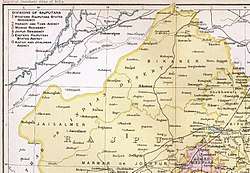
Bikaner State
| Bikaner State बीकानेर रियासत | ||||||
| Princely State of British India | ||||||
| ||||||
| ||||||
 | ||||||
| History | ||||||
| • | Established | 1465 | ||||
| • | Independence of India | 1947 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| • | 1931 | 60,391 km2 (23,317 sq mi) | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| • | 1931 | 936,218 | ||||
| Density | 15.5 /km2 (40.2 /sq mi) | |||||
| Today part of | Rajasthan, India | |||||

_(8441306001).jpg)




Bikaner State was a princely state in the Bikaner region from 1465 to 1947. Its capital was the city of Bikaner in the northern area of present-day Rajasthan State in India.
Covering an area of 60,391 km2 (23,317 sq mi), Bikaner State was one of the largest states under the Rajputana Agency. Heeding the call of Vallabhbhai Patel to integrate the princely states into the new independent India, Bikaner's last king, Maharaja Sadul Singh, advised by his dewan K. M. Panikkar, a respected historian, was one of the first rulers of a princely state to display willingness to join the Indian Union. By issuing a public appeal in April 1947 to his fellow princes to join the Constituent Assembly of India, the Maharaja of Bikaner set an example for other heads of the native states to follow.[1]
History
The state of Bikaner was founded in 1465. It became a British protectorate on 9 March 1818. Its rulers were Rajputs belonging to the Rathore dynasty. They were accorded a 17 gun salute by the British authorities.[2] By the time of Indian Independence, the territory of the state of Bikaner shared a border with Pakistan. The accession to the Indian Union was signed by the Maharaja on 7 August 1947.[3]
Maharajas
- 1465 - 1504 Rao Bika
- 1504 - 1505 Rao Nar Singh (Naro)
- 1505 - 1526 Rao Loonkaran
- 1526 - 1542 Rao Jait Singh
- 1542 - 1571 Rao Kalyan Mal (acknowledged the suzerainty of Emperor Akbar)
- 1571 - 1612 Rao / Raja Rai Singh I (Important General in the Mughal army. Given title of Raja. From 1585 to 1594 he was employed in the Deccan by Emperor Akbar, where he was Subedar of Burhanpur)
- 1612 - 1613 Raja Dalpat (Sur Singh revolted against his elder brother Dalpat and killed him along with his guards with the consent of Emperor Jahangir)
- 1613 - 1631 Raja Sur Singh
- 1631 - 1667 Raja Karan Singh (deposed by Aurangzeb and exiled to Karanapura in the Deccan)
- 1667 - 1669 Interregnum
- 1669 - 1698 Maharaja Anup Singh (First to be granted title of Maharaja by Emperor Aurangzeb)
- 19 Jun 1698 – 15 Dec 1700: Maharaja Sarup Singh (b. 1689 – d. 1700)
- 15 Dec 1700 – 16 Dec 1735: Maharaja Sujan Singh (b. 1690 – d. 1735)
- 16 Dec 1735 – 15 May 1746: Maharaja Zorawar Singh (b. 1713 – d. 1746)
- 15 May 1746 – 25 Mar 1787: Maharaja Gaj Singh (b. 1723 – d. 1787)
- 25 Mar 1787 – 25 Apr 1787: Maharaja Raj Singh II (b. 1744 – d. 1787)
- 25 Apr 1787 – 9 Oct 1787: Maharaja Pratap Singh (b. 1781 – d. 1787)
- 25 Apr 1787 – 25 Mar 1828: Maharaja Surat Singh (Regent to 9 Oct 1787) (b. 1766 – d. 1828)
- 25 Mar 1828 – 7 Aug 1851: Maharaja Ratan Singh (b. 1790 – d. 1851)
- 7 Aug 1851 – 16 May 1872: Maharaja Sardar Singh (b. 1818 – d. 1872)
- 16 May 1872 – 19 Aug 1887: Maharaja Dungar Singh (b. 1854 – d. 1887)
- 19 Aug 1887 – 2 Feb 1943: Maharaja Ganga Singh (b. 1880 – d. 1943) (from 24 Jul 1901, Sir Ganga Singh)
- 19 Aug 1887 – 16 Dec 1898: the British Political Agents-Regent
