Banja Luka
| Banja Luka Бања Лука | ||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||
  Counter-clockwise from top: Panoramic view of Banja Luka, Cathedral of Christ the Saviour, Kastel Fortress on the left bank of the Vrbas River | ||
| ||
 Location of Banja Luka (municipality) within Republika Srpska | ||
 Banja Luka Location of Banja Luka (city) | ||
| Coordinates: 44°46′N 17°11′E / 44.767°N 17.183°ECoordinates: 44°46′N 17°11′E / 44.767°N 17.183°E | ||
| Country | Bosnia and Herzegovina | |
| Entity | Republika Srpska | |
| Geographical region | Krajina | |
| Government | ||
| • Mayor | Igor Radojičić (SNSD) | |
| Area | ||
| • City | 1,238.91 km2 (478.35 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 163 m (535 ft) | |
| Population (2013 census)[1] | ||
| • City | 185,042 | |
| • Urban | 150,997 | |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) | |
| Postal code | 78000 | |
| Area code(s) | +387 51 | |
| Website |
www | |
Banja Luka (Serbian Cyrillic: Бања Лука; pronounced [bǎɲa lǔːka]) or Banjaluka (Serbian Cyrillic: Бањалука), is the second largest city of Bosnia and Herzegovina and the de facto capital of the Republika Srpska entity. Traditionally, it has been the centre of the Bosanska Krajina region, located in the northwestern part of the country. According to the 2013 census, Banja Luka has 185,042 inhabitants.
It is home of the University of Banja Luka as well as numerous state and entity institutions of Bosnia and Herzegovina. The city lies on the river Vrbas and is well known in the countries of the former Yugoslavia for being full of tree-lined avenues, boulevards, gardens and parks.[2]
Name
The name "Banja Luka" was first mentioned in a document dated 6 February 1494, by Vladislav II. The name is interpreted as "Ban's meadow", from the words ban ("a medieval dignitary"), and luka ("a valley" or "a meadow"). The identity of the ban and the meadow in question remain uncertain, and popular etymology combines the modern words banja ("bath" or "spa"), or bajna ("marvelous") and luka ("port"). A different interpretation is suggested by the Hungarian name "Lukácsbánya", i.e. "Luke's Mine", which is also the meaning of Slovak "Banja Luka". In modern usage, the name is pronounced and usually declined (u Banjaluci) as one word, and often written as such; the citizens reportedly prefer the form with inflected adjective (u Banjoj Luci).[3]
Geography
Overview

Banja Luka covers some 96.2 km2 (37.1 sq mi) of land in Bosnia and Herzegovina, on the Vrbas River. The city is located at 44°47′N 17°11′E / 44.78°N 17.19°E. Banja Luka's downtown is at 163 m (534.78 ft) above sea level, surrounded by hills.
The source of the Vrbas River is about 90 km (56 mi) to the south. The tributary rivers Suturlija, Crkvena, and Vrbanja flow into the Vrbas at Banja Luka. Banja Luka has also a number of springs close by.
The area around Banja Luka is mostly woodland, although there are mountains a little further from the city. The city itself is built in the Banja Luka valley, which is located at the transition between high and low mountain areas. The most notable of these mountains are Manjača (1,214 m), Čemernica (1,338 m), and Tisovac. These are all part of the Dinaric Alps mountain range.
Settlements
The city of Banja Luka (aside from city proper) comprises the following settlements:
- Agino Selo
- Barlovci
- Bastasi
- Bistrica
- Bočac
- Borkovići
- Bronzani Majdan
- Cerici
- Čokori
- Debeljaci
- Dobrnja
- Dragočaj
- Drakulić
- Dujakovci
- Goleši
- Jagare
- Kmećani
- Kola
- Kola Donja
- Krmine
- Krupa na Vrbasu
- Kuljani
- Lokvari
- Lusići
- Ljubačevo
- Melina
- Motike
- Obrovac
- Pavići
- Pavlovac
- Pervan Donji
- Pervan Gornji
- Piskavica
- Ponir
- Potkozarje
- Prijakovci
- Priječani
- Prnjavor Mali
- Radmanići
- Radosavska
- Ramići
- Rekavice
- Slavićka
- Stratinska
- Stričići
- Subotica
- Šargovac
- Šimići
- Šljivno
- Verići
- Vilusi
- Zalužani
- Zelenci
Climate
Banja Luka has a moderate humid subtropical climate with mild winters with frequent frosts and warm summers. The warmest month of the year is July, with an average temperature of 22.8 °C (73.0 °F). The coldest month of the year is January, when temperatures average near freezing at 1.7 °C (35.1 °F).
