이
| ||||||||||||
Korean
Pronunciation
- IPA(key)[i]
- Phonetic Hangul[이]
|
Etymology 2
First attested in the Hunmin jeongeum eonhae (訓民正音諺解本 / 훈민정음언해본), 1446, as Middle Korean 이 (i).
See also
| Korean demonstratives edit | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Determiner | 이 | 그 | 저 | 어느 | |
| Pronoun | Human | 이이 | 그이 | 저이 | 뉘 |
| 이분 | 그분 | 저분 | 어느 분 | ||
| 이자 | 그자 | 저자 | |||
| 이놈 | 그놈 | 저놈 | 어느 놈 | ||
| 이년 | 그년 | 저년 | 어느 년 | ||
| 얘 | 걔 | 쟤 | |||
| Object | 이 | (그) | (저) | 어느 | |
| 이것 | 그것 | 저것 | 어느 것 | ||
| 이거 | 그거 | 저거 | 어느 거 | ||
| Place | 여기 | 거기 | 저기 | 어디 | |
| 이곳 | 그곳 | 저곳 | 어느 곳 | ||
| Direction | 이쪽 | 그쪽 | 저쪽 | 어느 쪽 | |
| Time | 이때 | 그때 | 접때 | 언제 | |
| Verb | 이러다 | 그러다 | 저러다 | 어쩌다 | |
| 이리하다 | 그리하다 | 저리하다 | 어찌하다 | ||
| Adjective | 이렇다 | 그렇다 | 저렇다 | 어떻다 | |
| 이러하다 | 그러하다 | 저러하다 | 어떠하다 | ||
| Adverb | 이리 | 그리 | 저리 | 어찌 | |
| 이렇게 | 그렇게 | 저렇게 | 어떻게 | ||
| 이만큼 | 그만큼 | 저만큼 | 얼마만큼(얼만큼) | ||
Etymology 3
Of native Korean origin. Possibly cognate with Old Japanese い (i, emphatic nominative particle).
Particle
이 • (i)
- A particle marking a grammatical subject ending with a consonant.
- A particle marking a grammatical complement ending with a consonant, before 되다 (doeda, “to become”) and 아니다 (anida, “(to be) not”).
- An adverbial particle 으로/로 (euro/ro) can replace the complement marker 이/가 (i/ga) when the verb is 되다 (doeda, “to become”).
- A particle marking an object of desire.
- 쟨 짜장면이 먹고 싶다(고 하)는데? (Jyaen jjajangmyeoni meokgo sipda(go ha)neunde?, “She says she wants to eat jajangmyeon.”)
Synonyms
- 가 (ga) (marks a grammatical subject ending with a vowel)
See also
Etymology 4
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
—이 • (-i)
- a suffix deriving a passive verb.
- 저는 희망을 봅니다. (Jeoneun huimang-eul bomnida., “I see hope.”) → 저에게 희망이 보입니다. (Jeo-ege huimang-i boimnida., “Hope is seen to me.”)
—이 • (-i)
- a suffix deriving a causative verb.
- 저는 희망을 봅니다. (Jeoneun huimang-eul bomnida., “I see hope.”) → 저는 이분들께 희망을 보여 드리고 싶습니다. (Jeoneun ibundeulkke huimang-eul boyeo deurigo sipseumnida., “I want to show these people hope.”)
- 천장이 높군. (Cheonjang-i nopgun., “The ceiling is high.”) → 천장을 높이어야(하)겠군. (Cheonjang-eul nopieoya(ha)getgun., “I guess the ceiling needs raising.”)
Synonyms
Etymology 5
First attested in the Yongbi eocheonga (龍飛御天歌 / 용비어천가), 1447, as Middle Korean 이 (i).
Noun
이 • (i)
Etymology 6
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
—이 • (-i)
Etymology 7
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
—이 • (-i)
- (after a stem of an adjective) a suffix deriving an adverb. -ly.
- (after repeating a single-syllable noun) a suffix deriving an adverb.
Usage notes
The suffix -i is used for adjectives not ending in -hada, and the suffix -hi is implemented for that case. For example, 많다 (manta, “many”) turns into 많이 (mani, “a lot”) whereas 깔끔하다 (kkalkkeumhada, “neat”) becomes 깔끔히 (kkalkkeumhi, “neatly”). However, if -hada is suffixed after consonants k and s, -i is sometimes used rather than -hi, as in 깊숙이 (gipsugi, “deeply”) from 깊숙하다 (gipsukhada, “deep”) and 깨끗이 (kkaekkeusi, “cleanly”) from 깨끗하다 (kkaekkeuthada, “clean”), while many adjectives like 솔직하다 (soljikhada, “frank”) still take -hi. Whether to use -i or -hi depends on its pronunciation, which is very confusing even to natives.[1]
The conjugation for this suffix is similar to the infinite form, but not the same. Especially, the p-irregular adjectives (ㅂ 불규칙 용언) take 이 (i) not 위 (wi); for instance, 가깝다 (gakkapda, “near”) → 가까이 (gakkai, “nearly”).
Also, note that only a limited number of adverbs are frequently used which are formed by affixing -i or -hi.
