Leicester
Coordinates: 52°38′N 1°8′W / 52.633°N 1.133°W
| Leicester | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| City and unitary authority area | |||
| |||
| Motto(s): "Semper Eadem" {Constant / Always the Same / "'the Eternal Urbs'"} | |||
 Location within Leicestershire | |||
 Leicester Location within England  Leicester Location within the United Kingdom  Leicester Location within Europe | |||
| Coordinates: 52°38′N 1°08′W / 52.633°N 1.133°W | |||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||
| Constituent country | England | ||
| Region | East Midlands | ||
| Ceremonial county | Leicestershire | ||
| Founded | AD c.47 as Ratae Corieltauvorum, by the Romans | ||
| City status | Restored 1919 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Unitary authority | ||
| • Body | Leicester City Council | ||
| • Lord Mayor | Ted Cassidy[1] | ||
| • City Mayor | Peter Soulsby | ||
| • Leadership | Elected mayor and cabinet | ||
| • Admin HQ |
City Hall 115 Charles St Leicester LE1 1FZ | ||
| • MPs |
| ||
| Area: ⎋City 4.9 km ⎋Urban 8.5 km ⎋Metro 9.6 mi | |||
| • City | 28.3 sq mi (73.3 km2) | ||
| • Urban | 87 sq mi (225 km2) | ||
| • Metro | 290 sq mi (750 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 205 ft (62.5 m) | ||
| Population | |||
| • City | 329,839[2] | ||
| • Density | 12,000/sq mi (4,500/km2) | ||
| • Urban | 508,916[3] | ||
| • Urban density | 5,900/sq mi (2,260/km2) | ||
| • Metro | 836,484[4] | ||
| • Metro density | 3,070/sq mi (1,185/km2) | ||
| Ethnicity (2011)[5] | |||
| • City |
| ||
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) | ||
| Postcode | LE | ||
| Dialling code | 0116 | ||
| Geocode | SK584044 (Grid ref.) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | GB-LCE | ||
| Statistical areas |
UKF21 (NUTS 3) 00FN (ONS) E06000016 (GSS) | ||
| Police | Leicestershire Police | ||
| Website |
www | ||
Leicester (/ˈlɛstər/ (![]()
The 2016 mid year estimate of the population of the City of Leicester unitary authority was 348,300, an increase of approximately 18,500 (![]()
Leicester is at the intersection of two major railway lines—the north/south Midland Main Line and the east/west Birmingham to London Stansted CrossCountry line; as well as the confluence of the M1/M69 motorways and the A6/A46 trunk routes. Leicester is the home to football club Leicester City and rugby club Leicester Tigers.
Name
The name of Leicester is recorded in the 9th-century History of the Britons as Cair Lerion (whence Welsh Caerlŷr), and in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle as Ligora-ceastre. In the Domesday Book of 1086, it is recorded as Ledecestre.[9] The first element of the name, Ligora or Legora, is explained as a Brittonic river name, in a suggestion going back to William Somner (1701) an earlier name of the River Soar, cognate with the name of the Loire.[10][11] The second element of the name comes from the Latin castrum which is reflected in both Welsh cair and Anglo-Saxon ceastre.
Based on the Welsh name (given as Kaerleir), Geoffrey of Monmouth proposes a king Leir of Britain as an eponymous founder in his Historia Regum Britanniae (12th century).[12]
History
Prehistory
Leicester is one of the oldest cities in England, with a history going back at least two millennia. The native Iron Age settlement encountered by the Romans at the site seems to have developed in the 2nd or 1st centuries BC.[13] Little is known about this settlement or the condition of the River Soar at this time, although roundhouses from this era have been excavated and seem to have clustered along roughly 8 hectares (20 acres) of the east bank of the Soar above its confluence with the Trent. This area of the Soar was split into two channels: a main stream to the east and a narrower channel on the west, with a presumably marshy island between. The settlement seems to have controlled a ford across the larger channel. The later Roman name was a latinate form of the Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf. Gaelic rath and the nearby villages of Ratby and Ratcliffe[14]), suggesting the site was an oppidum. The plural form of the name suggests it was initially composed of several villages.[14] The Celtic tribe holding the area was later recorded as the "Coritanians" but an inscription recovered in 1983 showed this to have been a corruption of the original "Corieltauvians".[15][16] The Corieltauvians are believed to have ruled over roughly the area of the East Midlands.
Roman

It is believed that the Romans arrived in the Leicester area around AD 47, during their conquest of southern Britain.[17] The Corieltauvian settlement lay near a bridge on the Fosse Way, a Roman road between the legionary camps at Isca (Exeter) and Lindum (Lincoln). It remains unclear whether the Romans fortified and garrisoned the location, but it slowly developed from around the year 50 onwards as the tribal capital of the Corieltauvians under the name Ratae Corieltauvorum. In the 2nd century, it received a forum and bathhouse. In 2013, the discovery of a Roman cemetery found just outside the old city walls and dating back to AD 300 was announced.[17] The remains of the baths of Roman Leicester can be seen at the Jewry Wall; recovered artifacts are displayed at the adjacent museum.
Medieval
Knowledge of the town following the Roman withdrawal from Britain is limited. Certainly there is some continuation of occupation of the town, though on a much reduced scale in the 5th and 6th centuries. Its memory was preserved as the Cair Lerion[18] of the History of the Britons.[19] Following the Saxon invasion of Britain, Leicester was occupied by the Middle Angles and subsequently administered by the kingdom of Mercia. It was elevated to a bishopric in either 679 or 680; this see survived until the 9th century, when Leicester was captured by Danish Vikings. Their settlement became one of the Five Burghs of the Danelaw, although this position was short-lived. The Saxon bishop, meanwhile, fled to Dorchester-on-Thames and Leicester did not become a bishopric again until the Church of St Martin became Leicester Cathedral in 1927. The settlement was recorded under the name Ligeraceaster in the early 10th century.[20]

Following the Norman conquest, Leicester was recorded by William's Domesday Book as Ledecestre. It was noted as a city (civitas) but lost this status in the 11th century owing to power struggles between the Church and the aristocracy and did not become a legal city again until 1919.
Geoffrey of Monmouth composed his History of the Kings of Britain around the year 1136, naming a King Leir as an eponymous founder figure.[21] According to Geoffrey's narrative, Cordelia had buried her father beneath the river in a chamber dedicated to Janus and his feast day was an annual celebration.[22]
When Simon de Montfort became Lord of Leicester in 1231, he gave the city a grant to expel the Jewish population[23] "in my time or in the time of any of my heirs to the end of the world". He justified his action as being "for the good of my soul, and for the souls of my ancestors and successors".[24] Leicester's Jews were allowed to move to the eastern suburbs, which were controlled by de Montfort's great-aunt and rival, Margaret, Countess of Winchester, after she took advice from the scholar and cleric Robert Grosseteste.[25] There is evidence that Jews remained there until 1253, and perhaps enforcement of the banishment within the city was not rigorously enforced. De Montfort however issued a second edict for the expulsion of Leicester's Jews in 1253, after Grosseteste's death.[26] De Montfort's many acts of anti-Jewish persecution in Leicester and elsewhere mass murder were part of a wider pattern that led to the expulsion of the Jewry from England in 1290.[27]
During the C14th the earls of Leicester and Lancaster enhanced the prestige of the town. Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster and of Leicester founded a hospital for the poor and infirm in the area to the south of the castle now known as The Newarke (the "new work"). Henry's son, the great Henry of Grosmont, 4th Earl of Lancaster and of Leicester, who was made first Duke of Lancaster, enlarged and enhanced his father's foundation, and built the collegiate Church of the Annunciation of Our Lady of The Newarke.[28] This church (a little of which survives in the basement of the Hawthorn Building of De Montfort University) was destroyed during the reign of King Edward VI. It became an important pilgrimage site because it housed a thorn said to be from the Crown of Thorns, given to the Duke by the King of France. The church (described by Leland in the C16th as "not large but exceeding fair") also became, effectively, a Lancastrian mausoleum. Duke Henry's daughter Blanche of Lancaster married John of Gaunt and their son Henry Bolingbroke became King Henry IV when he deposed King Richard II. The Church of the Annunciation was the burial place of Duke Henry, who had earlier had his father re-interred here. Later it became the burial place of Constance of Castile, Duchess of Lancaster (second wife of John of Gaunt) and of Mary de Bohun, first wife of Henry Bolingbroke (Henry IV) and mother of King Henry V (she did not become queen because she died before Bolingbroke became king). John of Gaunt died at Leicester Castle in 1399. When his son became king, the Earldom of Leicester and the Duchy of Lancaster became royal titles (and the latter remains so).

