Coastal Andhra
| Coastal Andhra Costa Andhra | |
|---|---|
| Region of Andhra Pradesh | |
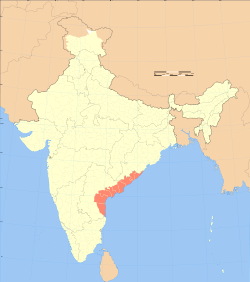 Map of India with Coastal Andhra highlighted in red | |
| Country |
|
| State | Andhra Pradesh |
| Population | |
| • Total | 3,41,93,868 |
| Languages | |
| • Official | Telugu |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| Vehicle registration | AP |
| Largest city | Visakhapatnam |


Coastal Andhra (Kōstā Āndhra), is a region in the state of Andhra Pradesh, India. This region was part of Madras State before 1953 and Andhra State from 1953 to 1956. According to the 2011 census, it has an area of 95,442 square kilometres (36,850 sq mi) which is 57.99% of the total state area and a population of 34,193,868 which is 69.20% of Andhra Pradesh state population. This area includes the coastal districts of Andhra Pradesh between the Eastern Ghats and the Bay of Bengal, from the northern border with Odisha to south of the delta of the Krishna River.
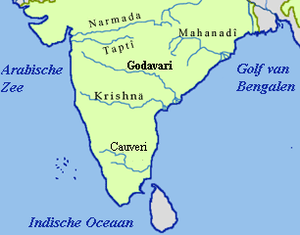
Coastal Andhra has rich agricultural land, owing to the delta of the Godavari and Krishna rivers. The prosperity of Coastal Andhra can be attributed to its rich agricultural land and an abundant water supply from these two rivers. Rice grown in paddy fields is the main crop, with pulses and coconuts also being important. The fishing industry is also important to the region.
History

The state of Andhra emerged to a political power during the reign of Maurya Dynasty. Megasthenes mentioned that Andhra was a flourishing empire of the Satavahana's from the times before christ. Coastal Andhra was also ruled by the famous Chalukyas in between the period of the 7th Century and the 10th century CE. This period was followed by the reign of many other dynasties such as the Cholas, the Kakatiyas as well as the Vijayanagar Empire.
According to 11th century inscriptions, coastal Andhra is bounded by Mahendragiri mountains (in north-eastern border with Gajapati district of Orissa), Kalahasti temple (in Chittoor district near the border of Nellore district), Srisailam temple (in Kurnool district near the border of Mahbubnagar district and Prakasham district).[1]
The Gajapati and Ganjam districts of Odisha were granted to the French East India Company around 1752. Later they were transferred by the French to the British. Nellore, which extends as far as Ongole Taluk, was later received from the Nawab of Arcot, under an establishment. Some parts of present-day Nellore and Chitoor were in the hands of Venkatagiri Rajas. The British made an arrangement with the Raja of Venkatagiri in 1802 to claim power in those territories also.
The districts of Andhra (Circar) and Rayalaseema were ceded by the Nizams to the Britishers, which became part of Madras Presidency.[2]
Geography
Coastal Andhra is located in the eastern region of the state of Andhra Pradesh and comprises six districts. It borders Uttarandhra, Rayalaseema regions of the state and the states of Telangana, Odisha. The presence of the Krishna and Godavari River makes the area fertile for irrigation.[3] The coastal line of this region is the second longest in the country, extending up to 974 km.[3]
Demographics
The area had a total population of 34,195,655 as per 2011 Census of India. The main and most spoken language is Telugu.[4]
Culture
Kuchipudi is the classical dance form of the state, which was originated in the Kuchipudi village of Krishna district.[5]
Cuisine
Rice is the staple food in the Kosta cuisine and is usually consumed with a variety of curries and lentil soups or broths. Cuisine of Coastal Andhra is influenced by sea food varieties.
Politics
Six coastal Andhra districts are:[6] East Godavari, West Godavari, Krishna, Guntur, Prakasam and Nellore.
Chief Ministers from the region are:
- Tanguturi Prakasam Panthulu – 1st Chief Minister of Andhra State (Prakasam).
- Bezawada Gopala Reddy – 2nd Chief Minister of Andhra State (Nellore).
- Kasu Brahmananda Reddy – 3rd Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Guntur).
- Bhavanam Venkatarami Reddy – 8th Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Guntur).
- N.T.Rama Rao – 10th Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Krishna).
- Nadendla Bhaskara Rao – 11th Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Guntur).
- Nedurumalli Janardhana Reddy – 12th Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Nellore).
- K.Rosaiah – 15th Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh (Guntur).
Cities and towns


Vijayawada, Guntur, Rajahmundry, Kakinada, Eluru, Nellore, Ongole. Other major towns in the region are Machilipatnam, Gudivada, Tenali, Narasapuram, Gudur, Kavali, Tadepalligudem, Bhimavaram, Amalapuram, Narasaraopet, Chilakaluripet, Kandukur, Chirala
Tourism
Buddhist hub