Annual precipitation for Banja Luka (is about 1,037.2 millimetres (41 inches). Banja Luka has an average of 104 rainy days a year. Due to the city's latitude, it snows in Banja Luka almost every year. Strong winds come from the north and northeast. Sometimes southern winds which bring hot weather are also prevalent.
| Climate data for Banja Luka | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.3 (72.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.0 (84.2) |
31.8 (89.2) |
35.2 (95.4) |
37.9 (100.2) |
41.6 (106.9) |
41.1 (106) |
40.2 (104.4) |
30.9 (87.6) |
27.1 (80.8) |
23.2 (73.8) |
41.6 (106.9) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) |
7.8 (46) |
13.7 (56.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
23.2 (73.8) |
27.3 (81.1) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.1 (86.2) |
24.3 (75.7) |
18.5 (65.3) |
13.0 (55.4) |
7.2 (45) |
18.4 (65.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 1.7 (35.1) |
2.5 (36.5) |
7.3 (45.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
16.8 (62.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.8 (73) |
22.3 (72.1) |
17.1 (62.8) |
11.8 (53.2) |
7.3 (45.1) |
2.8 (37) |
12.1 (53.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.1 (28.2) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
1.8 (35.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
10.0 (50) |
14.4 (57.9) |
16.0 (60.8) |
15.6 (60.1) |
11.4 (52.5) |
7.0 (44.6) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −22.8 (−9) |
−21.5 (−6.7) |
−18.2 (−0.8) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
0.0 (32) |
4.0 (39.2) |
6.7 (44.1) |
6.1 (43) |
0.0 (32) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−18.0 (−0.4) |
−22.8 (−9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 71.7 (2.823) |
67.6 (2.661) |
77.8 (3.063) |
86.5 (3.406) |
98.3 (3.87) |
109.2 (4.299) |
73.9 (2.909) |
74.2 (2.921) |
83.9 (3.303) |
103.9 (4.091) |
89.5 (3.524) |
100.8 (3.969) |
1,037.2 (40.835) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 8.9 | 9.7 | 9.4 | 9.2 | 9.8 | 8.1 | 7.9 | 5.8 | 7.9 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 10.2 | 104.0 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 80 | 73 | 69 | 71 | 71 | 70 | 73 | 78 | 82 | 84 | 83 | 76 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 54 | 71 | 125 | 158 | 206 | 222 | 272 | 238 | 186 | 133 | 70 | 46 | 1,781 |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst (temperatures, 1992–2016, extremes 1973–2016, precipitation, 1926–2016, precipitation days, 1992–2016, humidity, 1973–1991 and sun, 1961–1990)[4][5][lower-alpha 1] | |||||||||||||
History
Roman times
The history of inhabitation of the area of Banja Luka dates back to ancient times. There is a substantial evidence of the Roman presence in the region during the first few centuries A.D., including an old fort "Kastel" (Latin: Castra) in the centre of the city. The area of Banja Luka was entirely in the kingdom of Illyria and then a part of the Roman province of Illyricum, which split into provinces of Pannonia and Dalmatia of which Castra became a part. Ancient Illyrian maps call the settlement in Banja Luka's present day location as Ad Ladios,[6] a settlement located on the river Vrbas.
Middle Ages
Slavs settled in the Balkans in the 6th century. Medieval fortresses in the vicinity of Banja Luka include Vrbas (1224), župa Zemljanik (1287), Kotor Varoš (1323), Zvečaj (1404), and Bočac (1446). The name "Banja Luka" was first mentioned in a document dated 6 February 1494, by Vladislav II.
