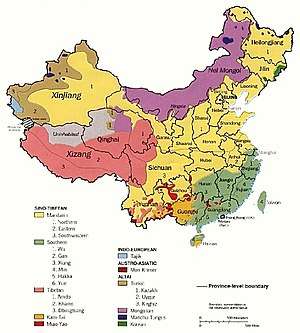
Languages of China
There are several hundred languages in China. The predominant language is Standard Chinese, which is based on central Mandarin, but there are hundreds of related Chinese languages, collectively known as Hanyu (simplified Chinese: 汉语; traditional Chinese: 漢語; pinyin: Hànyǔ, 'Han language'), that are spoken by 92% of the population. The Chinese (or 'Sinitic') languages are typically divided into seven major language groups, and their study is a distinct academic discipline.[5] They differ as much from each other morphologically and phonetically as do English, German and Danish. There are in addition approximately 300 minority languages spoken by the remaining 8% of the population of China.[6] The ones with greatest state support are Mongolian, Tibetan, Uyghur and Zhuang.
| Part of a series on the |
| Culture of China |
|---|
 |
| History |
| People |
| Languages |
|
| Cuisine |
| Festivals |
|
Music and performing arts |
|
Media
|
|
Monuments |
|
Organisations
|
|
 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANCIENT | ||||||||
| Neolithic c. 8500 – c. 2070 BCE | ||||||||
| Xia c. 2070 – c. 1600 BCE | ||||||||
| Shang c. 1600 – c. 1046 BCE | ||||||||
| Zhou c. 1046 – 256 BCE | ||||||||
| Western Zhou | ||||||||
| Eastern Zhou | ||||||||
| Spring and Autumn | ||||||||
| Warring States | ||||||||
| IMPERIAL | ||||||||
| Qin 221–207 BCE | ||||||||
| Han 202 BCE – 220 CE | ||||||||
| Western Han | ||||||||
| Xin | ||||||||
| Eastern Han | ||||||||
| Three Kingdoms 220–280 | ||||||||
| Wei, Shu and Wu | ||||||||
| Jin 266–420 | ||||||||
| Western Jin | ||||||||
| Eastern Jin | Sixteen Kingdoms | |||||||
| Northern and Southern dynasties 420–589 | ||||||||
| Sui 581–618 | ||||||||
| Tang 618–907 | ||||||||
| (Wu Zhou 690–705) | ||||||||
| Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms 907–979 |
Liao 916–1125 | |||||||
| Song 960–1279 | ||||||||
| Northern Song | Western Xia | |||||||
| Southern Song | Jin | Western Liao | ||||||
| Yuan 1271–1368 | ||||||||
| Ming 1368–1644 | ||||||||
| Qing 1636–1912 | ||||||||
| MODERN | ||||||||
| Republic of China on mainland 1912–1949 | ||||||||
| People's Republic of China 1949–present | ||||||||
| Republic of China on Taiwan 1949–present | ||||||||
According to the 2010 edition of the Nationalencyklopedin, 955 million out of China's then-population of 1.34 billion spoke some variety of Mandarin Chinese as their first language, accounting for 71% of the country's population.[7] According to the 2019 edition of Ethnologue, 904,000,000 people in China spoke some variety of Mandarin as their first language in 2017.[8]
Standard Chinese, known in China as Putonghua, based on the Mandarin dialect of Beijing, is the official national spoken language for the mainland and serves as a lingua franca within the Mandarin-speaking regions (and, to a lesser extent, across the other regions of mainland China). Several other autonomous regions have additional official languages. For example, Tibetan has official status within the Tibet Autonomous Region and Mongolian has official status within Inner Mongolia. Language laws of China do not apply to either Hong Kong or Macau, which have different official languages (Cantonese, English and Portuguese) than the mainland.
