Kavala
| Kavala Καβάλα | |
|---|---|
 Panoramic view | |
 Kavala Location within the region  | |
| Coordinates: 40°56′N 24°24′E / 40.933°N 24.400°ECoordinates: 40°56′N 24°24′E / 40.933°N 24.400°E | |
| Country | Greece |
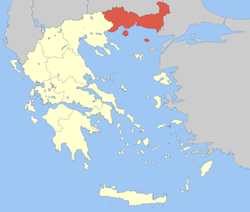
| Administrative region | East Macedonia and Thrace |
| Regional unit | Kavala |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 351.4 km2 (135.7 sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 112.6 km2 (43.5 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 53 m (174 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population (2011)[1] | |
| • Municipality | 70,501 |
| • Municipality density | 200/km2 (520/sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 58,790 |
| • Municipal unit density | 520/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| Community[1] | |
| • Population | 56,371 (2011) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 65x xx |
| Area code(s) | 2510 |
| Vehicle registration | KB |
| Website | kavala.gov.gr |
Kavala (Greek: Καβάλα, Kavála [kaˈvala]) is a city in northern Greece, the principal seaport of eastern Macedonia and the capital of Kavala regional unit.
It is situated on the Bay of Kavala, across from the island of Thasos and on the Egnatia motorway, a one-and-a-half-hour drive to Thessaloniki (160 kilometres (99 miles) west) and a forty-minute drive to Drama (37 km (23 miles) north) and Xanthi (56 km (35 miles) east).
Names
In Antiquity the name of the city was Neapolis ('new city', like many Greek colonies). During the Middle Ages, it was renamed Christoupolis ('city of Christ').
Etymology
The etymology of the modern name of the city is disputed. Some mention an ancient Greek village Skavala near the town. Other proposals include either from the Italian cavallo (= horse), or from the Hebrew Kabbalah due to the city's large Jewish population in the past. Its nickname is The cyan city (Η γαλάζια πόλη).
History
Antiquity

The city was founded in the late 7th century BC by settlers from Thassos. It was one of several Thassian colonies along the coastline, all founded in order to take advantage of rich gold and silver mines, especially those located in the nearby Pangaion mountain (which were eventually exploited by Phillip II of Macedonia).
Worship of Parthenos / the Virgin, a female deity of Greek–Ionian origin associated with Athena, is archaeologically attested in the Archaic period. At the end of the 6th century BC Neapolis claimed independence from Thassos and began issuing its own silver coins with the head of Gorgo (γοργὀνειο) on one side. A few decades later a large Ionic temple made from Thassian marble replaced the Archaic one. Parts of it can now be seen in the town's archaeological museum.
In 411 BC, during the Peloponnesian War, Neapolis was besieged by the allied armies of the Spartans and the Thassians but remained faithful to Athens. Two Athenian honorary decrees in 410 and 407 BC rewarded Neapolis for its loyalty.
Neapolis was a town of Macedonia, located 14 km (9 mi) from the harbour of Philippi. It was a member of the Second Athenian League; a pillar found in Athens mentions the contribution of Neapolis to the alliance.
Roman Era
The military Roman road Via Egnatia passed through the city and helped commerce to flourish. It became a Roman civitas in 168 BC, and was a base for Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, before their defeat in the Battle of Philippi.[2]
The Apostle Paul landed at Kavala on his first voyage to Europe.[3]
Byzantine, Bulgarian and Crusader Era

In the 6th century, Byzantine emperor Justinian I fortified the city in an effort to protect it from barbarian raids. In later Byzantine times the city was called Christoupolis (Χριστούπολις, "city of Christ") and belonged to the theme of Macedonia. The first surviving mention of the new name is in a taktikon of the early 9th century. The city is also mentioned in the "Life of St. Gregory of Dekapolis". In the 8th and 9th centuries, Bulgarian attacks forced the Byzantines to reorganise the defence of the area, giving great care to Christoupolis with fortifications and a notable garrison. Bulgarians also ruled it briefly. In 926 the Byzantine general (strategos) Basil Klaudon reconstructed the town's fallen walls according to an inscription now in the archaeological museum. Thanks to its location, the city experienced an economic resurgence, securing contact between Constantinople and Thessaloniki.
