of the Hudson Valley.
History
The area of present-day Ulster County was called "Esopus" by Dutch settlers: it was then part of the New Netherland Colony. In 1652, Thomas Chambers, a freeholder from the Manor of Rensselaerswyck, purchased land at Esopus and began trading there. In 1654, Johan de Hulter, owner of 20% of the Killian van Rensselaer Company was granted a patent, together with the patents of Christoffel Davids, and Jacob Jansen Stoll, this supplies evidence of the first permanent settlement, that grows into the village of Wiltwijck, later: Kingston. In 1683, the Duke of York created twelve counties in his province. Ulster County was one of them. Its boundaries at that time included the present Sullivan County, and portions of the present Delaware, Orange, and Greene Counties.
In 1777, the capital of New York State (the first state capital of independent New York) was established at Kingston, though it was subsequently moved to Kerhonkson when the British burned Kingston.
In 1797, portions of Otsego and Ulster Counties were split off to create Delaware County.
In 1798, the southernmost towns in Ulster County were moved into Orange County, to compensate Orange for breaking away the southernmost portion of that county in order to form Rockland County.
In 1800, portions of Albany and Ulster Counties were split off to create Greene County.
In 1809, Sullivan County was split off from Ulster County.
During the American Civil War volunteers were recruited from the more affluent families of the County to form the 139th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment.
The Lake Mohonk Mountain House on Shawangunk Ridge was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1986.[3]
Geography

According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,161 square miles (3,010 km2), of which 1,124 square miles (2,910 km2) is land and 37 square miles (96 km2) (3.1%) is water.[4]
Ulster County is in the southeast part of New York State, south of Albany, immediately west of the Hudson River. Much of the county is within the Catskill Mountains and the Shawangunk Ridge. Ulster County has Minnewaska State Park, Mohonk Preserve, Sundown State Park, VerNooykill State Forest, Witches Hole State Forest, and Shawangunk Ridge State Forest and Sam's Point Preserve, which includes rare dwarf pine trees and VerKeerderkill falls.
The highest point is Slide Mountain, at approximately 4,180 feet (1,270 m) above sea level. The lowest point is sea level along the Hudson River.
Adjacent counties
- Greene County — north
- Columbia County — northeast
- Dutchess County — southeast
- Orange County — south
- Sullivan County — southwest
- Delaware County — northwest
National protected area
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 29,370 | — | |
| 1800 | 24,855 | −15.4% | |
| 1810 | 26,576 | 6.9% | |
| 1820 | 30,934 | 16.4% | |
| 1830 | 36,550 | 18.2% | |
| 1840 | 45,822 | 25.4% | |
| 1850 | 59,384 | 29.6% | |
| 1860 | 76,381 | 28.6% | |
| 1870 | 84,075 | 10.1% | |
| 1880 | 85,838 | 2.1% | |
| 1890 | 87,062 | 1.4% | |
| 1900 | 88,422 | 1.6% | |
| 1910 | 91,769 | 3.8% | |
| 1920 | 74,979 | −18.3% | |
| 1930 | 80,155 | 6.9% | |
| 1940 | 87,017 | 8.6% | |
| 1950 | 92,621 | 6.4% | |
| 1960 | 118,804 | 28.3% | |
| 1970 | 141,241 | 18.9% | |
| 1980 | 158,158 | 12.0% | |
| 1990 | 165,304 | 4.5% | |
| 2000 | 177,749 | 7.5% | |
| 2010 | 182,493 | 2.7% | |
| Est. 2016 | 179,225 | [5] | −1.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[6] 1790-1960[7] 1900-1990[8] 1990-2000[9] 2010-2013[1] | |||
As of the census[10] of 2010, there were 181,440 people, 67,499 households, and 43,536 families residing in the county. The population density was 158 people per square mile (61/km²). There were 77,656 housing units at an average density of 69 per square mile (27/km²). The racial makeup of the county, as of 2008, was 83.2% White, 6.50% Black or African American, 0.3% Native American, 1.7% Asian, 0.03% Pacific Islander, 2.15% from other races, and 1.70% from two or more races. 7.6% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 19.2% were of Italian, 16.8% Irish, 15.5% German, 6.8% English, and 4.7% American ancestry according to Census 2000. 90.3% spoke English, 4.5% Spanish, 1.2% Italian, and 1.0% German as their first language.