Ottoman rule
Banja Luka fell to the Ottomans in 1527. It became the seat of the Sanjak of Bosnia some time prior to 1554, until 1580 when the Bosnia Eyalet was established. Bosnian beylerbeys were seated in Banja Luka until 1639.[7] Ferhad Pasha Sokolović, a relative of Grand Vizier Mehmed-pasha Sokolović, had upon his return to Bosnia in 1574, begun the building of over 200 buildings ranging from artisan and sales shops to wheat warehouses, baths and mosques. Among more important commissions were the Ferhadija and Arnaudija mosques during which construction a plumbing infrastructure was laid that served surrounding residential areas.[8] This stimulated the economic and urban development of Banja Luka, which soon became one of the leading commercial and political centres in Bosnia. It was also sanjak centre in Bosna Eyalet. In 1688, the city was burned down by the Austrian army, but it quickly recovered. Later periodic intrusions by the Austrian army stimulated military developments in Banja Luka, which made it into a strategic military centre. Orthodox churches and monasteries near Banja Luka were built in the 19th century. Also, Sephardic Jews and Trappists migrated to the city in the 19th century and contributed to the early industrialisation of the region by building mills, breweries, brick factories, textile factories and other important structures.
The Trappist monastery built in the 19th century lent its name to the neighbourhood of Trapisti and has left a large legacy in the area through its famous Trappist cheese and its beer production.
In 1835 and 1836, during the Ottoman administration, numerous people from the Banja Luka Krajina emigrated to Lešnica, Lipnica and Loznica, the villages around Loznica, and to Šabac.[9]
Austro-Hungarian rule
.jpg)
For all its leadership to the region however, Banja Luka as a city was not modernised until Austro-Hungarian occupation in the late 19th century that brought westernisation to Banja Luka. Railroads, schools, factories, and infrastructure appeared, and were developed, which led to a modern city
Yugoslavia
After World War I, the town became the capital of the Vrbas Banovina, a province of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. The provincial capital owed its rapid progress to the first Ban Svetislav Milosavljević. During that time, the Banski dvor and its twin sister, the Administration building, the Serbian Orthodox Church of the Holy Trinity, a theatre and a museum were built, the Grammar School was renovated, the Teachers College enlarged, a city bridge was also built and the park renovated. 125 elementary schools were functioning in Banja Luka in 1930. The revolutionary ideas of the time were incubated by the "Pelagić" association and the Students' Club. Banja Luka naturally became the organisational centre of anti-fascist work in the region.
World War II
During World War II, Banja Luka was part of the Independent State of Croatia. Most of Banja Luka's Serbs and Jews were deported to concentration camps such as Jasenovac and Stara Gradiška. On 7 February 1942, Ustaše paramilitaries, led by a Franciscan monk, Miroslav Filipović (aka Tomislav Filipović-Majstorović), killed more than 2,300 Serbs (among them 500 children)[10] in Drakulić, Motike and Šargovac (a part of the Banja Luka municipality).
The city's Orthodox church of the Holy Trinity was totally demolished by the Ustaše, as was the Church of St. George in Petrićevac. The Bishop of Banja Luka, Platon Jovanović, was arrested by the Ustaše on 5 May 1941, and was tortured and killed. His body was thrown into the Vrbanja river.[11] The city was liberated by the Yugoslav Partisans on 22 April 1945.
1969 earthquake
On 26 and 27 October 1969, two devastating earthquakes (6.0 and 6.4 on the Richter scale) damaged many buildings in Banja Luka. Around 20 to 23 people were killed, and over a thousand injured.[12] A large building called Titanik in the centre of the town was razed to the ground, and the area was later turned into a central public square. With contributions from all over Yugoslavia, Banja Luka was repaired and rebuilt. That was a period when a large Serb population moved to the city from the surrounding villages, and from more distant areas in Herzegovina.
Bosnian War
During the 1990s, the city underwent considerable changes when the Bosnian War broke out. Upon the declaration of Bosnian-Herzegovinian independence and the establishment of the Republika Srpska, Banja Luka became the de facto centre of the entity's politics.

