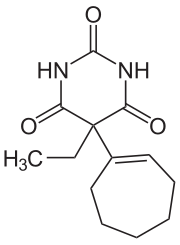
Heptabarb
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | G-475 |
| Routes of administration | Oral[1] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 83%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 6.1-11.2 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Renal[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.007.371 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H18N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 250.294 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Heptabarb (INN; Eudan, Medapan, Medomin, Noctyn), also known as heptabarbitone (BAN) or heptabarbital, is a sedative and hypnotic drug of the barbiturate family.[2][3] It was used in Europe for the treatment of insomnia from the 1950s onwards, but has since been discontinued.[2][3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Breimer DD, de Boer AG (December 1975). "Pharmacokinetics and relative bioavailability of heptabarbital and heptabarbital sodium after oral administration to man". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 9 (2–3): 169–78. doi:10.1007/bf00614014. PMID 9299.
- 1 2 C. R Ganellin; D. J Triggle; F.. Macdonald (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. CRC Press. p. 1003. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- 1 2 Index nominum 2000: international drug directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 513. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
This article is issued from
Wikipedia.
The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike.
Additional terms may apply for the media files.