During a Norman raid of Macedonia in 1185, the city was captured and burned. In 1302, the Catalans failed to capture the city. In order to prevent them from coming back, the Byzantine emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos built a new long defensive wall. In 1357 two Byzantine officers and brothers, Alexios and John, controlled the city and its territory. Excavations have revealed the ruins of an early Byzantine basilica under an Ottoman mosque in the Old Town. It was used until the late Byzantine era.
Ottoman Era
The Ottoman Turks first captured the city in 1387 and completely destroyed it in 1391, as a Mount Athos chronicle testifies. Kavala was part of the Ottoman Empire from 1387 to 1912. In the middle of the 16th century, Ibrahim Pasha, Grand Vizier of Suleiman the Magnificent, contributed to the town's prosperity and growth by the construction of an aqueduct.[4] The Ottomans also extended the Byzantine fortress on the hill of Panagia. Both landmarks are among the most recognizable symbols of the city today.
Mehmet Ali, the founder of a dynasty that ruled Egypt, was born in Kavala in 1769. His house has been preserved as a museum.
20th century



Kavala was briefly occupied by the Bulgarians during the first Balkan War in 1912, but was finally occupied by Greece in 1913 during a successful landing operation by the Greek Navy that was commanded by the famous admiral Pavlos Kountouriotis.
In August 1916 rests of the IV Army Corps, stationed at Kavala under Ioannis Hatzopoulos surrendered to the advancing Bulgarian Army. These events provoked a military revolt in Thessaloniki, which led to the establishment of the Provisional Government of National Defence, and eventually Greece's formal entry into the First World War.
After the Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922, the city entered a new era of prosperity because of the labour offered by the thousands of refugees that moved to the area from Asia Minor. The development was both industrial and agricultural. Kavala became greatly involved in the processing and trading of tobacco. Many buildings related to the storage and processing of tobacco from that era are preserved in the city.
During World War II and after the fall of Athens, the Nazis awarded Kavala back to Bulgarian allies in 1941, causing the city to suffer once again, but it finally was liberated in 1944. Almost the entire Jewish community of the city was exterminated during the Occupation.
In the late 1950s Kavala expanded towards the sea by reclaiming land from the area west of the port.
In 1967, King Constantine II left Athens for Kavala in an unsuccessful attempt to launch a counter-coup against the military junta.
Historical population
| Year | Town | Municipal unit | Municipality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961 | 44,517 | 44,978 | – |
| 1971 | 46,234 | 46,887 | – |
| 1981 | 56,375 | 56,705 | – |
| 1991 | 56,571 | 58,025 | – |
| 2001 | 58,663 | 63,293 | – |
| 2011 | 54,027 | 58,790 | 70,501 |
Administration

Municipality
The municipality of Kavala was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the two former municipalities, which became municipal units:[5]
| Municipal unit | Population (2011)[1] | Area (km²)[6] |
|---|---|---|
| Kavala | 58,790 | 112.599 |
| Filippoi | 11,711 | 238.751 |
The municipality has an area of 351.35 square kilometres (135.66 square miles).[6] The population of the new municipality is 70,501 (2011). The seat of the municipality is in Kavala. Some of the most important communities inside new municipality are:
| Community | Population |
|---|---|
| Kavala | 56,371 |
| Krinides | 3,365 |
| Amygdaleonas | 2,724 |
| Nea Karvali | 2,225 |
| Zygos | 2,057 |
Subdivisions
Kavala is built amphitheatrically, with most residents enjoying superb views of the coast and sea. Some of the regions inside Kavala are:
| Agia Varvara | Agios Athanasios | Agios Ioannis | Agios Loukas | Chilia |
| Dexameni | Kalamitsa | Kentro | Neapolis | Panagia |
| Perigiali | Potamoudia | Profitis Ilias | Timios Stavros | Vyronas |
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Kavala is twinned with:
|
Partnerships
|
Province
The province of Kavala (Greek: Επαρχία Καβάλας) was one of the provinces of the Kavala Prefecture. Its territory corresponded with that of the current municipality Kavala, and part of the municipal unit Eleftheroupoli.[8] It was abolished in 2006.