Nearly all of Banja Luka's Croats and Bosniaks were expelled during the war and all of the city's 16 mosques including the Ferhat Pasha Mosque were destroyed.[13] A court ruling resulted in the authorities of Banja Luka having to pay $42 million for the destruction of the mosques.[13] [14] Later, an estimated 40,000 Serbs from Croat- and Bosniak-dominated areas of Bosnia, having been exiled from their homes, settled in Banja Luka.[15] However, the Banja Luka district court later overturned the ruling stating that the claims had exceeded a three-year statute of limitations.[16] The Bosniak community vowed to appeal against the decision.[17]
On 7 May 2001, several thousand Serb nationalists attacked a group of Bosniaks and members of the diplomatic corps attending a ceremony of marking the reconstruction of the historic 16th-century Ferhadija mosque.[18][19][20][21] There were indications of police collaboration.[22] More than 30 individuals were injured during the attack, and on 26 May, Murat Badić, who had been in a coma after the attack, died from head injuries.[23] Fourteen Bosnian Serb nationalists were jailed for starting the riots.[24]
Demographics
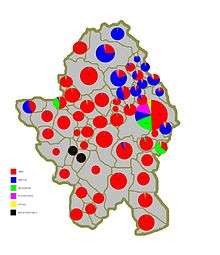
The 2013 census in Bosnia indicated a population of 185,042, overwhelmingly Serbs.[25][26] During the war from 1992-95 some 60,000 people, mostly Bosniaks and Croats, left Banja Luka.[27]
Ethnic composition
| Ethnicity | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Serbs | 165,750 | 89.57% |
| Bosniaks | 7,681 | 4.15% |
| Croats | 5,104 | 2.76% |
| Others | 6,507 | 3.52% |
| Total | 185,042 | 100% |
Religious composition
| Religion | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Serbian Orthodox Church | 168,985 | 90.25% |
| Islam | 10,526 | 4.07% |
| Roman Catholic Church | 4,842 | 2.62% |
| Agnostic | 412 | 0.22% |
| Atheist | 855 | 0,45% |
| Others | 4,422 | 2.32% |
| Total | 190042 | 100% |
| Census of the municipality of Banja Luka | ||||||
| year of census | 2013 | 1991 | 1981 | 1971 | ||
| Serbs | 165,750 (89.57%) | 106,826 (54.61%) | 93,389 (50.86%) | 92,465 (58.25%) | ||
| Croats | 5,104 (2.75%) | 29,026 (14.83%) | 30,442 (16.57%) | 33,371 (21.02%) | ||
| Bosniaks | 7,681 (4.15%) | 28,558 (14.59%) | 21,726 (11.83%) | 24,268 (15.28%) | ||
| Yugoslavs | 0.00 (0.00%) | 23,656 (12.08%) | 31,347 (17.07%) | 4,684 (2.95%) | ||
| others | 3,437 (1.85%) | 7,626 (3.89%) | 6,714 (3.65%) | 3,948 (2.48%) | ||
| total | 185,042 | 195,692 | 183,618 | 158,736 | ||
| City of Banja Luka | ||||||
| year of census | 1991 | 1981 | 1971 | 1879 | ||
| Serbs | 70,155 (49.03%) | 51,839 (41.82%) | 41,297 (45.46%) | 1,893 (19.8%) | ||
| Bosniaks | 27,689 (19.35%) | 20,916 (16.87%) | 23,411 (25.77%) | 6,474 (67.7%) | ||
| Croats | 15,700 (10.97%) | 16,314 (13.16%) | 17,897 (19.70%) | 1,006 (10.5%) | ||
| Yugoslavs | 22,645 (15.82%) | 30,318 (24.46%) | 4,606 (5.07%) | |||
| others | 6,890 (4.81%) | 4,550 (3.67%) | 3,620 (3.98%) | 187 (2%) | ||
| total | 143,079 | 123,937 | 90,831 | 9,560 | ||
Government

Banja Luka plays an important role on different levels of Bosnia and Herzegovina's government structures. Banja Luka is the centre of the government for the Municipality of Banja Luka. A number of entity and state institutions are seated in the city. The Republika Srpska Government and the National Assembly are based in Banja Luka.
The Bosnia and Herzegovina State Agencies based in the city include the Indirect Taxation (VAT) Authority, the Deposit Insurance Agency as well as a branch of the Central Bank of Bosnia and Herzegovina (formerly the National Bank of Republika Srpska). Austria, Croatia, France, Germany, Serbia, the United Kingdom and the United States maintain diplomatic representation through consulates-general in Banja Luka.
Economy
Although the city itself was not directly affected by the Bosnian war in the early 1990s, its economy was. For four years, Banja Luka fell behind the world in key areas such as technology, resulting in a rather stagnant economy. However, in recent years, the financial services sector has gained in importance in the city. In 2002, the trading began on the newly established Banja Luka Stock Exchange. The number of companies listed, the trading volume and the number of investors have increased significantly. A number of big companies such as Telekom Srpske, Rafinerija ulja Modriča, Banjalučka Pivara and Vitaminka are all listed on the exchange and are traded regularly. Investors, apart from those from Slovenia, Croatia and Serbia, now include a number of investment funds from the EU, and from Norway, the United States, Japan and China.