At the end of the War of the Roses, King Richard III was buried in Leicester's Greyfriars Church a Franciscan Friary and Church which was demolished after its dissolution in 1538. The site of that church is now covered by more modern buildings and a car park. There was a legend his corpse had been cast into the river, while some historians[29] argued his tomb and remains were destroyed during the dissolution of the monasteries under Henry VIII. However, in September 2012, an archaeological investigation of the car park revealed a skeleton[30] which DNA testing helped verify to be related to two descendants of Richard III's sister.[31] It was concluded that the skeleton was that of Richard III because of the DNA evidence and the shape of the spine. In 2015 Richard III was reburied in pride of place near the high altar in Leicester Cathedral.
Modern
Tudor

On 4 November 1530, Cardinal Thomas Wolsey was arrested on charges of treason and taken from York Place. On his way south to face dubious justice at the Tower of London, he fell ill. The group escorting him was concerned enough to stop at Leicester to rest at Leicester Abbey. There, Wolsey's condition quickly worsened. He died on 29 November 1530 and was buried at Leicester Abbey, now Abbey Park.
Lady Jane Grey, who claimed the English throne for nine days in June 1553, was born at Bradgate Park near Leicester around 1536.[32]
Queen Elizabeth I's intimate and former suitor, Robert Dudley, was given the Earldom of Leicester.
Stuart
The Corporation of Leicester opposed the efforts of Charles I of England to disafforest the nearby Leicester Forest, believing them to be likely to throw many of its residents into poverty and need of relief. Sir Miles Fleetwood was sent to commission the disafforestation and division of lands being used in common.[33] Riots destroyed enclosures in spring 1627 and 1628, following a pattern of anti-enclosure disturbances found elsewhere including the Western Rising.[34]
Petitions challenging the enclosures were presented by the Corporation of Leicester and borough residents to the King and Privy Council. They were unsuccessful so petitioned the House of Lords in June 1628 who however supported Fleetwood but asked for proceedings made by the Crown against the rioters to be dropped. Compensation made to the legal residents of the forest was reasonably generous by comparison with other forests. The Corporation received 40 acres (16 ha) for relief of the poor.[35]
Civil War
Leicester was a Parliamentarian (colloquially called Roundhead) stronghold during the English Civil War. In 1645, King Charles I of England and Prince Rupert decided to attack the (then) town to draw the New Model Army away from the Royalist (colloquially called Cavaliers) headquarters of Oxford. Royalist guns were set up on Raw Dykes and, after an unsatisfactory response to a demand for surrender,the assault began at 3pm on 30 May 1645 by a Royalist battery opposite the Newarke. The city was sacked on 31 May 1645, and hundreds of people were killed by Rupert's cavalry. One witness said, “they fired upon our men out of their windows, from the tops of houses, and threw tiles upon their heads. Finding one house better manned than ordinary, and many shots fired at us out of the windows, I caused my men to attack it, and resolved to make them an example for the rest; which they did. Breaking open the doors, they killed all they found there without distinction.” It was reported that 120 houses had been destroyed and that 140 wagons of plunder were sent to the Royalist stronghold of Newark. [36]
Following the Parliamentarian victory over the Royalists at the Battle of Naseby on 14 June 1645 Leicester was recovered by Parliament on 18 June 1645.
Industrial era

Leicester, Hotel Street
The construction of the Grand Union Canal in the 1790s linked Leicester to London and Birmingham. In 1832, the railway arrived in Leicester. in the form of The Leicester and Swannington Railway which provided a supply of coal to the town from nearby collieries.[37] The Midland Counties Railway (running from Derby to Rugby) linked the town to the national network by 1840. A direct link to London St Pancras Station was established by the Midland Railway in the 1860s. These developments encouraged and accompanied a process of industrialisation which intensified throughout the reign of Queen Victoria. Factories began to appear, particularly along the canal and river, and districts such as Frog Island and Woodgate were the locations of numerous large mills. Between 1861 and 1901, Leicester's population increased from 68,100 to 211,600 and the proportion employed in trade, commerce, building, and the city's new factories and workshops rose steadily. Hosiery, textiles, and footwear became the major industrial employers: manufacturers such as N. Corah & Sons and the Cooperative Boot and Shoe Company were opening some of the largest manufacturing premises in Europe. They were joined, in the latter part of the century, by engineering firms such as Kent Street's Taylor and Hubbard (crane makers and founders), Vulcan Road's William Gimson & Company (steam boilers and founders), and Martin Street's Richards & Company (steel works and founders).
The politics of Victorian Leicester were lively and very often bitter. Years of consistent economic growth meant living standards generally increased, but Leicester was a stronghold of Radicalism. Thomas Cooper, the Chartist, kept a shop in Church Gate. There were serious Chartist riots in the town in 1842 and again six years later.[38] The Leicester Secular Society was founded in 1851 but secularist speakers such as George Holyoake were often denied the use of speaking halls. It was not until 1881 that Leicester Secular Hall was opened. The second half of the 19th century also witnessed the creation of many other institutions, including the town council, the Royal Infirmary, and the Leicester Constabulary. It also benefited from general acceptance (and the Public Health Acts ) that municipal organisations had a responsibility to provide for the town's water supply, drainage, and sanitation. In 1853, backed with a guarrantee of dividends by the Corporation the Leicester Waterworks Company built a reservoir at Thornton for the supply of water to the town . This guarrantee was made possible by the Public Health Act 1847 and an amending local Act of Parliament of 1851. In 1866 another amending Act enabled the Corporation to take shares in the company to enable another reservoir at Cropston, completed in 1870. The Corporation was later able to buy the waterworks and build another reservoir at Swithland, completed in the 1890s.[39]
Leicester became a county borough in 1889, although it was abolished with the rest in 1974 as part of the Local Government Act. The city regained its unitary status apart from Leicestershire in 1997. The borough had been expanding throughout the 19th century, but grew most notably when it annexed Belgrave, Aylestone, North Evington, Knighton, and Stoneygate in 1892.
Early 20th century

In 1900, the Great Central Railway provided another link to London, but the rapid population growth of the previous decades had already begun to slow by the time of Queen Victoria's death in 1901. World War I and the subsequent epidemics had further impacts. Nonetheless, Leicester was finally recognised as a legal city once more in 1919 and, in 1927, again became a cathedral city on the consecration of St Martin's Church as the Cathedral. A second major extension to the boundaries following the changes in 1892 took place in 1935, with the annexation of the remainder of Evington, Humberstone, Beaumont Leys, and part of Braunstone. A third major revision of the boundaries took place in 1966, with the net addition to the city of just over 450 acres (182 ha). The boundary has remained unchanged since that time.

Leicester's diversified economic base and lack of dependence on primary industries meant it was much better placed than many other cities to weather the tariff wars of the 1920s and Great Depression of the 1930s. The Bureau of Statistics of the newly formed League of Nations identified Leicester in 1936 as the 2nd-richest city in Europe[40] and it became an attractive destination for refugees fleeing persecution and political turmoil in continental Europe. Firms such as Corah and Liberty Shoes used their reputation for producing high-quality products to expand their businesses. These years witnessed the growth in the city of trade unionism and particularly the co-operative movement. The Co-op became an important employer and landowner; when Leicester played host to the Jarrow March on its way to London in 1936, the Co-op provided the marchers with a change of boots. In 1938, Leicester was selected as the base for Squadron 1F, the first A.D.C.C (Air Defence Cadet Corp), the predecessor of the Air Training Corps.
Contemporary
The years after World War II, particularly from the 1960s onwards, brought many social and economic challenges.
Urban expansion; central rapprochement