There were 67,499 households out of which 30.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 49.20% were married couples living together, 10.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 35.50% were non-families. Of all households, 27.90% were made up of individuals and 10.20% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.47 and the average family size was 3.03.
In the county, the population was spread out with 23.50% under the age of 18, 8.70% from 18 to 24, 29.70% from 25 to 44, 24.70% from 45 to 64, and 13.30% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females, there were 99.10 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.60 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $42,551, and the median income for a family was $51,708. Males had a median income of $36,808 versus $27,086 for females. The per capita income for the county was $20,846. About 7.20% of families and 11.40% of the population were below the poverty line, including 13.00% of those under age 18 and 8.70% of those age 65 or over.
Government and politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third Parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 41.3% 35,239 | 52.3% 44,597 | 6.4% 5,454 |
| 2012 | 37.4% 29,759 | 60.0% 47,752 | 2.7% 2,115 |
| 2008 | 37.4% 33,300 | 60.9% 54,320 | 1.7% 1,529 |
| 2004 | 43.1% 37,821 | 54.3% 47,602 | 2.6% 2,289 |
| 2000 | 42.8% 33,447 | 48.8% 38,162 | 8.5% 6,628 |
| 1996 | 35.5% 26,212 | 48.6% 35,852 | 16.0% 11,787 |
| 1992 | 36.2% 29,223 | 40.7% 32,886 | 23.2% 18,712 |
| 1988 | 56.8% 41,173 | 42.4% 30,744 | 0.9% 640 |
| 1984 | 63.9% 47,372 | 35.7% 26,445 | 0.4% 285 |
| 1980 | 55.0% 36,709 | 33.2% 22,179 | 11.7% 7,838 |
| 1976 | 53.4% 35,353 | 45.6% 30,190 | 0.9% 610 |
| 1972 | 68.5% 46,883 | 31.2% 21,371 | 0.3% 179 |
| 1968 | 57.6% 34,798 | 34.6% 20,886 | 7.8% 4,703 |
| 1964 | 40.0% 23,749 | 59.8% 35,486 | 0.2% 91 |
| 1960 | 61.2% 36,418 | 38.7% 23,017 | 0.1% 67 |
| 1956 | 76.4% 43,034 | 23.6% 13,321 | 0.0% 0 |
| 1952 | 69.4% 36,141 | 30.2% 15,733 | 0.3% 171 |
| 1948 | 64.3% 28,941 | 32.1% 14,441 | 3.6% 1,630 |
| 1944 | 61.0% 26,703 | 38.7% 16,943 | 0.3% 117 |
| 1940 | 57.0% 27,186 | 42.8% 20,403 | 0.2% 107 |
| 1936 | 55.3% 24,678 | 42.9% 19,118 | 1.8% 815 |
| 1932 | 52.9% 21,002 | 45.6% 18,092 | 1.6% 627 |
| 1928 | 62.5% 25,418 | 34.9% 14,200 | 2.7% 1,077 |
| 1924 | 63.3% 20,048 | 29.6% 9,361 | 7.1% 2,251 |
| 1920 | 66.4% 19,001 | 30.6% 8,759 | 3.0% 852 |
| 1916 | 56.6% 10,734 | 41.2% 7,807 | 2.3% 430 |
| 1912 | 38.3% 7,485 | 43.6% 8,510 | 18.1% 3,531 |
| 1908 | 53.1% 10,475 | 43.4% 8,560 | 3.6% 705 |
| 1904 | 53.1% 11,356 | 44.5% 9,516 | 2.3% 501 |
| 1900 | 53.7% 11,348 | 44.2% 9,349 | 2.1% 444 |
| 1896 | 56.3% 11,100 | 41.3% 8,140 | 2.4% 471 |
| 1892 | 46.3% 9,450 | 48.0% 9,808 | 5.7% 1,157 |
| 1888 | 49.6% 10,825 | 48.0% 10,487 | 2.4% 526 |
| 1884 | 48.7% 9,929 | 48.4% 9,870 | 2.9% 586 |
In recent history, Ulster County has voted Democratic. In 2004 John Kerry defeated George W. Bush by 54–43%, in 2008 Barack Obama defeated John McCain by 61–38%, and in 2012 Barack Obama defeated Mitt Romney by 60–37%. The county is currently being represented by Republican John Faso in Congress, and is located in New York's 19th congressional district.
