Administrative divisions of India
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of India |
|
|
|
|
|
———————
Legislatures: ——————— Urban bodies: |
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision (e.g., the mandals of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana correspond to tehsils of Uttar Pradesh and other Hindi-speaking states but to talukas of Gujarat, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu).[1]
The smaller subdivisions (villages and blocks) exist only in rural areas. In urban areas, urban local bodies exist instead of these rural subdivisions.
Zones
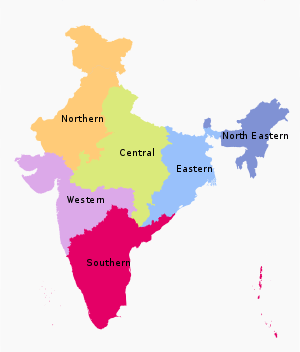
The States have been grouped into six zones having an Advisory Council "to develop the habit of cooperative working" among these States. Zonal Councils were set up vide Part-III of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956. The North Eastern States' special problems are addressed by another statutory body - The North Eastern Council, created by the North Eastern Council Act, 1971.[2] The present composition of each of these Zonal Councils is as under:[3]
- Northern Zonal Council, comprising Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, and Rajasthan;
- North-Eastern Zonal Council, comprising Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura; The State of Sikkim has also been included in the North Eastern Council vide North Eastern Council (Amendment) Act, 2002 notified on 23 December 2002.[4]
- Central Zonal Council, comprising the States of Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh;
- Eastern Zonal Council, comprising Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal;
- Western Zonal Council, comprising Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra;
- Southern Zonal Council, comprising Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep are not members of any of the Zonal Councils.[5] However, they are presently special invitees to the Southern Zonal Council[6]
States and union territories
India is composed of 29 states and 7 union territories (including a national capital territory).[7] The union territories are governed by administrators, appointed by the President of India. Two of the territories (Delhi and Puducherry) have been given partial statehood, with elected legislatures and executive councils of ministers, but limited powers.
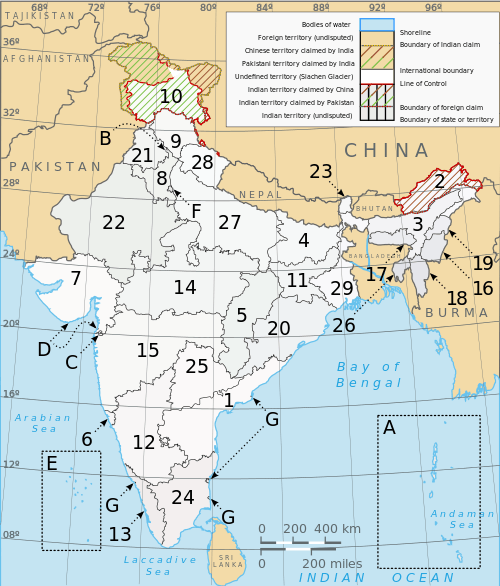
- States
- Union territories
| Number | Union territory | Code | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Andaman and Nicobar Islands | AN | Port Blair |
| B | Chandigarh | CH | Chandigarh (also the capital of Haryana and Punjab) |
| C | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | DN | Silvassa |
| D | Daman and Diu | DD | Daman |
| E | Lakshadweep | LD | Kavaratti |
| F | National Capital Territory of Delhi | DL | New Delhi |
| G | Puducherry | PY | Pondicherry |
Regions
This is a list of unofficial, or quasi-official, regions of India. Some are geographic regions, others ethnic, linguistic, dialect, or cultural regions, and some correspond to historic countries, states or provinces.
The six regions
| Name | Population (2011 census) | Largest local | Area | States | Union Territories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central India | 100,525,580 | Indore | 443,443 km2 | 2 | - |
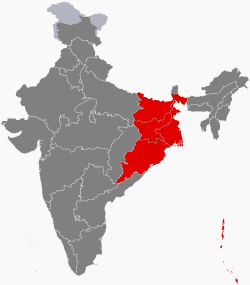
| East India | 226,925,195 | Kolkata | 418,323 km2 | 4 | 1 |
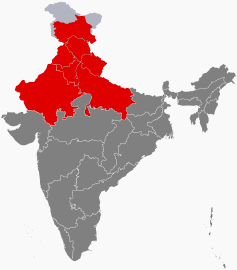
| North India | 376,809,728 | Delhi | 1,010,731 km2 | 7 | 2 |
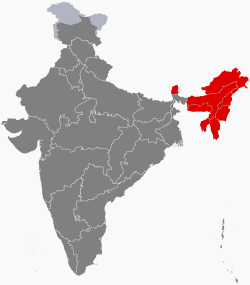
| Northeast India | 45,587,982 | Guwahati | 262,230 km2 | 8 | - |
| South India | 253,051,953 | Bangalore | 635,780 km2 | 5 | 2 |
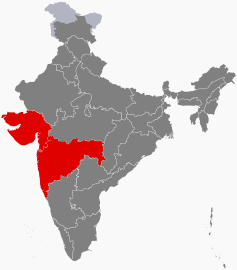
| Western India | 173,343,821 | Mumbai | 508,032 km2 | 3 | 2 |
Regions within states
Some states consist of regions, which have no official administrative governmental status. They are purely geographic regions; some correspond to historic countries, states or provinces. A region may comprise one or more divisions, averaging about three divisions per region. However, the boundaries of the regions and the boundaries of the divisions do not always coincide exactly. So far there has been no movement to give the regions official administrative status. If this was to be done, it would presumably require that the boundaries of the regions be slightly modified so that they correspond exactly with their constituent districts.