Mass housebuilding continued across Leicester for some 30 years after 1945. Existing housing estates such as Braunstone were expanded, while several completely new estates – of both private and council tenure – were built. The last major development of this era was Beaumont Leys in the north of the city, which was developed in the 1970s as a mix of private and council housing. There was a steady decline in Leicester's traditional manufacturing industries and, in the city centre, working factories and light industrial premises have now been almost entirely replaced. Many former factories, including some on Frog Island and at Donisthorpe Mill, have been badly damaged by fire. Rail and barge were finally eclipsed by automotive transport in the 1960s and 1970s: the Great Central and the Leicester and Swannington both closed and the northward extension of the M1 motorway linked Leicester into England's growing motorway network. With the loss of much of the city's industry during the 1970s and 1980s, some of the old industrial jobs were replaced by new jobs in the service sector, particularly in retail. The opening of the Haymarket Shopping Centre in 1971 was followed by a number of new shopping centres in the city, including St Martin's Shopping Centre in 1984 and the Shire Shopping Centre in 1992.[41] The Shires was subsequently expanded in September 2008 and rebranded as Highcross.[42] By the 1990s, as well, Leicester's central position and good transport links had established it as a distribution centre; the southwestern area of the city has also attracted new service and manufacturing businesses.
Immigration

Since World War II Leicester has experienced large scale immigration from across the world. Many Polish servicemen were prevented from returning to their homeland after the war by the communist regime[43], and they established a small community in Leicester. Economic migrants from the Irish Republic continued to arrive throughout the post war period. Immigrants from the Indian sub-continent began to arrive in the 1960s, their numbers boosted by Asians arriving from Kenya and Uganda in the early 1970s.[44][45]
In 1972, Idi Amin announced that the entire Asian community in Uganda had 90 days to leave the country.[46] Shortly thereafter, the Leicester City Council launched a campaign aimed at dissuading Ugandan Asians from migrating to the city.[47] The adverts did not have their intended effect, instead making more migrants aware of the possibility of settling in Leicester.[48] Nearly a quarter of initial Ugandan refugees (around 5000 to 6000) settled in Leicester, and by the end of the 1970s around another quarter of the initially dispersed refugees had made their way to Leicester.[49] Officially, the adverts were taken out for fear that immigrants to Leicester would place pressure on city services and at least one person who was a city councillor at the time says he believes they were placed for racist reasons.[50] The initial advertisement was widely condemned, and taken as a marker of anti-Asian sentiment throughout Britain as a whole, although the attitudes that resulted in the initial advertisement were changed significantly in subsequent decades,[51] not least because the immigrants included the owners of many of "Uganda's most successful businesses."[52]
Forty years later, Leicester's mayor Sir Peter Soulsby expressed his regret for the behaviour of the council at the time.[50]
In the 1990s, a group of Dutch citizens of Somali origin settled in the city. Since the 2004 enlargement of the European Union a significant number of East European migrants have settled in the city. While some wards in the northeast of the city are more than 70% South Asian, wards in the west and south are all over 70% white. The Commission for Racial Equality (CRE) had estimated that by 2011 Leicester would have approximately a 50% ethnic minority population, making it the first city in Britain not to have an indigenous white British majority.[53] This prediction was based on the growth of the ethnic minority populations between 1991 (Census 1991 28% ethnic minority) and 2001 (Census 2001 – 36% ethnic minority). However Professor Ludi Simpson at the University of Manchester School of Social Sciences said in September 2007 that the CRE had "made unsubstantiated claims and ignored government statistics" and that Leicester's immigrant and minority communities disperse to other places.[54][55][56]
The Leicester Multicultural Advisory Group[57] is a forum, set up in 2001 by the editor of the Leicester Mercury, to co-ordinate community relations with members representing the council, police, schools, community and faith groups, and the media.
Geography
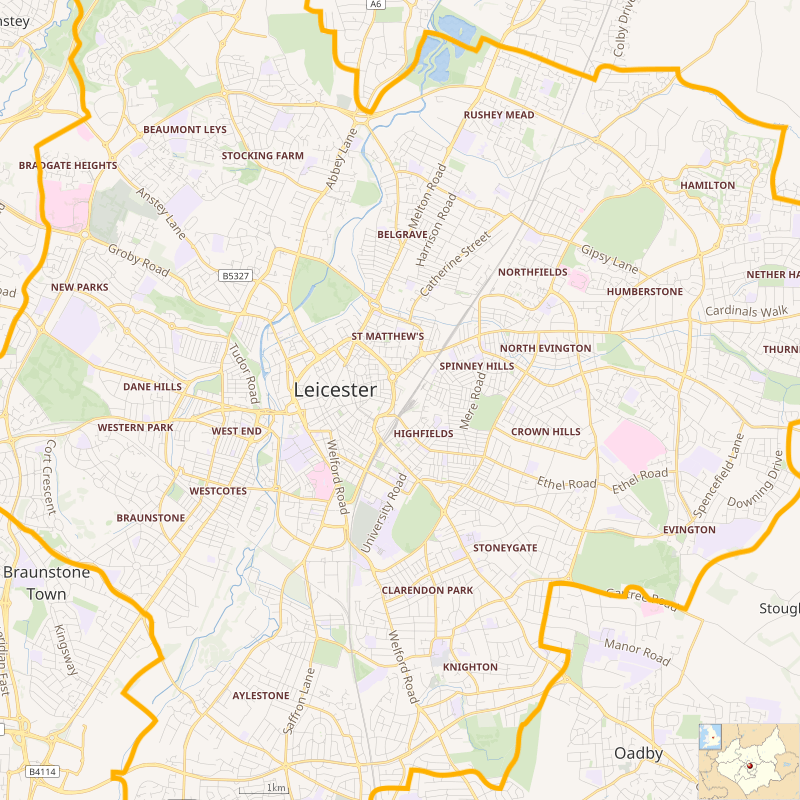 |
| Map of Leicester showing some of the localities and suburbs |
The Office for National Statistics has defined a Leicester Urban Area (LUA); broadly the immediate Leicester conurbation, although without administrative status. The LUA contains the unitary authority area and several towns, villages and suburbs outside the city's administrative boundaries.
Climate

