Bazedoxifene
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.232.728 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
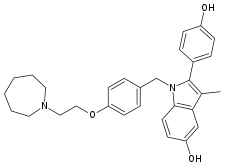
| Formula | C30H34N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 470.603 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Bazedoxifene, or bazedoxifene acetate, is a medication for bone problems and possibly (pending more study) for cancer. It is a third-generation selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM).[1] Since late 2013 it has had U.S. FDA approval for bazedoxifene as part of the combination drug DUAVEE in the prevention (not treatment) of postmenopausal osteoporosis. It is also being studied for possible treatment of breast cancer and pancreatic cancer.[2]
Chemistry
The drug is a member of the 2-phenylindole group of SERMs, along with zindoxifene and pipendoxifene.[3]
History
Development
Bazedoxifene was developed by Pfizer following the completion of their takeover of Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. It is the result of an exclusive research collaboration between Wyeth Pharmaceuticals and Ligand Pharmaceuticals.
Approval
The drug was approved in the European Union by the European Medicines Agency on April 27, 2009.[4]
On October 3, 2013 the FDA approved the combination product of bazedoxifene 20 mg with 0.45 mg Premarin (conjugated estrogens) for the treatment of menopausal osteoporosis and the treatment of moderate to severe hot flushes. This is the first approved menopausal hormone therapy product that contains a SERM (bazedoxifene) and an estrogen.
References
- ↑ Biskobing, D. M. (2007). "Update on bazedoxifene: A novel selective estrogen receptor modulator". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2 (3): 299–303. PMC 2685267. PMID 18044180.
- ↑ http://medicalxpress.com/news/2013-06-osteoporosis-drug-growth-breast-cancer.html
- ↑ Gordon W. Gribble (9 October 2010). Heterocyclic Scaffolds II:: Reactions and Applications of Indoles. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 14–. ISBN 978-3-642-15732-5.
- ↑ "EPARs for authorised medicinal products for human use - Conbriza". European Medicines Agency. 26 May 2009. Archived from the original on 11 June 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-08.