Ratchaburi Province
| Ratchaburi ราชบุรี | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Province | |||
| |||
 Map of Thailand highlighting Ratchaburi Province | |||
| Country | Thailand | ||
| Capital | Ratchaburi | ||
| Government | |||
| • Governor | Chaiwat Chuenkosum (since April 2017) | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 5,196.5 km2 (2,006.4 sq mi) | ||
| Area rank | Ranked 43rd | ||
| Population (Ranked 28th) | |||
| • Total | 871,714 | ||
| • Density | 170/km2 (430/sq mi) | ||
| • Density rank | Ranked 22nd | ||
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) | ||
| ISO 3166 code | TH-70 | ||

Ratchaburi (Thai: ราชบุรี, pronounced [râːt.t͡ɕʰā.bū.rīː]) or "Rat Buri" (pronounced [râːt bū.rīː]) is one of the western provinces (changwat) of Thailand. Neighbouring provinces are (from north clockwise) Kanchanaburi, Nakhon Pathom, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram and Phetchaburi. In the west it borders the Tanintharyi Division of Myanmar.
Ratchaburi is 80 kilometres west of Bangkok and borders Burma to the west with the Tanaosi Range as a natural border.[1] The Mae Klong River flows through the centre of Ratchaburi town.
Geography

Ratchaburi Province is a medium-sized province with an area of about 5,196 km2. The eastern part of the province contains the flat river plains of the Mae Klong River, crisscrossed by many khlongs. The most famous tourist spot in this area are the floating markets of Damnoen Saduak. The west of the province is more mountainous, and includes the Tanawsri mountain range. As the mountains are made mostly of limestone, there are several caves containing stalactites. Some caves are inhabited by large colonies of bats, and it is an impressive sight when they swarm out in the evening to feed. Other caves like the Khao Bin are accessible for visitors. The main river of the western part is the Phachi River.
On the left bank of the Phachi River is the Chaloem Phra Kiat Thai Prachan National Park.
The area of Ratchaburi province is divided into three parts. First, the border in the west which is shared with Burma and is about 60 km long. The second contains the Tenasserim mountains and forests with an elevation of about 200–300 meters. The central area of the province is rich in wetlands due to river flow. Ratchaburi has important natural resources are forest which it have area about 38% of the province. Moreover, it has minerals such as tin, tantalum, feldspar, quartz, limestone, and marlstone.[2]
History

The history of the city of Ratchaburi dates back to the Dvaravati period, when it was an important city of the Mon Kingdom. Of the city of Khu Bua nearby only ruins remains. According to legend it dates back to the mythical Suvannabhumi Kingdom predating Dvaravati.
"Ratchaburi" means 'the land of the king'.[3] Ratchaburi dates back to ancient times and was important during the Dvaravati period. The city of Ratchburi is on the banks of the Mae Klong River and was a town of the Suvarnabhumi Kingdom.
Demographics
Hill tribes, mostly Karen living near the Myanmar border, make up about one percent of the population. Some Mon, Lawa, Lao, Chinese and Khmer minorities live in the province.[4]
Ratchaburi is 98.3 percent Buddhist.[5]:Table 4
Symbols
The provincial seal shows the royal sword above the royal sandals on a phan (tray), as the name Ratchaburi means "city of the king". The name derives from the fact that King Rama I was born here. The provincial slogan is Beautiful women of Photharam, beautiful women of Baan Pong, the city of earthenware jars, shadow plays at Wat Khanon, magnificent caves, floating market at Damnoen, bats, delicious Yii Sok fish.[6]
The provincial flower is the Pink Shower Tree (Cassia bakeriana), and the provincial tree is Wrightia pubescens.
Administrative divisions
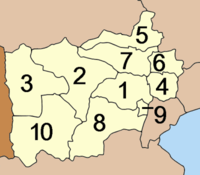
The province is divided into 10 districts (amphoe).[7] The districts are further subdivided into 104 sub-districts (tambons) and 935 villages (mubans).
|
|
There are three towns (thesaban mueang), Ratchaburi, Ban Pong and Photharam, and 11 townships (thesaban tambon).
Transportation
Rail
The main railway station in Ratchaburi is Ratchaburi Railway Station.
Health
Ratchaburi Hospital is the main hospital of the province.
References
- ↑ "Ratchaburi". Tourist Authority of Thailand (TAT). Archived from the original on 2015-05-20. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- ↑ "Ratchaburi have important "natural resources"". Retrieved 4 Nov 2013.
- ↑ Choomjit, Y. (1994). History of Ratchaburi. Bangkok: Odienstore.
- ↑ Svasti, Pichaya (14 September 2017). "Time-travelling along the Mae Klong River". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 16 September 2017.
- ↑ "Population by religion, region and area, 2015" (PDF). National Statistical Office (NSO). Retrieved 2017-10-12.
- ↑ "Welcome to Ratchaburi Province, Thailand". Welcome to Ratchaburi Province, Thailand. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 28 May 2015.
- ↑ Ratchaburi is divided into "10 districts", Retrieved 4 Nov 2013, from http://www.encyclopediathai.org/sunthai/center/ratburi/ratburi.htm Archived 2012-12-15 at the Wayback Machine.
External links

- Ratchaburi Thai Only
- English Website of Province Archived May 6, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- Ratchaburi Samanachan Archived March 31, 2012, at the Wayback Machine.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ratchaburi Province. |
Coordinates: 13°31′44″N 99°48′52″E / 13.52889°N 99.81444°E