Economy
Traditionally the primary occupation of the population of Kavala was fishing. The fishermen of the town were well known all over northern Greece.
After the country's industrialization, Kavala also became a center of the tobacco industry in northern Greece. The building of the Municipal Tobacco Warehouse still stands today.
Oil deposits were found outside the city in the mid-20th century and are currently exploited by an oil rig.
Climate
Kavala has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) that borders on a semi-arid climate (Köppen climate classification "BSk" or "BSh" depending on the system used) with annual average precipitation of 460 mm (18.1 in). Snowfalls are sporadic, but happen more or less every year. The humidity is always very high.
The absolute maximum temperature ever recorded was 38.0 °C (100 °F), while the absolute minimum ever recorded was −16.1 °C (3 °F).[9]
| Climate data for Kavala Weather Station 2006-2018 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
19.9 (67.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
11.3 (52.3) |
19.6 (67.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.9 (46.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.8 (74.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.1 (80.8) |
22.2 (72) |
16.7 (62.1) |
12.7 (54.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.2 (39.6) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.8 (46) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.3 (61.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.7 (42.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 57.5 (2.264) |
65.4 (2.575) |
68.2 (2.685) |
37.8 (1.488) |
48.7 (1.917) |
51.8 (2.039) |
25.4 (1) |
21.4 (0.843) |
49.8 (1.961) |
64.7 (2.547) |
48.6 (1.913) |
62.0 (2.441) |
601.3 (23.673) |
| Average precipitation days | 9.2 | 9.1 | 11.6 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 9.3 | 91 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 64.9 | 65.0 | 66.6 | 65.8 | 67.8 | 67.8 | 68.4 | 68.8 | 67.7 | 65.8 | 66.1 | 67.7 | 66.9 |
| Source: meteokav.gr | |||||||||||||
Education and research

- The Technological Educational Institute of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace (Greek: ΤΕΙ Ανατολικής Μακεδονίας και Θράκης) is a public institute providing education at university level in the region of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace. The main campus of the institute located in St. Lukas, Kavala and is approximately 132,000 m2 with buildings covering an area of 36,000 m2.The campus is home to two faculties (Faculty of Engineering Sciences and Faculty of Business and Economics) with a total of nine departments.
- MSc in Management and Information Systems[10]
- Fisheries Research Institute (FRI)[11] is one of the five specialized research institutes of N.AG.RE.F, being responsible to conduct research and to promote technological development in the fishery sector. The institute is located 17 km (11 mi) from Kavala, in Nea Peramos, at the centre of a marine area with rich fishery grounds and high biodiversity in the surrounding lagoons, lakes and rivers.
- Institute of Mohamed Ali for the Research of the Eastern Tradition (IMARET)[12] is a registered NGO with the Hellenic Ministry of Foreign Affairs, which was established by concerned citizens in Kavala. Its aims include the study of the Egyptian influence in Greece and vice versa. The intra-cultural exchange and dialogue, as well as the promotion of art as a means of intra-cultural understanding. The first major co-operation partner is Cultnat of Bibliotheca Alaxandrina with the aim of documenting and digitizing the architectural heritage of the Mohamed Ali era in Egypt and Greece. The most important event that takes place every year at the institute is the International Roman Law Moot Court Competition.
- Historical & Literary Archives of Kavala[13] is a non-profiteering, public utility foundation. Its foundation was not subsidized by the Greek State, neither by any other enterprise of the private sector. Its operational cost is covered only by its founders and by infrequent aids of the local self-government.
- Egnatia Aviation[14] is a private training college for pilots that started training in Greece in July 2006. The facilities of Egnatia Aviation are mostly located in the former passengers' terminal of the Kavala International Airport "Alexander the Great".
Culture
Festivals and events
Kavala hosts a wide array of cultural events, which mostly take place during the summer months. The top festival is the Festival of Philippi[15] which lasts from July to September and includes theatrical performances and music concerts. Since 1957, it has been the city's most important cultural event and one of the most important of Greece.
