Gondia
| Gondia Gondiya | |
|---|---|
| City | |
| Nickname(s): Rice City | |
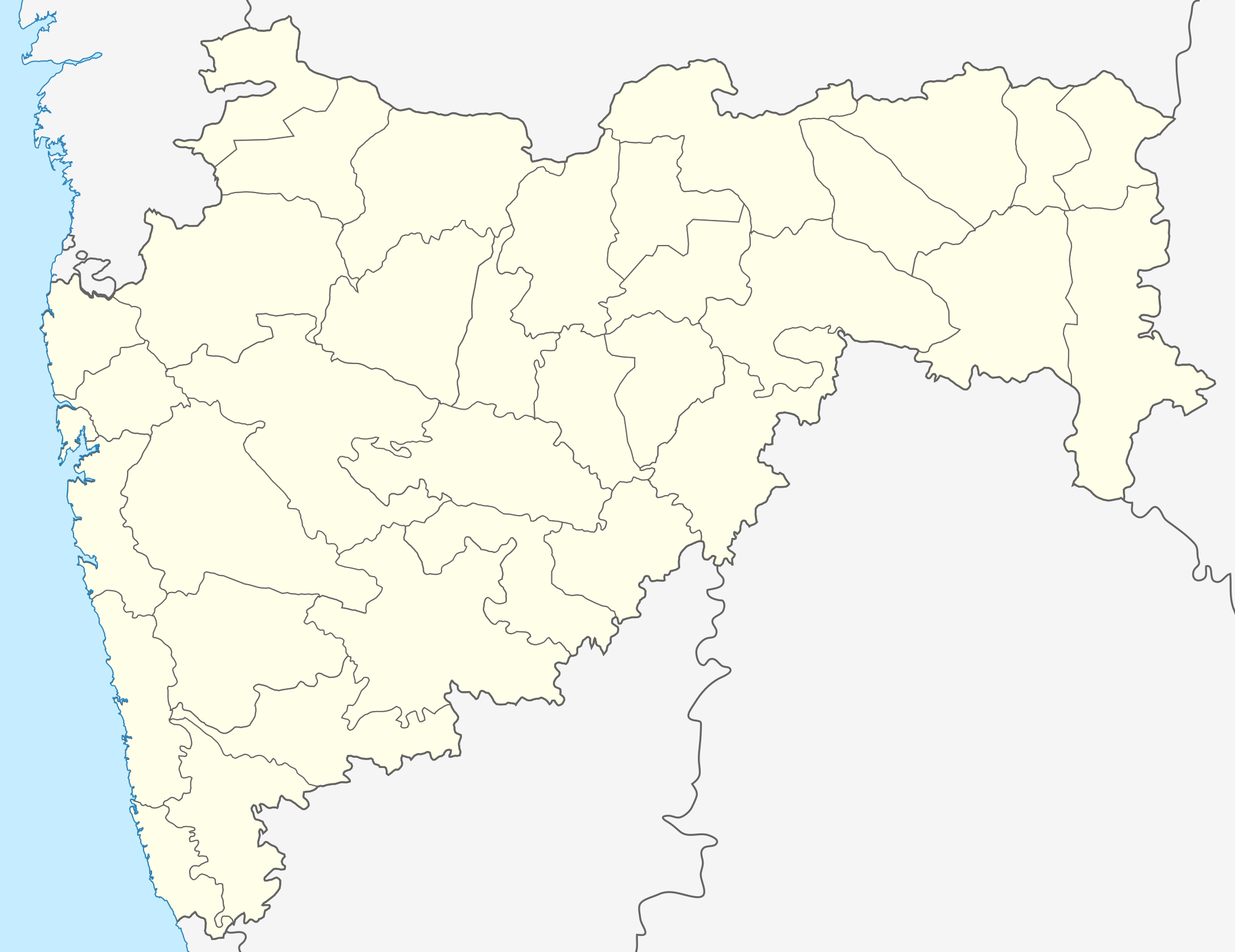 Gondia Location in Maharashtra, India | |
| Coordinates: 21°27′35″N 80°11′42″E / 21.4598°N 80.195°ECoordinates: 21°27′35″N 80°11′42″E / 21.4598°N 80.195°E | |
| Country | India |
| State | Maharashtra |
| District | Gondia |
| Government | |
| • Type | Local |
| • Body | Municipal Council |
| Area | |
| • Total | 30 km2 (10 sq mi) |
| Elevationd | 300 m (1,000 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] (urban agglomeration ≈ 180,000) | |
| • Total | 132,821 |
| • Rank | 354 |
| • Density | 4,400/km2 (11,000/sq mi) |
| Language | |
| • Official | Marathi |
| Time zone | UTC+5:30 (IST) |
| PIN | 441601,441614 |
| Telephone code | +91-07182 |
| Vehicle registration | MH-35 |
| Sex ratio | 991 per 1000 male. ♂/♀ |
| Website |
gondia |
Gondia (also spelled Gondiya) is a city in the state of Maharashtra in Central India which serves the administrative headquarters of the eponymous administrative district.[2] Gondia is also known as "Rice City" due to the abundance of rice mills in the area.[3]
Gondia is very close to the state of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and is considered the gateway to Maharashtra from central and eastern India. The city has the a railway junction and is also notable for its historic airport. Gondia municipality was established in 1920 At that time Gondia had only 10 wards population up to 20,000 and an area of 7.5 sq km. At present Gondia has 42 wards, as well as population nearing up to 2 lacs. The urbanization has crossed municipal limits merging into nearby villages like Kudwa, Katangi, Fulchur, Nagra, Karanja, Murri, Pindkepar, and Khamari. The Ministry of Urban Development has recently announced to merge 20 nearby villages into Gondia to give the city status of Municipal corporation.