Leicester experiences a maritime climate with mild to warm summers and cool winters, rain spread throughout the year, and low sunshine levels. The nearest official Weather Station was Newtown Linford, about 5 miles (8.0 km) northwest of Leicester city centre and just outside the edge of the urban area. However, observations stopped there in 2003. The current nearest weather station is Market Bosworth, about 10 miles (16 km) west of the city centre.
The highest temperature recorded at Newtown Linford was 34.5 °C (94.1 °F) during August 1990,[58] although a temperature of 35.1 °C (95.2 °F) was achieved at Leicester University during August 2003.[59] More typically the highest temperature would reach 28.7 °C (83.7 °F) – the average annual maximum.[60] 11.3 °C (52.3 °F) days of the year should attain a temperature of 25.1 °C (77.2 °F) or above.[61]
The lowest temperature recorded at Newtown Linford was −16.1 °C (3.0 °F) during January 1963.[62] Typically, 54.9 air frosts will be recorded during the course of the year.
Rainfall averages 684.4 mm per year,[63] with 1 mm or more falling on 120.8 days.[64] All averages refer to the period 1971–2000.
| Climate data for Newtown Linford, elevation 119 m, 1971–2000, extremes 1960–2003 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 13.6 (56.5) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.9 (75) |
26.5 (79.7) |
31.5 (88.7) |
32.3 (90.1) |
34.5 (94.1) |
27.7 (81.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
16.2 (61.2) |
14.6 (58.3) |
34.5 (94.1) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) |
6.9 (44.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
12.2 (54) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
21.4 (70.5) |
21.1 (70) |
17.7 (63.9) |
13.5 (56.3) |
9.1 (48.4) |
7.1 (44.8) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) |
0.5 (32.9) |
2.1 (35.8) |
3.3 (37.9) |
6.0 (42.8) |
8.7 (47.7) |
10.8 (51.4) |
10.7 (51.3) |
8.8 (47.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
2.8 (37) |
1.3 (34.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −16.1 (3) |
−11.7 (10.9) |
−11.1 (12) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
2.8 (37) |
2.8 (37) |
0.0 (32) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−7.4 (18.7) |
−14.4 (6.1) |
−16.1 (3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 61.65 (2.4272) |
48.91 (1.9256) |
51.86 (2.0417) |
43.86 (1.7268) |
50.83 (2.0012) |
63.07 (2.4831) |
46.08 (1.8142) |
59.25 (2.3327) |
61.50 (2.4213) |
60.58 (2.385) |
60.34 (2.3756) |
68.82 (2.7094) |
684.37 (26.9437) |
| Source: KNMI[65] | |||||||||||||
Government
Leicester is divided into three Parliamentary constituencies, all controlled by the Labour Party : Leicester East, represented by Keith Vaz, Leicester South, represented by Jon Ashworth, and Leicester West represented by Liz Kendall. In April 2011 the then Leicester South MP Sir Peter Soulsby left the House of Commons to seek election as Mayor of Leicester.
On 5 May 2011, Peter Soulsby became the first directly elected Mayor of Leicester.
Before the creation of an elected executive Mayor the post of civic mayor and later Lord Mayor existed. The first mayor of Leicester was a Norman knight, Peter fitz Roger ("Peter, son of Roger") in 1251.[66][67] Following the restoration of city status this title was elevated to "Lord Mayor." In 1987 the first Asian Mayor of Leicester was indirectly elected by the councillors, Councillor Gordhan Parmar.[68] After institution of a directly elected mayor in 2011 the Lord Mayor of Leicester still exists as a ceremonial role under Leicester City Council.[69]
On 1 April 1997, Leicester City Council became a unitary authority. Before then, local government was a two-tier system: the city and county councils were responsible for different aspects of local government services: this system is still in place in the rest of Leicestershire. Leicestershire County Council retained its headquarters at County Hall in Glenfield, just outside the city boundary but within the urban area. The administrative offices of Leicester City Council are in the centre of the city at 115 Charles Street, having moved from Welford Place. The buildings at Welford Place have been demolished and the site is to be developed into a complex of offices and plazas. Some services (particularly the police and the ambulance service) still cover the whole of the city and county/ies, but for the most part the councils are independent.
Leicester is divided into 21 administrative wards: Abbey, Aylestone, Beaumont Leys, Belgrave, Braunstone Park & Rowley Fields, Castle, Evington, Eyres Monsell, Fosse, Humberstone & Hamilton, Knighton, North Evington, Rushey Mead, Saffron, Spinney Hills, Stoneygate, Thurncourt, Troon, Westcotes, Western, and Wycliffe.[70]
After a long period of Labour administration (since 1979), the city council from May 2003 was run by a Liberal Democrat/Conservative coalition under Roger Blackmore, which collapsed in November 2004. The minority Labour group ran the city until May 2005, under Ross Willmott, when the Liberal Democrats and Conservatives formed a new coalition, again under the leadership of Roger Blackmore.
In the local government elections of 3 May 2007, Leicester's Labour Party once again took control of the council in what can be described as a landslide victory. Gaining 18 new councillors, Labour polled on the day 38 councillors, creating a governing majority of +20. Significantly however, the Green Party gained its first councillors in the Castle Ward, after losing on the drawing of lots in 2003, though one of these subsequently resigned and the seat was lost to Labour in a by-election on 10 September 2009.[71] The Conservative Party saw a decrease in their representation. The Liberal Democrat Party was the major loser, dropping from 25 councillors in 2003 to only 6 in 2007.
In the local government elections of 5 May 2011 and those of May 2015, Labour won 52 of the city's 54 seats, with the Conservatives and Liberal Democrats winning one seat each.[72]
Political control
The current composition of Leicester City Council is as follows:
| Party | Seats | |
|---|---|---|
| Labour | 51 | |
| Conservative | 1 | |
| Liberal Democrat | 1 | |
| Independent | 1 | |
Coat of arms

The Corporation of Leicester's coat of arms was first granted to the city at the Heraldic Visitation of 1619, and is based on the arms of the first Earl of Leicester, Robert Beaumont. The charge is a cinquefoil ermine, on a red field, and this emblem is used by the city council.
After Leicester became a city again in 1919, the city council applied to add to the arms. Permission for this was granted in 1929, when the supporting lions, from the Lancastrian Earls of Leicester, were added.
The motto "Semper Eadem" was the motto of Queen Elizabeth I, who granted a royal charter to the city. It means "always the same" but with positive overtones meaning unchanging, reliable or dependable, and united. The crest on top of the arms is a white or silver legless wyvern with red and white wounds showing, on a wreath of red and white. The legless wyvern distinguishes it as a Leicester wyvern as opposed to other wyverns. The supporting lions are wearing coronets in the form of collars, with the white cinquefoil hanging from them.
Demography
Demographic comparatives
In the 2011 census, the population of the Leicester unitary authority was 329,839, an increase of 11.8% compared to the United Kingdom Census 2001 figure of 279,921. The wider Leicester Urban Area,[73] showed an estimated population of 509,000. The population of the Leicester unitary authority is marginally higher than that of Nottingham, while Nottingham has a higher urban area population compared to Leicester. Eurostat's Larger Urban Zone listed the population of the Leicester LUZ at 836,484 (2011) just above that of their East Midland neighbour; metropolitan and city region populations tend to be similar. According to the 2011 census Leicester had the largest proportion of people aged 19-and-under in the East Midlands at 27 per cent. Coventry, to the south west, has a population of 352,900 (2016 est.) compared to Leicester's 348,300 at the same date. Nonetheless, Coventry has an area one third greater than Leicester's, approximately equivalent to a combined 'Leicester + Oadby and Wigston' with a respective population of 404,100 (2016 est.).
The Eurostat regional yearbook 2015 classifies Leicester as one of country's eleven 'Greater Cities', together with Birmingham and Nottingham in the Midlands. Leicester is second only to Bristol as the largest unitary authority city in England (List of English districts by population 2015 estimates), and ninth largest counting both unitary authority cities and cities within metropolitan counties.
| Leicester compared[74] | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| UK Census 2011 | Leicester | East Midlands | England |
| Total population | 329,839 | 4,533,222 | 53,012,456 |
| Foreign born | 33.6% | 9.9% | 13.8% |
| White (2001) | 63.9% | 93.5% | 90.9% |
| White (2011) | 50.6% | 89.3% | 85.5% |
| South Asian (2001) | 29.9% | 4.0% | 4.6% |
| South Asian (2011) | 31.8% | 5.1% | 5.5% |
| Black (2001) | 3.1% | 0.9% | 2.3% |
| Black (2011) | 6.3% | 1.7% | 3.4% |
| Mixed (2001) | 2.3% | 1.9% | 1.3% |
| Mixed (2011) | 3.5% | 1.4% | 2.2% |
| East Asian and Other (2001) | 0.8% | 0.5% | 0.9% |
| East Asian and Other (2011) | 5.3% | 1.3% | 2.2% |
| Christian | 32.4% | 58.8% | 59.4% |
| Muslim | 18.6% | 3.1% | 5.0% |
| No religion | 17.4% | 15.2% | 24.7% |
| Hindu | 15.2% | 2.0% | 1.5% |
| OTHERS | n% | N2% | N3% |
| English as a main language | 69.3% | 93.3% | 90.9% |
In terms of ethnic composition, according to the 2011 census, 50.6% of the population was White (45.1% White British, 0.8% White Irish, 0.1% Gypsy or Irish Traveller, 4.6% Other White), 37.1% Asian (28.3% Indian, 2.4% Pakistani, 1.1% Bangladeshi, 1.3% Chinese, 4.0% Other Asian), 3.5% of mixed race (1.4% White and Black Caribbean, 0.4% White and Black African, 1.0% White and Asian, 0.7% Other Mixed), 6.3% Black (3.8% African, 1.5% Caribbean, 1.0% Other Black), 1.0% Arab and 1.6% of other ethnic heritage.[75]
Christians were the largest religious group in the city in 2011 at 32.4%, with Muslims next (18.6%), followed by Hindus (15.2%), Sikhs (4.4%), Buddhists (0.4%), and Jews (0.1%). In addition, 0.6% belonged to other religions, 22.8% identified with no religion and 5.6% did not respond to the question.[76]
The city is home to places of worship or gathering for all the faith groups mentioned and many of their respective sub-denominations. In the case of Judaism, for example, with only 0.1% declaring it as their faith, the city hosts three active synagogues: one Liberal, one Orthodox and one Messianic.
Leicester is the second fastest growing city in the country.[77]
Languages
A demographic profile of Leicester published by the city council in 2008 noted:
Alongside English, around 70 languages and/or dialects spoken in the city. In addition to English and the primary western and central European languages, eight ethnic languages are sometimes heard: Gujarati is the preferred language of 16% of the city's residents, Punjabi 3%, Somali 4% and Urdu 2%. Other smaller language groups include Hindi, Bengali. With continuing migration into the city, new languages and or dialects from Africa, the Middle East and Eastern Europe are also being spoken in the city.
In certain primary schools in Leicester, English may not be the preferred language of 45% of pupils and the proportion of children whose first language is known, or believed to be, other than English, is significantly higher than other cities in the Midlands or the UK as a whole.[78]
Certain European languages such as Polish will undoubtedly feature in current statistics, although their prevalence may reduce subsequently as future generations rapidly assimilate or return to places of origin, given cultural and geographic proximity and changes in the geo-political environment.
Leicester is believed to be the birthplace of the modern standard English language.[79]
Population change
| Historic and projected Population growth in Leicester since 1901 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 1901 | 1911 | 1921 | 1931 | 1939 | 1951 | 1961 | 1971 | 2001 | 2011 | 2016 | 2021 | 2026 | 2031 | ||
| Population | 211,579 | 227,222 | 234,143 | 239,169 | 261,339 | 285,181 | 273,470 | 284,208 | 279,921 | 329,839 | 348,343 | 362,500 | 376,000 | 390,000 | ||
| Source: A Vision of Britain through Time[80] | ONS[81] | ONS Projections[82] | ||||||||||||||
As one of the fastest growing cities in the country, the ONS 2014 basis population projections indicate the city will be home to 400,000 inhabitants by around 2035.
Economy