Spoken languages
The spoken languages of nationalities that are a part of the People's Republic of China belong to at least nine families:
- The Sino-Tibetan family: 19 official ethnicities (including the Han and Tibetans)
- The Tai–Kadai family: several languages spoken by the Zhuang, the Bouyei, the Dai, the Dong, and the Hlai (Li people). 9 official ethnicities.
- The Hmong–Mien family: 3 official ethnicities
- The Austroasiatic family: 4 official ethnicities (the De'ang, Blang, Gin (Vietnamese), and Wa)
- The Turkic family: Uyghurs, Kazakhs, Salars, etc. 7 official ethnicities.[9]
- The Mongolic family: Mongols, Dongxiang, and related groups. 6 official ethnicities.[9]
- The Tungusic family: Manchus (formerly), Hezhe, etc. 5 official ethnicities.
- The Koreanic family: Korean language
- The Indo-European family: 2 official ethnicities (the Russians and Tajiks (actually Pamiri people). There is also a heavily Persian-influenced Äynu language spoken by the Äynu people in southwestern Xinjiang who are officially considered Uyghurs.
- The Austronesian family: 1 official ethnicity (the Gaoshan, who speak many languages of the Formosan branch), 1 unofficial (the Utsuls, who speak the Tsat language but are considered Hui.)
Below are lists of ethnic groups in China by linguistic classification. Ethnicities not on the official PRC list of 56 ethnic groups are italicized. Respective Pinyin transliterations and Chinese characters (both simplified and traditional) are also given.
Sino-Tibetan
- Sinitic
- Chinese/Han, Hàn, 汉, 漢
- Mandarin Chinese/Guanhua, Guānhuà, 官话, 官話
- Jin Chinese, jìn, 晋, 晉
- Wu Chinese, ngu1, 吴, 吳
- Huizhou Chinese, Huī, 徽
- Yue Chinese, Yuè, 粤
- Ping Chinese, Píng, 平
- Gan Chinese, Gàn, 赣, 贛
- Xiang Chinese, Xiāng, 湘
- Hakka language, Kèjiā, 客家
- Min Chinese, Mǐn, 闽, 閩
- Bai, Bái, 白
- Chinese/Han, Hàn, 汉, 漢
- Tibeto-Burman
Kra–Dai
(Possibly the ancient Bǎiyuè 百越)
- Kra
- Gelao, Gēlǎo, 仡佬
- Kam–Sui
- Hlai/Li, Lí, 黎
- Tai
- Zhuang (Vahcuengh), Zhuàng, 壮, 壯
- Northern Zhuang, Běibù Zhuàngyǔ, 北部壮语, 北部壯語
- Southern Zhuang, Nánbù Zhuàngyǔ, 南部壮语, 南部壯語
- Bouyei, Bùyī, 布依
- Dai, Dǎi, 傣
- Tai Lü language, Dǎilèyǔ, 傣仂语, 傣仂語
- Tai Nüa language, Déhóng Dǎiyǔ, 德宏傣语, 德宏傣語
- Tai Dam language, Dǎinǎyǔ, 傣哪语; Dǎidānyǔ, 傣担语
- Tai Ya language, Dǎiyǎyǔ, 傣雅语
- Tai Hongjin language, Hónghé Dǎiyǔ, 红金傣语, 紅金傣語
- Zhuang (Vahcuengh), Zhuàng, 壮, 壯
Turkic
- Karluk
- Kipchak
- Oghuz
- Salar, Sǎlá, 撒拉
- Siberian
- Western Yugur, Yùgù, 裕固
- Fuyu Kyrgyz, Fúyú Jí'ěrjísī, 扶餘吉爾吉斯
- Tuvan, túwǎ, 圖瓦
- Old Uyghur, Huíhú, 回鶻 (extinct)
- Old Turkic, Tūjué, 突厥 (extinct)
Mongolic