Ulster long had a county-scale version of a council-manager government, with the county legislature hiring a county administrator to handle executive functions. The chair of the legislature had a great deal of power and was only accountable to the voters of his own district. The only countywide elected officials were the district attorney, Holley Carnright, 2008 to present and sheriff, Paul Van Blarcum, 2007 to present.
In 2006, voters approved the first-ever county charter, changing to an elected executive branch. Two years later, Mike Hein, the last appointed county administrator, became Ulster's first elected county executive.[12]
| Name | Party | Term |
|---|---|---|
| Michael P. Hein | Democratic | January 1, 2009 – present |
Legislative authority is vested in the County Legislature, which consists of 23 members elected from individual districts, as directed by a county charter reapportionment mandate starting in late 2010.[13] The current composition of the Legislature is as follows (10 Democrats, 10 Republicans, 1 Unaffiliated who caucuses with the Democrats, 1 Independent who caucuses with the Republicans, and 1 Conservative who caucuses with the Republicans to give them a 12-11 majority):
| District | Legislator | Party | Residence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mary Wawro | Conservative (Caucuses with Republicans) | Saugerties |
| 2 | Joseph Maloney | Independence (Caucuses with Republicans) | Saugerties |
| 3 | Dean Fabiano | Republican | Glasco |
| 4 | James Maloney, Vice Chair | Republican | Kingston |
| 5 | Lynn Eckert | Democratic | Kingston |
| 6 | David Donaldson | Democratic | Kingston |
| 7 | Brian Woltman | Republican | Kingston |
| 8 | Laura Petit | Democratic | Esopus |
| 9 | Herbert Litts lll | Republican | Highland |
| 10 | Mary Beth Maio, Majority Leader | Republican | Highland |
| 11 | Richard Gerentine | Republican | Marlboro |
| 12 | Kevin Roberts | Republican | Plattekill |
| 13 | Kenneth Ronk Jr., Chairman | Republican | Wallkill |
| 14 | Craig Lopez, Majority Whip | Republican | Pine Bush |
| 15 | Rev. Julius Collins | Democratic | Ellenville |
| 16 | Tracey Bartels | Unaffiliated (Caucuses with Democrats) | Gardiner |
| 17 | James Delaune | Democratic | New Paltz |
| 18 | Heidi Haynes | Republican | Accord |
| 19 | Manna Jo Greene | Democratic | Cottekill |
| 20 | Hector Rodriguez, Minority Leader | Democratic | New Paltz |
| 21 | Lynn Archer | Democratic | Accord |
| 22 | Kathy Nolan | Democratic | Boiceville |
| 23 | Johnathan Heppner, Minority Whip | Democratic | Woodstock |
Recreation

Ulster County contains a large part of Catskill Park and the Catskill Forest Preserve. The former Delaware and Hudson Canal brought Pennsylvania coal to Kingston on the Hudson. Former Orleans band member John Hall served in the Ulster County legislature before moving to the 19th Congressional District to run for Congress.
