Charleston County, South Carolina
Charleston County is located in the U.S. state of South Carolina along the Atlantic coast. As of the 2010 census, its population was 350,209,[1] making it the third most populous county in South Carolina (behind Greenville and Richland counties). Its county seat is Charleston.[2] The county was created in 1901 by an act of the South Carolina State Legislature.
Charleston County | |
|---|---|
 Charleston County Courthouse | |
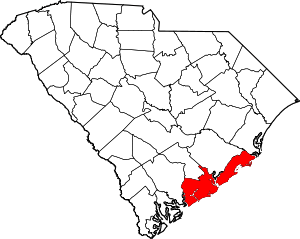 Location within the U.S. state of South Carolina | |
 South Carolina's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 32°49′N 79°54′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1769 |
| Seat | Charleston |
| Largest city | Charleston |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,358 sq mi (3,520 km2) |
| • Land | 916 sq mi (2,370 km2) |
| • Water | 442 sq mi (1,140 km2) 33% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 350,209 |
| • Estimate (2019) | 411,406 |
| • Density | 260/sq mi (100/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional districts | 1st, 6th |
| Website | www |
Charleston County is included in the Charleston- North Charleston, SC Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Geography
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 1,358 square miles (3,520 km2), of which 916 square miles (2,370 km2) is land and 442 square miles (1,140 km2) (33%) is water.[3] It is the largest county in South Carolina by total land and water area.
Adjacent counties
- Berkeley County - north
- Georgetown County - northeast
- Colleton County - west
- Dorchester County - northwest
National protected areas
- Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge
- Charles Pinckney National Historic Site
- Ernest F. Hollings ACE Basin National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Fort Moultrie National Monument
- Fort Sumter National Monument
- Francis Marion National Forest (part)
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 66,985 | — | |
| 1800 | 57,480 | −14.2% | |
| 1810 | 63,179 | 9.9% | |
| 1820 | 80,212 | 27.0% | |
| 1830 | 86,338 | 7.6% | |
| 1840 | 82,661 | −4.3% | |
| 1850 | 72,805 | −11.9% | |
| 1860 | 70,100 | −3.7% | |
| 1870 | 88,863 | 26.8% | |
| 1880 | 102,800 | 15.7% | |
| 1890 | 59,903 | −41.7% | |
| 1900 | 88,006 | 46.9% | |
| 1910 | 88,594 | 0.7% | |
| 1920 | 108,450 | 22.4% | |
| 1930 | 101,050 | −6.8% | |
| 1940 | 121,105 | 19.8% | |
| 1950 | 164,856 | 36.1% | |
| 1960 | 216,382 | 31.3% | |
| 1970 | 247,650 | 14.5% | |
| 1980 | 276,974 | 11.8% | |
| 1990 | 295,039 | 6.5% | |
| 2000 | 309,969 | 5.1% | |
| 2010 | 350,209 | 13.0% | |
| Est. 2019 | 411,406 | [4] | 17.5% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[5] 1790-1960[6] 1900-1990[7] 1990-2000[8] 2010-2015[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[9] of 2000, there were 309,969 people, 143,326 households, and 97,448 families residing in the county. The population density was 338 people per square mile (130/km²). There were 141,031 housing units at an average density of 154 per square mile (59/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 61.9% White, 34.5% Black or African American, 0.26% Native American, 1.12% Asian, 0.06% Pacific Islander, 0.99% from other races, and 1.16% from two or more races. 2.40% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 9.6% were of American, 9.5% English, 9.1% German and 7.6% Irish ancestry.
There were 123,326 households out of which 28.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 43.20% were married couples living together, 15.90% had a female householder with no husband present, and 37.20% were non-families. 28.30% of all households were made up of individuals and 8.10% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.42 and the average family size was 3.01.
In the county, the age distribution of the population shows 23.70% under the age of 18, 12.00% from 18 to 24, 30.30% from 25 to 44, 22.00% from 45 to 64, and 11.90% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 34 years. For every 100 females, there were 93.50 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.50 males.
The median income for a household in the county is $37,810, and the median income for a family was $47,139. Males had a median income of $32,681 versus $25,530 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,393. About 12.40% of families and 16.40% of the population were below the poverty line, including 22.90% of those under age 18 and 12.70% of those age 65 or over.
In the 2000 census, the county population was classified as about 86% urban. The Charleston-North Charleston Metropolitan Statistical Area includes the populations of Charleston, Berkeley, and Dorchester counties.
2010 census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 350,209 people, 144,309 households, and 85,692 families residing in the county.[10] The population density was 382.3 inhabitants per square mile (147.6/km2). There were 169,984 housing units at an average density of 185.6 per square mile (71.7/km2).[11] The racial makeup of the county was 64.2% white, 29.8% black or African American, 1.3% Asian, 0.3% American Indian, 0.1% Pacific islander, 2.7% from other races, and 1.6% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 5.4% of the population.[10] In terms of ancestry, 11.3% were German, 11.0% were English, 10.2% were Irish, and 9.8% were American.[12]
Of the 144,309 households, 27.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 40.5% were married couples living together, 14.7% had a female householder with no husband present, 40.6% were non-families, and 30.1% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.36 and the average family size was 2.96. The median age was 35.9 years.[10]
The median income for a household in the county was $48,433 and the median income for a family was $61,525. Males had a median income of $42,569 versus $34,195 for females. The per capita income for the county was $29,401. About 11.5% of families and 16.5% of the population were below the poverty line, including 24.5% of those under age 18 and 10.8% of those age 65 or over.[13]
Government
From 1895 to 1973, when the state constitution was amended to provide for home rule in the counties, the counties had limited powers, under what was called "county purpose doctrine."[14] Essentially they were governed by the General Assembly through their state legislative delegation and, with one state senator per county, the state senator was particularly powerful. In the 1940s, Charleston County adopted a council-manager form of county government to better handle its needs.[15] In 1975 the state's Home Rule Act established a larger role for the county governments.
Charleston County has a large geographic area represented by a nine-member county council. Into the 1960s, most African Americans were excluded from voting by the state's disenfranchising constitution and practices. This gradually changed after passage of the federal Voting Rights Act of 1965.
Since 1969, members of the county commission were elected in a modified at-large system for nine seats, with elections every two years for staggered four-year terms, from four residency districts. Three Council seats are reserved for residents of the City of Charleston, three for residents of North Charleston, two for residents of West Ashley, and one for a resident of East Cooper.[16][17] The council elects a chairman from its members for a limited term of two years, but chairs can be re-elected. Charleston County was "one of only three counties in South Carolina to elect its entire county council at-large. It was "the only county with a majority white population to do so."[16] At-large positions favors candidates who can attract a majority of the votes, reducing representation from smaller portions of the population or geographic area.
In 1989 county residents proposed a referendum to change representation on the county council to election from single-member districts, which would have provided more opportunity for the sizable minority to elect candidates of their choice. This proposal was narrowly defeated in what both the county and the US government later defined as a racially polarized election. It was supported by 98% of the African-American minority voters; 75% of the white-majority voters rejected the referendum.[17] In practice, the at-large system resulted in the dilution of votes of the significant minority of African-American voters, who comprise more than one-third of the electorate. In practice, the minority voters were unable to elect a candidate of their choice in all but a few elections in the three decades since the system was established.[17]
In January 2001, the US Department of Justice filed suit against the county government for racial discrimination based on the at-large system, which the suit contended violates Sec.2 of the Voting Rights Act of 1965 by diluting voting power.[18] The Department had tried to negotiate with the county over changes in November 2000. Four voters independently filed suit as plaintiffs against the County on the same basis, and the District Court combined the cases. Justice officials noted that the at-large seats dilute the voting strength of the African-American minority in the county, who in 2000 comprised 34.5% of the population. In all but a few cases over three decades, they have been unable to elect candidates of their choice to the county commission. Whites (European Americans) comprise 61.9 percent of the population in the county.[9] Since the late 20th century, the white majority has elected Republican Party candidates.
The DOJ officials noted that the voting preference issue is not just a question of ethnicity; voters in black precincts in the county had rejected a Republican African American as a candidate for the council; they supported the Democratic at-large candidate. The suit noted that historically, black and white precincts in Charleston County have consistently supported different candidates for the Council. It noted that, because of the white majority and the large geographic area, which increases costs for campaigning, "white bloc voting usually results in the defeat of candidates who are preferred by black voters."[18] DOJ noted that blacks lived in compact areas of the county, were cohesive in voting, and could comprise the majority in three districts if the county seats were apportioned as nine single-member districts. They could vote and gain representation proportional to their part of the citizenry.[18]
In United States v. Charleston County, SC (March 2003), the District Court ruled that Charleston County improperly diluted the voting strength of African-American voters "by maintaining an at-large voting system in a manner which violated Section 2." It enjoined the county from using that system, noting that the "Order is radically not a condemnation of the citizenry of Charleston County but rather a recognition that the specific bulwark of an at-large system, in twisted concert with the particular geographic and historical realities of this County, unlawfully and institutionally inhibit a community of voters in Charleston County from equal access to the electoral process."[19]
The county appealed. In July 2003, the 4th Circuit Appeals Court found that historic voting in the county was racially polarized and that minority candidates had mostly not been successful in seeking office, two conditions that related to satisfying the law.[17] As of July of that year, the 4th Circuit Court affirmed the District Court's ruling,[20] and on 29 April 2004 issued its written decision affirming the District Court.[16] Based on historical and economic analysis, the courts found that race was a more important issue than partisanship in influencing the outcome of the elections.[16] The county appealed to the US Supreme Court, and a certiorari was denied in November 2004.[21]
The County Council system was changed in 2004 to elect individuals from nine single-member districts, with members serving four-year staggered terms. As of January 2015, elected members of the council include 4 White Republicans, 2 White Democrats and 3 African-American Democrats.[22] Republican Elliott Summey was elected by council members as chairman, replacing Democrat Teddie Pryor, who had served for six years. Summey had served as his vice-chair for five years. Pryor was first elected to the council in 2004. Summey was first elected in 2008.[23]
Politics
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 42.8% 75,443 | 50.6% 89,299 | 6.6% 11,603 |
| 2012 | 48.0% 77,629 | 50.4% 81,487 | 1.6% 2,591 |
| 2008 | 45.2% 69,822 | 53.6% 82,698 | 1.2% 1,914 |
| 2004 | 51.6% 70,297 | 46.8% 63,758 | 1.7% 2,261 |
| 2000 | 52.2% 58,229 | 44.4% 49,520 | 3.3% 3,727 |
| 1996 | 50.3% 48,675 | 45.1% 43,571 | 4.6% 4,442 |
| 1992 | 48.0% 47,403 | 40.6% 40,095 | 11.4% 11,251 |
| 1988 | 59.3% 49,149 | 39.8% 32,977 | 1.0% 790 |
| 1984 | 63.8% 53,779 | 35.0% 29,481 | 1.2% 1,000 |
| 1980 | 55.1% 44,111 | 40.9% 32,727 | 4.0% 3,174 |
| 1976 | 49.2% 34,010 | 49.6% 34,328 | 1.2% 817 |
| 1972 | 68.8% 39,863 | 29.1% 16,855 | 2.1% 1,229 |
| 1968 | 43.5% 24,282 | 32.8% 18,343 | 23.7% 13,255 |
| 1964 | 69.1% 32,509 | 30.9% 14,564 | |
| 1960 | 63.9% 21,223 | 36.1% 12,010 | |
| 1956 | 29.9% 7,487 | 16.1% 4,028 | 54.1% 13,558 |
| 1952 | 66.9% 20,087 | 33.2% 9,959 | |
| 1948 | 4.1% 562 | 19.2% 2,660 | 76.8% 10,671 |
| 1944 | 13.8% 1,184 | 73.0% 6,260 | 13.3% 1,137 |
| 1940 | 14.4% 1,372 | 85.6% 8,145 | |
| 1936 | 5.0% 417 | 95.1% 8,015 | |
| 1932 | 7.7% 451 | 91.7% 5,351 | 0.5% 31 |
| 1928 | 29.0% 1,759 | 70.8% 4,298 | 0.3% 18 |