Cosmopolis is an international festival held in the Old Town of Kavala that offers an acquaintance with cultures around the world through dancing and musical groups, traditional national cuisines, cinema, and exhibits at the kiosks of participant countries. The first festival took place in 2000, and from 2002 until 2009 was organised annually. It was revived in 2016 with a participation of 250 artists and musicians from all over the world.[16]
Giannis Papaioannou's Festival includes concerts and music seminars.[17]
Ilios ke Petra (Sun and Stone) (July) is a festival held in "Akontisma" of Nea Karvali. The event is of folkloric character, with the participation of traditional dancing groups from all over the world.
Wood Water Wild Festival[18] is an outdoor activities festival, inspired by nature. It includes live bands and DJ sets, body&mind activities, a book fair, outdoor theatre, ecology, camping, and debates.
Kavala AirSea Show[19] is an annual air show held in late June.
Various cultural events are held in all municipalities of Kavala during the summer months.
Cuisine
Fish and seafood, as well as the products of the local livestock breeding and agricultural sectors are the prevailing elements of Kavala cuisine. In Kavala, the traditional local recipes have been influenced by the cuisine of the refugees from Pontos, Asia Minor and Kappadokia.
Fresh fish and seafood, salted food, mackerel "gouna" (sun dried mackerel on the grill), sardine pantremeni, mussels with rice, herring saganaki, anchovies wrapped in grape leaves, and stuffed eggplant are some very renowned recipes in Kavala and the coastal settlements of the region. The grapes, wine and tsipouro produced in the area, as well as the kourabiedes (sugar-coated almond biscuits) from Nea Karvali, are particularly famous.
Transport
.jpg)
Highway network
European route E90 runs through the city and connects Kavala with the other cities. The Egnatia Motorway (A2) lies north of the city. One can enter the city from one of two junctions: Kavala West and Kavala East. Kavala has regular connection with Interregional Bus Lines (KTEL) from and to Thessaloniki and Athens.
Airport
The Kavala International Airport "Alexander the Great" (27 km (17 mi) from Kavala) is connected with Athens by regularly scheduled flights and with many European cities by scheduled and charter flights.
Port
Kavala is connected with all the islands of the Northern Aegean Sea with frequent itineraries of various ferry lines.
Bus
The city is connected with all of the large Greek cities such as Thessaloniki and Athens. All of the local villages are also connected via bus lines. The cost of tickets is very cheap. There is also a shuttle bus in Kavala with these lines:
- Vironas – Kallithea
- Dexameni
- Cemetery
- Kipoupoli – Technological Institute
- Agios Loukas
- Profitis Ilias
- Stadium
- Kalamitsa – Batis (only in summer)
- Agios Konstantinos
- Neapoli
- Hospital – Perigiali
Sports

- Kavala F.C.: AO Kavala (Greek: Athlitikos Omilos Kavala, Αθλητικός Όμιλος Καβάλα), the Athletic Club Kavala, is a professional association football club based in Kavala. The club plays in the municipal Kavala Stadium "Anthi Karagianni".[20]
- Kavala B.C.: Enosi Kalathosfairisis Kavalas (Greek: Ένωση Καλαθοσφαίρισης Καβάλας – Basketball Union of Kavala) is a Greek professional basketball club in Kavala. The club is also known as E.K. Kavalas. The club's full Greek name is Ένωση Καλαθοσφαίρισης Καβάλας (Kavala Basketball Union or Kavala Basketball Association). The club competes in the Greek League.
- Kavala '86: a women's football club, founded in 1986, with panhellenic titles in Greek women football
- Kavala Chess Club:[21] Chess is very popular in Kavala and the local chess club ranks top in Greece, enjoying plenty of success both domestically and internationally. The highlight is the club's annual International Open, which takes place every August in Kavala and attracts the biggest names in chess from all over the globe.
- Nautical Club of Kavala (1945, Ναυτικός Ομιλος Καβάλας, ΝΟΚ): maritime sports (swimming, yachting, water polo)
- Kavala Titans (2009, Τιτάνες Καβάλας): rugby union/rugby league
Ecclesiastical history


Christopolis was important enough in the Late Roman province of Macedonia Secunda to be a suffragan of its capital Philippi's Metropolitan Archbishopric, but the Catholic succession ended.
Titular see
The diocese of Christopolis was nominally restored in 1933 as a Latin Catholic titular bishopric.
