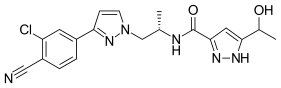
Darolutamide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ODM-201; BAY-1841788 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal antiandrogen |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolites | ORM-15341[1] |
| Elimination half-life |
Parent: 15.8 hours[1] Metabolite: 10.0 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H19ClN6O2 |
| Molar mass | 398.85 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Darolutamide (developmental code names ODM-201, BAY-1841788) is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) – specifically, a selective antagonist of the androgen receptor (AR) – which is under development by Orion and Bayer HealthCare for the treatment of advanced, castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC).[2][3][4] As of April 2018, it is in phase III clinical trials for this indication.[2] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Medical uses
Darolutamide is intended for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer.[3][4]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Relative to enzalutamide (MDV3100 or Xtandi) and apalutamide (ARN-509 or Erleada), two other recent NSAAs, darolutamide shows some advantages.[4] Darolutamide appears to negligibly cross the blood–brain barrier.[4] This is beneficial due to the reduced risk of seizures and other central side effects from off-target GABAA receptor inhibition that tends to occur in NSAAs that are structurally similar to enzalutamide.[4] Moreover, in accordance with its lack of central penetration, darolutamide does not seem to increase testosterone levels in mice or humans, unlike other NSAAs.[4] Another advantage is that darolutamide has been found to block the activity of all tested/well-known mutant ARs in prostate cancer, including the recently identified clinically-relevant F876L mutation that produces resistance to enzalutamide and apalutamide.[4] Finally, darolutamide shows higher affinity and inhibitory efficacy at the AR (Ki = 11 nM relative to 86 nM for enzalutamide and 93 nM for apalutamide; IC50 = 26 nM relative to 219 nM for enzalutamide and 200 nM for apalutamide) and greater potency/efficaciousness in non-clinical models of prostate cancer.[4]
ORM-15341 is the main active metabolite of darolutamide.[4] It is a full antagonist of the AR similarly, with an affinity (Ki) of 8 nM and an IC50 of 38 nM.[4]
Unlike enzalutamide and apalutamide, darolutamide shows no inhibition or induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes at therapeutic concentrations.[5]
Pharmacokinetics
The mean terminal half-lives of darolutamide and its active metabolite ORM-15341 at steady-state are 15.8 hours and 10.0 hours, respectively.[1] The half-lives are independent of dosage with 200–1800 mg/day dosages of darolutamide.[1] The half-life of darolutamide is far shorter than that of enzalutamide (1.6 hours and 18.3 hours in mice, respectively), necessitating higher dosages and more frequent administration in the case of darolutamide.[6]
Chemistry
Darolutamide is structurally distinct from any other known or established antiandrogens, including enzalutamide and apalutamide.[6]
History
Clinical trials
Darolutamide has been studied in phase I and phase II clinical trials and has thus far been found to be effective and well-tolerated,[7] with the most commonly reported side effects including fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea.[8][9] No seizures have been observed.[9][10] As of April 2018, darolutamide is in phase III trials for CRPC.[2][4]
Society and culture
Generic names
Darolutamide is the generic name of the drug and its INN and USAN.[11] It is also known by its developmental code names ODM-201 and BAY-1841788.[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Fizazi, Karim; Massard, Christophe; Bono, Petri; Jones, Robert; Kataja, Vesa; James, Nicholas; Garcia, Jorge A; Protheroe, Andrew; Tammela, Teuvo L; Elliott, Tony; Mattila, Leena; Aspegren, John; Vuorela, Annamari; Langmuir, Peter; Mustonen, Mika (2014). "Activity and safety of ODM-201 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (ARADES): an open-label phase 1 dose-escalation and randomised phase 2 dose expansion trial". The Lancet Oncology. 15 (9): 975–985. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70240-2. ISSN 1470-2045. PMID 24974051.
- 1 2 3 4 5 http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800033671
- 1 2 Fizazi K, Albiges L, Loriot Y, Massard C (2015). "ODM-201: a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor in castration-resistant prostate cancer". Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 15 (9): 1007–17. doi:10.1586/14737140.2015.1081566. PMC 4673554. PMID 26313416.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Moilanen AM, Riikonen R, Oksala R, Ravanti L, Aho E, Wohlfahrt G, Nykänen PS, Törmäkangas OP, Palvimo JJ, Kallio PJ (2015). "Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies". Sci Rep. 5: 12007. doi:10.1038/srep12007. PMC 4490394. PMID 26137992.
- ↑ http://meetinglibrary.asco.org/content/114000117-144
- 1 2 Moilanen, Anu-Maarit; Riikonen, Reetta; Oksala, Riikka; Ravanti, Laura; Aho, Eija; Wohlfahrt, Gerd; Nykänen, Pirjo S.; Törmäkangas, Olli P.; Palvimo, Jorma J.; Kallio, Pekka J. (2015). "Discovery of ODM-201, a new-generation androgen receptor inhibitor targeting resistance mechanisms to androgen signaling-directed prostate cancer therapies". Scientific Reports. 5: 12007. doi:10.1038/srep12007. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 4490394. PMID 26137992.
- ↑ "ODM-201 is safe and active in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer". Cancer Discov. 4 (9): OF10. 2014. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2014-150. PMID 25185192.
- ↑ Pinto Á (2014). "Beyond abiraterone: new hormonal therapies for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer". Cancer Biol. Ther. 15 (2): 149–55. doi:10.4161/cbt.26724. PMC 3928129. PMID 24100689.
- 1 2 Fizazi K, Massard C, Bono P, Jones R, Kataja V, James N, Garcia JA, Protheroe A, Tammela TL, Elliott T, Mattila L, Aspegren J, Vuorela A, Langmuir P, Mustonen M (2014). "Activity and safety of ODM-201 in patients with progressive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (ARADES): an open-label phase 1 dose-escalation and randomised phase 2 dose expansion trial". Lancet Oncol. 15 (9): 975–85. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70240-2. PMID 24974051.
- ↑ Agarwal N, Di Lorenzo G, Sonpavde G, Bellmunt J (2014). "New agents for prostate cancer". Ann. Oncol. 25 (9): 1700–9. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdu038. PMID 24658665.
- ↑ https://chem.nlm.nih.gov/chemidplus/rn/1297538-32-9
External links