Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa
| Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa | |
|---|---|
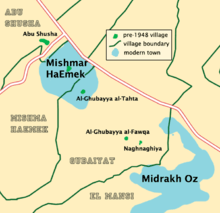 Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa in historical context | |
 Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa | |
| Arabic | الغبية الفوقا |
| Also spelled | Ghubayya al Fauqa[1] |
| Subdistrict | Haifa |
| Coordinates | 32°36′5″N 35°9′5″E / 32.60139°N 35.15139°ECoordinates: 32°36′5″N 35°9′5″E / 32.60139°N 35.15139°E |
| Palestine grid | 164/223 |
| Population | 1130[2][3] (1945) |
| Date of depopulation | April 8–9, 1948[1] |
| Cause(s) of depopulation | Military assault by Yishuv forces |
Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa was a Palestinian Arab village in the Haifa Subdistrict. It was depopulated during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine on April 8, 1948, during the Battle of Mishmar HaEmek. It was located 28 km southeast of Haifa.
History
During the early Ottoman era, in 1596 the village appeared under the name of Gubayya in the tax registers, being part of the nahiya (subdistrict) of Sahil Atlit in the Sanjak (district) of Lajjun. It had a population of 39 households; an estimated 215 people, all Muslim. They paid a fixed tax-rate of 25% on agricultural products, including wheat, barley, summer crops, goats and beehives, and water buffaloes; the taxes totalled 21,690 akçe.[4][5]
Al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa shared an elementary school built by the Ottomans in 1888 with the nearby villages of al-Ghubayya-al-Tahta and al-Naghnaghiyya. The school was later closed during the British Mandate period. The village had its own mosque.[5]
British Mandate era
In the 1922 census of Palestine, conducted by the British Mandate authorities, Ghabba al-Fuqa had a population of 41 Muslims.[6] In the 1931 census, the two al-Ghubayya village were counted together, and the total population was 200 Muslims, in 38 houses.[7]
In 1945 the population was counted with the neighbouring al-Ghubayya-al-Tahta and al-Naghnaghiyya, and together they had a population of 1,130 Muslims,[2] with a total of 12,139 dunams of land according to an official land and population survey.[3] Of this, 209 dunams were for plantations and irrigable land, 10,883 for cereals,[8] while a total of 1,047 dunams were non-cultivable land.[9]
1948 and aftermath
On 8 and 9 April 1948, the Haganah raided al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa, al-Ghubayya-al-Tahta and Khirbet Beit Ras, and proceeded to blow them up in the following days.[10] The report on 9 April from the Golani Brigade stated that they were "preparing to destroy the villages when we evacuate them."[11] They destroyed al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa the following night.[12]
Following the war the area was incorporated into the State of Israel. By 1992 the kibbutz of Mishmar HaEmek was using some of al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa's former land as pastures.[5]
References
- 1 2 Morris, 2004, p. xviii, village #150. Also gives cause of depopulation.
- 1 2 Department of Statistics, 1945, p. 13
- 1 2 Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 47
- ↑ Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 157
- 1 2 3 Khalidi, 1992, p. 160
- ↑ Barron, 1923, Table XI, Sub-district of Haifa, p. 33
- ↑ Mills, 1932, p. 90
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 90
- ↑ Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. Village Statistics, April, 1945. Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p. 139
- ↑ Morris, 2004, p. 242; note #598; Morris, 2004, p. 296
- ↑ Morris, 2004, p. 346; note #28; Morris, 2004, p. 397
- ↑ Morris, 2004, p. 346; note #29; Morris, 2004, p. 397
Bibliography
- Barron, J. B., ed. (1923). Palestine: Report and General Abstracts of the Census of 1922. Government of Palestine.
- Department of Statistics (1945). Village Statistics, April, 1945. Government of Palestine.
- Hadawi, Sami (1970). Village Statistics of 1945: A Classification of Land and Area ownership in Palestine. Palestine Liberation Organization Research Centre.
- Hütteroth, Wolf-Dieter; Abdulfattah, Kamal (1977). Historical Geography of Palestine, Transjordan and Southern Syria in the Late 16th Century. Erlanger Geographische Arbeiten, Sonderband 5. Erlangen, Germany: Vorstand der Fränkischen Geographischen Gesellschaft. ISBN 3-920405-41-2.
- Khalidi, Walid (1992). All That Remains: The Palestinian Villages Occupied and Depopulated by Israel in 1948. Washington D.C.: Institute for Palestine Studies. ISBN 0-88728-224-5.
- Mills, E., ed. (1932). Census of Palestine 1931. Population of Villages, Towns and Administrative Areas. Jerusalem: Government of Palestine.
- Morris, Benny (2004). The Birth of the Palestinian Refugee Problem Revisited. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-00967-6.
- al-Qawuqji, Fauzi (1972): Memoirs of al-Qawuqji, Fauzi in Journal of Palestine Studies
- "Memoirs, 1948, Part I" in 1, no. 4 (Sum. 72): 27-58., dpf-file, downloadable
- "Memoirs, 1948, Part II" in 2, no. 1 (Aut. 72): 3-33., dpf-file, downloadable
External links
- Welcome To al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa
- al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa, Zochrot
- Survey of Western Palestine, Map 8: IAA, Wikimedia commons
- al-Ghubayya al-Fawqa, from the Khalil Sakakini Cultural Center
- Al-Ghubayya Al-Fouqa, from Dr. Moslih Kanaaneh
- Remembering al-Ghubayyat, booklet about the al-Ghubayyat villages, 03/2010
- Tour to the al-Ghubayyat villages, by Umar Ighbariyye, 20.3.2010, Zochrot