Leicester has the largest economy in the East Midlands. A recent study by emda/Experian estimated the GVA to be £15.3 billion.[83] Companies that have their principal offices or significant sites in Leicester and the surrounding area include; Brantano Footwear, Dunelm Mill, Next, Shoe Zone, Everards brewing and associated, KPMG, Mazars, Cambridge & Counties Bank, HSBC and Santander banking, Hastings Insurance, British Gas, British Telecom, Caterpillar (Inc.), Topps Tiles and DHL.[84]
The city has historically had a strong association with the production of textiles, clothing and shoes. While important companies such as Corah, Liberty Shoes and Equity Shoes have closed, companies such as Next and Boden are still active in the city. Moreover, in recent years the higher transport prices and longer lead-times associated with globalised production in Asia mean some textile manufacturers are locating to the city.[85][86]
Engineering
Engineering Companies include Jones & Shipman (machine tools and control systems), Richards Engineering (foundry equipment), Transmon Engineering (materials handling equipment) and Trelleborg (suspension components for rail, marine, and industrial applications). Local commitment to nurturing British engineers includes apprenticeship schemes with local companies, and academic-industrial connections with the engineering departments at Leicester University, De Montfort University, and nearby Loughborough University. Leicester was also home to the famous Gents' of Leicester clock manufacturers.
Shopping
Central Leicester has two primary shopping "malls" – Highcross Leicester and the Haymarket Shopping Centre: - The Haymarket Shopping Centre was opened on the site in 1974, and was the first to be built in the City, with parking for up to 500 cars on several levels, two levels of shopping with bus station, and it is also the site of the Haymarket Theatre. - Highcross Leicester opened in 2008 after work to redevelop "The Shires Centre" was completed at a cost of £350 million (creating 120 stores, 15 restaurants, a cinema, 110,000 m2 of shopping space).
St Martin's Square and the Leicester Lanes area has numerous designer and specialist shops; several of the city's Victorian arcades are located in the same neighbourhood. Leicester Market is the largest outdoor covered market in Europe selling a wide variety of goods.
Central Leicester is the location for several department stores including John Lewis, Debenhams.
The Golden Mile is the name given to a stretch of Belgrave Road renowned for its authentic Indian restaurants, sari shops, and jewellers; the Diwali celebrations in Leicester are focused on this area and are the largest outside the sub-continent[87]
Food and drink
Henry Walker was a successful pork butcher who moved from Mansfield to Leicester in the 1880s to take over an established business in High Street. The first Walker's crisp production line was in the empty upper storey of Walker's Oxford Street factory in Leicester. In the early days the potatoes were sliced by hand and cooked in an ordinary fish and chip fryer. In 1971 the Walker's crisps business was sold to Standard Brands, an American firm, who sold on the company to Frito-Lay. Walker's crisps makes 10 million bags of crisps per day at two factories in Beaumont Leys, and is the UK's largest grocery brand.[88] The Beaumont Leys manufacturing plant is world's largest crisp factory.[89]
Meanwhile, the sausage and pie business was bought out by Samworth Brothers in 1986. Production outgrew the Cobden Street site and pork pies are now manufactured at a meat processing factory and bakery in Beaumont Leys, coincidentally near to the separately owned crisp factories. Sold under the Walker's name and under UK retailers own brands such as Tesco,[90] over three million hot and cold pies are made each week. Henry Walker's butcher shop at 4–6 Cheapside sold Walker's sausages and pork pies until March 2012 when owner Scottish Fife Fine Foods went bust, although the shop is temporarily open and selling Walker's pies for the Christmas 2012 season.[91]
Landmarks

There are ten Scheduled Monuments in Leicester and thirteen Grade I listed buildings: some sites, such as Leicester Castle and the Jewry Wall, appear on both lists.
20th-century architecture: Leicester University Engineering Building (James Stirling & James Gowan : Grd II Listed), Kingstone Department Store, Belgrave Gate (Raymond McGrath : Grd II Listed), National Space Centre tower.
Older architecture:
Parks: Abbey Park, Botanic Gardens, Castle Gardens, Gorse Hill City Farm, Grand Union Canal, Knighton Park, Nelson Mandela Park, River Soar, Victoria Park, Watermead Country Park.
Industry: Abbey Pumping Station, National Space Centre, Great Central Railway.
Places of worship: Holy Cross Priory (Roman Catholic), Shree Jalaram Prarthana Mandal (Hindu temple),[92] the Stake Centre of the LDS Church's Stake, four Christadelphian meeting halls,[93] Jain Centre,[94] Leicester Cathedral, Leicester Central Mosque,[95] Masjid Umar[96] (Mosque),[97] Guru Nanak Gurdwara (Sikh), Neve Shalom Synagogue (Progressive Jewish).
Historic buildings: Town Hall, Guildhall, Belgrave Hall, Jewry Wall, Secular Hall, Abbey, Castle, St Mary de Castro, The City Rooms, Newarke Magazine Gateway.
Shopping: Abbey Lane-grandes surfaces, Beaumont Shopping Centre, Belvoir Street/Market Street, Fosse Shopping Park, Golden Mile, Haymarket Shopping Centre, Highcross, Leicester Lanes, Leicester Market, Oadby, St Martin's Square, Silver Arcade area, Thurmaston Retail Village & Wigston.
Sport: King Power Stadium – Leicester City FC, Welford Road – Leicester Tigers, Grace Road – Leicestershire County Cricket Club, Beaumont Sports Complex - Leicester Lions Speedway, Leicester Sports Arena – Leicester Riders, Saffron Lane sports centre – Leicester Coritanian Athletics Club
Panoramic view; Suburban Leicester WNW viewed from LE1 VII

Transport
Air
East Midlands Airport (EMA), at Castle Donington 20 miles (32 km) north northwest of the City is the closest international airport. The airport is a national hub for mail/freight networks.
Alternatively, Birmingham Airport (BHX),located 38 miles (61 km) west southwest of Central Leicester, is about a 45 to 60 minute drive and can be reached by train, changing at Birmingham (New Street). London Luton Airport (LTN), about 74 miles (119 km) to the southeast, can be reached in 1 h 30 mins to 1 h 45 mins by road or main line train services. Heathrow Airport (LHR) is a 102 miles (164 km) 2 - 3 hour journey to the south by motorway, or rail travelling on East Midlands Trains and LUL/Heathrow Express/Heathrow Connect.
Leicester Airport (LRC) is a small airport some 6 miles (10 km) east of Leicester City Centre and does not currently operate scheduled services.
Note: distances from Every Street, Leicester LE1 VI
Buses
Leicester has two main bus stations: St Margaret's Bus Station and the new and re-commissioned (May 2016) Haymarket Bus Station.
There are three permanent Park and Ride sites at Meynells Gorse (Leicester Forest East), Birstall and Enderby; buses operate every 15 mins from all sites. The park and ride services are branded as quicksilver shuttle and are contracted to Roberts Coaches from the City Council and County Council, buses use a purpose built terminal near St. Nicholas Circle.
The main bus operators for Leicester and the surrounding area are Arriva Fox County, Centrebus, First Leicester, Hinckley Bus (Part of Arriva Midlands), Kinchbus, Leicester Bus, and Stagecoach Midlands.
National Cycle Network
National Cycle Network Route 6 passes through Leicestershire along with other secondary routes. The Leicester Bike Park is in Town Hall Square. 'Cycle Works' Bike Mechanic Training Centre is in Wellington Street Adult Education Centre and former Central Lending Library.
Rail
Mainline rail

