Neum
| Neum Неум | |
|---|---|
|
| |
 Location of Neum municipality (shown in red) within Bosnia and Herzegovina | |
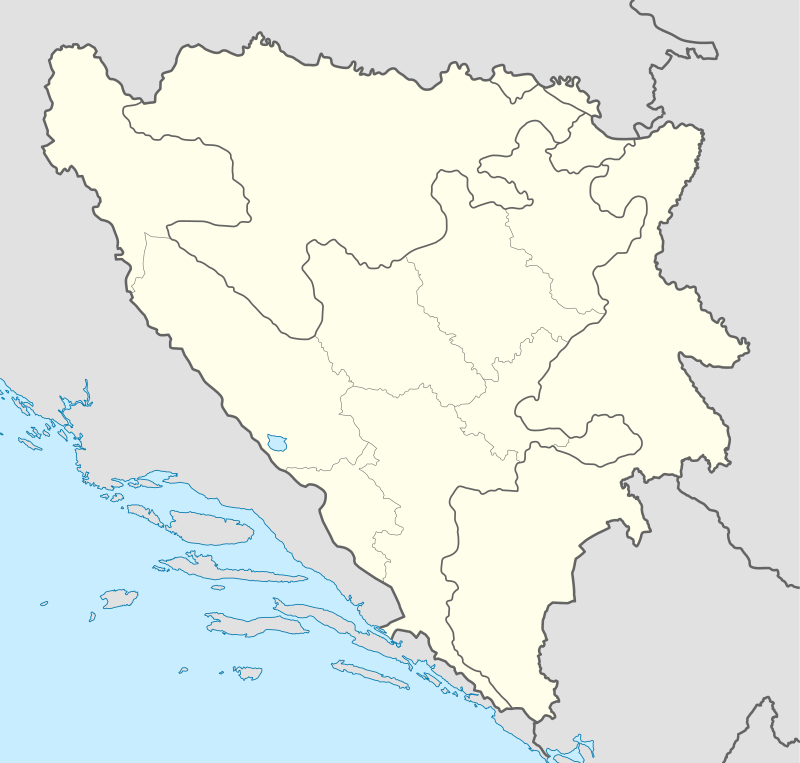 Neum Location of Neum (town) | |
| Coordinates: 42°55′30″N 17°37′00″E / 42.92500°N 17.61667°E | |
| Country |
|
| Entity | Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina |
| Canton | Herzegovina-Neretva |
| Government | |
| • Municipality president | Živko Matuško (HDZ) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 225 km2 (87 sq mi) |
| Population (2013 census) | |
| • Total | 4,960 |
| • Density | 22/km2 (60/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Area code(s) | +387 36 |
| Website |
www |
 Luka Neum Lighthouse | |
 Bosnia and Herzegovina | |
| Location |
Neum Bosnia and Herzegovina |
|---|---|
| Coordinates | 42°55′08″N 17°37′02″E / 42.918806°N 17.617111°E |
| Year first constructed | n/a |
| Foundation | concrete base |
| Construction | metal tower[1] |
| Tower shape | cylindrical post with balcony and light[1] |
| Markings / pattern | red tower |
| Height | 6 metres (20 ft)[2] |
| Focal height | 5 metres (16 ft)[2] |
| Range | 4 nautical miles (7.4 km; 4.6 mi)[2] |
| Characteristic | Fl R 3s.[2] |
| Admiralty number | E3521.5[1] |
| NGA number | 13800[2] |
Neum (Serbo-Croatian pronunciation: [nɛ̌um], Serbian Cyrillic: Неум) is a town and municipality located in Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is the only town to be situated along Bosnia and Herzegovina's 20 km (12 mi) of coastline,[3] making it the country's only access to the Adriatic Sea. In 2009 the municipal (općina) population was 4,605 and in 1991 the population of the town proper was 4,268.