- Mongolian, Měnggǔ, 蒙古
- Oirat, wèilātè, 衛拉特
- Torgut Oirat, tǔěrhùtè, 土爾扈特
- Buryat, bùlǐyàtè, 布里亞特
- Daur, Dáwò'ěr, 达斡尔
- Southeastern
- Monguor, Tǔ [Zú], 土[族]
- Eastern Yugur, Yùgù, 裕固
- Dongxiang, Dōngxiāng, 东乡, 東鄉
- Bonan, Bǎoān, 保安
- Kangjia, Kāngjiā, 康家语, 康加語
- Monguor, Tǔ [Zú], 土[族]
- Tuoba, Tuòbá, 拓跋 (extinct)
- Para-Mongolic
Austroasiatic
- Palaung-Wa
- Vietnamese/Kinh, Jīng, 京
Austronesian
- Formosan languages, Gāoshān, 高山
- Tsat, Huíhuī 回輝
Unclassified
- Ruan-ruan (Rouran), Rúrú, 蠕蠕 (extinct)
Written languages
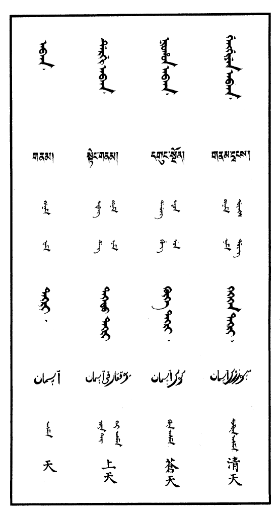
The following languages traditionally had written forms that do not involve Chinese characters (hanzi):
- The Dai – Tai Lü language or Tai Nüa language – Tai Lü alphabet or Tai Nüa alphabet
- The Kazakhs – Kazakh language – Kazakh Arabic alphabet
- The Koreans – Korean language – Chosŏn'gŭl alphabet
- The Kyrgyz – Kyrgyz language – Kyrgyz Arabic alphabet
- The Manchus – Manchu language – Manchu alphabet
- The Mongols – Mongolian language – Mongolian alphabet
- The Naxi – Naxi language – Dongba characters
- The Sui – Sui language – Sui script
- The Tibetans – Tibetan language – Tibetan alphabet
- The Uyghurs – Uyghur language – Uyghur Arabic alphabet
- The Xibe – Xibe language – Manchu alphabet
- The Yi – Yi language – Yi syllabary
Many modern forms of spoken Chinese languages have their own distinct writing system using Chinese characters that contain colloquial variants. These typically are used as sound characters to help determine the pronunciation of the sentence within that language:
- Written Cantonese
- Chữ nôm – Vietnamese
- Written Hokkien
- Shanghainese
Some formerly have used Chinese characters
- The Jurchens (Manchu ancestors) – Jurchen language – Jurchen script
- The Koreans – Korean language – Hanja
- The Khitans (Mongolic people) – Khitan language – Khitan scripts
- The Tanguts (Sino-Tibetan people) – Tangut language – Tangut script
- The Zhuang (Tai people) – Zhuang languages – Sawndip
During Qing dynasty, palaces, temples, and coins have sometimes been inscribed in five scripts:
During the Mongol Yuan dynasty, the official writing system was:
- 'Phags-pa script

Chinese banknotes contain several scripts in addition to Chinese script. These are:
Other writing system for Chinese languages in China include:
- Nüshu script
Ten nationalities who never had a written system have, under the PRC's encouragement, developed phonetic alphabets. According to a government white paper published in early 2005, "by the end of 2003, 22 ethnic minorities in China used 28 written languages."