The rail network is of growing importance in Leicester, and with the start of Eurostar international services from London St Pancras International in November 2007 Leicester railway station has gained connections at St Pancras station to Lille, Brussels and Paris onwards.
InterCity services are operated by East Midlands Trains providing connectivity on 'fast' and 'semi-fast' services to London and the south east, and to major cities and towns in the East Midlands and Yorkshire in addition to providing local services within the East Midlands region. Trans-regional services to the West Midlands and East Anglia are provided by CrossCountry, enabling connexions at nearby Nuneaton onto the West Coast mainline and at Peterborough with the East Coast mainline.
The 99 miles (159 km) from Leicester Railway Station to London St Pancras International on the Midland Main Line, are covered in an average of 1h 25m during the morning peak, with journey times as low as 1h 06m later in the day. Transfers onto London Underground or Thameslink train services to London City or West End add another 15 to 25 minutes to the journey time and to Canary Wharf, double. The journey time to Sheffield is around one hour, with Leeds and York taking approximately two. Birmingham is 50 minutes away and Cambridge via Peterborough can be reached in around 1 hour 55m with further direct services available onto Stansted Airport in north Essex.
Great Central Railway
The decommissioned Leicester Central railway station is on the late Victorian Great Central Railway line that ran from London Marylebone northwards. Beeching cuts closed the route in the late 1960s. A preserved section, however, remains operational in the East Midlands centred on Loughborough Great Central railway station providing touristic services through central Leicestershire, passing Swithland Reservoir on to the Leicester North railway station terminus.
Road
Leicester is at the midpoint; Junctions 21, 21A and 22, of the primary English north/south M1 motorway between London and Leeds/York. This is where the M1 motorway transects with one of the primary northeast/southwest routes; the M69 motorway/A46 corridor linking to the A1 and M6 motorway at Newark-on-Trent and Coventry respectively. The M42 motorway towards Birmingham Airport terminates in North West Leicestershire some 12 miles (19 km) west northwest of the Leicester urban area.
Leicester is at the nexus of the A6/(A14), A50, A47 and A607 trunk roads and A426 and A5199 primary routes.
Education
Schools
Leicester is home to a number of comprehensive schools and independent schools. There are three sixth form colleges, all of which were previously grammar schools.
The Leicester City Local Education Authority initially had a troubled history when formed in 1997 as part of the local government reorganisation – a 1999 Ofsted inspection found "few strengths and many weaknesses", although there has been considerable improvement since then.
Tudor Grange Samworth Academy an academy whose catchment area includes the Saffron and Eyres Monsell estates, was co-sponsored by the Church of England and David Samworth, chairman of Samworth Brothers pasty makers.
Under the "Building Schools for the Future" project, Leicester City Council has contracted with developers Miller Consortium for £315 million to rebuild Beaumont Leys School, Judgemeadow Community College, the City of Leicester College in Evington, and Soar Valley College in Rushey Mead, and to refurbish Fullhurst Community College in Braunstone.[98]
Leicester City Council underwent a major reorganisation of children's services in 2006, creating a new Children and Young People's Services department.
Tertiary



Leicester is home to two universities, the University of Leicester, which attained its Royal Charter in 1957 and was ranked 12th by the 2009 Complete University Guide,[99] and De Montfort University, which opened in 1969 as Leicester Polytechnic and achieved university status in 1992.
It is also home to the National Space Centre off Abbey Lane, due in part to the University of Leicester being one of the few universities in the UK to specialise in space sciences.
Culture

The city hosts annually a Caribbean Carnival and parade (the largest in the UK outside London), Diwali celebrations, the largest comedy festival in the UK Leicester Comedy Festival and a Pride Parade (Leicester Pride). Belgrave Road, not far from the city centre, is colloquially known as "The Golden Mile" because of the number of Jewellers.
The Leicester International Short Film Festival is an annual event; it commenced in 1996 under the banner title of "Seconds Out". It has become one of the most important short film festivals in the UK and usually runs in early November, with venues including the Phoenix Square.[100][101][102]

Notable arts venues in the city include:
- Curve: Purpose-designed performing arts centre, designed by Rafael Viñoly, opened in Autumn 2008,[103]
- The De Montfort Hall
- The Haymarket Theatre
- The Little Theatre
- The Peepul Centre, Designed by Andrzej Blonski Architects, the £15 million building was opened in 2005 and houses an auditorium, restaurant, cyber café, gym and dance studio for the local people, as well as being used for conferences and events. The centre has even been host to former Prime Minister Gordon Brown and other senior Labour Party figures for hustings during the deputy leadership contest.
- Phoenix Square, which in 2009, replaced the Phoenix Arts Centre.
- The Sue Townsend Theatre - which opened in the former Phoenix Arts Centre.
Museums
 Newarke Houses Museum (Grade II*)
Newarke Houses Museum (Grade II*)


Music
In popular culture
Leicester is the setting for the fictional diaries of Adrian Mole, created by Sue Townsend. In the early books he lives in a suburb of Leicester and attends a local school where he first meets "the love of his life", Pandora Braithwaite.
After a period of years spent working in Oxford and London Mole returns to Leicester and gets a job in a second-hand bookshop and a flat in an "upmarket" development on a swan-infested waterfront which is a barely disguised representation of the area near to St. Nicholas Circle. Vastly in debt he is forced to move to the fictional village of Mangold Parva. The local (fictional) MP for the town of Ashby de la Zouch is none other than his old flame Pandora Braithwaite.
Leicester is the setting for Rod Duncan's novels, the Fall of the Gas-Lit Empire series and the Riot trilogy.
Leicester and the surrounding county are settings for several Graham Joyce novels, including Dark Sister, The Limits of Enchantment and Some Kind of Fairy Tale.
The Clarendon Park and New Walk areas of the city, along with an unnamed Charnwood village ("vaguely based upon Cossington", according to the author) are some of the settings of the 2014 novel "The Knot of Isis" by Chrid McGordon.
Leicester is the setting for the British children book series, The Sleepover Club, by authors Rose Impey, Narinder Dhami, Lorna Read, Fiona Cummings, Louis Catt, Sue Mongredien, Angie Bates, Ginny Deals, Harriet Castor and Jana Novotny Hunter.
Notable feature films made in the city are The Girl with Brains in Her Feet 1997, Jadoo 2013 and Yamla Pagla Deewana 2 2013.
Sport
Leicester Tigers have been the most successful English rugby union club since the introduction of a league in 1987, winning it a record ten times, four more than either Bath or Wasps. They last won the Premiership title in 2013.[104][105]

Leicester City F.C. are a professional football club based at the King Power Stadium who play in the Premier League. They were promoted as champions of the Football League Championship in the 2013–14 season, a return to the top flight of English football after a decade away, and won the Premier League title in 2016, despite the odds of them winning at the start of the season being 5000/1.[106][107][108]
Leicester Riders are the oldest professional basketball team in the country. In 2016, they moved into the new Charter Street Leicester Community Sports Arena.[109]
Leicestershire County Cricket Club who are a professional cricket club based at Grace Road, Leicester currently play in the second tier of the county championship.They won the County Championship in 1996 and 1998.[110]
Public services
In the public sector, University Hospitals Leicester NHS Trust is one of the larger employers in the city, with over 12,000 employees working for the Trust. Leicester City Primary Care Trust employs over 1,000 full and part-time staff providing healthcare services in the city. Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust[111] employs 3,000 staff providing mental health and learning disability services in the city and county.
In the private sector are Nuffield Hospital Leicester and the Spire Hospital Leicester.
Notable people
Local media
Leicester is home to the Leicester Mercury newspaper, and the Midlands Asian Television channel known as MATV Channel 6.