Features
Neum has steep hills, sandy beaches, and several large tourist hotels. Prices tend to be lower than in neighboring Croatia, making it popular with shoppers. Tourism, and the commerce it brings, is the leading contributor to the economy of the area. Border formalities with Croatia are relaxed at peak times.
Neum has about 5,000 beds for tourists, 1,810 in hotels with the remaining capacity in motels, villas, and private accommodation. Tourism in Neum is active only in the coastal region. The inland area behind Neum has a rich archeological history and untouched wilderness and is starting to develop agricultural tourism.
Geography
Overview
Neum is 60 kilometers (37 mi) from Dubrovnik (80 km or 50 mi from the Dubrovnik Airport), 70 km (43 mi) from Mostar and Međugorje and 30 km (19 mi) from Ploče and Metković, both of which have railway stations.
The Bosnia and Herzegovina coastal strip of Neum cuts off the southernmost Croatian territory from the rest of Croatia. This is a result of the Treaty of Karlowitz of 1699. With its admission to the European Union, Croatia had to apply EU regulations at its border crossings, including the passage through the Neum section.
The construction of the Pelješac Bridge, which would bypass Neum entirely, has significance for Croatia's integrity and also for its future Schengen Area membership and the EU as a whole. It would significantly improve traffic flow and the traffic connection of Dubrovnik to the rest of mainland Croatia, avoiding crossing the external borders of the EU at Neum, negotiating long, costly queues and strict customs checks twice within the space of 20 km.
Encouraged by the recent developments in Croatia - Slovenia maritime border dispute (June 2017), the ruling Bosniak Party of Democratic Action (SDA) and other Bosnian political parties have decided to obstruct the €420 million worth project previously approved by the EU. The EU Commission has already allocated €357 million of Cohesion Policy funds to build the bridge. It should be completed by 2022.
Neum is planned to be a freight port. There are plans to build a real seaport, rail and a motorway and thus the Croatian bridge must have a high clearance according to the view of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Today the main freight port for Bosnia and Herzegovina is Ploče (in Croatia) further north, which has a railway to Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Subdivision
The municipality includes the town of Neum (municipal seat) and several villages:
Babin Do, Borut, Brestica, Broćanac, Brštanica, Cerovica, Cerovo, Crnoglav, Dobri Do, Dobrovo, Donji Drijen, Donji Zelenikovac, Dubravica, Duži, Glumina, Gornje Hrasno, Gradac, Hotanj Hutovski, Hutovo, Kiševo, Moševići, Prapratnica, Previš, Rabrani, Vinine and Žukovica.
Border crossings

Neum has two border crossing checkpoints with Croatia on the European route E65 or Adriatic Highway which connects the two parts of Croatia's Dalmatian coast. Neum 1 is located to the northwest of the city, with the Klek border checkpoint on the Croatian side. Neum 2 is located to the southeast, with the Croatian border checkpoint at Zaton Doli.
History
The Neum corridor dates back to the Treaty of Karlovci of 1699, whereby the Republic of Ragusa was separated from the Dalmatian possessions of its rival Venice by two buffer zones ceded by Venice to the Ottoman empire: north of its territory is Neum and the bay of Klek, and south of its territory is Sutorina with the port of Herceg-Novi on the Bay of Kotor, now part of Montenegro since 1947.[4]
The Karlovci borders were reaffirmed in 1718 by the Treaty of Požarevac, but then the Ottomans, tired of negotiating in vain with Venice for a widening of their maritime access, simply usurped the territory of Gornji Klek and most of the Klek peninsula from the Republic of Ragusa, which it had bought from King Stjepan of Bosnia at the end of the 14th century. After the fall of the Venetian Republic in 1797 and the Vienna Congress in 1815, the Austrian Empire, which had annexed both the Dalmatian possessions of Venice and the territory of Dubrovnik, tried to buy back the Neum and Sutorina enclaves from the Ottomans, but in vain. Instead, it stationed a warship to block access to the port of Neum until the Treaty of Berlin, which gave Vienna the whole of Bosnia-Herzegovina in 1878. Neum had been under Ottoman control for 179 years.
