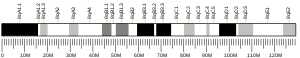
Function
This gene is a member of the bestrophin gene family of anion channels. Bestrophin genes share a similar gene structure with highly conserved exon-intron boundaries, but with distinct 3' ends. Bestrophins are transmembrane proteins that contain a homologous region rich in aromatic residues, including an invariant arg-phe-pro motif. Mutation in one of the family members (bestrophin 1) is associated with vitelliform macular dystrophy. The bestrophin 2 gene is mainly expressed in the non-pigmented ciliary epithelium and colon.[7][8]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000039987 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000052819 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Stohr H, Marquardt A, Nanda I, Schmid M, Weber BH (May 2002). "Three novel human VMD2-like genes are members of the evolutionary highly conserved RFP-TM family". Eur J Hum Genet. 10 (4): 281–284. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200796. PMID 12032738.
- ↑ Pifferi S, Pascarella G, Boccaccio A, Mazzatenta A, Gustincich S, Menini A, Zucchelli S (Aug 2006). "Bestrophin-2 is a candidate calcium-activated chloride channel involved in olfactory transduction". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 103 (34): 12929–12934. doi:10.1073/pnas.0604505103. PMC 1568948. PMID 16912113.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: BEST2 bestrophin 2".
- ↑ Marmorstein AD, Cross HE, Peachey NS (May 2009). "Functional roles of bestrophins in ocular epithelia". Prog Retin Eye Res. 28 (3): 206–226. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2009.04.004. PMC 2740978. PMID 19398034.
Further reading
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–45. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Tsunenari T, Sun H, Williams J, et al. (2003). "Structure-function analysis of the bestrophin family of anion channels". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (42): 41114–41125. doi:10.1074/jbc.M306150200. PMC 2885917. PMID 12907679.
- Sun H, Tsunenari T, Yau KW, Nathans J (2002). "The vitelliform macular dystrophy protein defines a new family of chloride channels". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (6): 4008–4013. doi:10.1073/pnas.052692999. PMC 122639. PMID 11904445.
- Marquardt A, Stöhr H, Passmore LA, et al. (1998). "Mutations in a novel gene, VMD2, encoding a protein of unknown properties cause juvenile-onset vitelliform macular dystrophy (Best's disease)". Hum. Mol. Genet. 7 (9): 1517–1525. doi:10.1093/hmg/7.9.1517. PMID 9700209.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, et al. (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–156. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–174. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.