DESOXY
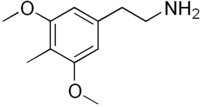
4-Desoxymescaline, or 4-methyl-3,5-dimethoxyphenethylamine, is a mescaline analogue related to other psychedelic phenethylamines. It is commonly referred to as DESOXY. DESOXY was discovered by Alexander Shulgin and published in his book PiHKAL.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-4-methyl-phenyl)-ethylamine | |
| Other names
3,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylphenethylamine 2-(3,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylphenyl)ethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H17NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 195.26 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Effects
The effects of DESOXY vary significantly from mescaline, despite their chemical similarity.
Dosage
A typical dosage is within the range of 40–120 mg and lasts 6–8 hours.[1]
Legality
In 1970 the Controlled Substances Act placed mescaline into Schedule I in the United States. It is similarly controlled in other nations. Depending on whether or not it is intended for human consumption, 4-desoxymescaline could be considered an analogue of mescaline, under the Federal Analogue Act and similar bills in other countries, making it illegal to manufacture, buy, possess, or distribute without a DEA or related license.
DESOXY is also an isomer of 2C-D which would cause it to fall within the definitions outlined by the Federal Analogue Act
References
- Shulgin, Alexander; Ann Shulgin (September 1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story. Berkeley, California: Transform Press. ISBN 0-9630096-0-5. OCLC 25627628.
External links
- Alexander Shulgin, Jacob, P. Structure-Activity Relationships of the Classic Hallucinogens and Their Analogs. NIDA Research Monograph 146 (Hallucinogens: An Update), 1994.
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
Drugs described in PiHKAL | |
|---|---|
|