| 1924 | 11.9% 361 | 84.5% 2,554 | 3.6% 108 |
| 1920 | 11.3% 373 | 88.4% 2,929 | 0.4% 13 |
| 1916 | 6.3% 129 | 93.6% 1,929 | 0.1% 2 |
| 1912 | 1.8% 34 | 90.4% 1,760 | 7.9% 154 |
| 1904 | 10.0% 195 | 90.0% 1,750 | |
| 1900 | 13.6% 271 | 86.5% 1,729 |
Emergency services
Volunteer Rescue Squad
The Volunteer Rescue Squad is a volunteer organization consisting of over 50 members and a medical control physician. Members are certified in a variety of emergency skills, including auto extrication, structural collapse/urban search and rescue, diving, large animal rescue, rural search and rescue, and high angle / technical rescue. In addition, many squad members are First Responders, EMT's and Paramedics. The current chief of the squad is Chief Brian Hinton. Hinton is a police officer for the City of Charleston Police Department. Charleston County Volunteer Rescue Squad Website
EMS And Local Hospitals
Emergency medical services (EMS) for the city are provided by Charleston County Emergency Medical Services (CCEMS) & Berkeley County Emergency Medical Services (BCEMS). The city is served by the EMS and 911 services of both Charleston and Berkeley counties since the city is part of both counties.
Charleston is the primary medical center for the eastern portion of the state. The city has several major hospitals located in the downtown area: Medical University of South Carolina Medical Center (MUSC), Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical Center,[25] and Roper Hospital.[26] MUSC is the state's first school of medicine, the largest medical university in the state, and the sixth-oldest continually operating school of medicine in the United States. The downtown medical district is experiencing rapid growth of biotechnology and medical research industries coupled with substantial expansions of all the major hospitals. Additionally, more expansions are planned or underway at another major hospital located in the West Ashley portion of the city: Bon Secours-St Francis Xavier Hospital.[27] The Trident Regional Medical Center[28] located in the City of North Charleston and East Cooper Regional Medical Center[29] located in Mount Pleasant also serve the needs of residents of the city of Charleston.
Recreation
The Charleston County Park and Recreation Commission (CCPRC) operates numerous facilities within Charleston County.[30]
Beach parks:
- Kiawah Beachwalker County Park, Kiawah Island, South Carolina
- Isle of Palms County Park, Isle of Palms, South Carolina
- Folly Beach County Park, Folly Beach, South Carolina
Fishing piers:
- Folly Beach Fishing Pier, Folly Beach, South Carolina
- Mt. Pleasant Pier, Mount Pleasant, South Carolina
Marinas and boat landings:
- Cooper River Marina
- Multiple county-wide boat landings
Day parks:
- Palmetto Islands County Park, Mount Pleasant, South Carolina
- Caw Caw Nature and History Interpretive Center, Ravenel, South Carolina
- North Charleston Wannamaker County Park, North Charleston, South Carolina
- Mullet Hall Equestrian Center, Johns Island, South Carolina
- James Island County Park, Charleston, South Carolina
- Old Towne Creek County Park, West Ashley- Charleston, South Carolina
Water parks:
- Splash Island at Palmetto Islands County Park
- Splash Zone at James Island County Park
- Whirlin' Waters at North Charleston Wannamaker County Park
Off-leash dog parks are offered at James Island, Palmetto Islands, and North Charleston Wannamaker County Park.
James Island County Park, approximately 11 minutes by car from downtown Charleston, features a 50-foot climbing wall and bouldering cave; cabin, RV, and tent camping facilities; rental facilities, fishing dock, challenge course, kayaking programs, summer camps, paved trails, and many special events such as the Lowcountry Cajun Festival (usually the first weekend in April), East Coast Canoe and Kayak Festival (3rd weekend in April), Holiday Festival of Lights (mid-November through the first of the year), and the summer outdoor reggae concerts.
Communities
Cities
- Charleston (county seat) (partly in Berkeley County)
- Folly Beach
- Isle of Palms
- North Charleston (partly in Dorchester County and Berkeley County)
Towns
Census-designated place
- Ladson (partly in Berkeley County)
- West Ashley
Districts
- Awendaw-McClellanville Consolidated Fire District - Made up of unincorporated parts of Northern Charleston County, the Town of Awendaw, and the Town of McClellanville.
- James Island Public Service District - Made up of unincorporated parts of the island.
- North Charleston Public Service District - Responsible for sewer lines and treatment in the City of North Charleston.
- St. John's Fire District - Serving Kiawah Island, Seabrook Island, unincorporated John's Island, and Wadmalaw Island
- Saint Andrews Public Service District - Made up of unincorporated parts of West Ashley.
- St. Pauls Fire District - Made up of all of the Towns of Hollywood, Ravenel, Meggett and unincorporated parts of the southern end of Charleston County.
- West Ashley
Notable residents
- Pernessa C. Seele (1954- ), immunologist, founder and CEO of the Balm in Gilead, Inc., an international organization based in Harlem, New York, to promote religious communities' role in education and prevention of HIV/AIDS, and support of families.[31]
- Also see List of people from Charleston, South Carolina for many more notable residents
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on February 22, 2016. Retrieved November 22, 2013.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on 2011-05-31. Retrieved 2011-06-07.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 30, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- Forstall, Richard L., ed. (March 27, 1995). "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. April 2, 2001. Retrieved March 16, 2015.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2011-05-14.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-03-09.
- Charlie B. Tyler, "The South Carolina Governance Project", University of South Carolina, 1998, p. 221
- Tyler (1998), "The South Carolina Governance Project"], p. 222
- UNITED STATES v. CHARLESTON COUNTY SOUTH CAROLINA (Decided: 29 April 2004) Archived 10 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine, US Court of Appeals, 4th Circuit, accessed 22 January 2015
- United States v. Charleston County, SC, Nos. 03-2111; 03-2112, Dept. of Justice, Appeals for the 4th Circuit Court
- DAVID FIRESTONE (19 January 2001). "U.S. Sues Charleston County, S.C., Alleging Violation of Black Voting Rights". New York Times. Retrieved December 23, 2012.
- "U.S. v. CHARLESTON COUNTY | 316 F.Supp.2d 268 (2003) | pp2d2681559 | Leagle.com". Leagle. Archived from the original on 2015-04-11. Retrieved 2018-03-13.
- "CIVIL RIGHTS ACCOMPLISHMENTS: ACTIVELY ENFORCING THE VOTING RIGHTS ACT OF 1965" Archived 2015-01-23 at the Wayback Machine, Press Release, Department of Justice, 23 July 2003, accessed 22 January 2015
- Cases Raising Claims Under Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act: United States v. Charleston County (D. S.C. 2001) Archived 2015-01-24 at the Wayback Machine, Civil Rights Division, US Dept. of Justice, 2005
- "Charleston County Council", Charleston County, SC, accessed 22 January 2015
- Prentiss Findlay, "Elliott Summey becomes new Charleston County Council chairman", The Post and Courier, 6 January 2015
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-03-13.
- "Ralph H. Johnson VA Medical Center". Charleston.va.gov. Retrieved 2017-05-30.
- Messmer, Carly. "Charleston Hospital – Roper Hospital – Roper St. Francis – Roper St. Francis". Ropersaintfrancis.com.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on April 20, 2009. Retrieved 2009-12-14.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- RC. "Compassionate Pregnancy & Child Birth Services – East Cooper Medical Center". Archived from the original on February 1, 2009.
- "Charleston County Parks and Recreation | Official Website". www.charlestoncountyparks.com. Archived from the original on 2013-09-03. Retrieved 2018-03-13.
- Dorie J. Gilbert and Ednita M. Wright, African American Women and HIV/AIDS, Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Company, 2003, p. 154, accessed 23 January 2009
External links
| Wikisource has the text of an 1879 American Cyclopædia article about Charleston County, South Carolina. |
- Charleston County Official Website
- Charleston County history and images