Etymology 8
Of native Korean origin.
Suffix
—이 • (-i)
- (after the stem of the sequential form of an adjective) one of the familiar style declarative endings.
Etymology 9
From First attested in the 번역박통사 (beonyeokbaktongsa) 飜譯朴通事/飜译朴通事, before 1517, as Middle Korean ᅀᅵ (). [1]
Usage notes
- Used primarily with Sino-Korean count words, or in reading numbers literally. In modern Korean, numbers are almost always written in Arabic numerals.
- 이 means “second” if it is directly put before a noun other than modern units.
- 이 층 ― i cheung ― second floor
- 두 층 ― du cheung ― two floors
- 이 팀 ― i tim ― Team 2
- 두 팀 ― du tim ― two teams
Synonyms
- 둘 (dul) (native Korean)
References
- ᄉᆞ이 ᄠᅮ미 ᅀᅵ십 릿 ᄯᅡ히니 (sᆞi ᄠumi ᅀisip rit ᄯahini) from 번역박통사 (beonyeokbaktongsa) 1517, 상:11
Etymology 10
Korean reading of various Chinese characters.
Syllable
이 (i)
| Extended content |
|---|
|
Etymology 11
Sino-Korean word from 李
Proper noun
(South Korea) 이 • (I) (hanja 李), due to 두음 법칙 (頭音法則, dueum beopchik)
- (South Korea) A surname, the second most common surname in South Korea.
Alternative forms
(North Korea) 李 (lǐ) 리 (ri)
Usage notes
Etymology 12
Sino-Korean word from 理
Noun
이 • (i) (hanja 理)
- (South Korea) to govern (South Korea Spelling, due to 두음 법칙 (頭音法則, dueum beopchik))
Alternative forms
- (North Korea) 리 (ri) to govern
Derived terms
Etymology 13
South Korean reading of various Chinese characters, originally 리 (ri).
Syllable
이 (i)
Alternative forms
- (North Korea) 리 (ri)
Usage notes
In South Korea, the original Sino-Korean reading 리 (ri) is used if the hanja is not part of the first syllable of a Sino-Korean compound word. The change in reading and family name spelling from 리 (ri) to 이 (i) is known as 두음 법칙 (頭音法則, dueum beopchik).
Etymology 14
First attested in the Seokbo sangjeol (釋譜詳節 / 석보상절), 1447, as Middle Korean 니 (ni). [1]
Noun
이 • (i)
Alternative forms
- (South Korea) 니 (ni) (now suffixal due to 두음 법칙 (頭音法則, dueum beopchik))
Derived terms
- (South Korea) 덧니 (deonni, “snaggletooth/teeth”)
- (North Korea) 덧이 (deosi, “snaggletooth/teeth”)
- (South Korea) 송곳니 (songgonni, “canine tooth/teeth”)
- (North Korea) 송곳이 (songgosi, “canine tooth/teeth”)
- (South Korea) 아랫니 (araenni, “lower tooth/teeth”)
- (North Korea) 아래이 (araei, “lower tooth/teeth”)
- (South Korea) 앞니 (amni, “incisor(s)”)
- (North Korea) 앞이 (api, “incisor(s)”)
- (South Korea) 윗니 (winni, “upper tooth/teeth”)
- (North Korea) 웃이 (usi, “upper tooth/teeth”)
- (South Korea) 어금니 (eogeumni, “molar(s)”)
- (North Korea) 어금이,엄이 (eogeumi,eomi, “molar(s)”)
References
- 齒ᄂᆞᆫ 니라 (齒nᆞn nira ), 훈민정음(언해본) (hunminjeong-eum(eonhaebon)), 1447.
Derived terms
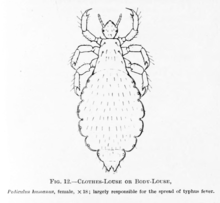
- 거웃니 (geounni, “pubic louse”)
- 닭니 (dangni, “bird louse”)
- 머릿니 (meorinni, “head louse”)
- 사면발니 (samyeonballi, “crab louse”)
- 옷엣니 (osenni, “body louse”)
Etymology 16
South Korean reading of various Chinese characters, originally 니 (ni).
Syllable
이 (i)
- (South Korea) 泥: mud
- (South Korea) 尼: Buddhist nun
- (South Korea) 柅: overgrown
- (South Korea) 濔: lots of
- (South Korea) 膩: greasy
- (South Korea) 馜: strong fragrance
- (South Korea) 㦐: feel good
- (South Korea) 呢: whisper
- (South Korea) 怩: ashamed
- (South Korea) 祢: Father's Shrine
Alternative forms
- (North Korea) 니 (ni)
Usage notes
In South Korea, the original Sino-Korean reading 니 (ni) is used if the hanja is not part of the first syllable of a Sino-Korean compound word. The change in reading and family name spelling from 니 (ni) to 이 (i) is known as 두음 법칙 (頭音法則, dueum beopchik).
References
- Supreme Court of the Republic of Korea (대한민국 대법원, Daehanmin-guk daebeobwon) (2015). Table of Hanja for Personal Names (인명용한자표, inmyeong-yonghanjapyo).