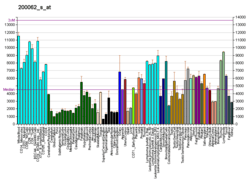
60S ribosomal protein L30
60S ribosomal protein L30 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL30 gene.[5][6]
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the 60S subunit. The protein belongs to the L30E family of ribosomal proteins. It is located in the cytoplasm. This gene is co-transcribed with the U72 small nucleolar RNA gene, which is located in its fourth intron. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000156482 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000058600 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Feo S, Davies B, Fried M (Jun 1992). "The mapping of seven intron-containing ribosomal protein genes shows they are unlinked in the human genome". Genomics. 13 (1): 201–207. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(92)90221-D. PMID 1577483.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RPL30 ribosomal protein L30".
Further reading
- Wool IG, Chan YL, Glück A (1996). "Structure and evolution of mammalian ribosomal proteins". Biochem. Cell Biol. 73 (11–12): 933–947. doi:10.1139/o95-101. PMID 8722009.
- Kato S, Sekine S, Oh SW, et al. (1995). "Construction of a human full-length cDNA bank". Gene. 150 (2): 243–250. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90433-2. PMID 7821789.
- Kenmochi N, Kawaguchi T, Rozen S, et al. (1998). "A map of 75 human ribosomal protein genes". Genome Res. 8 (5): 509–23. doi:10.1101/gr.8.5.509. PMID 9582194.
- Yoshihama M, Uechi T, Asakawa S, et al. (2002). "The human ribosomal protein genes: sequencing and comparative analysis of 73 genes". Genome Res. 12 (3): 379–390. doi:10.1101/gr.214202. PMC 155282. PMID 11875025.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, et al. (2004). "A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway". Nat. Cell Biol. 6 (2): 97–105. doi:10.1038/ncb1086. PMID 14743216.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–2127. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Beausoleil SA, Villén J, Gerber SA, et al. (2006). "A probability-based approach for high-throughput protein phosphorylation analysis and site localization". Nat. Biotechnol. 24 (10): 1285–1292. doi:10.1038/nbt1240. PMID 16964243.
- De Bortoli M, Castellino RC, Lu XY, et al. (2006). "Medulloblastoma outcome is adversely associated with overexpression of EEF1D, RPL30, and RPS20 on the long arm of chromosome 8". BMC Cancer. 6: 223. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-6-223. PMC 1578584. PMID 16968546.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.