Divisions
Some of the Indian states are subdivided into divisions which have official administrative governmental status and each division is headed by senior IAS officer called Divisional Commissioner, each further comprising several districts:
Districts
States and territories (or divisions) are further subdivided into districts (zilla), of which there are 696 (as of 2016). Each District is headed by an IAS officer called District Magistrate.
Sub-district
Tehsils, talukas, mandals, sub-divisions, CD Blocks, headed by a Tehsildar or Talukdar or MRO or Block Development Officer, comprise several villages or village clusters. The governmental/ elected bodies at the Tehsil level are called the panchayat samiti.
States use varying names for their sub-districts. Detailed information is as follows:[10]
| State | Sub–district | Number of sub–districts |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Mandal | 664[11] |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Circle | 149 |
| Assam | Circle | 155 |
| Bihar | CD Block | 533 |
| Chhattisgarh | Tehsil | 97 |
| Goa | Taluka | 11 |
| Gujarat | Taluka | 226 |
| Haryana | Tehsil | 67 |
| Himachal Pradesh | Tehsil/ Sub-tehsil | 109 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Tehsil | 59 |
| Jarkhand | CD Block | 210 |
| Karnataka | Taluka | 175 |
| Kerala | Taluka | 63 |
| Madhya Pradesh | Tehsil | 259 |
| Maharashtra | Taluka | 353 |
| Manipur | Sub-division | 38 |
| Meghalaya | CD Block | 39 |
| Mizoram | CD Block | 22 |
| Nagaland | Circle | 93 |
| Odisha | Police station | 485 |
| Punjab | Tehsil | 72 |
| Rajasthan | Tehsil | 241 |
| Sikkim | 9 | |
| Tamil Nadu | Taluka | 201 |
| Telangana | Mandal | 452 |
| Tripura | CD Block | 38 |
| Uttar Pradesh | Tehsil | 350 |
| Uttarakhand | Tehsil | 48 |
| West Bengal | CD Block | 341 |
| Union Territory | Sub–district | Number of sub–districts |
|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Tehsil | 7 |
| Lakshadweep | Sub-division | 4 |
| Chandigarh | Tehsil | 1 |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | Taluka | 1 |
| Daman and Diu | Taluka | 2 |
| Delhi | Tehsil | 34 |
| Puducherry | Commune Panchayat | 10 |
Rural level
Blocks
The block or Community development block or C.D.Block is often the next level of administrative division after the tehsil.
| State | C.D.Block | Number of C.D.Blocks |
|---|---|---|
| Meghalaya | C.D.Block | 39 |
| Mizoram | C.D.Block | 22 |
| Bihar | C.D.Block | 533 |
| Jharkhand | C.D.Block | 263[12] |
| Tripura | C.D.Block | 58 |
| Uttarakhand | C.D.Block | 95 |
| West Bengal | C.D.Block | 341 |
Villages
Villages are often the lowest level of subdivisions in India. The governmental bodies at the village level are called Gram Panchayat, of which there were an estimated 256,000 in 2002. Each Gram Panchayat covers a large village or a cluster of smaller villages with a combined population exceeding 500 Gram Sabha. Clusters of villages are also sometimes called Hobli or Patti.
Habitations
Certain governmental functions and activities - including clean water availability, rural development, and education - are tracked at a sub-village level.[13] These hamlets are termed "habitations". India is composed of 1,714,556 habitations [14] In some states, most villages have a single habitation; in others (notably Kerala and Tripura) there is a high ratio of habitations to villages.[15]
Metropolitan area
A metro area usually comprises multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighbourhoods, townships, cities, exurbs, suburbs, counties, districts, states, and even nations like the eurodistricts. As social, economic and political institutions have changed, metropolitan areas have become key economic and political regions. Metropolitan areas include one or more urban areas, as well as satellite cities, towns and intervening rural areas that are socio-economically tied to the urban core, typically measured by commuting patterns The metropolitan cities of India are: Mumbai, New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Pune, Hyderabad and Bengaluru.
Historic
See also
- Autonomous regions of India
- Indian states rankings
- Local Governance in India
- Cultural Zones of India
References
- ↑ "Archived copy - Table 1.1 - India at a Glance - Administrative Division - 2001" (PDF). Office of the Registrar General of India, New Delhi. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 18 August 2018.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 April 2012. Retrieved 2012-03-25.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 8 May 2012. Retrieved 2012-03-07.
- ↑ "Zonal Council". mha.nic.in. Archived from the original on 12 May 2017. Retrieved 26 October 2016.
- ↑ "THE STATES REORGANISATION ACT, 1956 (ACT NO.37 OF 1956) PART – III ZONES AND ZONAL COUNCILS" (PDF). Interstatecouncil.nic.in. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "PRESENT COMPOSITION OF THE SOUTHERN ZONAL COUNCIL" (PDF). Interstatecouncil.nic.in. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 6 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-05. States and Union Territories of India - Source - Government of India Official Website
- ↑ "Vijayawada is Andhra Pradesh's new capital". Deccanchronicle.com. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "Appointed Day for Telangana State". Newindianexpress.com. Retrieved 27 December 2017.
- ↑ "Statement showing the Nomenclature and Number of Sub-Districts in States/UTs". Office of The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India, New Delhi. 2010–2011. Retrieved 3 October 2011.
- ↑ "List of Mandals" (PDF). msmehyd.ap.nic.in. Andhra Pradesh State. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- ↑ "Names of Blocks of Jharkhand". Jharkhandi Baba. 2017-10-21. Retrieved 2017-10-21.
- ↑ Indian Department of Drinking Water Supply Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑
- ↑ Indian Department of Education Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine.