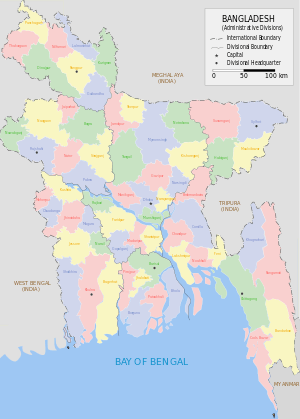
Districts of Bangladesh
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Bangladesh |
|
Constitution and law |
|
|
 |
The divisions of Bangladesh are divided into 64[1] districts, or zila (Bengali জিলা/জেলা=Zela/zila). The capital of a district is called a district seat (zila sadar). The districts are further subdivided into 493 sub-districts or upazila (উপজেলা upojela).
Administration
Deputy commissioner
A deputy commissioner (popularly abbreviated to "DC") is the executive head of the district. Deputy commissioners are appointed by the government from the deputy secretary BCS Administration Cadre.
District councils
A district council (or zila parishad) is a local government body at the district level.[2] The Bengali word parishad means council and zila parishad translates to district council.
The functions of a district council include construction and maintenance of roads, and bridges, building hospitals and dispensaries, schools and educational institutions, health facilities and sanitation, tube wells for drinking water, rest houses, and coordination of activities of the Union parishads within the district.
List of districts
See also
References
- ↑ "বাংলাদেশ জাতীয় তথ্য বাতায়ন - গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ সরকার". bangladesh.gov.bd.
- ↑ Kamal Siddiqui. "Local Government". In Sirajul Islam. Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh. Asiatic Society of Bangladesh.