Telfair County, Georgia
Telfair County is a county located in the central portion of the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the population was 16,500.[1] The largest city and county seat is McRae-Helena.[2]
Telfair County | |
|---|---|
 Telfair County Courthouse in McRae-Helena | |
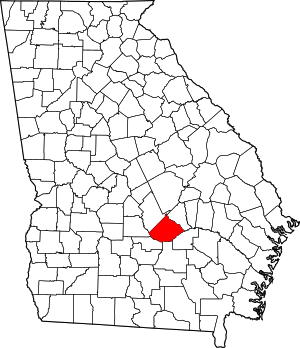 Location within the U.S. state of Georgia | |
 Georgia's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 31°56′N 82°56′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | December 10, 1807 |
| Named for | Edward Telfair |
| Seat | McRae-Helena |
| Largest city | McRae-Helena |
| Area | |
| • Total | 444 sq mi (1,150 km2) |
| • Land | 437 sq mi (1,130 km2) |
| • Water | 6.7 sq mi (17 km2) 1.5%% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 15,876 |
| • Density | 38/sq mi (15/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 8th |
| Website | telfaircounty |
In 2009 researchers from the Fernbank Museum of Natural History announced having found artifacts they associated with the 1541 Hernando de Soto Expedition at a private site near the Ocmulgee River, the first such find between Tallahassee, Florida and western North Carolina. De Soto's expedition was well recorded, but researchers have had difficulties finding artifacts from sites where he stopped. This site was an indigenous village occupied by the historic Creek people from the early 15th century into the 16th century. It was located further southeast than de Soto's expedition was thought to go in Georgia.[3]
History

Archaeologists associated with Atlanta's Fernbank Museum of Natural History have excavated a 2,000-acre (8.1 km2) plot near McRae-Helena and approximately a mile from the Ocmulgee River, beginning in 2005. In 2009 they announced finding evidence of a Spanish settlement dating to the first half of the 16th century.[4] The archaeologists originally believed that the artifacts may have come from a settlement founded by Spanish leader Lucas Vázquez de Ayllón from Hispaniola in 1526 and briefly occupied by hundreds of colonists. The group encountered hard conditions and fewer than 200 survived to return to Hispaniola.[5]
Additional research suggests that the site instead was one visited in 1541 by the de Soto Expedition. Researchers have recovered Murano glass beads, made in Venice, Italy, and brought by the Spanish for trading with Native Americans; pottery fragments, and iron weapons. Some of the beads bear a chevron pattern. Such beads have been identified as a hallmark of the de Soto expedition, due to the limited period of time in which they were produced. Excavations have also produced six metal objects, including three iron tools and a silver pendant.[6]
The site is further west than scholars had earlier believed that the de Soto expedition had traveled, based on documentation from his expedition. This was the first evidence found of his expedition between Tallahassee, Florida, where excavations have revealed artifacts of his expedition, and western North Carolina[4] where another site has been found.
What we have now is the best-documented collection of Spanish artifacts in Georgia; many are unique, and they are the only examples of certain artifacts ever found outside Florida.
This site is believed to have been a Native American community, occupied from the end of the 15th century through the first decades of the 16th century. At that time, they had neither glass nor metal goods.[6] Blanton presented a paper on his findings on November 5, 2009 at the Southeastern Archaeological Conference in Mobile, Alabama.[4]
The historic Creek people occupied much of this area of Georgia. Telfair County was established by European Americans on December 10, 1807 as part of Georgia. Development of the county largely took place after Indian Removal in the 1830s of the Creek Confederacy, who had occupied a large territory, including the southern two thirds of present-day Georgia, for thousands of years. They were removed to Indian Territory west of the Mississippi River, in today's Oklahoma. The county is named for Edward Telfair, the sixteenth governor of Georgia and a member of the Continental Congress.[7]
Many of the first European-American settlers were Scottish immigrants and Scots-Irish migrants who traveled down the backcountry from Pennsylvania and Virginia.[8]
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 444 square miles (1,150 km2), of which 437 square miles (1,130 km2) is land and 6.7 square miles (17 km2) (1.5%) is water.[9] The county contains at least 50 artesian wells.
The southern two-thirds of Telfair County, bordered by a line from Milan east to Lumber City, are located in the Lower Ocmulgee River sub-basin of the Altamaha River basin. The northern portion of the county is located in the Little Ocmulgee River sub-basin of the same Altamaha River basin.[10]
Major highways














Adjacent counties
- Wheeler County (northeast)
- Jeff Davis County (southeast)
- Coffee County (south)
- Ben Hill County (southwest)
- Wilcox County (west)
- Dodge County (northwest)
- Laurens County(north)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1810 | 744 | — | |
| 1820 | 2,104 | 182.8% | |
| 1830 | 2,136 | 1.5% | |
| 1840 | 2,763 | 29.4% | |
| 1850 | 3,026 | 9.5% | |
| 1860 | 2,713 | −10.3% | |
| 1870 | 3,245 | 19.6% | |
| 1880 | 4,828 | 48.8% | |
| 1890 | 5,477 | 13.4% | |
| 1900 | 10,083 | 84.1% | |
| 1910 | 13,288 | 31.8% | |
| 1920 | 15,291 | 15.1% | |
| 1930 | 14,997 | −1.9% | |
| 1940 | 15,145 | 1.0% | |
| 1950 | 13,221 | −12.7% | |
| 1960 | 11,715 | −11.4% | |
| 1970 | 11,381 | −2.9% | |
| 1980 | 11,445 | 0.6% | |
| 1990 | 11,000 | −3.9% | |
| 2000 | 11,794 | 7.2% | |
| 2010 | 16,500 | 39.9% | |
| Est. 2018 | 15,876 | [11] | −3.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[12] 1790-1960[13] 1900-1990[14] 1990-2000[15] 2010-2013[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[16] of 2000, there were 11,794 people, 4,140 households, and 2,873 families living in the county. The population density was 27 people per square mile (10/km²). There were 5,083 housing units at an average density of 12 per square mile (4/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 59.71% White, 38.44% Black or African American, 0.03% Native American, 0.20% Asian, 1.16% from other races, and 0.47% from two or more races. 1.82% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race.