A number of financial services regulators, such as the Republika Srpska Securities Commission and the RS Banking Agency are headquartered in Banja Luka. This, along with the fact that some of the major banks in Bosnia, the Deposit Insurance Agency and the value-added tax (VAT) authority are all based in the city, has helped Banja Luka establish itself as a major financial centre of the country. In 1981 Banja Luka's GDP per capita was 97% of the Yugoslav average.[29]
Culture

The Museum of Republika Srpska inherited the Ethnographic Museum established in 1930, and broadened its setting with collections of archeology, history, art history and nature. The Museum of Modern Art of Republika Srpska, also called MSURS, the Museum of Contemporary Art, displays exhibitions of both domestic and worldwide artists.
Banja Luka is home to the National Theatre and National Library, both dating from the first half of the 20th century, and of numerous other theatres. The headquarters of the Archives of Republika Srpska is situated in the building known as Carska kuća or Imperial House, built around 1880. It has been in continuous public use longer than any other structure in Banja Luka.

One of the most famous cultural sites in Banja Luka is the cultural centre of "Banski Dvor" (Halls of the Ban), built in the 1930s as the residence for the Bans of the Vrbas Banovina.
In the city there are many Cultural Artistic Associations. The oldest is CAA "Pelagić" (founded 1927), one of the oldest institutions of this kind in Bosnia and Herzegovina.[30]
Sport

Banja Luka has one major football stadium and several indoor sports halls. The local handball, basketball and football teams bear the traditional name Borac (fighter). The three football teams from Banja Luka are Borac Banja Luka (2010/2011 season champions of Premier League of Bosnia and Herzegovina), BSK Banja Luka, and Omladinac Banja Luka (both in the First League of the Republika Srpska), FK Naprijed Banja Luka and FK Vrbas Banja Luka
Borac Banja Luka is the most popular football club in the Republika Srpska. The club has won several major trophies in its history such as trophies as a champion of Mitropa Cup, Yugoslav Cup, Premier League of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia and Herzegovina Football Cup, First League of the Republika Srpska, Republic Srpska Cup. They have participated in UEFA Champions League and UEFA Europa League.
The city has a long tradition of handball. RK Borac Banjaluka was the European Champion in 1976, the European Vice-Champion in 1975 and the winner of the IHF Cup in 1991.
Recently, tennis has taken on a bigger role in the city. The local tennis tournament, "Memorijal Trive Vujića", has become professional and has been awarded ATP status in 2001, with the rank of a Challenger. The Banja Luka Challenger takes place in September each year. In 2005, the European Championships in Rafting were held on the Vrbas river. In 2006, the Davis Cup matches of the Europe/Africa Zone Group III took place in the city. Since 2015, the city hosts the Banjaluka Half-marathon.
Transportation

.jpg)

Public transportation within Banja Luka is exclusively operated by the bus services. Over thirty bus lines connect downtown with the rest of the city and its suburbs. The oldest bus link in the city is line No 1. Taxis are also readily available. The expressway E-661 (locally known as M-16) leads north to Croatia from Banja Luka by way of Gradiška, near the Bosnian/Croatian border. A wide range of bus services are available to most neighbouring and larger towns in Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as to regional and European destinations such as Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Germany, France, Italy, Montenegro, The Netherlands, Serbia, Sweden, Switzerland and Slovakia.
Banja Luka is the hub of the railway services of Željeznice Republike Srpske, comprising one half of the railway network of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Services operate to most northern Bosnian towns, and two modern air-conditioned 'Talgo' trains run to Sarajevo every day. However, services are relatively slow and infrequent compared with neighbouring countries.