Ulster County has continued to be a popular vacation destination for many decades. The County is home to many outdoor landscapes, including the Catskill Mountains, the Hudson River, Minnewaska State Park, Catskill Park, Shawangunk Mountains and the Shawangunk Ridge. Each offers various recreation opportunities, including hiking, bicycling, skiing, horseback riding, kayaking, rock climbing, hunting and fishing.
The County also includes more than 40 miles of rail trails along the Hudson Valley Rail Trail, Wallkill Valley Rail Trail, and O&W Rail Trail. The Walkway Over the Hudson, the world’s longest pedestrian and bicycle bridge which spans the Hudson River, is connected within Ulster County trails.
Ulster County has also played a role in some significant moments in U.S. history. The Senate House State Historic Site in Kingston, New York is where, in early 1777, American colonists met to ratify the New York Constitution.
The Ulster County Fair has been held in New Paltz for many years and is promoted as "The Best Six Days of Summer". County run recreation areas include the Ulster County Pool in New Paltz and the Ulster Landing Park in Saugerties.
Transportation
The New York State Thruway Interstate 87 runs north–south through the county, carrying traffic to and from New York City and its surroundings.
Public transportation in Ulster County is provided by Trailways of New York to and from New York City and Albany, and along Routes 28 and 23, Ulster County Area Transit on major state and US road corridors in the county, and by Kingston Citibus in Kingston.
Communities
City
- Kingston (county seat)
Towns
Villages
Census-designated places
- Accord
- Clintondale
- Cragsmoor
- East Kingston
- Gardiner
- Glasco
- High Falls
- Highland
- Hillside
- Hurley
- Kerhonkson
- Lake Katrine
- Lincoln Park
- Malden-on-Hudson
- Marlboro
- Milton
- Napanoch
- Phoenicia
- Pine Hill
- Plattekill
- Port Ewen
- Rifton
- Rosendale Hamlet
- Saugerties South
- Shokan
- Stone Ridge
- Tillson
- Walker Valley
- Wallkill
- Watchtower
- West Hurley
- Woodstock
- Zena
Hamlets
See also
References
- 1 2 "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved October 13, 2013.
- ↑ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ↑ "National Historic Landmarks Program – Lake Mohonk Mountain House". National Park Service. Archived from the original on November 10, 2013. Retrieved December 7, 2013.
- ↑ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Archived from the original on May 19, 2014. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved June 9, 2017.
- ↑ "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 8, 2015.
- ↑ "American FactFinder". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ↑ Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org.
- ↑ Brooks, Paul (November 5, 2008). "Hein wins big as first Ulster County executive". Times-Herald Record. Ottaway Community Newspapers. Retrieved November 21, 2008.
- ↑ Ulster reapportionment panel to revamp Legislature. DailyFreeman.com. Retrieved on August 9, 2013.
Bibliography
- Clearwater, Alphonso T. (1907). A History of Ulster County, New York. Kingston, NY: W.J. Van Deusen.
- Fried, Marc B. (1975). The Early History of Kingston & Ulster County, NY. Marbletown, NY: Ulster County Historical Society.
- Sylvester, Nathaniel Bartlett (1880). History of Ulster County, New York, with Illustrations and Biographical Sketches of its Prominent Men and Pioneers: Part Second: History of the Towns of Ulster County. Philadelphia, PA: Everts & Peck. OCLC 2385957.
- Ulster County Historians (1984). The History of Ulster County, With Emphasis upon the Last 100 Years, 1883–1983. Kingston, NY: Ulster County Historians. OCLC 11345209.
- Van Buren, Augustus H. (1923). A History of Ulster County Under the Dominion of the Dutch. Kingston, NY. OCLC 1131828.
- Zimm, Louise Hasbrouck (1946). Southeastern New York: A History of the Counties of Ulster, Dutchess, Orange, Rockland and Putnam. New York: Lewis Historical Publishing Co.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ulster County, New York. |