- 2 Feb 1943 – 15 Aug 1950: Maharaja Sadul Singh (b. 1902 – d. 1950) (from 1 Jan 1946, Sir Sadul Singh)
- 1950 - 1971 Maharaja Karni Singh (Privy purses were withdrawn in 1971 and post & titles were also withdrawn)
- Narendra Singh, no official titles as they were abolished by the govt.
- Ravi Raj Singh – present
Dewans
The Dewans and Chief Ministers of the state were:
- 1460-1465 Bachhraj (Mantri-Dewan / Jodhpur) / Rao Jodha
- 1465-1505 Bachhraj (Founding Dewan / Bikaner) / Rao Bika
- 1504-1526 Karam Singh Bachhawat (Descendants of Bachhraj were known as Bachhawats) / Rao Nar Singh and Rao Loonkaran
- 1526-1535 Var Singh Bachhawat / Rao Jait Singh
- 1535-1542 Nagraj Bachhawat / Rao Jait Singh and Rao Kalyan Mal
- 1542-1571 Sangram Singh Bachhawat / Rao Kalyan Mal
- 1571-1591 Mehta Karam Chand Bachhawat (Title of Mehta granted by Emperor Akbar) / Rao Kalyan Mal and Raja Rai Singh
- 1619-1620 Mehta Bhag Chand Bachhawat / Raja Sur Singh
- 1619-1620 Mehta Lakshmi Chand Bachhawat / Raja Sur Singh
- 17.. – 26 Feb 1733: Anand Ram Khawas (d. 1733)
- 1735 – Feb 1751: Mohta Bakhtawar Singh (1st time) (b. 1707 – d. 1779)
- Feb 1751 – 1752: Amar Singh Chaturbhujani
- 1752 – 1756: Mohta Bakhtawar Singh (2nd time) (s.a.)
- 1756 – Dec 1757: Mohta Prithvi Singh
- 1757 – 1762: Mohta Bakhtawar Singh (3rd time) (s.a.)
- 1762 – Sep 1765: Shah Mool Chand Bardiya
- Sep 1765 – 1779: Mohta Bakhtawar Singh (4th time) (s.a.)
- 1779 – 178.: Mohta Swaroop Singh
- 178. – 1787: Mohta Thakursi
- 1787 – 1791: Mohta Madho Rai
- 1791 – 1794: Pratap Mal Baid
- 1794 – 1805: Mohta Rao Sahib Singh Gun Roop
- Apr 1805 – Apr 1815: Amar Chand Surana
- Apr 1815 – Feb 1816: Mohta Bhomji
- Feb 1816 – 1828: Abhai Singh Mohta
- 1828 – 184.: Hindu Mal Baid
- c. 1841: Sri Narayan Singh Bhati
- 1844 – 1852?: Sarana Shri Lakshmichand
- 1852 – 1853: Guman Singh Baid (1st time)
- 1853 – 1853: Leeladhar Mohta + Jalam Chand Kochar
- 1853 – 1854: Lachhi Ram Rakhecha
- 1854 – 1856: Guman Singh Baid (2nd time)
- 1856: Pandit Dojainant
- 1856 – 1863: Ram Lal Dwarkani (1st time)
- 1864 – 1865: Guman Singh Baid (3rd time)
- 1865 – 1866: Ram Lal Dwarkani (2nd time)
- 1866: Man Mal Rakhecha
- 1866 (3 months): Sheo Lal Nahata
- 1867 (15 days): Fateh Chand Surana
- 1867: Ganga Ram Purohit
- 1867: Shah Mal Kochar
- 1868: Man Mal Rakhecha
- 1868: Sheo Lal Mohta
- 1868: Lakshmi Chand Nahata
- Jun 1868 – Aug 1869: Visayat Hussain
- Aug 1869 – 13 Dec 1873: Pandit Manphool
- Dec 1873 – 188.: Maharaj Lal Singh
- 188. – 1884?: Maharao Hari Singh Baid
- 1884 – 11 Oct 1888: Amin Muhammad
- 12 Dec 1888 – 1896: Sodhi Hukam Singh
- 1896 – 1898: Raghubar Singh Chauhan
- 1898 – 1903: Hamidu Zafar Khan
- 1903 – 1916: Post abolished
Chief ministers
- 1916 – 19..: Shri Bhairon Singh
- 7 Sep 1920 – Jan 1925: Prince Kunwar Sardul Singh (s.a.)
- 26 august2018 -vasundra rajay sindhiya
Dewans
The post of Dewan was reinstated in 1927.
- 1927 – 1934: Manubhai Nandshankar Mehta (b. 1868 – d. 1946)
- 3 Oct 1932 – 31 Oct 1934: Ram Prasad Dube (acting)
- 1 Nov 1934 – Jan 1936: Maharaj Shri Bhairun Singh
- Jan 1936 – Dec 1936: Thakur Sadul Singh
- Dec 1936 – 1938?: V.N. Mehta
- Dec 1938 – Jul 1939: Kailash Narain Haksar (b. 1878 – d. 1954)
- Jul 1939 – 1944?: Sire Mal Bapna (b. 1882 – d. 1964)
- 1944 – 13 Mar 1948: Kavalam Madhava Panikkar (b. 1895 – d. 1963)
- 14 Mar 1948 – Oct 1948: Kanwar Jaswant Singh
- Oct 1948 – 30 Mar 1949: Cadambi Sheshachar Venkatachar (b. 1899 – d. 1999)
Family tree of the rulers of Bikaner