Banja Luka International Airport (IATA: BNX, ICAO: LQBK) is located 23 km (14 mi) north of Banja Luka. The airport is served by Air Serbia, which operates daily flights to Belgrade. There is also Banja Luka Zalužani Airfield, a small airstrip. Ryanair has announced first flights from Bosnia and Herzegovina, including Banja Luka, to Brussels, Memmingen and Stockholm, starting from the end of October 2018. [31]
International relations
Twin towns – Sister cities
Banja Luka twinned with the following cities:[32]
People
- Petar Kočić, Bosnian novelist
- Ivan Franjo Jukić, Bosnian writer
- Marijan Beneš, boxer and poet, European amateur champion
- Anton Josipović, boxer, Olympic champion
- Ivan Merz, Catholic lay academic; beatified by Pope John Paul II
- Tomislav Knez, football player, Olympic champion and European Championship silver medalist
- Velimir Sombolac, football player and manager, Olympic champion
- Nikola Pejaković, Serbian actor and musician
- Anton Josipović, boxer, Olympic champion
- Mustafa Nadarević, actor
- Franjo Komarica, Roman Catholic Bishop of Banja Luka
- Slađana Golić, basketball player, Olympic and World Championships silver medalist
- Neven Subotić, Serbian footballer
- Muhamed Filipović, Bosnian philosopher, historian and writer
- Nasiha Kapidžić-Hadžić, Bosnian writer and poet
- Milorad Dodik, President of Republika Srpska
- Milorad Karalić, handball player, Olympic champion
- Ivan Ljubičić, Croatian tennis player, World No. 3 and Olympic bronze medalist
- Nela Eržišnik, actress and comedian
- Saša Lošić, Bosnian singer and composer
- Marija Šestić, Bosnian singer
- Romana Panić, singer
- Božidar Jović, handball player
- Abid Kovačević, retired footballer
- Nikola Pejaković, actor
- Mladen Bojinović, Serbian handball player, World Championship bronze medalist
- Aleksandar Knežević, Serbian handball player, European Championship bronze medalist
- Osman Karabegović, politician
- Zlatko Saračević, Croatian handball player, Olympic and World champion
- Draženko Mitrović, Serbian athlete, two-time Paralympic silver medalist and European champion
- Ognjen Vranješ, Bosnian footballer
- Saša Čađo, Serbian basketball player, Olympic bronze medalist and European champion
- Srđan Babić, Serbian footballer, World U-20 champion
- Srđan Grahovac, footballer
- Darko Maletić, footballer
- Nikola Čačić, Serbian tennis player
- Srđan Vujmilović, photographer
Gallery
- Monument of Petar Kočić
 Krajina Square
Krajina Square Banski dvor
Banski dvor

 Kastel fortress
Kastel fortress Petar Kočić park
Petar Kočić park Manjača Lake
Manjača Lake Vrbas River
Vrbas River.jpg)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Banja Luka. |
Footnotes and references
Footnotes
- ↑ Station ID for Banja Luka is 14542 Use this station ID to locate the sunshine duration
References
- ↑ Preliminary Results of the 2013 Census of Population, Households and Dwellings in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Sarajevo. 5 November 2013. Retrieved 5 November 2013
- ↑ "АСБЛ >> General information". www.banjaluka.rs.ba.
- ↑ Ivan Lovrenović, " ‘Serb’ towns in Bosnia", BH Dani, 20 July 2001
- ↑ "Klimatafel von Banja Luka/Bosnien und Herzegowina" (PDF). Baseline climate means (1961-1990) from stations all over the world (in German). Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ↑ "Station 14542 Banja Luka". Global station data 1961–1990—Sunshine Duration. Deutscher Wetterdienst. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ↑ "Ad Ladios: a Pleiades place resource". Pleiades: a gazetteer of past places.
- ↑ Društvo istoričara Bosne i Hercegovine (1952). Godišnjak: Annuaire.
Бања Лука је постала сједиште босанског санџака нешто прије 1554 и остала то све до 1580 када је основан босански пашалук. У Бањој Луци су столовали и босански беглербези све до године 1639.
- ↑ Kolovos, Elias (2007). The Ottoman Empire, the Balkans, the Greek lands: toward a social and economic history: studies in honor of John C. Alexander. Isis Press. p. 192. ISBN 975-428-346-X. ISBN 9789754283464.
- ↑ Jovan Cvijić, Balkansko poluostrvo i južnoslovenske zemlje /Balkan Peninsula and South Slav Countries/ (Belgrade: Zavod za izdavanje udžbenika, 1966), pp. 151-152.
- ↑ "Radio-Televizija Republike Srpske". Rtrs.tv. 29 August 2011. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ↑ Svestenomucenik Platon, spc.org.yu; accessed 14 December 2015.
