目
| ||||||||
Translingual
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Stroke order | |||
|---|---|---|---|
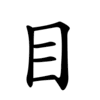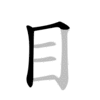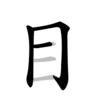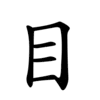 | |||
Han character
目 (radical 109, 目+0, 5 strokes, cangjie input 月山 (BU), four-corner 60101, composition ⿴囗𠄠)
- Kangxi radical #109, ⽬.
References
- KangXi: page 798, character 25
- Dai Kanwa Jiten: character 23105
- Dae Jaweon: page 1213, character 21
- Hanyu Da Zidian: volume 4, page 2467, character 1
- Unihan data for U+76EE
Chinese
| simp. and trad. |
目 | |
|---|---|---|
| variant forms | 𥃦 𡇡 𥆤 | |
Glyph origin
| Historical forms of the character 目 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shang | Western Zhou | Warring States | Shuowen Jiezi (compiled in Han) | Liushutong (compiled in Ming) | |
| Oracle bone script | Bronze inscriptions | Qin slip script | Ancient script | Small seal script | Transcribed ancient scripts |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Characters in the same phonetic series (目) (Zhengzhang, 2003) | |
|---|---|
| Old Chinese | |
| 瞐 | *mroːɡ |
| 苜 | *moːd, *muɡ |
| 目 | *muɡ |
Pictogram (象形) – human eye, now rotated 90 degrees. Compare the Egyptian hieroglyph 𓁹.
Etymology
From Proto-Sino-Tibetan *s-mjak ~ s-mik. Cognate with Tibetan མིག (mig, “eye”), Burmese မျက် (myak, “eye, face”).
Pronunciation
Definitions
目
- (literary or Min) eye
- ⇒ 眼
- † eyesight
- † to look; to view; to see
- † to wink at
- † to judge; to comment on
- † opinion; viewpoint
- † to view as; to regard
- † hole; eyelet
- † item; entry
- † title; headline
- † section
- † list; catalogue; table of contents
- † name
- † target; goal
- † chief; head; leader
- (taxonomy) order
Synonyms
- (eye):
Compounds
|
|
|
Further reading
- “Entry #1864”, in 臺灣閩南語常用詞辭典 [Dictionary of Frequently-Used Taiwan Minnan] (in Chinese and Min Nan), Ministry of Education, R.O.C., 2011.
Japanese
Readings
Etymology 1
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 目 |
| め Grade: 1 |
| kun’yomi |
⟨me2⟩ → */məɨ/ → /me/
From Old Japanese.[1] Shift from ma below, formed through fusion of 目 (ma, unbound form) + い (i, emphatic nominal particle). Now the modern Japanese term for eye.
May also be cognate with 芽 (me, “bud, shoot”),[1] perhaps from the “visually prominent feature” sense.
Alternative forms
Noun
- an eye
- visually prominent feature of something:
- Short for 賽の目 (sai no me, “dice pip”).
- 2015 January 10, “
悪 魔 のサイコロ [Demon’s Die]”, in 決闘者の栄光 -記憶の断片- side:武藤遊戯 [Duelist Road -Piece of Memory- side: Mutō Yūgi], Konami:- ①:サイコロを1回振る。相手フィールドのモンスターの攻撃力・守備力は、ターン終了時まで出た目の数×100ダウンする。
- Ichi: Saikoro o ikkai furu. Jibun fīrudo no monsutā no kōgekiryoku shubiryoku wa, tān shūryōji made deta me no kazu × hyaku daun suru.
- ①: Roll a die once. Until the end of this turn, the attack and defense strength of the monsters on your opponent’s field decreases by the result × 100.
- ①:サイコロを1回振る。相手フィールドのモンスターの攻撃力・守備力は、ターン終了時まで出た目の数×100ダウンする。
- 2015 September 19, “サイコロン [Dicyclone]”, in STRUCTURE DECK R -真帝王降臨- [STRUCTURE DECK R -Advent of the True Sovereign-], Konami:
- ①:サイコロを1回振り、出た目の効果を適用する。
- Ichi: Saikoro o ikkai furi, deta me no kōka o tekiyō suru.
- ①: Roll a die once, then apply an effect accordingly to the result.
- ①:サイコロを1回振り、出た目の効果を適用する。
-
- experience
- Short for 賽の目 (sai no me, “dice pip”).
Derived terms
- 目垢 (meaka, “eye gunk”)
- 眼医者 (meisha, “an eye doctor”)
- 眼鏡 (megane, “glasses”)
- 目糞 (mekuso), 目屎 (mekuso, “eye gunk”)
- 盲 (mekura, “blindness”)
- 目尻 (mejiri, “the corner of an eye”)
- 目玉 (medama, “eyeball”)
- 目付き (metsuki, “look#Noun, expression of the eyes”)
- 目脂 (meyani, “eye gunk”)
- 赤目 (akame, “red eyes”)
- 片目 (katame, “one eye”)
- 生真面目 (kimajime, “person who is too serious”)
- 黒目 (kurome, “black iris, an eye with large pupils or irises”)
- 血眼 (chime, “bloodshot eyes”)
- 近眼 (chikame, “nearsightedness”)
- 茶目 (chame, “playfulness”)
- 猫目石 (nekomeishi, “cat's eye (jewel)”)
- パンダ目 (pandame, “black eye”)
- 一目 (hitome)
- 雪目 (yukime, “snow blindness”)
- 横目 (yokome, “sidelong glance”)
Suffix
Etymology 2
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 目 |
| ま Grade: 1 |
| kun’yomi |
From Old Japanese[1] as the older, unbound form of 目 (me2).
Cognate with 見る (miru, “to see”). Never found in isolation in modern Japanese. Remains as the first syllable of various compounds.
Derived terms
- 睫 (matsuge, “eyelash”)
- 瞼 (mabuta), 瞼 (manabuta, “eyelid”)
- 前 (mae)
- 瞬く (matataku, “to blink, wink”)
- 瞬く (mabataku, “to blink, wink”)
- 瞬ぐ (majirogu, “to blink, wink”)
- 眼 (manako, “eyeball”)
- 眦 (manajiri, “corner of the eye”)
- 眼間 (manakai, “between one's eyes”)
- 眉 (mamie, “eyebrow”)
- 眉 (mayu, “eyebrow”)
- 眼差し (manazashi, “look, gaze”)
- 目深 (mabuka, “wearing low over one's eyes”)
- まのあたり (just before one's eyes)
Etymology 3
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 目 |
| もく Grade: 1 |
| goon |
From Middle Chinese 目 (MC mɨuk̚). The 呉音 (goon, literally “Wu sound”) reading, so likely the initial borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Noun
Derived terms
- 目迎 (mokugei, “turning one's gaze towards the direction from which someone is coming”)
- 目撃 (mokugeki, “witnessing something”)
- 目今 (mokukon), 目今 (mokkon)
- 目算 (mokusan, “eyeballing something, making a visual estimate or calculation of something”)
- 目視 (mokushi, “looking at something with one's own eyes”)
- 目次 (mokuji}, “table of contents”)
- 目笑 (mokushō, “smiling with one's eyes; smiling at one another, catching another's eye and smiling or laughing”)
- 目睫 (mokushō, “eyes and eyelashes; extremely close by”)
- 目食耳視 (mokushoku jishi, “eating with one's eyes, looking with one's ears→ choosing foods based on what they look like instead of their taste, and choosing fashions based on what people say instead of how comfortable they are → all style and no substance”)
- 目銭 (mokusen): a kind of tax levied in the Kamakura and Muromachi periods; a tax on sake bottles; a property tax based on the area of agricultural land
- 目前 (mokuzen, “right before one's eyes, right away, imminent, immediate”)
- 目送 (mokusō, “following something or someone with one's eyes”)
- 目測 (mokuso, “eyeballing a distance or length”)
- 目代 (mokudai): an agent or executor of a lord starting from the late Heian period; an on-site official or deputy starting from the Kamakura period; a local administrator in the Edo period
- 目的 (mokuteki, “intent, purpose, goal, objective”)
- 目途 (mokuto, “mark, guide, target”)
- 目睹 (mokuto, “witnessing something”)
- 目標 (mokuhyō, “target, goal, aim; landmark”)
- 目礼 (mokurei, “greeting or acknowledging someone with one's eyes”)
- 目録 (mokuroku, “list, a catalog”)
- 目論見 (mokuromi), 目論 (mokuron, “plan, a scheme, a design, a plot”)
- 目論む (mokuromu, “to plan, to scheme, to design, to plot”)
- 目割れ (mokuware, “plot, conspiracy, or other hidden plan being exposed or found out”)
- 細目 (saimoku, “details, particulars, breakdown”)
- 真面目 (shinmenmoku, “real appearance or worth of something; serious”)
- 新面目 (shinmenmoku, “new appearance or look for something”)
- 不面目 (fumenmoku, “dishonor, loss of face”)
- 面目 (menmoku, “one's honor, one's metaphorical face; external appearance”)
Verb
Conjugation
| Stem forms | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imperfective (未然形) | 目し | もくし | moku shi | |
| Continuative (連用形) | 目し | もくし | moku shi | |
| Terminal (終止形) | 目する | もくする | moku suru | |
| Attributive (連体形) | 目する | もくする | moku suru | |
| Hypothetical (仮定形) | 目すれ | もくすれ | moku sure | |
| Imperative (命令形) | 目せよ¹ 目しろ² |
もくせよ¹ もくしろ² |
moku seyo¹ moku shiro² | |
| Key constructions | ||||
| Passive | 目される | もくされる | moku sareru | |
| Causative | 目させる 目さす |
もくさせる もくさす |
moku saseru moku sasu | |
| Potential | 目できる | もくできる | moku dekiru | |
| Volitional | 目しよう | もくしよう | moku shiyō | |
| Negative | 目しない | もくしない | moku shinai | |
| Negative continuative | 目せず | もくせず | moku sezu | |
| Formal | 目します | もくします | moku shimasu | |
| Perfective | 目した | もくした | moku shita | |
| Conjunctive | 目して | もくして | moku shite | |
| Hypothetical conditional | 目すれば | もくすれば | moku sureba | |
| ¹ Written imperative ² Spoken imperative | ||||
Etymology 4
| Kanji in this term |
|---|
| 目 |
| ぼく Grade: 1 |
| kan’on |
From Middle Chinese 目 (MC mɨuk̚). The 漢音 (kan'on, literally “Han sound”) reading, so likely a later borrowing from Middle Chinese.
Compare modern Min Nan 目 (bo̍k).
Only used in compounds.
Derived terms
- 瞬目 (shunboku, “blink of an eye, moment, instant”)
- 真面目 (shinmenboku, “real appearance or worth of something; serious”)
- 新面目 (shinmenboku, “new appearance or look for something”)
- 不面目 (fumenboku, “dishonor, loss of face”)
- 面目 (menboku), 面目 (meiboku, “one's honor, one's metaphorical face; external appearance”)
Korean
Northern Amami-Oshima
Okinawan
Derived terms
- 尻ぬ目 (ちびぬみー]], chibi nu mī, “anus”)
- 陰目 (ほーみー]], hōmī, “vagina”)
- 目口 (みーくち]], mīkuchi, “facial expression”)
- 目涙 (みーなだ, mīnada, “tear”)
- 目屋, 眼屋 (みーやー, mīyā, “ophthalmologist”)
- 目眼鏡 (みーがんちょー, mīganchō, “glasses”)
- 目ん玉, 眼ん玉 (みんたま, mintama, “eyeball”)
Southern Amami-Oshima
Toku-No-Shima
Vietnamese
Han character
目: Hán Việt readings: mục (
目: Nôm readings: mục[2][1][4][5], mụt[6][1]
Compounds
References
- Bonet (1899).
- Nguyễn et al. (2009).
- Trần (2004).
- Génibrel (1898).
- Taberd & Pigneau de Béhaine (1838).
- Hồ (1976).