BBC Radio Leicester was the first BBC Local Radio station in Britain, opening on 8 November 1967. Other analogue FM radio stations are Leicester Community Radio for English speaking over 35's, Demon FM which is Leicester's community and student radio station broadcasting from Demontfort University, Takeover Radio is the first ever children's radio station in the UK to be produced and presented by children, Capital FM East Midlands Gem 106, 106.6 Smooth Radio and Hindu Sanskar Radio, which only broadcasts during Hindu religious festivals. BBC Asian Network and Sabras Radio broadcast on AM.
The local DAB multiplex has the following stations:
- Capital FM East Midlands
- BBC Radio Leicester
- Sabras Radio
- Highways Agency Traffic Radio
- XFM
- Classic Gold GEM
- Gem 106
- Asian Plus – also known as Hindu Sanskar Radio
- Takeover Radio
- Smooth Radio
There are two hospital radio stations in Leicester, Radio Fox and Radio Gwendolen.
Twin cities
Leicester is twinned with six cities.[112]
|
Since 1973, the fire services of Leicester and twin city Krefeld have played each other in an annual 'friendly' football match.[115]
References
- ↑ Dan J Martin (21 May 2015). "Ted Cassidy takes the chains as Leicester's new ceremonial lord mayor". Leicester Mercury. Archived from the original on 22 May 2015. Retrieved 11 May 2015.
- ↑ 2011 census
- ↑ Leicester Urban Area 2011
- ↑ Eurostat's Leicester 'Functional Urban Area' 2011: <> (Central) Metropolitan area
- ↑ "2011 Census: Key Statistics for Local Authorities in England and Wales". ONS. Retrieved 25 December 2012
- ↑ "Leicester", Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 28 August 2015
- ↑ "The National forest". The National forest. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ↑ "2011 Leicestershire Census". Leicestershire Statistics and Research. Archived from the original on 20 September 2014. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- ↑ Thompson (1849), Appendix B: Leograceaster—The Saxon Name of Leicester, pp. 448 f.; Thompson (1849), pp. 7 f.
- ↑ Stevenson, W. H. (1918). "A note on the derivation of the name 'Leicester'". The Archaeological Journal. Royal Archaeological Institute (London). 75: 30 , f. Dudley, John (1848). "Etymology of the Name of Leicester". The Gentleman's Magazine. Vol. 184. pp. 580–582. citing Wilford, Asiatick Researches vol. ii. No. 2 (1812), p. 45: "The learned Somner says that the river which runs by it [Leicester] was formerly called Leir by the same contraction [from Legora], and it is probably the river Liar of the anonymous geographer. Mr. Somner, if I be not mistaken, places the original own of Ligora near the source of the Lear, now the Soar".
- ↑ Gelling et al. (eds.), The names of towns and cities in Britain, B. T. Batsford, 1970, p. 122.
- ↑ Geoffrey, Vol. II, Ch. 11.
- ↑ http://archaeologydataservice.ac.uk/archsearch/record.jsf?titleId=1919223 "Archeological Data Service excavation records"
- 1 2 Thompson (1849), Appendix A: Ratæ—Roman Leicester, pp. 443 ff.
- ↑ Tomlin, R S O (1983). "Roman Leicester, a Corrigendum: For Coritani should we read Corieltauvi?". Transactions of the Leicester Archaeological and Historical Society. 48.
- ↑ Tomlin, R S O (1983). "Non Coritani sed Corieltauvi". The Antiquaries Journal. 63. doi:10.1017/s0003581500066579.
- 1 2 "Richard III team makes second Leicester car park find". BBC news Leicester. 4 May 2013. Retrieved 4 May 2013.
- ↑ Nennius (attrib.). Theodor Mommsen (ed.). Historia Brittonum, VI. Composed after AD 830. (in Latin) Hosted at Latin Wikisource.
- ↑ Ford, David Nash. "The 28 Cities of Britain" at Britannia. 2000.
- ↑ Mills, A.D. (1991). A Dictionary of English Place-Names. Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 208. ISBN 0-19-869156-4.
- ↑ Galfridus Monemutensis [Geoffrey of Monmouth]. Historia Regum Britanniæ. c. 1136. (in Latin) J.A. Giles & al. (trans.) as History of the Kings of Britain, Vol. II, Ch. 11 in Six Old English Chronicles. 1842. Hosted at Wikisource.
- ↑ Geoffrey of Monmouth. Lewis Thorpe (trans.) as The History of the Kings of Britain, pp. 81 & 86. Harmondsworth, 1966. William Shakespeare took the name of his King Lear from Geoffrey; there is now a statue of the final scene of Shakespeare's Lear in Watermead Country Park.Paul A. Biggs, Sandra Biggs, Leicestershire & Rutland Walks with Children, Sigma Leisure, 2002, p. 44.
- ↑ Mundill (2002), p265
- ↑ Maddicott 1996, p.15
- ↑ Levy, S (1902), p38-39
- ↑ See Levy, S (1902), p39
- ↑ See Mundill (2002)
- ↑ Charles James Billson, Mediaeval Leicester (Leicester, 1920)
- ↑ e.g., Williamson, David (1998). The National Portrait Gallery History of the Kings and Queens of England. National Portrait Gallery Publications. p. 81.
- ↑ "Richard III dig: Have they found their man in Leicester?".
- ↑ Lawless, Jill (4 February 2013). "Richard III team confirms skeleton found under parking lot is remains of England's king". The Star. j
- ↑ "Official Website of the British Monarchy – Jane". Archived from the original on 1 May 2015.
- ↑ Buchanan Sharp (1980), In contempt of all authority, Berkeley: University of California Press, ISBN 0-520-03681-6, 0520036816 p70-71
- ↑ Sharp, p58-59
- ↑ Sharp, p88
- ↑ "1645:The Storming of Leicester and the Battle of Naseby".
- ↑ Elliott, Malcolm (1979). Victorian Leicester. London and Chichester: Phillimore. p. 26. ISBN 0-85033-327-X.
- ↑ "Chartism in Leicestershire". A Web of English History. Dr Marjie Bloy.
- ↑ Elliott, Malcolm.op cit pages 62 -64 and 124-135
- ↑ William, David (13 October 2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. New Africa Press. p. 127. ISBN 9987160212.
- ↑ "A History of Leicester". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 17 January 2012. Retrieved 2012-01-08.
- ↑ "Poles". www.encyclopedia.chicagohistory.org. Retrieved 2018-02-09.
- ↑ Leicester's Ugandan Asian success story. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ↑ A history of Leicester. Retrieved 28 November 2010.
- ↑ "From Kampala to Leicester". Leicester City Council. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ↑ Lowther, Ed (30 January 2013). "Government warned not to repeat 'folly' of Uganda anti-immigration adverts". BBC. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ↑ "Leicester City Council to thank Indian immigrants". Immigration Matters. 10 September 2012. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ↑ Huttman, Elizabeth D.; editor,; Blauw, Wim; co-editors, Juliet Saltman, (1991). Urban housing segregation of minorities in Western Europe and the United States. Durham: Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0822310600.
- 1 2 "Ugandan Asians advert 'foolish', says Leicester councillor". BBC News. 8 August 2012. Retrieved 7 April 2013.
- ↑ Marett, Valerie (1989). Immigrants settling in the city. Leicester: Leicester University Press. ISBN 978-0718512835.
- ↑ "Forty years ago today: A tyrant's whim boosted our city's fortunes". Leicester Mercury. 4 August 2012. Retrieved 6 April 2017.
- ↑ Equality and Human Rights Commission – home page Archived 30 September 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Research (The University of Manchester)".
- ↑ Research2 Archived 29 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ "Research". cre.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 30 September 2007.
- ↑ http://www.media4diversity.eu/en/content/leicester-multicultural-advisory-group%5Bpermanent+dead+link%5D
- ↑ "August 1990 Maximum". Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "August 2003 Maximum". Archived from the original on 19 August 2003. Retrieved 23 February 2012.
- ↑ "1971-00 Average annual maximum". Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "Max > 25 °C days". Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "Jan 1963 Minimum". Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "1971-00 average rainfall". Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ "1971-00 average raindays". Retrieved 23 February 2011.
- ↑ "Climate Normals and extremes". KNMI. July 2011. Retrieved 26 February 2011.
- ↑ Agnes Johnson Glimpses of ancient Leicester – Page 60 1891 "The first Mayor of Leicester, A.D. 1251.
- ↑ The history of the boroughs and municipal corporations of the ... – Page 229 Henry Alworth Merewether, Archibald John Stephens – 1835 "The mayor of Leicester and his brethren, having, with the consent of the commonalty, by the last ordinance, placed the town under the government of the aldermen, appear, in the 4th year of the reign of King Henry VII., to have adopted 1488. a ..."