Language policy
The Chinese language policy in mainland China is heavily influenced by the Soviet nationalities policy and officially encourages the development of standard spoken and written languages for each of the nationalities of China. However, in this schema, Han Chinese are considered a single nationality and the official policy of the People's Republic of China (PRC) treats the different varieties of Chinese differently from the different national languages, even though their differences are as significant as those between the various Romance languages of Europe. While official policies in mainland China encourage the development and use of different orthographies for the national languages and their use in educational and academic settings, realistically speaking it would seem that, as elsewhere in the world, the outlook for minority languages perceived as inferior is grim.[10] The Tibetan Government-in-Exile argue that social pressures and political efforts result in a policy of sinicization and feels that Beijing should promote the Tibetan language more. Because many languages exist in China, they also have problems regarding diglossia. Recently, in terms of Fishman's typology of the relationships between bilingualism and diglossia and his taxonomy of diglossia (Fishman 1978, 1980) in China: more and more minority communities have been evolving from "diglossia without bilingualism" to "bilingualism without diglossia." This could be an implication of mainland China's power expanding.[11]
Study of foreign languages
English has been the most widely-taught foreign language in China, as it is a required subject for students attending university.[12][13] Other languages that have gained some degree of prevalence or interest are Japanese, Korean, Spanish, Portuguese, and Russian.[14][15][16] During the 1950s and 1960s, Russian had some social status among elites in mainland China as the international language of socialism.
In the late 1960s, English replaced the position of Russian to become the most studied foreign language in China. After the Reform and Opening-up policy in 1988, English was taught in public schools starting in the third year of primary school.[1][2]
Russian, French, and German language classes have been made widely available in universities and colleges.[17] In Northeast China, there are many bilingual schools (Mandarin-Japanese; Mandarin-Korean; Mandarin-Russian), in these schools, students learn languages other than English.
The Economist, issue April 12, 2006, reported that up to one fifth of the population was learning English. Gordon Brown, the former British Prime Minister, estimated that the total English-speaking population in China would outnumber the native speakers in the rest of the world in two decades.[18]
There have been a growing number of students studying Arabic, due to reasons of cultural interest and belief in better job opportunities.[19] The language is also widely studied amongst the Hui people.[20] In the past, literary Arabic education was promoted in Islamic schools by the Kuomintang when it ruled mainland China.[21]
There have also been a growing number of students choosing to learn Urdu, due to interest in Pakistani culture, close ties between the respective nations, and job opportunities provided by the CPEC.[22]
Interest in Portuguese and Spanish have increased greatly, due in part to Chinese investment in Latin America as well as in African nations such as Angola, Mozambique, and Cape Verde. Portuguese is also one of the official languages in Macau, although its use had stagnated since the nation's transfer from Portugal to the PRC. It was estimated in 2016 that 2.3% of Macau's locals spoke the language,[23][24] although with government backing since then, interest in it has increased.[25]
Use of English
In China, English is used as a lingua franca in several fields, especially for business settings,[26] and in schools to teach Standard Mandarin to people who are not Chinese citizens.[27] English is also one of the official languages in Hong Kong.
See also
- Language Atlas of China
- Linguistic Atlas of Chinese Dialects
- Secession in China
- Varieties of Chinese
- List of varieties of Chinese
- Han Chinese subgroups
- Demographics of the People's Republic of China
- Ethnic issues in China
- Hong Kong English
- Languages of Hong Kong
- Languages of Macau
- Macanese Portuguese
- Nationalities of China
- Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages
- Cantonese
- Standard Chinese
- Chinglish
References


- "English Craze Hits Chinese Language Standards - YaleGlobal Online". yaleglobal.yale.edu. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- "Asians Offer Region a Lesson – in English". Archived from the original on 2010-02-19. Retrieved 2010-03-06.
- "Faguowenhua". Faguowenhua.com. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- "RI ranks No. 2 in learning Japanese language". The Jakarta Post. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- Dwyer, Arienne (2005). The Xinjiang Conflict: Uyghur Identity, Language Policy, and Political Discourse (PDF). Political Studies 15. Washington: East-West Center. pp. 31–32. ISBN 978-1-932728-29-3.
Tertiary institutions with instruction in the languages and literatures of the regional minorities (e.g., Xinjiang University) have faculties entitled Hanyu xi ("Languages of China Department") and Hanyu wenxue xi ("Literatures of the Languages of China Department").
