Metaescaline
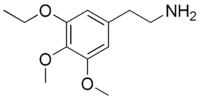
Metaescaline (3,4-dimethoxy-5-ethoxyphenethylamine) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug. It is an analog of mescaline. Metaescaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL, the dosage range is listed as 200–350 mg, and the duration listed as 8–12 hours.[1] Metaescaline produces mental insights, entactogenic, MDMA-like effects, and TOMSO-like activation. Little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of metaescaline, though it has been studied to a limited extent in comparison with other related compounds.[2][3][4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3-Ethoxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethanamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H19NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 225.288 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
- Substituted phenethylamine
- Phenethylamine
- Psychedelics, dissociatives and deliriants
References
- Metaescaline entry in PiHKAL
- Jacob P 3rd, Shulgin AT. Sulfur analogues of psychotomimetic agents. 3. Ethyl homologues of mescaline and their monothio analogues. J Med Chem. 1984 Jul;27(7):881-8. PMID 6737431 doi:10.1021/jm00373a013
- Clare BW. Structure-activity correlations for psychotomimetics. 1. Phenylalkylamines: electronic, volume, and hydrophobicity parameters. J Med Chem. 1990 Feb;33(2):687-702. PMID 2299636 doi:10.1021/jm00164a036
- Clare BW. The frontier orbital phase angles: novel QSAR descriptors for benzene derivatives, applied to phenylalkylamine hallucinogens. J Med Chem. 1998 Sep 24;41(20):3845-56. PMID 9748359 doi:10.1021/jm980144c
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.