- ↑ What participation by foreign residents in public life at local ... – Page 91 Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of Europe – 2000 "In 1981 serious riots broke out in the city that were dubbed "race riots" in Highfields and the City centre. ... In 1987 the first Asian Mayor of Leicester was elected, Councillor Gordhan Parmar and the first Asian Member of Parliament, Keith Vaz
- ↑ "Leicester's elected mayor reports lord mayor over parking". BBC. August 2011.
- ↑ "Leicester City Mayor and Councillors Archived 21 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine.", Leicester City Council, July 2016. Retrieved 13 January 2017
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 4 February 2010. Retrieved 2010-02-17.
- ↑ "Elections and voting".
- ↑ "2011 Census - Built-up areas". ONS. Retrieved 8 September 2013.
- ↑ United Kingdom Census 2001 (2001). "Leicester (Local Authority)". neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk. Retrieved 28 December 2007.
- ↑ "2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales". ONS. Retrieved 12 December 2012.
- ↑ "2011 Census: Religion, local authorities in England and Wales". United Kingdom Census 2011. Office for National Statistics.
- ↑ "Our fast-growing city needs backing from Government". Leicester Mercury. Archived from the original on 23 June 2015. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ "The Diversity of Leicester May 2008, A Demographic Profile". Leicester City Council. Archived from the original on 8 January 2009. Retrieved 16 November 2008.
- ↑ "BBC News | UK | Leicester's legacy to the world?". news.bbc.co.uk. Retrieved 2017-08-17.
- ↑ http://www.visionofbritain.org.uk/data_cube_table_page.jsp?data_theme=T_POP&data_cube=N_TPop&u_id=10042744&c_id=10001043&add=N
- ↑ mid year estimate
- ↑ ONS population projections 2014 base / projections uplifted by '21-1,800/'26-2,100/'36-2,500 given underestimation at 2016 - 2,250/
- ↑ "Welcome prospectleicestershire.co.uk - BlueHost.com". Archived from the original on 14 August 2009. Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ "Cat - Products & Services – Europe - Caterpillar".
- ↑ "Leicester in spotlight for textiles boost". Leicester Mercury. 11 January 2011. Archived from the original on 5 May 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ↑ "Far Eastern costs boost textile firm". Leicester Mercury. 15 September 2010. Archived from the original on 5 May 2013. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ↑ Panesar, Jeevan (13 October 2006); "Diwali in Leicester, BBC, Accessed 25 January 2011.
- ↑ Walkers Crisps, Coming to the crunch Archived 12 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine. – The Manufacturer, October 2006
- ↑ "404".
- ↑ "Walker & Son". Samworth Brothers. Retrieved 30 March 2017.
- ↑ Mack, Tom (15 December 2012); "Temporary pop-up Walkers pork pie shop to open in Cheapside, Leicester, for Christmas Archived 17 December 2012 at the Wayback Machine., Leicester Mercury, Accessed 17 December 2012.
- ↑ "Leicester 360° Images – 360-degree tour of Shree Jalaram Prathana Mandal". BBC. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ↑ "Leicester Christadelphians". Leicester Christadelphians. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ↑ "Leicester 360° Images – 360-degree tour of Jain Centre". BBC. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ↑ "islamiccentre.org". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ "Masjid Umar - Leicester". Retrieved 29 June 2015.
- ↑ "Leicester – In Pictures – Masjid Umar mosque". BBC. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ↑ Schools building deal is signed and sealed Archived 13 May 2015 at the Wayback Machine. – Leicester Mercury, 19 December 2007
- ↑ "The main league table 2009". The Independent. 23 April 2008.
- ↑ Pascale, Adele (2 November 2005). "Leicester Short Film Festival: CAN 2005". BBC Leicester.
- ↑ Barry Turner. The Screenwriter's Handbook 2010. Palgrave Macmillan. 2009. Page 218. (The Screenwriter's Handbook 2009, p 232).
- ↑ Turner, Robin (7 March 2013). "So Where's the Main Threat to the Welsh Bid to Be City of Culture?". Western Mail.
- ↑ "Curve website". Archived from the original on 14 July 2006.
- ↑ Farmer, Stuart; Hands, David. Tigers - Official history of Leicester Football Club. The Rugby DevelopmentFoundation. p. 16. ISBN 978-0-9930213-0-5.
- ↑ Osborne, Chris (25 May 2013). "Aviva Premiership final: Leicester 37-17 Northampton". BBC Sport. Retrieved 20 June 2013.
- ↑ "Bookies set to hand over £15m if Leicester win title". ITV News. 2 May 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ↑ Rayner, Gordon; Brown, Oliver. "Leicester City win Premier League and cost bookies biggest ever payout". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 2 May 2016.
- ↑ Wood, Greg (3 May 2016). "The 5,000-1 payouts on Leicester only tell part of Premier League betting story". The Guardian. Retrieved 6 May 2016.
- ↑ Leicester Riders web site club history. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- ↑ Leiscestershire County Cricket Club web site. Retrieved May 18, 2016.
- ↑ "Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust - Home".
- ↑ "Twinning". Leicester City council. Archived from the original on 2 October 2010. Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- ↑ "Strasbourg, Twin City". Strasbourg.eu & Communauté Urbaine. Archived from the original on 28 July 2013. Retrieved 21 August 2013.
- ↑ "British towns twinned with French towns [via WaybackMachine.com]". Archant Community Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 5 July 2013. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
- ↑ Brown, Tom (31 July 2013). "Twin towns: Do we still need them?". BBC East Midlands Today. BBC News. Retrieved 7 August 2013.
- Secondary sources
- Biggs, Paul A.; Biggs, Sandra (2002). Leicestershire & Rutland Walks with Children. Sigma Leisure.
- Dudley, John (1848). "Etymology of the Name of Leicester". The Gentleman's Magazine. Vol. 184.
- Gelling; et al., eds. (1970). The names of towns and cities in Britain. B. T. Batsford.
- Hoskins, W. G. (1957). Leicestershire: an illustrated essay on the history of the landscape. London: Hodder & Stoughton.
- Pascale, Adele (2 November 2005). "Leicester Short Film Festival: CAN 2005". BBC Leicester.
- Sharp, Buchanan (1980). In contempt of all authority. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 58–59, 70–1, 88. ISBN 0-520-03681-6.
- Levy, S. "Notes on Leicester Jewry." Transactions (Jewish Historical Society of England) 5 (1902): 34-42. https://www.jstor.org/stable/29777626
- Geoffrey of Monmouth (1966). Thorpe, Lewis, ed. The History of the Kings of Britain. Harmondsworth.
- Robin R. Mundill (2002), England's Jewish Solution, Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-52026-3, OL 26454030M
- * Stevenson, W. H. (1918). "A note on the derivation of the name 'Leicester'". The Archaeological Journal. Royal Archaeological Institute (London). 75.
- Tomlin, R S O (1983). "Roman Leicester, a Corrigendum: For Coritani should we read Corieltauvi?". Transactions of the Leicester Archaeological and Historical Society: 48.
- Tomlin, R S O (1983). "Non Coritani sed Corieltauvi". The Antiquaries Journal: 63. doi:10.1017/s0003581500066579.
- Nennius. Mommsen, Theodor, ed. "Historia Brittonum" (in Latin). VI: 830.
- Turner, Barry (2009). The Screenwriter's Handbook 2010. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 218.
- Wilford, J. (1812). "History of Leicester". Asiatick Researches. ii. (2).
- William, David (13 October 2010). UK Cities: A Look at Life and Major Cities in England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. New Africa Press. ISBN 9987160212.
- Williamson, David (1998). The National Portrait Gallery History of the Kings and Queens of England. National Portrait Gallery Publications.
- Newspapers
- Turner, Robin (7 March 2013). "So Where's the Main Threat to the Welsh Bid to Be City of Culture?". Western Mail.
- Martin, Dan J. (21 May 2015). "Ted Cassidy takes the chains as Leicester's new ceremonial lord mayor". Leicester Mercury.
- BBC news Leicester (4 May 2013). "Richard III team makes second Leicester car park find".
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Leicester. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Leicester. |