In 1918, as a consequence of Vienna's defeat, Neum joined the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes which would start being called "Yugoslavia" in 1929. Under Karađorđević, the Yugoslav Government ignored the borders inherited from history twice: in 1929, when the Neum Region was included in the Littoral Banovina, and in 1939 when, following the Cvetković–Maček Agreement, it was included in the Banovina of Croatia. Tito's federal Yugoslavia was founded on the principle, declared at the 1943 AVNOJ in Jajce and comparatively well-respected by the Đilas commission in 1945, of establishing the federated Republics in their borders of 1878 which is why the Neum enclave is now part of the independent Republic of Bosnia-Herzegovina, including most of the Klek peninsula (Ponta Kleka, Rep Kleka), the two islets Veliki and Mali Školj and the rock of Lopata in the Bay of Klek.[5]
Climate
Neum has warm summers and mild winters.
The average sea temperature ranges from 13 °C (55 °F) in January to 28 °C (82 °F) in July and August. Popular activities include swimming and sun bathing, beach-going, boating, and various other water-sports.
Demographics
The municipality of Neum shrank in size from 1971 to 1991; it had 4,781 residents in 1971, and decreased to 4,268 twenty years later. According to the 1991 census, 87.6% of the residents were Croats, 4.9% Serbs, 4.39% Bosniaks and other nationalities.
The actual town of Neum had 1,993 residents in 1991, with a higher (91%) proportion of Croats. According to the 2013 census 97.6% of the population are ethnic Croats.[6]
2013 Census
| Municipality | Nationality | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Bosniaks |
% |
Croats |
% |
Serbs |
% | ||
| Neum | 63 | 01.35 | 4,543 | 97.63 | 21 | 0.45 | 4,653 |

Culture

Neum celebrates the feast of Our Lady of Good Health as its municipal day. As part of the celebrations, Neum hosts the Music Festival Etnofest Neum. The town also hosts the Neum Animated Film Festival.[8]
The linđo is traditionally danced in the Neum region.[9]
Neum is home to local branches of the cultural organizations Matica hrvatska and HKD Napredak.[10][11]
Sport

Neum has a water polo club VK Jadran Neum, which is a member of the Croatian Water Polo Federation.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 "Bosnia and Herzegovina". The Lighthouse Directory. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Retrieved 1 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 List of Lights, Pub. 113: The West Coasts of Europe and Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, Black Sea and Azovskoye More (Sea of Azov) (PDF). List of Lights. United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency. 2015.
- ↑ Bosnia-and-Herzegovina Neum britannica.com, britannica.com, 2015-09-09
- ↑ The attribution of Sutorina and Herceg-Novi to the Republic of Montenegro in 1947, a departure from the principle of respecting the borders inherited from history affirmed by Tito in 1943, is rumored to be the consequence of a deal between Đuro Pucar and Blažo Jovanović (Source: "Neum i granični problemi" ("Neum and the border issues"), Poskok.info, December 14th, 2012)
- ↑ Source: "Neum i granični problemi", Poskok.info, December 14th, 2012
- ↑ "www.statistika.ba". Retrieved 12 September 2018.
- ↑ http://www.popis.gov.ba/popis2013/knjige.php?id=0
- ↑ Neum Animated Film Festival Archived 2008-09-16 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ 50. Split Summer
- ↑ Matica hrvatska
- ↑ HKD Napredak
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Neum. |
- Future Port of Neum
- Bosnian Border Police
- Neum city portal / Neumski gradski portal
- Official website of Neum (In Croatian and English)
- Neum City info
- Neum City info
- Info and accommodation in Neum
Coordinates: 42°55′30″N 17°37′00″E / 42.92500°N 17.61667°E