It is vacant, having had the following, far from consecutive, incumbents of the lowest (episcopal) rank, except the latest (archiepiscopal, intermediary rank):
- Jean Isembert, Dominican Order (O.P.) (1450.05.11 – 1465.09.08)
- Jaime Perez de Valencia, Augustinian Order (O.E.S.A.) (1468.10.01 – 1490.08.03)
- Ausiás Carbonell, O.P. (1509.04.16 – 1532.12.09)
- Enrique Rutil (1525.11.10 – ?)
- Bishop-elect Francisco de Jaén (1530.12.05 – ?)
- Francisco Estaña (1534.12.16 – 1549.06.23)
- Gian Antonio Fassano (1544.06.04 – 1568.09.10)
- Juan Segría (1547.11.28 – 1568.07.23) as Auxiliary Bishop of Valencia (Spain) (1547.11.28 – 1568.07.23); later Metropolitan Archbishop of Sassari (Sardinia, Italy) (1568.07.23 – death 1569.09.26), Metropolitan Archbishop of Palermo (Sicily, Italy) (1569.09.26 – 1569 not possessed)
- Pedro Coderos (1570.02.20 – 1579.10.21) as Auxiliary Bishop of Valencia (Spain) (1570.02.20 – 1579.10.21); later Metropolitan Archbishop of Otranto (Italy) (1579.10.21 – 1585)
- Marcin Szyszkowski (1603.11.24 – 1604.06)
- Ludovico de Taragni, Benedictine Order (O.S.B.) (1612.03.21 – ?)
- Michael Chumer, Friars Minor (O.F.M.) (1639.10.03 – 1651.06.30)
- Maxime Tessier (1951.05.28 – 1955.05.08)
- Otto Spülbeck (1955.06.28 – 1958.06.23)
- Michael William Hyle (1958.07.03 – 1960.03.02)
- Titular Archbishop Sante Portalupi (1961.10.14 – 1984.03.31), papal diplomat, as Apostolic Nuncio to Honduras (1959.01.29 – 1967.09.27), Apostolic Nuncio to Nicaragua (1959.01.29 – 1967.09.27), Apostolic Delegate to Libya (1967.09.27 – 1979.12.15), Apostolic Pro-Nuncio to Algeria (1972 – 1979.12.15), Apostolic Pro-Nuncio to Tunisia (1972 – 1979.12.15), Apostolic Pro-Nuncio to Morocco (1976 – 1979.12.15), Apostolic Nuncio to Portugal (1979.12.15 – 1984.03.31)
Postage stamps

Austria opened a post office in Kavala before 1864.[23] Between 1893 and 1903, the French post office in the city issued its own postage stamps; at first stamps of France overprinted with "Cavalle" and a value in piasters, then in 1902 the French designs inscribed "CAVALLE".
Notable figures
- Muhammad Ali Pasha of Kavala, the Albanian Wali (governor) of Egypt between 1805 and 1848 and founder of the modern state of Egypt
- Mohamed Sherif Pasha, Prime Minister of Egypt
- Christos Batzios, Greek actor and filmmaker
- Theodore Kavalliotis, Greek Orthodox priest, teacher and a figure of the Greek Enlightenment
- Vassilis Vassilikos, Greek writer and diplomat
- Konstantinos Mitroglou, Greek footballer
- George Georgiadis, Greek footballer
- Giorgos Chimonas (1938–2000), writer and translator
- Nikos Karageorgiou, (born 9 December 1962) Manager of Greek football team Ergotelis, based in Heraklion, Crete
- Anthi Karagianni, silver medalist in the Athens 2004 and Beijing 2008 Paralympic Games; the city's Municipal stadium is named after her
- Vasilis Karas, Greek singer
- Nikos Kourkoulis, Greek singer
- Leontios Petmezas, theorist, art historian, book critic, author and journalist
- Mitsos Partsalidis, first elected communist mayor in modern Greek history, back in 1 April 1934
- Christos Terzanidis, footballer
- Antigone Valakou, actress
- Despina Vandi, Greek singer
- Thanasis Efthimiadis, Greek actor
- Anna Verouli, 1982 Gold Medalist, European Championship, javelin thrower
- George Drakonakis, Javelin thrower - Ipc national Champion
- Zisis Vryzas (born 9 November 1973), former footballer
