Chandrapur district
| Chandrapur district Chanda | |
|---|---|
| District of Maharashtra | |
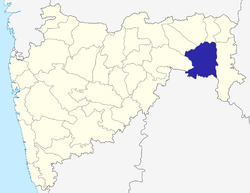 Location of Chandrapur district in Maharashtra | |
| Country | India |
| State | Maharashtra |
| Administrative division | Nagpur Division |
| Headquarters | Chandrapur |
| Tehsils | 1. Chandrapur, 2. Bhadravati, 3. Warora, 4. Chimur, 5. Nagbhid, 6. Bramhapuri, 7. Sindewahi, 8. Mul, 9. Saoli, 10. Gondpimpri, 11. Rajura, 12. Korpana, 13. Pomburna, 14. Ballarpur, 15. Jivati |
| Government | |
| • Assembly seats | 6 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 11,443 km2 (4,418 sq mi) |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 2,204,307 |
| • Density | 190/km2 (500/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 35.12 percent |
| Demographics | |
| • Literacy | 80.01 percent |
| • Sex ratio | 961 |
| Major highways | MH MSH 6, MH MSH 9, MH SH 233, MH SH 243 |
| Average annual precipitation | 1578 mm |
| Website | Official website |
Chandrapur District is a district in the Nagpur Division in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The district was formerly known as Chanda District, but was renamed in 1964. Chandrapur was the largest district in India until the Gadchiroli and Sironcha tehsils were split into separate districts. In 2011, the district population was 2,204,307.[1]
Chandrapur district is known for its super thermal power station, and its vast reserves of coal in Wardha Valley Coalfield.[2] Chandrapur also has large reservoirs of limestone which is a raw material for cement manufacturing in the district.
Tadoba National Park near Chandrapur city is one of India's twenty-eight Project Tiger reserves. The 2015 census of tigers found that 120 of Maharashtra's 170 tigers were located in Chandrapur district.[3]
Divisions

Chandrapur district comprises 23 census towns and 1792 villages spread over 15 talukas.[4]
| Subdivision | Talukas | Villages |
|---|---|---|
| Chandrapur | Chandrapur | 91 |
| Ballarpur | Ballarpur | 31 |
| Mul | Mul | 106 |
| Saoli | 111 | |
| Gondpimpri | Gondpimpri | 97 |
| Pombhurna | 71 | |
| Warora | Warora | 182 |
| Bhadravati | 154 | |
| Chimur | Chimur | 259 |
| Sindewahi | 115 | |
| Rajura | Rajura | 108 |
| Korpana | 110 | |
| Jiwati | 83 | |
| Bramhapuri | Bramhapuri | 136 |
| Nagbhid | 138 |
Politics
The district contains six Vidhan Sabha (legislative assembly) constituencies. They are Rajura, Chandrapur, Ballarpur, Warora, Bramhapuri and Chimur. Rajura, Chandrapur, Ballarpur, and Warora are part of the Chandrapur Lok Sabha constituency. Bramhapuri and Chimur are part of the Gadchiroli-Chimur Lok Sabha constituency.[5][6]
Demography
At the time of the 2011 census of India, Chandrapur district had a population of 2,204,307, which was 1.96 percent of the population of the Maharashtra state.[7] The district population density was 193 inhabitants per square kilometre (500/sq mi).[7] Between 2001 and 2011, the district population grew by 6.43 percent.[7] Females numbered 1,080,473 and males 1,123,834. For every 1,000 males, there were 961 females.[7] 80.01 percent of people in Chandrapur district were literate.[7]
Geography
The Chandrapur district is located in the far east of Maharashtra state. It is part of Nagpur division. The district lies the in the eastern part of the Vidarbha region. The Chandrapur district is located between 19.30’ N and 20.45’ N latitude and at 78.46’ E longitude. The district is surrounded by Bhandara and Nagpur districts at its northern side, Wardha and Yavatmal districts at its western side, Gadchiroli district on the eastern side and Adilabad district of Telangana State on the southern side. In the Survey of India degree sheet, it falls in NOS 55 LF and 56 I M.
Economy
The Chandrapur district has large deposits of coal.[8] Within the district is the Chandrapur Super Thermal Power Station managed by the Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Limited. The district also has limestone mines for the manufacturing of cement.[9]
In 1956, the Ballarpur Industries Limited paper mill was founded in the district. Raw materials such as bamboo, wood, sabai grass, soya bean and cottonseed oil, rags and yarn waste are sourced locally.[10]
Within the district is the Chandrapur ferroalloy plant, a Public Sector Unit engaged in the production of manganese based ferro-alloys.
See also
References
- ↑ ORGI. "Census of India: Search Details". www.censusindia.gov.in. Retrieved 2017-12-02.
- ↑ "New generating unit adds 500MW capacity to CSTPS - Times of India". The Times of India. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ↑ Joshi, Saili (2017-11-02). "Tadoba's Andhari Tiger Reserve: A big delight for nature enthusiasts". The Economic Times. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ↑ "Talukas in Chandrapur District, Maharashtra". www.census2011.co.in. Retrieved 2017-12-02.
- ↑ "District wise List of Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies". Chief Electoral Officer, Maharashtra website. Archived from the original on 18 March 2010. Retrieved 5 September 2010.
- ↑ "District wise List of Assembly and Parliamentary Constituencies". Chief Electoral Officer, Maharashtra website. Archived from the original on 18 March 2017. Retrieved 5 September 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Chandrapur District : Census 2011 data" (PDF). Directorate of Census Operations in Maharashtra. 2011.
- ↑ "Location Map | Western Coalfields Limited". westerncoal.nic.in. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ↑ "Mining Leases" (PDF). 2014.
- ↑ Bapat, S. P. (2006). Spatial Efficiency In Geography. Concept Publishing Company. p. 65. ISBN 9788180692826.
External links
- Official Website of Chandrapur District
- Chandrapur Land Information
- Chandrapur District Complaint Center