History
The region is named after the Gondi people, an Adivasi group in Central India. It was at one point ruled by the Mughal Empire.
During British rule in India, the Great Famine of 1876–78 provided an opportunity for the construction of a 150-kilometre-long (93 mi) metre-gauge rail link called the Nagpur Chhattisgarh Railway, connecting Nagpur with Rajnandgaon. Gondia railway station was created when this line began operation in December 1888. Bengal Nagpur Railway (BNR) was formed in 1887 to upgrade and extend this line, and in 1902 BNR was contracted to provide a railway line from Gondia to Jabalpur with branches from Nainpur to Mandla as well as Nainpur to Seoni and Chhindwara. With these links and the commerce they brought, Gondia grew and prospered.[4]
Economy
The city has a large number of rice mills and some small-scale tobacco industries as well.
Climate
| Climate data for Gondia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 27.6 (81.7) |
31.1 (88) |
35.2 (95.4) |
39.0 (102.2) |
42.1 (107.8) |
38.1 (100.6) |
30.5 (86.9) |
29.9 (85.8) |
30.8 (87.4) |
31.0 (87.8) |
29.3 (84.7) |
27.9 (82.2) |
32.7 (90.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.3 (55.9) |
15.4 (59.7) |
19.6 (67.3) |
24.6 (76.3) |
28.9 (84) |
27.4 (81.3) |
24.3 (75.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
23.9 (75) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.2 (59.4) |
12.9 (55.2) |
20.9 (69.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 18.0 (0.709) |
30.7 (1.209) |
16.0 (0.63) |
16.0 (0.63) |
13.7 (0.539) |
219.2 (8.63) |
503.9 (19.839) |
443.5 (17.461) |
222.3 (8.752) |
66.5 (2.618) |
22.9 (0.902) |
5.8 (0.228) |
1,578.5 (62.147) |
| Source: Government of Maharashtra | |||||||||||||
Transportation
Road

["Harda-Gondia NH-70 via Nagpur."]
The road distance between Harda to Gondia is 485 km, while the aerial distance from Harda to Gondia is 347 km.
There are no direct flights or trains or buses between Harda to Gondia. The most convenient and fastest way to travel from Harda to Gondia is to take a taxi from Harda to Itarsi then take Samta Express from Itarsi to Gondia. The cheapest way to reach Gondia from Harda is to take Punjab Mail from Harda to Itarsi then take Tamil Nadu Exp from Itarsi to Nagpur then take Howrah Express from Nagpur to Gondia.
Rail
Gondia Junction railway station is a junction in Maharashtra, with heavy passenger and goods traffic. It is an A-Grade station.
It lies on the Howrah–Mumbai route. The station has seven platforms, each with potable water, tea stalls, benches and waiting sheds. There is also a fruit stall and a bookstall. The station is equipped with air-conditioned waiting rooms for passengers travelling by upper accommodation classes and a waiting hall for passengers travelling by lower accommodation classes.
The Gondia–Jabalpur Junction (Madhya Pradesh) section of South East Central Railway runs north–south, along the valley of the Wainganga River. The line was formerly narrow gauge (762 mm [2 ft 6 in]) along its entire length, but the section between Gondia and Balaghat was converted to broad gauge in 2005–2006,[5] connecting Balaghat to India's national broad-gauge network. Work is underway to convert the Balaghat–Jabalpur section to broad gauge as well.
Railway milestones for Gondia include:
- 1888 – Gondia Railway Station was opened to the public.
- 1901 – Satpura Express began first class service.
- 1903 – The first portion of Gondia–Nainpur was opened.
- 1905 – Nainpur–Gondia line was extended to Jabalpur.
- 1908 – Gondia–Nagbhir–Nagpur line was opened for traffic. Mr. Manson was agent of BNR at that time.
- 1990-91 – Paniajob–Gondia and Gondia–Bhandara Road sections were electrified.[6]
- 1999 – Gauge-converted Gondia–Balharshah line opened.
- 2005 – Gauge-converted Gondia–Balaghat section opened.
Airport
Gondia Airport is situated near Kamtha Village, 12 km (7.5 mi) from Gondia. This airstrip was built by the British in 1940, during World War II.[7] Initially run by the Public Works Department, it was taken over by the state-owned Maharashtra Industrial Development Corporation (MIDC) from August 1998[8] to December 2005, after which it has been operated by the Airports Authority of India (AAI). The airport's runway has been extended to 2,300 metres (7,500 ft) to accommodate Airbus A-320, Boeing 737 and similar aircraft.[9]
Education
- M.I.E.T. College (Engineering)
- D.B. Science College, Gondia
- N.M.D. College, Gondia
- Government Medical College, Gondia
- Government Polytechnic college, gondia
- Government ITI Gondia
- Gurunanak school and junior college, Gondia
References
- ↑ "Gondiya (Gondia) District Population Census 2011, Maharashtra literacy sex ratio and density". Census2011.co.in. Retrieved 2014-08-23.
- ↑ "गोंदिया संकेतस्थळ". gondia.nic.in. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "Gondia District Map". www.mapsofindia.com. 2013-04-25. Retrieved 2018-01-19.
- ↑ "The Roaring Journey" (PDF). secr.indianrailways.gov.in.
- ↑ Railway Gazette International Supplement December 2007 p7
- ↑ "History of Electrification". IRFCA. Retrieved 2012-11-10.
- ↑ "Airstrips in Maharashtra". Maharashtra Public Works Department. Retrieved 1 April 2012.
- ↑ "MIDC airports". Archived from the original on 28 March 2012. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
- ↑ "Akola, Gondia next aviation hot spots". Times of India. 27 November 2007. Retrieved 30 January 2012.