- Theodoros Zagorakis (born 27 October 1971), former footballer, captain of national team of Greece-European champion 2004
- Anna Gerasimou, Greek tennis player
- Phoebe Calazans, Greek musician
- Kleon Krantonellis, architect
- Nasos Galakteros, basketball player
- Kyriakos Grizzly, powerlifter
Gallery
 Α painted cist grave votive funerary banquet, 4th century BC (Archaeological Museum of Kavala)
Α painted cist grave votive funerary banquet, 4th century BC (Archaeological Museum of Kavala).jpg) Statue of Muhammad Ali of Egypt, donation of Egypt
Statue of Muhammad Ali of Egypt, donation of Egypt Panoramic view
Panoramic view View to the Kavala aqueduct
View to the Kavala aqueduct Municipal Tobacco Warehouse
Municipal Tobacco Warehouse
 Chamber of Commerce
Chamber of Commerce Megali Leschi
Megali Leschi Holocaust memorial
Holocaust memorial
See also
References

- 1 2 3 "Απογραφή Πληθυσμού - Κατοικιών 2011. ΜΟΝΙΜΟΣ Πληθυσμός" (in Greek). Hellenic Statistical Authority.
- ↑ Appian, B.C. iv. 106; Dion Cass. xlvii. 35
- ↑ Acts, xvi. 11
- ↑ Kiel, Machiel (1971). "Observations on the History of Northern Greece during the Turkish Rule: Historical and Architectural Description of the Turkish Monuments of Komotini and Serres, their place in the Development of Ottoman Turkish Architecture and their Present Condition". Balkan Studies. 12: 416.
- ↑ Kallikratis law Greece Ministry of Interior (in Greek)
- 1 2 "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in Greek). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2015.
- ↑ https://www.sistercities-durham.com/kavala-greece
- ↑ "Detailed census results 1991" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 March 2016. (39 MB) (in Greek) (in French)
- ↑ "EMY-Εθνική Μετεωρολογική Υπηρεσία". Hnms.gr. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ↑ MSc in Management and Information Systems
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 24 May 2011.
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 14 May 2011. Retrieved 26 May 2011.
- ↑ Official website
- ↑ (in Greek) Φεστιβάλ κλασικής μουσικής «Γ. Α. Παπαϊωάννου»
- ↑ Wood Water Wild Festival
- ↑ Kavala AirSea Show
- ↑ "Anthi Karagianni Stadium".
- ↑
- ↑ Die Poststempel auf der Freimarken-Ausgabe 1867 von Österreich und Ungarn, Edwin Mueller, 1930, # 6814
- ↑ Handbook of Austria and Lombardy-Venetia Cancellations on the Postage Stamp Issues 1850–1864, by Edwin MUELLER, 1961, p.215
Bibliography
- Koukouli-Chrisanthaki Chaido, Kavala. Αrchaeological Museum of Kavala, Kavala: D.E.T.A., 2002 (in Greek).
- Stefanidou Emilia, The City-Port of Kavala during the Period of Turkish Rule. An Urban Survey (1391–1912), Kavala: Historical & Literary Archive of Kavala, 2007 (in Greek).
- Karagiannakidis Nikos – Likourinos Kyriakos, Neapolis-Christoupolis-Kavala, Kavala: Municipality of Kavala, 2009 (in Greek).
- Koutzakiotis Georges, Cavalla, une Échelle égéenne au XVIIIe siècle. Négociants européens et notables ottomans, Istanbul: The Isis Press, 2009.
- Roudometof Nikolaos (ed.), Notebooks of Bulgarian Occupation. Eastern Macedonia 1916–1918. v. 1, Kavala – Chrisoupoli – Eleutheroupoli, Kavala: Historical & Literary Archive of Kavala (in Greek).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kavala. |


- Official website (in Greek)
- The official website of the prefecture of Kavala – online since 1996
- GCatholic with titular incumbent biography links
- Official Blog of students of ATEI Kavalas
- sun disappeared – Fire Kavala 1985