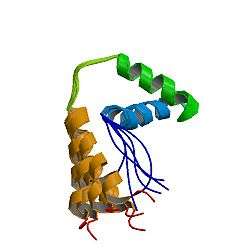
SOX6
Transcription factor SOX-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX6 gene.[5][6]
Function
The SOX gene family encodes a group of transcription factors defined by the conserved high mobility group (HMG) DNA-binding domain. Unlike most transcription factors, SOX transcription factors bind to the minor groove of DNA, causing a 70- to 85-degree bend and introducing local conformational changes.[supplied by OMIM][6]
Interactions
SOX6 has been shown to interact with CTBP2[7] and CENPK.[8]
It has also been demonstrated that SOX6 protein accumulates in the differentiating human erythrocytes, and then is able to downregulate its own transcription, by directly binding to an evolutionarily conserved consensus sequences located near SOX6 transcriptional start site.[9]
Sox6 appears to have a crucial role in the transcriptional regulation of globin genes, and in directing the terminal differentiation of red blood cells.[10] In addition, SOX6 may have a role in tumor growth of Ewing sarcoma.[11] A new role of Sox6 in renin and prorenin regulation was studied using a Sox KO mouse model in which Sox6 is only knockout in renin expressing cells. This study showed that renin promoter possesses the binding site for Sox6. The highlight of the study was that Sox6 is one of the key regulators of renin and prorenin regulation and JG cell expansion during low salt and dehydration in mice. PMID: 31760770; DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00095.2019
See also
- SOX genes
References
{{}}
Further reading
- Denny P, Swift S, Brand N, Dabhade N, Barton P, Ashworth A (June 1992). "A conserved family of genes related to the testis determining gene, SRY". Nucleic Acids Research. 20 (11): 2887. doi:10.1093/nar/20.11.2887. PMC 336939. PMID 1614875.
- Lefebvre V, Li P, de Crombrugghe B (October 1998). "A new long form of Sox5 (L-Sox5), Sox6 and Sox9 are coexpressed in chondrogenesis and cooperatively activate the type II collagen gene". The EMBO Journal. 17 (19): 5718–33. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.19.5718. PMC 1170900. PMID 9755172.
- Hagiwara N, Klewer SE, Samson RA, Erickson DT, Lyon MF, Brilliant MH (April 2000). "Sox6 is a candidate gene for p100H myopathy, heart block, and sudden neonatal death". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (8): 4180–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.8.4180. PMC 18189. PMID 10760285.
- Yamashita A, Ito M, Takamatsu N, Shiba T (September 2000). "Characterization of Solt, a novel SoxLZ/Sox6 binding protein expressed in adult mouse testis". FEBS Letters. 481 (2): 147–51. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01987-6. PMID 10996314.
- Hartley JL, Temple GF, Brasch MA (November 2000). "DNA cloning using in vitro site-specific recombination". Genome Research. 10 (11): 1788–95. doi:10.1101/gr.143000. PMC 310948. PMID 11076863.
- Wiemann S, Weil B, Wellenreuther R, Gassenhuber J, Glassl S, Ansorge W, et al. (March 2001). "Toward a catalog of human genes and proteins: sequencing and analysis of 500 novel complete protein coding human cDNAs". Genome Research. 11 (3): 422–35. doi:10.1101/gr.GR1547R. PMC 311072. PMID 11230166.
- Murakami A, Ishida S, Thurlow J, Revest JM, Dickson C (August 2001). "SOX6 binds CtBP2 to repress transcription from the Fgf-3 promoter". Nucleic Acids Research. 29 (16): 3347–55. doi:10.1093/nar/29.16.3347. PMC 55854. PMID 11504872.
- Cohen-Barak O, Yi Z, Hagiwara N, Monzen K, Komuro I, Brilliant MH (October 2003). "Sox6 regulation of cardiac myocyte development". Nucleic Acids Research. 31 (20): 5941–8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg807. PMC 219484. PMID 14530442.
- Wiemann S, Arlt D, Huber W, Wellenreuther R, Schleeger S, Mehrle A, et al. (October 2004). "From ORFeome to biology: a functional genomics pipeline". Genome Research. 14 (10B): 2136–44. doi:10.1101/gr.2576704. PMC 528930. PMID 15489336.
- Ueda R, Yoshida K, Kawakami Y, Kawase T, Toda M (2005). "Expression of a transcriptional factor, SOX6, in human gliomas". Brain Tumor Pathology. 21 (1): 35–8. doi:10.1007/BF02482175. PMID 15696967.
- Ueda R, Yoshida K, Kawakami Y, Kawase T, Toda M (2005). "Immunohistochemical analysis of SOX6 expression in human brain tumors". Brain Tumor Pathology. 21 (3): 117–20. doi:10.1007/BF02482186. PMID 15696972.
- Mehrle A, Rosenfelder H, Schupp I, del Val C, Arlt D, Hahne F, et al. (January 2006). "The LIFEdb database in 2006". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (Database issue): D415-8. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj139. PMC 1347501. PMID 16381901.
- Fernández-Lloris R, Osses N, Jaffray E, Shen LN, Vaughan OA, Girwood D, et al. (February 2006). "Repression of SOX6 transcriptional activity by SUMO modification". FEBS Letters. 580 (5): 1215–21. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.01.031. PMID 16442531.
- Ikeda T, Saito T, Ushita M, Yano F, Kan A, Itaka K, et al. (June 2007). "Identification and characterization of the human SOX6 promoter". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 357 (2): 383–90. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.03.133. PMID 17433257.
External links
- SOX6+protein,+human at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000110693 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000051910 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Cohen-Barak O, Hagiwara N, Arlt MF, Horton JP, Brilliant MH (March 2001). "Cloning, characterization and chromosome mapping of the human SOX6 gene". Gene. 265 (1–2): 157–64. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00346-8. PMID 11255018.
- "Entrez Gene: SOX6 SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 6".
- Murakami A, Ishida S, Thurlow J, Revest JM, Dickson C (August 2001). "SOX6 binds CtBP2 to repress transcription from the Fgf-3 promoter". Nucleic Acids Research. 29 (16): 3347–55. doi:10.1093/nar/29.16.3347. PMC 55854. PMID 11504872.
- Yamashita A, Ito M, Takamatsu N, Shiba T (September 2000). "Characterization of Solt, a novel SoxLZ/Sox6 binding protein expressed in adult mouse testis". FEBS Letters. 481 (2): 147–51. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01987-6. PMID 10996314.
- Cantu' C, Grande V, Alborelli I, Cassinelli L, Cantu' I, Colzani MT, et al. (January 2011). "A highly conserved SOX6 double binding site mediates SOX6 gene downregulation in erythroid cells". Nucleic Acids Research. 39 (2): 486–501. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq819. PMC 3025548. PMID 20852263.
- Cantù C, Ierardi R, Alborelli I, Fugazza C, Cassinelli L, Piconese S, et al. (March 2011). "Sox6 enhances erythroid differentiation in human erythroid progenitors". Blood. 117 (13): 3669–79. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-282350. PMID 21263153.
- Marchetto, Aruna; Ohmura, Shunya; Orth, Martin F.; Knott, Maximilian M. L.; Colombo, Maria V.; Arrigoni, Chiara; Bardinet, Victor; Saucier, David; Wehweck, Fabienne S.; Li, Jing; Stein, Stefanie (2020-05-15). "Oncogenic hijacking of a developmental transcription factor evokes vulnerability toward oxidative stress in Ewing sarcoma". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-16244-2. ISSN 2041-1723.