Coastal Andhra is one of the major Buddhist hubs in India after the Gangetic plains in Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh. Many remnants from large monasteries to small stupas are found in this region from Srikakulam district in the North to Nellore district in the South. The major Buddhist Remnant sites in this region are as Amaravati, Salihundam, Ramatheertham, Thotlakonda, Bavikonda, Bojjannakonda, Kummarilova,[7] Kodavali,[8] Bhattiprolu etc.
Rivers, lakes and wetlands
Andhra Pradesh contains 259 coastal wetlands, covering an area of 18,552 km2,[9] out of which 88 are manmade.
Lakes Kolleru and Pulicat are the two major lakes in Coastal Andhra. Kolleru, a natural sweet-water lake, is situated in the West Godavari district and serves as a natural flood-balancing reservoir for the two rivers. The lake is also an important habitat for up to 50,000 resident and migratory birds. The lake was declared a wildlife sanctuary in November 1999 under India's Wildlife Protection Act, and designated a wetland of international importance in November 2002 under the international Ramsar Convention. Pulicat is the largest salt water lake in the country, located in Nellore and spreads between Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu. This is one of the famous attractions in south India. In this region, the river Akhanda Godavari splits into several distributary branches, including the Gouthami, Vasishta, Vainatheya, and Vruddha Gouthami, before emptying into the Bay of Bengal.

Transport





- The East Coast Railway (ECoR) serves Srikakulam, Vizianagaram District, and part of Visakhapatnam district, including Visakhapatnam City. Vijayawada is the one of the busiest railway junctions in India, serving many express trains.
- Buses and trains originate from stations in this region, including Visakhapatnam, Kakinada Port, Kakinada Town railway station, Narsapuram, Machilipatnam, Vijayawada, Guntur, Nellore railway station, and Repalle.
- The airports in this region are Visakhapatnam Airport, an international airport; and Vijayawada Airport and Rajahmundry Airport, both domestic airports.
- Visakhapatnam Port and Kakinada Port are the major ports in Coastal Andhra. The state of Andhra Pradesh is the second-busiest maritime state (after Gujarat) in terms of cargo handled.[10] Visakhapatnam Port is the one of the busiest cargo-handling ports in the country.[11]
- Krishnapatnam Port at Nellore and Gangavaram Port are major private ports, and there are minor ports at Machilipatnam Port and Nizampatnam Port in Guntur.
Notable personalities
National flag design
Singers
Telugu literature, arts and cinema
- Nannayya
- Tikkana
- Tenali Ramakrishna
- Gurajada Apparao
- Kandukuri Veeresalingam
- Devulapalli Venkata Krishna Sastri
- Tripuraneni Ramaswamy Chowdary
- Gurram Jashuva
- S. V. Ranga Rao
- Ghantasala (singer)
- Pingali Venkayya
- Nandamuri Taraka Ramarao
- Akkineni Nageswara Rao
- Krishna Ghattamaneni
- Chiranjeevi
- Mahesh Babu Ghattamaneni
- Goparaju Ramachandra Rao
- Prabhas
- S. S. Rajamouli
Other
- Chadalawada Krishnamurthy TTD Chairman
See also
References
- ↑ Austin Cynthia Talbot Assistant Professor of History and Asian Studies University of Texas (23 August 2001). Precolonial India in Practice : Society, Region, and Identity in Medieval Andhra: Society, Region, and Identity in Medieval Andhra. Oxford University Press. pp. 36–. ISBN 978-0-19-803123-9.
- ↑ "Andhra Pradesh – end of an era". Business Standard. Hyderabad. 30 July 2013. Retrieved 8 April 2016.
- 1 2 "Administrative and Geographic profile" (PDF). msmehyd.ap.nic.in. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 September 2016. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ↑ "AP Government Portal – Official Andhra Pradesh State Govt. Portala Pradesh" (PDF). www.ap.gov.in. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ↑ "'Art has to be nurtured to sustain'". The Hindu. Retrieved 5 April 2017.
- ↑ "Districts of Coastal Andhra". mapsofindia. 19 April 2014.
- ↑ B.V.S. Bhaskar (16 February 2012). "Buddhist site found near Tuni". The Hindu. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- ↑ K.N. Murali Sankar (29 November 2011). "ASI gets tough with encroachers". The Hindu. Retrieved 29 July 2013.
- ↑ Wetlands of India report, ISRO
- ↑ P.Manoj (10 May 2013). "Dugarajapatnam in Andhra Pradesh to have new major port". Live Mint and The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ↑ Rama Mohan (13 July 2014). "AP to Set up Maritime Board to Develop Ports". ibtimes.co.in. International Business Times, India. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
External links