- Languages of China – from Lewis, M. Paul (ed.), 2009. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Sixteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. "The number of individual languages listed for China is 299. "
- Mikael Parkvall, "Världens 100 största språk 2007" (The World's 100 Largest Languages in 2007), in Nationalencyklopedin. Asterisks mark the 2010 estimates for the top dozen languages.
- China: Languages. In: Eberhard, David M., Gary F. Simons, and Charles D. Fennig (eds.). 2019. Ethnologue: Languages of the World. Twenty-second edition. Dallas, Texas: SIL International. Online version: http://www.ethnologue.com.
- Western Yugur is a Turkic language, whereas is Eastern Yugur a Mongolic language.
- The prospects for the long-term survival of Non-Han minority languages in the south of China Archived 2008-08-21 at the Wayback Machine
- Minglang Zhou, Multilingualism in China the politics of Writing reforms for minority languages 1949-2002 (2003)
- 宋薇. "Retooling English learning in China - USA - Chinadaily.com.cn". usa.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2019-06-22.
- "What Languages Are Spoken in China?". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2019-06-22.
- Phillips, Tom (2018-09-02). "Study of Portuguese and Spanish explodes as China expands role in Latin America". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- "Increasing number of middle schools offer Russian language courses - China - Chinadaily.com.cn". www.chinadaily.com.cn. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- "Top 6 Most Popular Foreign Language Teachers in China". top.at0086.com. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- "German language study on the rise worldwide". ICEF Monitor - Market intelligence for international student recruitment. 2015-04-30. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- "English beginning to be spoken here". The Economist. 2006-04-12.
- "More Chinese Students Study Arabic". www.academiccourses.com. 2017-12-18. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- Michael Dillon (1999), China's Muslim Hui community: migration, settlement and sects, Richmond: Curzon Press, p. 155, ISBN 978-0-7007-1026-3, retrieved 2010-06-28
- Stéphane A. Dudoignon; Hisao Komatsu; Yasushi Kosugi (2006). Intellectuals in the modern Islamic world: transmission, transformation, communication. Taylor & Francis. p. 251. ISBN 978-0-415-36835-3. Retrieved 2010-06-28.
- APP (2017-06-11). "Chinese students eager to learn Urdu anticipating job opportunities under CPEC". DAWN.COM. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- Keegan, Matthew. "Why Does Macau Speak Portuguese?". Culture Trip. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- "Macau Population 2019".
- "In Macau, the old colonial tongue is back in vogue". The Economist. 2018-11-08. ISSN 0013-0613. Retrieved 2019-06-23.
- Wang, Wenpu and Lin Wei (Chengdu Technological University). "Chinese English in as lingua franca in global business setting: A case study of on going emails of a foreign company in China." ICITCE 2015. SHS Web of Conferences 25, 01013 (2016). doi: 10.1051/shsconf/20162501013.
- Wang, Danping. "https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-6476-7_8." Language Alternation, Language Choice and Language Encounter in International Tertiary Education, Springer, 2013. pp 161-177. Print ISBN 978-94-007-6475-0. Online ISBN 978-94-007-6476-7. DOI 10.1007/978-94-007-6476-7_8. Published online on 23 May 2013.
Further reading
- Kane, D. (2006). The Chinese language: its history and current usage. North Clarendon, VT: Tuttle. ISBN 0-8048-3853-4
- Halliday, M. A. K., & Webster, J. (2005). Studies in Chinese language. London: Continuum. ISBN 0-8264-5874-2
- Ramsey, S. Robert (1987). The Languages of China (illustrated, reprint ed.). N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691014685. Retrieved 24 April 2014.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Hong, B. (1978). Chinese language use. Canberra: Contemporary China Centre, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0-909596-29-8
- Cheng, C. C., & Lehmann, W. P. (1975). Language & linguistics in the People's Republic of China. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0-292-74615-6