There were 4,140 households out of which 31.10% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 48.40% were married couples living together, 16.70% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.60% were non-families. 28.40% of all households were made up of individuals and 13.60% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.48 and the average family size was 3.01.
In the county, the population was spread out with 22.50% under the age of 18, 10.30% from 18 to 24, 30.10% from 25 to 44, 22.30% from 45 to 64, and 14.90% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 37 years. For every 100 females there were 110.90 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 113.20 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $26,097, and the median income for a family was $32,513. Males had a median income of $26,444 versus $19,970 for females. The per capita income for the county was $14,197. About 17.30% of families and 21.20% of the population were below the poverty line, including 26.40% of those under age 18 and 23.70% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 16,500 people, 5,543 households, and 3,609 families living in the county.[17] The population density was 37.7 inhabitants per square mile (14.6/km2). There were 7,297 housing units at an average density of 16.7 per square mile (6.4/km2).[18] The racial makeup of the county was 57.0% white, 36.5% black or African American, 0.6% Asian, 0.2% American Indian, 4.1% from other races, and 1.7% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 12.3% of the population.[17] In terms of ancestry, 32.1% were English, and 6.6% were American.[19]
Of the 5,543 households, 31.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 42.7% were married couples living together, 17.2% had a female householder with no husband present, 34.9% were non-families, and 30.8% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.41 and the average family size was 3.02. The median age was 39.2 years.[17]
The median income for a household in the county was $23,876 and the median income for a family was $36,109. Males had a median income of $27,278 versus $28,253 for females. The per capita income for the county was $13,420. About 23.3% of families and 31.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including 39.1% of those under age 18 and 29.5% of those age 65 or over.[20]
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 64.5% 2,450 | 34.6% 1,313 | 0.9% 33 |
| 2012 | 57.2% 2,480 | 41.6% 1,805 | 1.2% 53 |
| 2008 | 56.8% 2,486 | 42.6% 1,862 | 0.6% 28 |
| 2004 | 57.5% 2,171 | 42.1% 1,590 | 0.4% 15 |
| 2000 | 48.5% 1,693 | 50.9% 1,777 | 0.7% 23 |
| 1996 | 34.3% 1,143 | 55.7% 1,856 | 10.0% 333 |
| 1992 | 31.6% 1,324 | 53.4% 2,238 | 15.0% 630 |
| 1988 | 50.2% 1,805 | 49.1% 1,765 | 0.7% 25 |
| 1984 | 49.1% 1,980 | 50.9% 2,049 | |
| 1980 | 29.8% 1,173 | 68.5% 2,700 | 1.7% 68 |
| 1976 | 15.3% 637 | 84.7% 3,534 | |
| 1972 | 76.6% 2,245 | 23.4% 687 | |
| 1968 | 16.9% 720 | 24.4% 1,038 | 58.7% 2,502 |
| 1964 | 50.6% 1,914 | 49.5% 1,872 | |
| 1960 | 21.3% 791 | 78.7% 2,922 | |
| 1956 | 12.0% 284 | 88.0% 2,075 | |
| 1952 | 8.3% 243 | 91.7% 2,695 | |
| 1948 | 30.1% 339 | 63.2% 712 | 6.7% 76 |
| 1944 | 12.8% 174 | 87.2% 1,187 | |
| 1940 | 6.9% 104 | 92.2% 1,391 | 0.9% 13 |
| 1936 | 9.5% 121 | 90.5% 1,158 | |
| 1932 | 5.7% 45 | 93.6% 746 | 0.8% 6 |
| 1928 | 13.9% 332 | 86.1% 2,057 | |
| 1924 | 15.0% 264 | 78.7% 1,382 | 6.3% 111 |
| 1920 | 3.4% 37 | 96.7% 1,069 | |
| 1916 | 3.5% 29 | 93.5% 773 | 3.0% 25 |
| 1912 | 2.6% 19 | 94.7% 694 | 2.7% 20 |
See also
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- Hudson, Charles M. (1997). Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun. University of Georgia Press. pp. 157–162.
- "Archaeologists Track Infamous Conquistador Through Southeast". Science Daily. Retrieved November 9, 2009.
- Davis, Mark, "What Lies Beneath," Atlanta Journal-Constitution, 17 December 2007, p. C1
- Pousner, Howard, "Fernbank archaeologist confident he has found de Soto site", Atlanta Journal-Constitution, 6 November 2009; updated 2 February 2010
- Krakow, Kenneth K. (1975). Georgia Place-Names: Their History and Origins (PDF). Macon, GA: Winship Press. p. 223. ISBN 0-915430-00-2.
- Hellmann, Paul T. (May 13, 2013). Historical Gazetteer of the United States. Routledge. p. 239. Retrieved November 30, 2013.
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission Interactive Mapping Experience". Georgia Soil and Water Conservation Commission. Retrieved November 27, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 31, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved June 26, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 13, 2020. Retrieved December 30, 2015.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved March 22, 2018.