-

-

-
-


-

-

-



-

-
- Anand Singh
-


-

-
- Chhatar Singh (1762–1779)
- Dalel Singh
- Sagat Singh
- Lall Singh (1831–1887)

-

-

- XXIII. Karni Singh, Maharaja of Bikaner (1924-1988; titular Maharaja: 1950–1971; family head: 1971–1988)
- XXIV. Narendra Singh, Maharaja of Bikaner (1946–2003; family head: 1988–2003)
- Amar Singh (b. 1925)
- Chandra Shekhar Singh (b. 1948)
- XXV. Ravi Raj Singh, Maharaja of Bikaner (b. 1977; family head: 2003– )
- Chandra Shekhar Singh (b. 1948)
- XXIII. Karni Singh, Maharaja of Bikaner (1924-1988; titular Maharaja: 1950–1971; family head: 1971–1988)
-
- Lall Singh (1831–1887)
- Madan Singh
- Sagat Singh
- Dalel Singh
-

-

-

-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
See also
- History of Bikaner
- Political integration of India
- Rajputana Chronicles: Guns and Glories - The thousand-year story of the Bachhawat clan
References
- ↑ Ramachandra Guha, India after Gandhi: The History of the World's Largest Democracy. HarperCollins, 2007
- ↑ Rajput Provinces of India - Bikaner (Princely State)
- ↑ William Barton, The princes of India. Delhi 1983
- ↑ Bikaner - family genealogy
![]()
External links

- Beny, Roland; Matheson, Sylvia A. (1984). Rajasthan - Land of Kings. London: Frederick Muller. p. 200 pages. ISBN 0-584-95061-6.
- Crump, Vivien; Toh, Irene (1996). Rajasthan (hardback). London: Everyman Guides. p. 400 pages. ISBN 1-85715-887-3.
- Martinelli, Antonio; Michell, George (2005). The Palaces of Rajasthan. London: Frances Lincoln. p. 271 pages. ISBN 978-0-7112-2505-3.
- Tod, James. Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan, Volume II (With a Preface by Douglas Sladen). Oriental Books Reprint Corporation. 54, Jhansi Road, New Delhi-1100055.