- ↑ NOAA National Geographical Data Center, Significant Earthquake Database states that the 15:36 26 October 1969 earthquake was 6.0 magnitude (intensity 8 Mercalli scale) and killed 14 people and causing $50 million damage, whilst the 08:10 27 October 1969 earthquake was 6.4 magnitude (intensity 9 Mercalli scale) and killed 9 people. The earthquake location was 44.9 Lat 17.3 Long on 26 October, and 44.9 Lat 17.2 Long on 27 October. Both had a focal depth of 33.
Observing our environment from space: new solutions for a new millennium, proceedings of the 21st EARSeL Symposium, Paris, France, 14–16 May 2001, edited by Gérard Bégni, pub Taylor & Francis, 2002, p267 claims that the earthquake in the vicinity of Banja Luka in 1969 had a magnitude of 6.4. (Comparison of other earthquakes mentioned shows that this is 6.4 on the Richter scale.)
Chronology of Extreme Weather, by Ken Polsson, claims: "magnitude 6.4 earthquake occurs. 20 killed, 150 seriously injured, and 65,000 left homeless."
Sarajevo Rocked by Two Earthquakes BalkanInsight.com 31 March 2009, which claims that: "The biggest earthquake in Bosnia and Herzegovina's history took place in 26 and 27 October 1969... That tremor measured 5.4 on the Richter scale and between 7 and 8 on the Mercalli scale."
Gymnasium Banja Luka History Archived 6 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine. claims that the 26 October 1969 earthquake had an intensity of 7.5 on the Mercalli intensity scale, whilst the 27 October 1969 earthquake had an intensity of 8.5 on the Mercalli scale. - 1 2 "Serbs ordered to pay for mosques". BBC News. 20 February 2009. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ "Neriješena ubistva banjalučkih Hrvata". Orbus. 3 April 2007. Retrieved 13 March 2016.
- ↑ Perlez, Jane (7 August 1995). "CONFLICT IN THE BALKANS: THE SERBIAN REFUGEES; Serbs Become Latest Victims In Changing Fortunes of War". The New York Times. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ Mackic, Erna (13 November 2009). "Historic Decisions by Banja Luka Court". Balkan Investigative Reporting Network. Archived from the original on 20 February 2010.
- ↑ Saric, Velma (13 November 2009). "Bosnian Muslims Appeal Mosque Ruling". Institute for War & Peace Reporting.
- ↑ "UN: Officials Alarmed By Mob Violence In Bosnia". Archived from the original on 18 February 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-14.
- ↑ Strauss, Julius (8 May 2001). "Serb mob attacks Muslims". The Daily Telegraph. London, UK. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ "UN condemns Serb 'sickness'". BBC. 8 May 2001.
- ↑ "Bosnian Serb Crowd Beats Muslims at Mosque Rebuilding". The New York Times. 8 May 2001. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ "Helsinki Commission releases U.S. statement on tolerance and non-discrimination at osce human dimension implementation meeting". Helsinki Commission. 20 September 2001. Archived from the original on 11 May 2015.
- ↑ HRCC Human Rights Quarterly Report, 1 April-30 June 2001, HRCC Human Rights Quarterly Report, 1 April-30 June 2001
- ↑ "Bosnians jailed over mosque riots". BBC News. 21 October 2002. Retrieved 30 March 2010.
- ↑ "Popis 2013" (PDF) (in Bosnian, Croatian, and Serbian). Retrieved 22 July 2016.
- ↑ United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees. "War Crimes in Bosnia-Hercegovina: U.N. Cease-Fire Won't Help Banja Luka". UNHCR. Archived from the original on 14 October 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ↑ "OSCE Regional Centre Banja Luka: Fact Sheet" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 October 2006.
- ↑ "nacion po mjesnim.xls" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 October 2013. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ↑ Radovinović, Radovan; Bertić, Ivan, eds. (1984). Atlas svijeta: Novi pogled na Zemlju (in Croatian) (3rd ed.). Zagreb: Sveučilišna naklada Liber.
- ↑ "RKUD "Pelagić", Banja Luka". Rkud-pelagic.org. 13 August 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ↑ "Aerodrom Banjaluka: Od oktobra nove destinacije letova". Banjaluka.net. Retrieved July 30, 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Градови партнери [City of Banja Luka - Partner cities]. Administrative Office of the City of Banja Luka (in Serbian). Archived from the original on 2011-09-17. Retrieved 2013-08-09.
- ↑ e-patras.gr – Διεθνείς Σχέσεις0
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Banja Luka. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Banjaluka. |