60S ribosomal protein L28
60S ribosomal protein L28 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL28 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
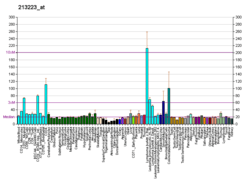
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the 60S subunit. The protein belongs to the L28E family of ribosomal proteins. It is located in the cytoplasm. Variable expression of this gene in colorectal cancers compared to adjacent normal tissues has been observed, although no correlation between the level of expression and the severity of the disease has been found. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome.[7]
References
- 1 2 3 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108107 - Ensembl, May 2017
- 1 2 3 GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030432 - Ensembl, May 2017
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ "Mouse PubMed Reference:".
- ↑ Frigerio JM, Dagorn JC, Iovanna JL (Jul 1995). "Cloning, sequencing and expression of the L5, L21, L27a, L28, S5, S9, S10 and S29 human ribosomal protein mRNAs". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1262 (1): 64–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4781(95)00045-i. PMID 7772601.
- ↑ Kenmochi N, Kawaguchi T, Rozen S, Davis E, Goodman N, Hudson TJ, Tanaka T, Page DC (Aug 1998). "A map of 75 human ribosomal protein genes". Genome Res. 8 (5): 509–23. doi:10.1101/gr.8.5.509. PMID 9582194.
- 1 2 "Entrez Gene: RPL28 ribosomal protein L28".
External links
- Human RPL28 genome location and RPL28 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Wool IG, Chan YL, Glück A (1996). "Structure and evolution of mammalian ribosomal proteins". Biochem. Cell Biol. 73 (11–12): 933–47. doi:10.1139/o95-101. PMID 8722009.
- Brown JR, Daar IO, Krug JR, Maquat LE (1985). "Characterization of the functional gene and several processed pseudogenes in the human triosephosphate isomerase gene family". Mol. Cell. Biol. 5 (7): 1694–706. doi:10.1128/mcb.5.7.1694. PMC 367288. PMID 4022011.
- Kato S, Sekine S, Oh SW, et al. (1995). "Construction of a human full-length cDNA bank". Gene. 150 (2): 243–50. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90433-2. PMID 7821789.
- Bortoluzzi S, d'Alessi F, Romualdi C, Danieli GA (2002). "Differential expression of genes coding for ribosomal proteins in different human tissues". Bioinformatics. 17 (12): 1152–7. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1152. PMID 11751223.
- Mammalian Gene Collection Program Team; Strausberg, R. L.; Feingold, E. A.; Grouse, L. H.; et al. (2002). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 99 (26): 16899–16903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kasai H, Nadano D, Hidaka E, et al. (2003). "Differential expression of ribosomal proteins in human normal and neoplastic colorectum". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 51 (5): 567–74. doi:10.1177/002215540305100502. PMID 12704204.
- Odintsova TI, Müller EC, Ivanov AV, et al. (2004). "Characterization and analysis of posttranslational modifications of the human large cytoplasmic ribosomal subunit proteins by mass spectrometry and Edman sequencing". J. Protein Chem. 22 (3): 249–58. doi:10.1023/A:1025068419698. PMID 12962325.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Villacé P, Marión RM, Ortín J (2004). "The composition of Staufen-containing RNA granules from human cells indicates their role in the regulated transport and translation of messenger RNAs". Nucleic Acids Res. 32 (8): 2411–20. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh552. PMC 419443. PMID 15121898.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, et al. (2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, et al. (2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.